Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infertility 1
Infertility 1
Uploaded by
Mikhaela Andree MarianoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Handbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityFrom EverandHandbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityMichael H. DahanNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus New OnsetDocument5 pagesType 2 Diabetes Mellitus New OnsetMOHANNADNo ratings yet
- TOG 2021 Volume 23 Issue 2Document72 pagesTOG 2021 Volume 23 Issue 2Lakshmi DheviNo ratings yet
- Level III Performance ChecklistDocument43 pagesLevel III Performance ChecklistMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Vidhya Finalised ThesisDocument84 pagesVidhya Finalised Thesisdr.vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Embryology Leeds AdsDocument1 pageClinical Embryology Leeds AdsWael BadranNo ratings yet
- Lewd Rules v3.5 PDFDocument9 pagesLewd Rules v3.5 PDFCaffi261050% (2)
- Medical School Companion Obstetrics and Gynecology Practice Question BookFrom EverandMedical School Companion Obstetrics and Gynecology Practice Question BookNo ratings yet
- Sign of Hyperandrogenism PDFDocument6 pagesSign of Hyperandrogenism PDFmisbah_mdNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Problems Among College Students: Prevalens and Treatment Seeking BehaviorsDocument8 pagesMenstrual Problems Among College Students: Prevalens and Treatment Seeking BehaviorsAlkausyari AzizNo ratings yet
- The Use of Aromatase Inhibitors in Infertility and GynecologyDocument9 pagesThe Use of Aromatase Inhibitors in Infertility and Gynecologyalan lowusNo ratings yet
- Non-Surgical and Surgical Management of Pelvic OrgDocument10 pagesNon-Surgical and Surgical Management of Pelvic OrgAhmed AnwarNo ratings yet
- Congenital Malformations of The Female Genital TractDocument7 pagesCongenital Malformations of The Female Genital TractDo le QuangNo ratings yet
- Mal Presentations Mal PositionsDocument4 pagesMal Presentations Mal PositionsMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Vault ProlapseDocument9 pagesVaginal Vault ProlapseOanaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Right Side Foetal Myocardial Performance Index in Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Right Side Foetal Myocardial Performance Index in Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes MellitusGabyliz Gonzalez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Written2 ADocument5 pagesWritten2 Aivan_gunawan_9No ratings yet
- Double Stimulations During The Follicular and Luteal Phases of Poor Responders in IVF:ICSI Programmes (Shanghai Protocol) - ScienceDirectDocument3 pagesDouble Stimulations During The Follicular and Luteal Phases of Poor Responders in IVF:ICSI Programmes (Shanghai Protocol) - ScienceDirectsamirNo ratings yet
- Ob Gyn PDFDocument29 pagesOb Gyn PDFShelley PantinopleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders During Pregnancy 2006Document223 pagesEndocrine Disorders During Pregnancy 2006STEPHANIE TALILAHNo ratings yet
- Tog Journal 2016Document61 pagesTog Journal 2016thevijay007100% (1)
- Acog Practice Bulletin Summary: Pregestational Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesAcog Practice Bulletin Summary: Pregestational Diabetes MellitusMaría Fernanda Palma AcostaNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Bowel and Bladder Injury Repair and Follow-Up After Gynecologic Surgery - 00006250-201902000-00012Document10 pages2019 - Bowel and Bladder Injury Repair and Follow-Up After Gynecologic Surgery - 00006250-201902000-00012Polyana FloresNo ratings yet
- TC11Document4 pagesTC11FrancisNo ratings yet
- Art PDFDocument38 pagesArt PDFLinguumNo ratings yet
- وتين ٥Document26 pagesوتين ٥Mohammad AlrefaiNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (Neha Martin Msc. NSG 2nd Year)Document13 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease (Neha Martin Msc. NSG 2nd Year)Gunu SinghNo ratings yet
- Table 4.1 AFS Classifi Cation System (: The Embryological-Clinical Classifi CationDocument111 pagesTable 4.1 AFS Classifi Cation System (: The Embryological-Clinical Classifi CationArya Syafaromania RachmaNo ratings yet
- Misoprostol - PPT 1Document61 pagesMisoprostol - PPT 1Hussein AminNo ratings yet
- How To Perform The Best Intrauterine Insemination A Review 2167 0250 1000140Document7 pagesHow To Perform The Best Intrauterine Insemination A Review 2167 0250 1000140Anand NNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument76 pagesEctopic PregnancyVivian Jean TapayaNo ratings yet
- SOAL Masuk 2018Document142 pagesSOAL Masuk 2018Yoza FirdaozNo ratings yet
- HypotoniaDocument45 pagesHypotoniaاثير اااNo ratings yet
