Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsPato 1
Pato 1
Uploaded by
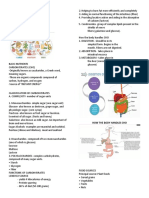
Febbio YoghatamaThe document summarizes the major digestive enzymes and glands in the human digestive system, including their substrates and products. It lists the main enzymes in the salivary glands, gastric glands, pancreas, and intestinal glands. The salivary glands produce amylase to break down starch. The gastric glands contain pepsin and lipase to break down proteins and triglycerides. The pancreas secretes a variety of enzymes to further break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The intestinal glands contain enzymes like sucrase, maltase, and lactase to break down disaccharides, as well as lipase.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Digestive System POGILDocument8 pagesDigestive System POGILLokesh BangaloreNo ratings yet
- 04 Eliciting Your Values PDFDocument24 pages04 Eliciting Your Values PDFKem Raj100% (1)
- Term Protector Product Summary: Important NoteDocument8 pagesTerm Protector Product Summary: Important NotesoxoNo ratings yet
- Career Research PaperDocument5 pagesCareer Research Paperapi-249918037100% (2)
- Pato 1Document1 pagePato 1Febbio YoghatamaNo ratings yet
- Digestive Gland Enzymes Substrates Products Salivary Glands Gastric Glands PancreasDocument1 pageDigestive Gland Enzymes Substrates Products Salivary Glands Gastric Glands PancreasFebbio YoghatamaNo ratings yet
- Digestion WorksheetDocument3 pagesDigestion WorksheetKyria JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Intestinal JuiceDocument25 pagesIntestinal JuicehamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Digestion and NutritionDocument22 pagesDigestion and NutritionUnknown UserNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument20 pagesBiological MoleculesUbaid Ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument11 pagesDigestion and AbsorptiondiadiaidaNo ratings yet
- Class X Biology Life Processes Assignment 7 Gist of Lesson TaughtDocument4 pagesClass X Biology Life Processes Assignment 7 Gist of Lesson TaughtBonto17777No ratings yet
- L2 Food NutrientsDocument11 pagesL2 Food NutrientsShannNo ratings yet
- Fat and Protein MetabolismDocument2 pagesFat and Protein MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Document7 pages6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Jay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of LifeDocument43 pagesChemicals of LifeHamza AnwarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual 1Document22 pagesUnderstanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual 1Jacqueline Reyes100% (50)
- Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10Th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10Th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFterry.kopecky657100% (10)
- Biology Notes 1Document2 pagesBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism 1Document61 pagesLipid Metabolism 1pierrewambura123No ratings yet
- Contemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual 1Document15 pagesContemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual 1pamela100% (47)
- 9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroDocument51 pages9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroPratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- Sotelo Pilsam Jr.-Biochemistry-Marine Biolog 2-2Document12 pagesSotelo Pilsam Jr.-Biochemistry-Marine Biolog 2-2Pilsam, Jr. SoteloNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Elvinna Rohmaliza Fitria Takhta MyogadwihDocument11 pagesCarbohydrates: Elvinna Rohmaliza Fitria Takhta MyogadwihTakhta AlfinaNo ratings yet
- SPIN HMS STBP2013 Lipid Metabolism I Sem II Sesi 2012-2013Document64 pagesSPIN HMS STBP2013 Lipid Metabolism I Sem II Sesi 2012-2013ayamgoreng456No ratings yet
- Activity 2 CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesActivity 2 CarbohydratesPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument112 pagesAnimal NutritionJessa PalbanNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Carbohydrate-Protein-LemakDocument13 pagesMetabolisme Carbohydrate-Protein-Lemakkristia wardaniNo ratings yet
