Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Hardware: Peripherals
Computer Hardware: Peripherals
Uploaded by
Dienizs Labini TadenaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Romania Free IPTV M3u Playlist 01-06-2022 - Latest Biss Key and New Frequency PowerVu Keys UpdateDocument1 pageRomania Free IPTV M3u Playlist 01-06-2022 - Latest Biss Key and New Frequency PowerVu Keys Updatedanipop1996No ratings yet
- Media and The Well-Being of Children and Adolescents (Amy B. Jordan, Daniel Romer) (Z-Library)Document305 pagesMedia and The Well-Being of Children and Adolescents (Amy B. Jordan, Daniel Romer) (Z-Library)stormhuang1213No ratings yet
- JAKA Zu 3 Cobot & JAKA Zu 3 Pro CobotDocument55 pagesJAKA Zu 3 Cobot & JAKA Zu 3 Pro CobotLEE HSUAN WEI A19EE0057100% (1)
- How To Use DC Power Supply To Repair Mobile Phones & Smartphones - CompressedDocument16 pagesHow To Use DC Power Supply To Repair Mobile Phones & Smartphones - CompressednCik Sukasuki75% (4)
- Case 20 LenovoDocument17 pagesCase 20 LenovoMohamad WafiyNo ratings yet
- Sauce & Spoon Project Plan: Task IDDocument50 pagesSauce & Spoon Project Plan: Task IDCharles Norton100% (1)
- Lesson Exemplar Standard - Module 1Document115 pagesLesson Exemplar Standard - Module 1Leu NameNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Computer - HardwareDocument22 pagesIGCSE Computer - HardwareNikhil YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Installing Computer System and NetworksDocument130 pagesModule 1 - Installing Computer System and Networksbenson01685% (26)
- 3 Day Live Online Power BI Training Brochure PDFDocument10 pages3 Day Live Online Power BI Training Brochure PDFCS ArkNo ratings yet
- La MadridDocument6 pagesLa MadridDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- ICT-scrap BookDocument15 pagesICT-scrap BookJham Ellen DaylusanNo ratings yet
- IT SkillsDocument25 pagesIT SkillsDivya GopranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer: L J PolytechnicDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Computer: L J PolytechnicAlpesh ThesiyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer NetworksDocument38 pagesBasic Computer Networkssabriela BulanadiNo ratings yet
- Online Discovery #1Document6 pagesOnline Discovery #1Ken YbañezNo ratings yet
- Introduction of The ICTDocument14 pagesIntroduction of The ICTBernadette GalanNo ratings yet
- HARDWAREDocument28 pagesHARDWAREshanikashyap556No ratings yet
- History of Computer: Elements of Information TechnologyDocument2 pagesHistory of Computer: Elements of Information TechnologyRenato Realisan EstradaNo ratings yet
- Lec2 - Computer Hardward and SoftwareDocument62 pagesLec2 - Computer Hardward and Softwarethuongquynhnhu2905No ratings yet
- Computer Applications Training ManualDocument76 pagesComputer Applications Training ManualPaul Minahan50% (2)
- ICT NetworkingDocument9 pagesICT NetworkingJannah Alexis OsmaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2. Computer HardwareDocument3 pagesExercise 2. Computer HardwareMikaela Mae GonzagaNo ratings yet
- C C CC CS: SCSC CSC C S C S CCC CSCCCDocument9 pagesC C CC CS: SCSC CSC C S C S CCC CSCCCRahul SuriNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Operating System Hardware Components: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document17 pagesUnit 2 - Operating System Hardware Components: Study Guide For Module No. 3Akirajane De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- LO5 Module 1 Installing Computer System and NetworksDocument145 pagesLO5 Module 1 Installing Computer System and NetworksKeith Hendrix FagyanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument12 pagesIntroduction To ComputersAishah JeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 ITDocument19 pagesAssignment 1 ITain borhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer SystemsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Computer Systemsfalconace94No ratings yet
- Lecture in ICTDocument33 pagesLecture in ICTAmeerNo ratings yet