- SEMEN Analisis WHODocument138 pagesSEMEN Analisis WHOAnanda Indrawan PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Infertility - الدوائيةDocument95 pagesInfertility - الدوائيةشعاع قحطانNo ratings yet
- POP June 10,2021 1Document48 pagesPOP June 10,2021 1Kerod AbebeNo ratings yet
- Embryo TransferDocument13 pagesEmbryo TransferGerwyn Gervacio CNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument8 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Green Top Guidelines 13Document29 pagesGreen Top Guidelines 13garfield1No ratings yet
- Retinoblastoma - EyeWikiDocument11 pagesRetinoblastoma - EyeWikimay171989No ratings yet
- Printable - Thesis On Bishop ScoreDocument103 pagesPrintable - Thesis On Bishop Scoreanuaurv100% (3)
- Figo ConsensusDocument44 pagesFigo ConsensusMargarita C. Ruiz HuertaNo ratings yet
- ToxichologyDocument36 pagesToxichologyWachi PampasNo ratings yet
- A Neonate With Acute Kidney Injury: Case PresentationDocument4 pagesA Neonate With Acute Kidney Injury: Case PresentationSahil DhamijaNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument14 pagesInfertilityDrChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ethical Considerations of Fetal TherapyDocument13 pagesEthical Considerations of Fetal TherapyRyan SadonoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Disorders of Endocrine System Ppt. Book (Lectures 1-6)Document467 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of Endocrine System Ppt. Book (Lectures 1-6)Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (1)
- Medical Diseases Complicating Pregnancy: by The Name of AllahDocument45 pagesMedical Diseases Complicating Pregnancy: by The Name of Allah'محمد علي' محمد لافيNo ratings yet
- Infertility ACOGDocument8 pagesInfertility ACOGRifdaNo ratings yet
- Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis of Infancy - UpToDateDocument14 pagesFood Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis of Infancy - UpToDateLisa MaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesPediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyNovi BaliNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle: Prepared By: Mrs Bini P S Amuel Assistant Professor, SSRC N, VapiDocument16 pagesMenstrual Cycle: Prepared By: Mrs Bini P S Amuel Assistant Professor, SSRC N, VapiBini Don DanielNo ratings yet
- New Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Paediatric Coeliac DiseaseDocument3 pagesNew Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Paediatric Coeliac DiseaseDiana NicaNo ratings yet
- Clinical MangementDocument19 pagesClinical MangementooiziungieNo ratings yet
- Genital FistulaeDocument15 pagesGenital Fistulaesangeetha francisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 - Hypoglycemia in ChildrenDocument32 pagesLecture 34 - Hypoglycemia in ChildrenjohnsonkkuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Myop in PregnancyDocument4 pagesMyop in PregnancySamuel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument14 pagesCerebral PalsyWaode SittrisnawatiNo ratings yet
- FIGO Guidelines - Prevention and Treatment of PPH Etc1Document12 pagesFIGO Guidelines - Prevention and Treatment of PPH Etc1karinasurakusumaNo ratings yet
- 2023 OB/GYN Coding Manual: Components of Correct CodingFrom Everand2023 OB/GYN Coding Manual: Components of Correct CodingNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument5 pagesPerioperative NursingMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- LM IntensiveDocument2 pagesLM IntensiveMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Activity1 Premise and ConclusionDocument1 pageActivity1 Premise and ConclusionMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Intrapartum: Preparing For The BabyDocument3 pagesAntepartum Intrapartum: Preparing For The BabyMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Additional Clinical Case Study TemplatesDocument4 pagesAdditional Clinical Case Study TemplatesMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Handout 1Document3 pagesPhysical Education Handout 1Mikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Ultraviolet Examination: I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment 8: Ultraviolet Examination: I. ObjectivesMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- City of Malolos: Bulacan State University College of NursingDocument13 pagesCity of Malolos: Bulacan State University College of NursingMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Procedure of Herbal PlantsDocument2 pagesProcedure of Herbal PlantsMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- First Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionDocument4 pagesFirst Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Data