- Bio q2w1Document2 pagesBio q2w1Jes RenNo ratings yet
- Pre Test: Prepared By: Patricia PradoDocument51 pagesPre Test: Prepared By: Patricia PradoLovely AlosadoNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Digestive SystemDocument49 pagesFourth Quarter Digestive SystemGrungy GamingNo ratings yet
- BiologiDocument17 pagesBiologiKanda BagaskaraNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization of The Human BodyDocument3 pagesLevels of Organization of The Human BodyJOAN KLAIRE I. LIBOTNo ratings yet
- 1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Document112 pages1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Clàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- GLM Biochemistry of GastroenterologyDocument14 pagesGLM Biochemistry of GastroenterologyEaint BoNo ratings yet
- L5 Digestion and AbsorptionDocument20 pagesL5 Digestion and Absorptionhafsahk09No ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules PDFDocument31 pagesBiological Macromolecules PDFAngeline CortezNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiochem ReviewerulynieveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MACRONUTRIENTSDocument11 pagesChapter 3 MACRONUTRIENTSSami InglesNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingDocument185 pagesBiological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingVj RanchesNo ratings yet
- Digestion Absorption 12 2019Document14 pagesDigestion Absorption 12 2019Karyan ShinNo ratings yet
- Shahina Akhter XIA Gulf Asian EnglishschoolDocument73 pagesShahina Akhter XIA Gulf Asian EnglishschoolraghavNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: By: Fritchy P. Forneas, RM, RN, ManDocument108 pagesBasic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: By: Fritchy P. Forneas, RM, RN, ManRoss AbangNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument31 pagesBiological Moleculesayu sri ningsihNo ratings yet
- 1 Notes Basic NutrientsDocument8 pages1 Notes Basic Nutrientsclear kNo ratings yet
- PDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Document45 pagesPDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Pratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument18 pagesBiological Macromoleculesdavemorte20No ratings yet
- Chapter 08 LipidDocument10 pagesChapter 08 Lipid楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism Session 1Document34 pagesLipid Metabolism Session 1KundaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules 1Document29 pagesBiological Molecules 1hamdan.ishaq16No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipid and AllDocument22 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipid and AllRaunak JalanNo ratings yet
- Lipid Digestion AbsorptionDocument35 pagesLipid Digestion Absorptionpranshutiwari820No ratings yet
- Lec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesDocument32 pagesLec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - LipidsDocument22 pagesChapter 5 - LipidsDale TelgenhoffNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'DOC-20221028-WA0000.' With YouDocument29 pagesI Am Sharing 'DOC-20221028-WA0000.' With Youbruh bruh 68No ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidsDocument38 pagesLipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidscheckmateNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 - 4Document13 pagesQ4 Week 3 - 4Claudie MabiniNo ratings yet
- DepEd Learning Activity Sheets LAS Science 10 Lesson 2Document7 pagesDepEd Learning Activity Sheets LAS Science 10 Lesson 2Lyrah Santuyo50% (2)
- MATERI 1b-TUBUH TERNAK DAN ZAT MAKANANDocument42 pagesMATERI 1b-TUBUH TERNAK DAN ZAT MAKANANRayhan PutraNo ratings yet
- Biological Science DepartmentDocument8 pagesBiological Science DepartmentInga Budadoy NaudadongNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument30 pagesBiochemistryvishal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportNo ratings yet