- Computer Applications Training ManualDocument76 pagesComputer Applications Training ManualJojo CansinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Computer & System Unit PDFDocument81 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Computer & System Unit PDFKumares Rao67% (3)
- TroubleshootingDocument60 pagesTroubleshootingAngel Xavier CalejaNo ratings yet
- 1.1-1 OHS Policies and ProceduresDocument6 pages1.1-1 OHS Policies and ProceduresRJ VillamerNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Management SystemDocument47 pagesInformation Technology Management Systemgilberthufana446877No ratings yet
- Computer Application in PharmacyDocument49 pagesComputer Application in PharmacyBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- History of ComputerDocument15 pagesHistory of ComputerSchmelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Hardware For Computer Operations: A. Computer-Based Information SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Hardware For Computer Operations: A. Computer-Based Information SystemRabeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- It Era Reviewer PrelimDocument11 pagesIt Era Reviewer PrelimLovejoy NicorNo ratings yet
- LoppDocument7 pagesLoppMaroine CharityNo ratings yet
- Shehroz Arshad CRN 128269Document7 pagesShehroz Arshad CRN 128269Muhammad SufyanNo ratings yet
- CSC100MIDTERM ReviewerDocument13 pagesCSC100MIDTERM ReviewerPrincess Noelyn TubilNo ratings yet
- MelkamtecnoDocument15 pagesMelkamtecnoMelkam tseganew TigabieNo ratings yet
- 2 Ais-Ch2-Dl-1-1Document11 pages2 Ais-Ch2-Dl-1-1SamirNo ratings yet
- It Era ReviewerDocument4 pagesIt Era ReviewerTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- Introduction of ESDocument4 pagesIntroduction of ESDimple AmudaNo ratings yet
- F15 - E-Technology: Genesis Tuition Centre (Handout 1)Document11 pagesF15 - E-Technology: Genesis Tuition Centre (Handout 1)Philip MwelwaNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument63 pagesInformation TechnologywahabedhiNo ratings yet
- NCM 110A Module 1 Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocument25 pagesNCM 110A Module 1 Computer Hardware and SoftwareKi PieNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy Notes Level 6Document49 pagesDigital Literacy Notes Level 6themagero999100% (1)
- Information TechnologyDocument178 pagesInformation TechnologySayed AfifyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument6 pagesIntroduction To ComputerGaelan IdrisNo ratings yet
- Chap1 - A, BDocument3 pagesChap1 - A, BGabrielle AlonzoNo ratings yet
- L2 ICT - UNIT 2: Technology Systems Revision Template: Subject Notes Revision Done CPUDocument9 pagesL2 ICT - UNIT 2: Technology Systems Revision Template: Subject Notes Revision Done CPUapi-571862049No ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument77 pagesTypes of ComputersRojen SabileNo ratings yet
- Computr Appltion 1 and 2Document46 pagesComputr Appltion 1 and 2george manNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals Application PRELIM ModuleDocument24 pagesComputer Fundamentals Application PRELIM ModuleTrisha Lei T. BatangNo ratings yet
- Book of TisqaadDocument20 pagesBook of Tisqaaddaahirclnaasir3No ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction To ITDocument35 pagesChap 1 Introduction To ITainamikhail954No ratings yet
- It Questions g7 - 022640Document8 pagesIt Questions g7 - 022640Celestine Lumuli MadataNo ratings yet
- ICT PracticalDocument8 pagesICT PracticaliroshiniwijesinheNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Firmware?: CPU CacheDocument5 pagesWhat Is Computer Firmware?: CPU CacheKaren NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Hardware FamiliarizationDocument42 pagesHardware FamiliarizationLeandro IsidroNo ratings yet
- HI M2 Introduction To Computer ConceptsDocument12 pagesHI M2 Introduction To Computer ConceptsErickson SongcalNo ratings yet
- COA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90Document89 pagesCOA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90BOBAN05No ratings yet