Base: City of MalolosDocument13 pagesAssessment Data Base: City of MalolosMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Medications Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesMedications Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Patients RightsDocument8 pagesPatients RightsMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Elimination: Lesson 5eDocument33 pagesUrinary Elimination: Lesson 5eMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Study Guideline and TemplateDocument19 pagesClinical Case Study Guideline and TemplateMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University: College of NursingDocument1 pageBulacan State University: College of NursingMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Consultation Form 1Document1 pageConsultation Form 1Mikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Disease Perception and Coping With Emotional Distress During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Survey Among Medical StaDocument12 pagesDisease Perception and Coping With Emotional Distress During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Survey Among Medical StaMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Hymenolepsis Nana: SyringeDocument4 pagesHymenolepsis Nana: SyringeMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Possible Causes of Cancer: Antineoplastic AgentsDocument7 pagesPossible Causes of Cancer: Antineoplastic AgentsMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Human BeingsDocument6 pagesReproduction in Human BeingsanjupalNo ratings yet
- TECHTALK#1Document299 pagesTECHTALK#1Smit PankhaniaNo ratings yet
- Legislative Oppression - Restricting Gestational Surrogacy ToDocument45 pagesLegislative Oppression - Restricting Gestational Surrogacy ToDrake Lawrence FuentabellaNo ratings yet
- Biology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational ServicesDocument2,088 pagesBiology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational Servicesteamindian gamersNo ratings yet
- CH8 Sacred Sex, Virgin and Wedding NightDocument14 pagesCH8 Sacred Sex, Virgin and Wedding NightTheVeiledGarden50% (2)
- 7th Grade Science StandardsDocument2 pages7th Grade Science Standardsapi-250657038No ratings yet
- Sexual-Contract Open Relationships PDFDocument6 pagesSexual-Contract Open Relationships PDFDarlene KasterNo ratings yet
- A Complete Beginner's Guide To Breast SexDocument2 pagesA Complete Beginner's Guide To Breast SexZahid EmuNo ratings yet
- SpermatozoaDocument7 pagesSpermatozoaSilvin Ezra AmoraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology RevisionDocument88 pagesIGCSE Biology RevisionAlex Parkinson100% (3)
- Scie5 Q2 Mod2 ChangesThatOccurDuringPuberty v3Document17 pagesScie5 Q2 Mod2 ChangesThatOccurDuringPuberty v3DanielMatsunagaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Insemination ManualDocument54 pagesArtificial Insemination ManualSteve Cris SanchezNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesDocument55 pagesReproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesTay Kai xin (Ahs)No ratings yet
- Erotic MassageDocument4 pagesErotic MassagesuzyNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument3 pagesArgumentative EssayMax ZinNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Inheritance PatternDocument22 pagesCell Division and Inheritance PatternSheraz ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Revision Work Sheet 2023-THIRD LANGUAGE-HINDIDocument6 pagesRevision Work Sheet 2023-THIRD LANGUAGE-HINDIadhihNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive System ReviewerJewel Arcega PartoNo ratings yet
- Kineme PhiliaDocument1 pageKineme PhiliaILAO, Danica S.No ratings yet
- Sci PPT Q2 WK 2 Day 1-5Document74 pagesSci PPT Q2 WK 2 Day 1-5mary antonette pagalNo ratings yet
- Stages of Children Development ShantellDocument7 pagesStages of Children Development ShantellShantell ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument30 pagesClass NotesdayakarsyamNo ratings yet
- July 9... CXC BiologyDocument58 pagesJuly 9... CXC BiologyShantay BurtonNo ratings yet
- Module in Science 6 - Reproduction of Non-Vascular PlantsDocument20 pagesModule in Science 6 - Reproduction of Non-Vascular PlantsMAYETTE PAYABANNo ratings yet
- SurrogacyDocument9 pagesSurrogacySangita HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument38 pagesQ4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionPhan MhiveNo ratings yet
- 04 - 2reproduction in ProtozoaDocument5 pages04 - 2reproduction in ProtozoaDipankar RoyNo ratings yet
- 7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13Document2 pages7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13WillSmith100% (1)