- Article. Loop Ileostomy Closure After Restorative Proctocolectomy. Outcome in 1504 Patients. 2005Document8 pagesArticle. Loop Ileostomy Closure After Restorative Proctocolectomy. Outcome in 1504 Patients. 2005Trí Cương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Basis For Projects Categorization, and Safeguards Instruments-FDocument31 pagesBasis For Projects Categorization, and Safeguards Instruments-FMelikteNo ratings yet
- Training Facilitators' GuideDocument16 pagesTraining Facilitators' GuideCharles MintahNo ratings yet
- Star Health and Allied Insurance Co - LTD.Document2 pagesStar Health and Allied Insurance Co - LTD.AshokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Wilhelm Wundt and The Founding of Psychology: Dr. Nancy AlvaradoDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Wilhelm Wundt and The Founding of Psychology: Dr. Nancy AlvaradoAdalene SalesNo ratings yet
- EngagingWithVideogames PDFDocument300 pagesEngagingWithVideogames PDFfatmama7031No ratings yet
- What Is NFPA 704Document5 pagesWhat Is NFPA 704Mada NafeaNo ratings yet
- A SWOT Analysis template-BBA 140Document6 pagesA SWOT Analysis template-BBA 140Tremor BandaNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Study of Microwave and Conventional SynthesisDocument8 pagesComparitive Study of Microwave and Conventional SynthesisvinayNo ratings yet
- Joyce's PrincipleDocument16 pagesJoyce's PrincipleCtv MontrealNo ratings yet
- Puerto Rico NPI Data EdirectoryDocument62 pagesPuerto Rico NPI Data EdirectoryNPI Data ServicesNo ratings yet
- PaintDocument22 pagesPaintZubair Ahmed KhaskheliNo ratings yet
- 1.b. Bronchiolitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument3 pages1.b. Bronchiolitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDavid CraigNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Mzizi JNDocument118 pagesDissertation Mzizi JNpamelaNo ratings yet
- Reflection (Setting Application 3)Document2 pagesReflection (Setting Application 3)DavidNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology - Medical Microbiology - NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pageEpidemiology - Medical Microbiology - NCBI Bookshelfshruti guptaNo ratings yet
- Obesity Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesObesity Reading ComprehensionDaniela SarmientoNo ratings yet
- ComplaintDocument27 pagesComplaintFOX 11 Los AngelesNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is Hum-WPS OfficeDocument7 pages1.1 What Is Hum-WPS OfficeJesie Bell Balaba BuroNo ratings yet
- MALPRACTICEDocument43 pagesMALPRACTICEDev LitaNo ratings yet
- Ebd 2023Document6 pagesEbd 2023dinaNo ratings yet
- May 2021 Mark Scheme 2BDocument17 pagesMay 2021 Mark Scheme 2BMeenakshie ChaudrieNo ratings yet
- Soal BHS ING SAS SM 2 2023 2024Document3 pagesSoal BHS ING SAS SM 2 2023 2024Hari EngkufNo ratings yet
- Updated Resume 2020Document1 pageUpdated Resume 2020api-516280936No ratings yet
- Book 4Document39 pagesBook 4fatha_87No ratings yet
- Stressing Factors in Nurses Who Work in The Sector of Urgency and EmergencyDocument9 pagesStressing Factors in Nurses Who Work in The Sector of Urgency and EmergencyIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Clinical Experience Reflection 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: Clinical Experience Reflection 1api-520930030No ratings yet
Pato 1
Pato 1
Uploaded by
Febbio Yoghatama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe document summarizes the major digestive enzymes and glands in the human digestive system, including their substrates and products. It lists the main enzymes in the salivary glands, gastric glands, pancreas, and intestinal glands. The salivary glands produce amylase to break down starch. The gastric glands contain pepsin and lipase to break down proteins and triglycerides. The pancreas secretes a variety of enzymes to further break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The intestinal glands contain enzymes like sucrase, maltase, and lactase to break down disaccharides, as well as lipase.