- An Introduction to Computers and Internet - A Practical PresentationFrom EverandAn Introduction to Computers and Internet - A Practical PresentationNo ratings yet
- Poor Water Supply and SanitationDocument1 pagePoor Water Supply and SanitationDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3E: Incomplete Immunization Criteria Score Computation Answer JustificationDocument6 pagesLabini, Dienizs Bsn-3E: Incomplete Immunization Criteria Score Computation Answer JustificationDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Rotation 2Document3 pagesCase Scenario Rotation 2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning: MedicationsDocument3 pagesDischarge Planning: MedicationsDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- DS 4 To 6Document8 pagesDS 4 To 6Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanDienizs Labini Tadena100% (1)
- Labini, Dienizs Act.1 CHNDocument4 pagesLabini, Dienizs Act.1 CHNDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDocument10 pagesDrug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Rhu Act. 2Document2 pagesRhu Act. 2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Kardex: GCS: 12-13/15 (M:5, V:4-5, E:3)Document11 pagesKardex: GCS: 12-13/15 (M:5, V:4-5, E:3)Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- MVH Ward Case ScenarioDocument3 pagesMVH Ward Case ScenarioDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDocument11 pagesDienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini - NCM 117 Skills Activity #1Document3 pagesDienizs Labini - NCM 117 Skills Activity #1Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDocument11 pagesDienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Face Sheet: Diabetes Millitus T2Document3 pagesClinical Face Sheet: Diabetes Millitus T2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario For ADHDDocument2 pagesCase Scenario For ADHDDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Do You Love MeDocument3 pagesDo You Love MeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- D123 DRQDocument1 pageD123 DRQDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument15 pagesUniversity of Northern PhilippinesDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Verbatim Storage and Accessories Product Catalogue Q1 2014 Low ResDocument20 pagesVerbatim Storage and Accessories Product Catalogue Q1 2014 Low ResEric WhitfieldNo ratings yet
- KNX Building Control SystemDocument11 pagesKNX Building Control SystemEnar PauNo ratings yet
- App Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksDocument23 pagesApp Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksFernandoNo ratings yet
- Nomad 30 Pocket Reader User GuideDocument6 pagesNomad 30 Pocket Reader User Guidemasab khanNo ratings yet
- LINSAY F10XHD USER Manual PDFDocument75 pagesLINSAY F10XHD USER Manual PDFgeorgegarcia2794No ratings yet
- Arnova 10d g3 An10dg3 Firmware - Updated April 2021Document15 pagesArnova 10d g3 An10dg3 Firmware - Updated April 2021Salahudeen AlirushanuNo ratings yet
- Full Circle Magazine - Issue 107 ENDocument62 pagesFull Circle Magazine - Issue 107 ENRoman SukochevNo ratings yet
- Linkyfi Location Engine 2022Document21 pagesLinkyfi Location Engine 2022i9nitexNo ratings yet
- 11 808 422 01Document2 pages11 808 422 01Louie DupayaNo ratings yet
- IB1901 G1 1feb2024Document21 pagesIB1901 G1 1feb2024nguyenminhkhoi1104No ratings yet
- Hdfcbank - Credit Card Rewards Catalogue PDFDocument157 pagesHdfcbank - Credit Card Rewards Catalogue PDFAnshul SaravgiNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Version 0.9.9.z.58 BETA III August 09, 2018Document34 pagesUser Manual: Version 0.9.9.z.58 BETA III August 09, 2018vfdbdfbdfNo ratings yet
- Youngest Entrepreneurs of India-Shravan and Sanjay KumaranDocument3 pagesYoungest Entrepreneurs of India-Shravan and Sanjay KumaranSneha DobariaNo ratings yet
- TU Cat UKDocument86 pagesTU Cat UKIeșiAfarăNo ratings yet
- Hype Cycle: For Emerging Technologies, 2010Document11 pagesHype Cycle: For Emerging Technologies, 2010mrgirishNo ratings yet
- A Level Product Design Example CourseworkDocument8 pagesA Level Product Design Example Courseworkafjwofermaavkm100% (2)