- ST SCI 10 wk1-2Document3 pagesST SCI 10 wk1-2Ivygrace NabitadNo ratings yet
Infertility 1
Infertility 1
Uploaded by
Mikhaela Andree MarianoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infertility 1
Infertility 1
Uploaded by
Mikhaela Andree MarianoCopyright:
Available Formats
Bulacan State University
City of Malolos Bulacan
COLLEGE OF NURSING
CARE OF MOTHER, CHILD AND ADOLESCENT (WELL CLIENTS)
NCM 107 Hand- out No: 2b
NURSING CARE OF INFERTILE COUPLE
A. Assessment
1. Common diagnostic studies to detect physiological factors associated with infertility
a. Female
1. Basal Body Temperature (BBT), or resting body temperature
Obtained by the woman taking her oral temperature each day prior to arising
from bed and graphing the results on a month long graph
Sudden dip occurs the day prior to ovulation and is followed by a rise of .5 to 1
degree F, which indicates ovulation; this rise will remain until menstruation
begins
Fertility awareness: includes monitoring the BBT and cervical mucus changes
to detect ovulation
2. Serum Hormone Testing: venous blood is drawn from infertile women to assess
levels of FSH and LH, which are indicators of ovarian functions
3. Postcoital exam
Exam that occurs 8-12 hours’ post- intercourse, 1or 2 days before expected
ovulation
Secretions are examined for:
Signs of infection
Number of active and non-motile spermatozoa
Sperm- mucus interaction
Consistency of cervical mucus
4. Endometrial biopsy
Obtaining an endometrial tissue sample for examination
5. Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
Detects uterine anomalies
6. Laparoscopy
b. Male semen analysis
Client ejaculates into specimen container
Ejaculate is examined microscopically for:
Number
Morphology
Motility
c. Male and female partner: anti- sperm antibody evaluation of cervical mucus and ejaculate
are tested for agglutination, an indication that secretory immunological reactions are occurring
between cervical mucus and spermatozoa.
2. Psychological factors associated with infertility
Many couples experience shame, guilt, blame, or stages of grief when diagnosed with
infertility as well as during treatment for infertility
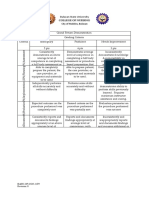
B. Priority Nursing Diagnosis:
1. Compromised Family Coping
2. Deficient Knowledge
3. Anxiety
4. Situational low self esteem
C. Implementation and collaborative care:
1. Education on how to:
a. Perform various procedures
b. The meaning of the results of tests and assessment
c. Self-monitoring during medication administration, and how assisted reproductive technologies are
performed
2. Hormonal therapy
3. Medications
4. Sperm washing for intrauterine insemination
5. Intrauterine insemination is a form of artificial insemination
6. In vitro insemination (IVF)
7. Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT)
8. Tubal embryo transfer (TET)
9. Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
D. Evaluation-
1. The couple’s knowledge is increased regarding:
Diagnostic studies
Infertility problem
Infertility treatment options
2. Clients experience decreased anxiety regarding infertility
3. The clients share their feelings openly
4. The clients make an informed decision to pursue or not pursue treatment for fertility
You might also like
- Handbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityFrom EverandHandbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityMichael H. DahanNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus New OnsetDocument5 pagesType 2 Diabetes Mellitus New OnsetMOHANNADNo ratings yet
- TOG 2021 Volume 23 Issue 2Document72 pagesTOG 2021 Volume 23 Issue 2Lakshmi DheviNo ratings yet
- Level III Performance ChecklistDocument43 pagesLevel III Performance ChecklistMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Vidhya Finalised ThesisDocument84 pagesVidhya Finalised Thesisdr.vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Embryology Leeds AdsDocument1 pageClinical Embryology Leeds AdsWael BadranNo ratings yet
- Lewd Rules v3.5 PDFDocument9 pagesLewd Rules v3.5 PDFCaffi261050% (2)
- Medical School Companion Obstetrics and Gynecology Practice Question BookFrom EverandMedical School Companion Obstetrics and Gynecology Practice Question BookNo ratings yet
- Sign of Hyperandrogenism PDFDocument6 pagesSign of Hyperandrogenism PDFmisbah_mdNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Problems Among College Students: Prevalens and Treatment Seeking BehaviorsDocument8 pagesMenstrual Problems Among College Students: Prevalens and Treatment Seeking BehaviorsAlkausyari AzizNo ratings yet
- The Use of Aromatase Inhibitors in Infertility and GynecologyDocument9 pagesThe Use of Aromatase Inhibitors in Infertility and Gynecologyalan lowusNo ratings yet