Original Description:
Original Title
pato1.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the major digestive enzymes and glands in the human digestive system, including their substrates and products. It lists the main enzymes in the salivary glands, gastric glands, pancreas, and intestinal glands. The salivary glands produce amylase to break down starch. The gastric glands contain pepsin and lipase to break down proteins and triglycerides. The pancreas secretes a variety of enzymes to further break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The intestinal glands contain enzymes like sucrase, maltase, and lactase to break down disaccharides, as well as lipase.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pagePato 1
Pato 1
Uploaded by
Febbio YoghatamaThe document summarizes the major digestive enzymes and glands in the human digestive system, including their substrates and products. It lists the main enzymes in the salivary glands, gastric glands, pancreas, and intestinal glands. The salivary glands produce amylase to break down starch. The gastric glands contain pepsin and lipase to break down proteins and triglycerides. The pancreas secretes a variety of enzymes to further break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The intestinal glands contain enzymes like sucrase, maltase, and lactase to break down disaccharides, as well as lipase.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Nama: FEBBIO YOGHATAMA NIM:201910410311041 Absen:40 Kelas: A
Digestive Enzymes Substrates Products
Gland
Salivary 1. Salivary amylase 1. Starch 1. Conversion to maltose
Glands and isomaltose
Gastric 1. Pepsin 1. Proteins 1. Smaller polypeptide
Glands 2. Gasrtic lipase 2. Triglyserides chains
2. Fatty acids and Glycerol
Pancreas 1. Trypsin 1. Proteins 1. Breaks polypeptide
2. Chymotrypsin 2. Proteins chains at arginine or
3. Carboxypeptidas 3. Proteins lysine residues
e 4. Carbohydrates 2. Cleaves carboxyl links
4. Pancreatic 5. Fat of hydrophobic amino
amylase Digests acids
5. Pancreatic lipase 3. Removes amino acids
Digests from the carboxyl end of
peptide chains
4. Hydrolyzes starches and
glycogen to form
maltose and isomaltose
5. Hydrolyzes fats mostly
triacylglycerols into
glycerol and fatty acids
Intestinal 1. Sucrase 1. Disaccharides 1. Monosaccharides
Glands 2. Maltase 2. Disaccharides 2. Monosaccharides
3. Lactase 3. Disaccharides 3. Monosaccharides
4. Lipase 4. Fats 4. Fatty acid and
5. Enterokinase 5. Trypsinogen 5. Glycerol trypsin
LITERATUR:
Seeley, R., VanPutte, C., Regan, J., Stephens, T., Tate, P., & Russo, A. (2013). Large Intestine
Objective. Seeley’s Anatomy & Physiology, (864), 860–910.
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse. (2010). The digestive system. The
Journal of Practical Nursing, 60(2), 7–9.
Dane, Senol & Hanninen, O. (2002). Enzymes of Digestion. Encyclopedia of Life Support
Systems, II.
Barnes, G. E. (1925). Digestive enzymes. Journal of the American Medical Association, 85(17),
1324. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1925.02670170058033
You might also like
- Digestive System POGILDocument8 pagesDigestive System POGILLokesh BangaloreNo ratings yet
- 04 Eliciting Your Values PDFDocument24 pages04 Eliciting Your Values PDFKem Raj100% (1)
- Term Protector Product Summary: Important NoteDocument8 pagesTerm Protector Product Summary: Important NotesoxoNo ratings yet
- Career Research PaperDocument5 pagesCareer Research Paperapi-249918037100% (2)
- Pato 1Document1 pagePato 1Febbio YoghatamaNo ratings yet
- Digestive Gland Enzymes Substrates Products Salivary Glands Gastric Glands PancreasDocument1 pageDigestive Gland Enzymes Substrates Products Salivary Glands Gastric Glands PancreasFebbio YoghatamaNo ratings yet
- Digestion WorksheetDocument3 pagesDigestion WorksheetKyria JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Intestinal JuiceDocument25 pagesIntestinal JuicehamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Digestion and NutritionDocument22 pagesDigestion and NutritionUnknown UserNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument20 pagesBiological MoleculesUbaid Ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument11 pagesDigestion and AbsorptiondiadiaidaNo ratings yet
- Class X Biology Life Processes Assignment 7 Gist of Lesson TaughtDocument4 pagesClass X Biology Life Processes Assignment 7 Gist of Lesson TaughtBonto17777No ratings yet
- L2 Food NutrientsDocument11 pagesL2 Food NutrientsShannNo ratings yet