- ZinioDocument28 pagesZinioDougNo ratings yet
- Rupesh Tiwari Create Your Own App With App Inventor 2 2016Document305 pagesRupesh Tiwari Create Your Own App With App Inventor 2 2016sunil sala100% (1)
- Critical Information Summary Telstra Stayconnected AdvancedDocument2 pagesCritical Information Summary Telstra Stayconnected AdvancedbebeceiciNo ratings yet
- Qlik Sense February 2020 Patch 3: Release NotesDocument30 pagesQlik Sense February 2020 Patch 3: Release Notesfonte_ushNo ratings yet
- Annual Analyst & Investor Meet FY11Document44 pagesAnnual Analyst & Investor Meet FY11sujith1202No ratings yet
- 2018 IKEA Catalog Press Kit PDFDocument28 pages2018 IKEA Catalog Press Kit PDFikhsan_ismu10No ratings yet
Computer Hardware: Peripherals
Computer Hardware: Peripherals
Uploaded by
Dienizs Labini TadenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Hardware: Peripherals
Computer Hardware: Peripherals
Uploaded by
Dienizs Labini TadenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Informatics Notes
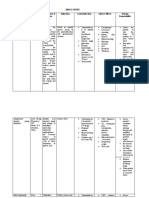
COMPUTER HARDWARE
HARDWARE
Quite simply, computer hardware is the physical components that a computer system
requires to function. It encompasses everything with a circuit board that operates within a
PC or laptop.
Without hardware, there would be no way of running the essential software that makes
computers so useful. Software is defined as the virtual programs that run on your
computer; that is, operating system, internet browser, word-processing documents, etc.
Although a computer can function only when both hardware and software are working
together, the speed of a system will largely rely on the hardware used.
PERIPHERALS
Peripheral devices are used to enter information and instructions into a computer for
storage or processing and deliver the processed data to a human operator or, in some
cases, a machine controlled by the computer. Such devices make up the peripheral
equipment of modern digital computer systems.
Peripherals are commonly divided into three kinds:
Input devices
- Converts incoming data and instructions into a pattern of electrical signals
in binary code that are comprehensible to a digital computer.
- Examples: typewriter-like keyboards, mouse, trackpad etc.
La Madrid, Hanna Mae B.
BSN 2E
Nursing Informatics Notes
Output devices
- Reverses the process, translating the digitized signals into a form
intelligible to the user.
- Examples: Laser printers, loudspeakers, headphones etc.
Storage devices (which partake of the characteristics of the first two)
(photos)
MEMORY
Random Access Memory, or RAM, is hardware found in the memory slots of the
motherboard. The role of RAM is to temporarily store on-the-fly information created by
programs and to do so in a way that makes this data immediately accessible.
The tasks that require random memory could be; rendering images for graphic design,
edited video or photographs, multi-tasking with multiple apps open (for example, running
a game on one screen and chatting via Discord on the other).
MOTHERHOOD
The motherboard is at the center of what makes a PC work. It houses the CPU and is a
hub that all other hardware runs through. The motherboard acts as a brain; allocating
power where it’s needed, communicating with and coordinating across all other
components – making it one of the most important pieces of hardware in a computer.
When choosing a motherboard, it’s important to check what hardware ports the
motherboard supplies. It’s vital to check how many USB ports, and what grade (USB 2.0,
La Madrid, Hanna Mae B.
BSN 2E
Nursing Informatics Notes
3.0, 3.1) they are, as well as what display ports are used (HDMI, DVI, RGB) and how
many of each there are. The ports on the motherboard will also help you define what
other hardware will be compatible with your computer, such as what type of RAM and
graphics card you can use.
Although the motherboard is just one piece of circuitry, it is home to another one of the
most important pieces of hardware: the processor.