- Non-Surgical and Surgical Management of Pelvic OrgDocument10 pagesNon-Surgical and Surgical Management of Pelvic OrgAhmed AnwarNo ratings yet
- Congenital Malformations of The Female Genital TractDocument7 pagesCongenital Malformations of The Female Genital TractDo le QuangNo ratings yet
- Mal Presentations Mal PositionsDocument4 pagesMal Presentations Mal PositionsMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Vault ProlapseDocument9 pagesVaginal Vault ProlapseOanaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Right Side Foetal Myocardial Performance Index in Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Right Side Foetal Myocardial Performance Index in Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes MellitusGabyliz Gonzalez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Written2 ADocument5 pagesWritten2 Aivan_gunawan_9No ratings yet
- Double Stimulations During The Follicular and Luteal Phases of Poor Responders in IVF:ICSI Programmes (Shanghai Protocol) - ScienceDirectDocument3 pagesDouble Stimulations During The Follicular and Luteal Phases of Poor Responders in IVF:ICSI Programmes (Shanghai Protocol) - ScienceDirectsamirNo ratings yet
- Ob Gyn PDFDocument29 pagesOb Gyn PDFShelley PantinopleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders During Pregnancy 2006Document223 pagesEndocrine Disorders During Pregnancy 2006STEPHANIE TALILAHNo ratings yet
- Tog Journal 2016Document61 pagesTog Journal 2016thevijay007100% (1)
- Acog Practice Bulletin Summary: Pregestational Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesAcog Practice Bulletin Summary: Pregestational Diabetes MellitusMaría Fernanda Palma AcostaNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Bowel and Bladder Injury Repair and Follow-Up After Gynecologic Surgery - 00006250-201902000-00012Document10 pages2019 - Bowel and Bladder Injury Repair and Follow-Up After Gynecologic Surgery - 00006250-201902000-00012Polyana FloresNo ratings yet
- TC11Document4 pagesTC11FrancisNo ratings yet
- Art PDFDocument38 pagesArt PDFLinguumNo ratings yet
- وتين ٥Document26 pagesوتين ٥Mohammad AlrefaiNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (Neha Martin Msc. NSG 2nd Year)Document13 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease (Neha Martin Msc. NSG 2nd Year)Gunu SinghNo ratings yet
- Table 4.1 AFS Classifi Cation System (: The Embryological-Clinical Classifi CationDocument111 pagesTable 4.1 AFS Classifi Cation System (: The Embryological-Clinical Classifi CationArya Syafaromania RachmaNo ratings yet
- Misoprostol - PPT 1Document61 pagesMisoprostol - PPT 1Hussein AminNo ratings yet
- How To Perform The Best Intrauterine Insemination A Review 2167 0250 1000140Document7 pagesHow To Perform The Best Intrauterine Insemination A Review 2167 0250 1000140Anand NNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument76 pagesEctopic PregnancyVivian Jean TapayaNo ratings yet
- SOAL Masuk 2018Document142 pagesSOAL Masuk 2018Yoza FirdaozNo ratings yet
- HypotoniaDocument45 pagesHypotoniaاثير اااNo ratings yet
- SEMEN Analisis WHODocument138 pagesSEMEN Analisis WHOAnanda Indrawan PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Infertility - الدوائيةDocument95 pagesInfertility - الدوائيةشعاع قحطانNo ratings yet
- POP June 10,2021 1Document48 pagesPOP June 10,2021 1Kerod AbebeNo ratings yet
- Embryo TransferDocument13 pagesEmbryo TransferGerwyn Gervacio CNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument8 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Green Top Guidelines 13Document29 pagesGreen Top Guidelines 13garfield1No ratings yet
- Retinoblastoma - EyeWikiDocument11 pagesRetinoblastoma - EyeWikimay171989No ratings yet
- Printable - Thesis On Bishop ScoreDocument103 pagesPrintable - Thesis On Bishop Scoreanuaurv100% (3)
- Figo ConsensusDocument44 pagesFigo ConsensusMargarita C. Ruiz HuertaNo ratings yet
- ToxichologyDocument36 pagesToxichologyWachi PampasNo ratings yet
- A Neonate With Acute Kidney Injury: Case PresentationDocument4 pagesA Neonate With Acute Kidney Injury: Case PresentationSahil DhamijaNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument14 pagesInfertilityDrChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ethical Considerations of Fetal TherapyDocument13 pagesEthical Considerations of Fetal TherapyRyan SadonoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Disorders of Endocrine System Ppt. Book (Lectures 1-6)Document467 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of Endocrine System Ppt. Book (Lectures 1-6)Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (1)
- Medical Diseases Complicating Pregnancy: by The Name of AllahDocument45 pagesMedical Diseases Complicating Pregnancy: by The Name of Allah'محمد علي' محمد لافيNo ratings yet