- Fat and Protein MetabolismDocument2 pagesFat and Protein MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- 6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Document7 pages6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Jay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of LifeDocument43 pagesChemicals of LifeHamza AnwarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual 1Document22 pagesUnderstanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual 1Jacqueline Reyes100% (50)
- Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10Th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition 10Th Edition Rolfes Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFterry.kopecky657100% (10)
- Biology Notes 1Document2 pagesBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism 1Document61 pagesLipid Metabolism 1pierrewambura123No ratings yet
- Contemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual 1Document15 pagesContemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual 1pamela100% (47)
- 9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroDocument51 pages9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroPratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- Sotelo Pilsam Jr.-Biochemistry-Marine Biolog 2-2Document12 pagesSotelo Pilsam Jr.-Biochemistry-Marine Biolog 2-2Pilsam, Jr. SoteloNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Elvinna Rohmaliza Fitria Takhta MyogadwihDocument11 pagesCarbohydrates: Elvinna Rohmaliza Fitria Takhta MyogadwihTakhta AlfinaNo ratings yet
- SPIN HMS STBP2013 Lipid Metabolism I Sem II Sesi 2012-2013Document64 pagesSPIN HMS STBP2013 Lipid Metabolism I Sem II Sesi 2012-2013ayamgoreng456No ratings yet
- Activity 2 CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesActivity 2 CarbohydratesPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument112 pagesAnimal NutritionJessa PalbanNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Carbohydrate-Protein-LemakDocument13 pagesMetabolisme Carbohydrate-Protein-Lemakkristia wardaniNo ratings yet
- Bio q2w1Document2 pagesBio q2w1Jes RenNo ratings yet
- Pre Test: Prepared By: Patricia PradoDocument51 pagesPre Test: Prepared By: Patricia PradoLovely AlosadoNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Digestive SystemDocument49 pagesFourth Quarter Digestive SystemGrungy GamingNo ratings yet
- BiologiDocument17 pagesBiologiKanda BagaskaraNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization of The Human BodyDocument3 pagesLevels of Organization of The Human BodyJOAN KLAIRE I. LIBOTNo ratings yet
- 1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Document112 pages1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Clàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- GLM Biochemistry of GastroenterologyDocument14 pagesGLM Biochemistry of GastroenterologyEaint BoNo ratings yet
- L5 Digestion and AbsorptionDocument20 pagesL5 Digestion and Absorptionhafsahk09No ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules PDFDocument31 pagesBiological Macromolecules PDFAngeline CortezNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiochem ReviewerulynieveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MACRONUTRIENTSDocument11 pagesChapter 3 MACRONUTRIENTSSami InglesNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingDocument185 pagesBiological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingVj RanchesNo ratings yet
- Digestion Absorption 12 2019Document14 pagesDigestion Absorption 12 2019Karyan ShinNo ratings yet
- Shahina Akhter XIA Gulf Asian EnglishschoolDocument73 pagesShahina Akhter XIA Gulf Asian EnglishschoolraghavNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: By: Fritchy P. Forneas, RM, RN, ManDocument108 pagesBasic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: By: Fritchy P. Forneas, RM, RN, ManRoss AbangNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument31 pagesBiological Moleculesayu sri ningsihNo ratings yet
- 1 Notes Basic NutrientsDocument8 pages1 Notes Basic Nutrientsclear kNo ratings yet
- PDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Document45 pagesPDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Pratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument18 pagesBiological Macromoleculesdavemorte20No ratings yet
- Chapter 08 LipidDocument10 pagesChapter 08 Lipid楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism Session 1Document34 pagesLipid Metabolism Session 1KundaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules 1Document29 pagesBiological Molecules 1hamdan.ishaq16No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipid and AllDocument22 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipid and AllRaunak JalanNo ratings yet