CPU
The CPU (Central Processing Unit or processor) is responsible for processing all
information from programs run by your computer. The ‘clock speed’, or the speed at
which the processor processes information, is measured in gigahertz (GHz).
This means that a processor advertising a high GHz rating will likely perform faster than a
similarly specified processor of the same brand and age.
The CPU itself is a core component of what makes a computer a computer, but it isn’t the
computer itself – it’s just the brains of the operation. It’s a small computer chip that sits
atop the main circuit board (motherboard) of a computer.
CPUs are built by placing billions of microscopic transistors onto a single computer chip.
Those transistors allow it to make the calculations it needs to run programs that are stored
on your system’s memory.
ADVANCED HARDWARE and mHealth
La Madrid, Hanna Mae B.
BSN 2E
Nursing Informatics Notes
ADVANCED HARDWARE
There is a lot of change taking place within the mobile market. Some phones are getting
simpler while others get more complex or “smarter”. Touch screen phones occasionally
look like small tablets while tablets start to look like large phones. Some tablets have
removable keyboard docks while some laptops can be used without their keyboard.
Laptops and desktop PCs both allow users to access cellular and wireless signals as easily
as a phone or tablet, while some phones can only be used on limited networks. New terms
are being coined to reflect these adaptations, such as “phablet” and “hybrid”, yet the basic
categories still remain.
BLUETOOTH
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard used for exchanging data between fixed and
mobile devices over short distances using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the
industrial, scientific and medical radio bands, from 2.400 to 2.485 GHz, and building
personal area networks (PANs).
Compatible hardware: Personal computers; smartphones; gaming consoles; audio devices
etc.
mHEALTH
La Madrid, Hanna Mae B.
BSN 2E
Nursing Informatics Notes
mHealth is defined by the WHO as the “medical and public health practice supported by
mobile devices, such as mobile phones, patient monitoring devices, personal digital
assistances and other wireless devices”.
MOBILE DEVICES
A mobile device is a general term for any type of handheld computer. These devices are
designed to be extremely portable, and they can often fit in your hand. Some mobile
devices—like tablets, e-readers, and smartphones—are powerful enough to do many of
the same things you can do with a desktop or laptop computer.
Advantages of mobile technology
o higher efficiency and productivity of staff.
o the quality and flexibility of service you offer your customers.
o the ability to accept payments wirelessly.
o increased ability to communicate in and out of the workplace.
o greater access to modern apps and services.
o improved networking capabilities.
WIFI
La Madrid, Hanna Mae B.
BSN 2E
Nursing Informatics Notes
Wi-Fi is the name of a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide
wireless high-speed Internet and network connections. A common misconception is that
the term Wi-Fi is short for "wireless fidelity," however this is not the case. Wi-Fi is
simply a trademarked phrase that means IEEE 802.11x.
Wi-Fi networks have no physical wired connection between sender and receiver by using
radio frequency (RF) technology -- a frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum
associated with radio wave propagation. When an RF current is supplied to an antenna,
an electromagnetic field is created that then is able to propagate through space.
La Madrid, Hanna Mae B.