- Lipid Digestion AbsorptionDocument35 pagesLipid Digestion Absorptionpranshutiwari820No ratings yet
- Lec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesDocument32 pagesLec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - LipidsDocument22 pagesChapter 5 - LipidsDale TelgenhoffNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'DOC-20221028-WA0000.' With YouDocument29 pagesI Am Sharing 'DOC-20221028-WA0000.' With Youbruh bruh 68No ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidsDocument38 pagesLipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidscheckmateNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 - 4Document13 pagesQ4 Week 3 - 4Claudie MabiniNo ratings yet
- DepEd Learning Activity Sheets LAS Science 10 Lesson 2Document7 pagesDepEd Learning Activity Sheets LAS Science 10 Lesson 2Lyrah Santuyo50% (2)
- MATERI 1b-TUBUH TERNAK DAN ZAT MAKANANDocument42 pagesMATERI 1b-TUBUH TERNAK DAN ZAT MAKANANRayhan PutraNo ratings yet
- Biological Science DepartmentDocument8 pagesBiological Science DepartmentInga Budadoy NaudadongNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument30 pagesBiochemistryvishal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportNo ratings yet
- Article. Loop Ileostomy Closure After Restorative Proctocolectomy. Outcome in 1504 Patients. 2005Document8 pagesArticle. Loop Ileostomy Closure After Restorative Proctocolectomy. Outcome in 1504 Patients. 2005Trí Cương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Basis For Projects Categorization, and Safeguards Instruments-FDocument31 pagesBasis For Projects Categorization, and Safeguards Instruments-FMelikteNo ratings yet
- Training Facilitators' GuideDocument16 pagesTraining Facilitators' GuideCharles MintahNo ratings yet
- Star Health and Allied Insurance Co - LTD.Document2 pagesStar Health and Allied Insurance Co - LTD.AshokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Wilhelm Wundt and The Founding of Psychology: Dr. Nancy AlvaradoDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Wilhelm Wundt and The Founding of Psychology: Dr. Nancy AlvaradoAdalene SalesNo ratings yet
- EngagingWithVideogames PDFDocument300 pagesEngagingWithVideogames PDFfatmama7031No ratings yet
- What Is NFPA 704Document5 pagesWhat Is NFPA 704Mada NafeaNo ratings yet
- A SWOT Analysis template-BBA 140Document6 pagesA SWOT Analysis template-BBA 140Tremor BandaNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Study of Microwave and Conventional SynthesisDocument8 pagesComparitive Study of Microwave and Conventional SynthesisvinayNo ratings yet
- Joyce's PrincipleDocument16 pagesJoyce's PrincipleCtv MontrealNo ratings yet
- Puerto Rico NPI Data EdirectoryDocument62 pagesPuerto Rico NPI Data EdirectoryNPI Data ServicesNo ratings yet
- PaintDocument22 pagesPaintZubair Ahmed KhaskheliNo ratings yet
- 1.b. Bronchiolitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument3 pages1.b. Bronchiolitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDavid CraigNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Mzizi JNDocument118 pagesDissertation Mzizi JNpamelaNo ratings yet
- Reflection (Setting Application 3)Document2 pagesReflection (Setting Application 3)DavidNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology - Medical Microbiology - NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pageEpidemiology - Medical Microbiology - NCBI Bookshelfshruti guptaNo ratings yet
- Obesity Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesObesity Reading ComprehensionDaniela SarmientoNo ratings yet
- ComplaintDocument27 pagesComplaintFOX 11 Los AngelesNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is Hum-WPS OfficeDocument7 pages1.1 What Is Hum-WPS OfficeJesie Bell Balaba BuroNo ratings yet
- MALPRACTICEDocument43 pagesMALPRACTICEDev LitaNo ratings yet
- Ebd 2023Document6 pagesEbd 2023dinaNo ratings yet
- May 2021 Mark Scheme 2BDocument17 pagesMay 2021 Mark Scheme 2BMeenakshie ChaudrieNo ratings yet
- Soal BHS ING SAS SM 2 2023 2024Document3 pagesSoal BHS ING SAS SM 2 2023 2024Hari EngkufNo ratings yet
- Updated Resume 2020Document1 pageUpdated Resume 2020api-516280936No ratings yet
- Book 4Document39 pagesBook 4fatha_87No ratings yet
- Stressing Factors in Nurses Who Work in The Sector of Urgency and EmergencyDocument9 pagesStressing Factors in Nurses Who Work in The Sector of Urgency and EmergencyIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Clinical Experience Reflection 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: Clinical Experience Reflection 1api-520930030No ratings yet