BSN 2E
You might also like
- Romania Free IPTV M3u Playlist 01-06-2022 - Latest Biss Key and New Frequency PowerVu Keys UpdateDocument1 pageRomania Free IPTV M3u Playlist 01-06-2022 - Latest Biss Key and New Frequency PowerVu Keys Updatedanipop1996No ratings yet
- Media and The Well-Being of Children and Adolescents (Amy B. Jordan, Daniel Romer) (Z-Library)Document305 pagesMedia and The Well-Being of Children and Adolescents (Amy B. Jordan, Daniel Romer) (Z-Library)stormhuang1213No ratings yet
- JAKA Zu 3 Cobot & JAKA Zu 3 Pro CobotDocument55 pagesJAKA Zu 3 Cobot & JAKA Zu 3 Pro CobotLEE HSUAN WEI A19EE0057100% (1)
- How To Use DC Power Supply To Repair Mobile Phones & Smartphones - CompressedDocument16 pagesHow To Use DC Power Supply To Repair Mobile Phones & Smartphones - CompressednCik Sukasuki75% (4)
- Case 20 LenovoDocument17 pagesCase 20 LenovoMohamad WafiyNo ratings yet
- Sauce & Spoon Project Plan: Task IDDocument50 pagesSauce & Spoon Project Plan: Task IDCharles Norton100% (1)
- Lesson Exemplar Standard - Module 1Document115 pagesLesson Exemplar Standard - Module 1Leu NameNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Computer - HardwareDocument22 pagesIGCSE Computer - HardwareNikhil YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Installing Computer System and NetworksDocument130 pagesModule 1 - Installing Computer System and Networksbenson01685% (26)
- 3 Day Live Online Power BI Training Brochure PDFDocument10 pages3 Day Live Online Power BI Training Brochure PDFCS ArkNo ratings yet
- La MadridDocument6 pagesLa MadridDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- ICT-scrap BookDocument15 pagesICT-scrap BookJham Ellen DaylusanNo ratings yet
- IT SkillsDocument25 pagesIT SkillsDivya GopranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer: L J PolytechnicDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Computer: L J PolytechnicAlpesh ThesiyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer NetworksDocument38 pagesBasic Computer Networkssabriela BulanadiNo ratings yet
- Online Discovery #1Document6 pagesOnline Discovery #1Ken YbañezNo ratings yet
- Introduction of The ICTDocument14 pagesIntroduction of The ICTBernadette GalanNo ratings yet
- HARDWAREDocument28 pagesHARDWAREshanikashyap556No ratings yet
- History of Computer: Elements of Information TechnologyDocument2 pagesHistory of Computer: Elements of Information TechnologyRenato Realisan EstradaNo ratings yet
- Lec2 - Computer Hardward and SoftwareDocument62 pagesLec2 - Computer Hardward and Softwarethuongquynhnhu2905No ratings yet
- Computer Applications Training ManualDocument76 pagesComputer Applications Training ManualPaul Minahan50% (2)
- ICT NetworkingDocument9 pagesICT NetworkingJannah Alexis OsmaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2. Computer HardwareDocument3 pagesExercise 2. Computer HardwareMikaela Mae GonzagaNo ratings yet
- C C CC CS: SCSC CSC C S C S CCC CSCCCDocument9 pagesC C CC CS: SCSC CSC C S C S CCC CSCCCRahul SuriNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Operating System Hardware Components: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document17 pagesUnit 2 - Operating System Hardware Components: Study Guide For Module No. 3Akirajane De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- LO5 Module 1 Installing Computer System and NetworksDocument145 pagesLO5 Module 1 Installing Computer System and NetworksKeith Hendrix FagyanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument12 pagesIntroduction To ComputersAishah JeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 ITDocument19 pagesAssignment 1 ITain borhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer SystemsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Computer Systemsfalconace94No ratings yet
- Lecture in ICTDocument33 pagesLecture in ICTAmeerNo ratings yet
- Computer Applications Training ManualDocument76 pagesComputer Applications Training ManualJojo CansinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Computer & System Unit PDFDocument81 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Computer & System Unit PDFKumares Rao67% (3)
- TroubleshootingDocument60 pagesTroubleshootingAngel Xavier CalejaNo ratings yet
- 1.1-1 OHS Policies and ProceduresDocument6 pages1.1-1 OHS Policies and ProceduresRJ VillamerNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Management SystemDocument47 pagesInformation Technology Management Systemgilberthufana446877No ratings yet
- Computer Application in PharmacyDocument49 pagesComputer Application in PharmacyBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- History of ComputerDocument15 pagesHistory of ComputerSchmelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Hardware For Computer Operations: A. Computer-Based Information SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Hardware For Computer Operations: A. Computer-Based Information SystemRabeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- It Era Reviewer PrelimDocument11 pagesIt Era Reviewer PrelimLovejoy NicorNo ratings yet
- LoppDocument7 pagesLoppMaroine CharityNo ratings yet
- Shehroz Arshad CRN 128269Document7 pagesShehroz Arshad CRN 128269Muhammad SufyanNo ratings yet
- CSC100MIDTERM ReviewerDocument13 pagesCSC100MIDTERM ReviewerPrincess Noelyn TubilNo ratings yet
- MelkamtecnoDocument15 pagesMelkamtecnoMelkam tseganew TigabieNo ratings yet
- 2 Ais-Ch2-Dl-1-1Document11 pages2 Ais-Ch2-Dl-1-1SamirNo ratings yet
- It Era ReviewerDocument4 pagesIt Era ReviewerTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- Introduction of ESDocument4 pagesIntroduction of ESDimple AmudaNo ratings yet
- F15 - E-Technology: Genesis Tuition Centre (Handout 1)Document11 pagesF15 - E-Technology: Genesis Tuition Centre (Handout 1)Philip MwelwaNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument63 pagesInformation TechnologywahabedhiNo ratings yet
- NCM 110A Module 1 Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocument25 pagesNCM 110A Module 1 Computer Hardware and SoftwareKi PieNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy Notes Level 6Document49 pagesDigital Literacy Notes Level 6themagero999100% (1)
- Information TechnologyDocument178 pagesInformation TechnologySayed AfifyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument6 pagesIntroduction To ComputerGaelan IdrisNo ratings yet
- Chap1 - A, BDocument3 pagesChap1 - A, BGabrielle AlonzoNo ratings yet
- L2 ICT - UNIT 2: Technology Systems Revision Template: Subject Notes Revision Done CPUDocument9 pagesL2 ICT - UNIT 2: Technology Systems Revision Template: Subject Notes Revision Done CPUapi-571862049No ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument77 pagesTypes of ComputersRojen SabileNo ratings yet
- Computr Appltion 1 and 2Document46 pagesComputr Appltion 1 and 2george manNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals Application PRELIM ModuleDocument24 pagesComputer Fundamentals Application PRELIM ModuleTrisha Lei T. BatangNo ratings yet
- Book of TisqaadDocument20 pagesBook of Tisqaaddaahirclnaasir3No ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction To ITDocument35 pagesChap 1 Introduction To ITainamikhail954No ratings yet
- It Questions g7 - 022640Document8 pagesIt Questions g7 - 022640Celestine Lumuli MadataNo ratings yet
- ICT PracticalDocument8 pagesICT PracticaliroshiniwijesinheNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Firmware?: CPU CacheDocument5 pagesWhat Is Computer Firmware?: CPU CacheKaren NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Hardware FamiliarizationDocument42 pagesHardware FamiliarizationLeandro IsidroNo ratings yet
- HI M2 Introduction To Computer ConceptsDocument12 pagesHI M2 Introduction To Computer ConceptsErickson SongcalNo ratings yet
- COA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90Document89 pagesCOA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90BOBAN05No ratings yet
- An Introduction to Computers and Internet - A Practical PresentationFrom EverandAn Introduction to Computers and Internet - A Practical PresentationNo ratings yet
- Poor Water Supply and SanitationDocument1 pagePoor Water Supply and SanitationDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3E: Incomplete Immunization Criteria Score Computation Answer JustificationDocument6 pagesLabini, Dienizs Bsn-3E: Incomplete Immunization Criteria Score Computation Answer JustificationDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Rotation 2Document3 pagesCase Scenario Rotation 2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning: MedicationsDocument3 pagesDischarge Planning: MedicationsDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- DS 4 To 6Document8 pagesDS 4 To 6Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanDienizs Labini Tadena100% (1)
- Labini, Dienizs Act.1 CHNDocument4 pagesLabini, Dienizs Act.1 CHNDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDocument10 pagesDrug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Rhu Act. 2Document2 pagesRhu Act. 2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Kardex: GCS: 12-13/15 (M:5, V:4-5, E:3)Document11 pagesKardex: GCS: 12-13/15 (M:5, V:4-5, E:3)Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- MVH Ward Case ScenarioDocument3 pagesMVH Ward Case ScenarioDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDocument11 pagesDienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini - NCM 117 Skills Activity #1Document3 pagesDienizs Labini - NCM 117 Skills Activity #1Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDocument11 pagesDienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Face Sheet: Diabetes Millitus T2Document3 pagesClinical Face Sheet: Diabetes Millitus T2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario For ADHDDocument2 pagesCase Scenario For ADHDDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Do You Love MeDocument3 pagesDo You Love MeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- D123 DRQDocument1 pageD123 DRQDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument15 pagesUniversity of Northern PhilippinesDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Verbatim Storage and Accessories Product Catalogue Q1 2014 Low ResDocument20 pagesVerbatim Storage and Accessories Product Catalogue Q1 2014 Low ResEric WhitfieldNo ratings yet
- KNX Building Control SystemDocument11 pagesKNX Building Control SystemEnar PauNo ratings yet
- App Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksDocument23 pagesApp Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksFernandoNo ratings yet
- Nomad 30 Pocket Reader User GuideDocument6 pagesNomad 30 Pocket Reader User Guidemasab khanNo ratings yet
- LINSAY F10XHD USER Manual PDFDocument75 pagesLINSAY F10XHD USER Manual PDFgeorgegarcia2794No ratings yet
- Arnova 10d g3 An10dg3 Firmware - Updated April 2021Document15 pagesArnova 10d g3 An10dg3 Firmware - Updated April 2021Salahudeen AlirushanuNo ratings yet
- Full Circle Magazine - Issue 107 ENDocument62 pagesFull Circle Magazine - Issue 107 ENRoman SukochevNo ratings yet
- Linkyfi Location Engine 2022Document21 pagesLinkyfi Location Engine 2022i9nitexNo ratings yet
- 11 808 422 01Document2 pages11 808 422 01Louie DupayaNo ratings yet
- IB1901 G1 1feb2024Document21 pagesIB1901 G1 1feb2024nguyenminhkhoi1104No ratings yet
- Hdfcbank - Credit Card Rewards Catalogue PDFDocument157 pagesHdfcbank - Credit Card Rewards Catalogue PDFAnshul SaravgiNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Version 0.9.9.z.58 BETA III August 09, 2018Document34 pagesUser Manual: Version 0.9.9.z.58 BETA III August 09, 2018vfdbdfbdfNo ratings yet
- Youngest Entrepreneurs of India-Shravan and Sanjay KumaranDocument3 pagesYoungest Entrepreneurs of India-Shravan and Sanjay KumaranSneha DobariaNo ratings yet
- TU Cat UKDocument86 pagesTU Cat UKIeșiAfarăNo ratings yet
- Hype Cycle: For Emerging Technologies, 2010Document11 pagesHype Cycle: For Emerging Technologies, 2010mrgirishNo ratings yet
- A Level Product Design Example CourseworkDocument8 pagesA Level Product Design Example Courseworkafjwofermaavkm100% (2)
- ZinioDocument28 pagesZinioDougNo ratings yet
- Rupesh Tiwari Create Your Own App With App Inventor 2 2016Document305 pagesRupesh Tiwari Create Your Own App With App Inventor 2 2016sunil sala100% (1)
- Critical Information Summary Telstra Stayconnected AdvancedDocument2 pagesCritical Information Summary Telstra Stayconnected AdvancedbebeceiciNo ratings yet
- Qlik Sense February 2020 Patch 3: Release NotesDocument30 pagesQlik Sense February 2020 Patch 3: Release Notesfonte_ushNo ratings yet
- Annual Analyst & Investor Meet FY11Document44 pagesAnnual Analyst & Investor Meet FY11sujith1202No ratings yet
- 2018 IKEA Catalog Press Kit PDFDocument28 pages2018 IKEA Catalog Press Kit PDFikhsan_ismu10No ratings yet