- Infertility ACOGDocument8 pagesInfertility ACOGRifdaNo ratings yet
- Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis of Infancy - UpToDateDocument14 pagesFood Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis of Infancy - UpToDateLisa MaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesPediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyNovi BaliNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle: Prepared By: Mrs Bini P S Amuel Assistant Professor, SSRC N, VapiDocument16 pagesMenstrual Cycle: Prepared By: Mrs Bini P S Amuel Assistant Professor, SSRC N, VapiBini Don DanielNo ratings yet
- New Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Paediatric Coeliac DiseaseDocument3 pagesNew Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Paediatric Coeliac DiseaseDiana NicaNo ratings yet
- Clinical MangementDocument19 pagesClinical MangementooiziungieNo ratings yet
- Genital FistulaeDocument15 pagesGenital Fistulaesangeetha francisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 - Hypoglycemia in ChildrenDocument32 pagesLecture 34 - Hypoglycemia in ChildrenjohnsonkkuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Myop in PregnancyDocument4 pagesMyop in PregnancySamuel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument14 pagesCerebral PalsyWaode SittrisnawatiNo ratings yet
- FIGO Guidelines - Prevention and Treatment of PPH Etc1Document12 pagesFIGO Guidelines - Prevention and Treatment of PPH Etc1karinasurakusumaNo ratings yet
- 2023 OB/GYN Coding Manual: Components of Correct CodingFrom Everand2023 OB/GYN Coding Manual: Components of Correct CodingNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument5 pagesPerioperative NursingMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- LM IntensiveDocument2 pagesLM IntensiveMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Activity1 Premise and ConclusionDocument1 pageActivity1 Premise and ConclusionMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Intrapartum: Preparing For The BabyDocument3 pagesAntepartum Intrapartum: Preparing For The BabyMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Additional Clinical Case Study TemplatesDocument4 pagesAdditional Clinical Case Study TemplatesMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Handout 1Document3 pagesPhysical Education Handout 1Mikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Ultraviolet Examination: I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment 8: Ultraviolet Examination: I. ObjectivesMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- City of Malolos: Bulacan State University College of NursingDocument13 pagesCity of Malolos: Bulacan State University College of NursingMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Procedure of Herbal PlantsDocument2 pagesProcedure of Herbal PlantsMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- First Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionDocument4 pagesFirst Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Data Base: City of MalolosDocument13 pagesAssessment Data Base: City of MalolosMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Medications Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesMedications Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Patients RightsDocument8 pagesPatients RightsMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Elimination: Lesson 5eDocument33 pagesUrinary Elimination: Lesson 5eMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Study Guideline and TemplateDocument19 pagesClinical Case Study Guideline and TemplateMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University: College of NursingDocument1 pageBulacan State University: College of NursingMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Consultation Form 1Document1 pageConsultation Form 1Mikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Disease Perception and Coping With Emotional Distress During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Survey Among Medical StaDocument12 pagesDisease Perception and Coping With Emotional Distress During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Survey Among Medical StaMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Hymenolepsis Nana: SyringeDocument4 pagesHymenolepsis Nana: SyringeMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Possible Causes of Cancer: Antineoplastic AgentsDocument7 pagesPossible Causes of Cancer: Antineoplastic AgentsMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Human BeingsDocument6 pagesReproduction in Human BeingsanjupalNo ratings yet
- TECHTALK#1Document299 pagesTECHTALK#1Smit PankhaniaNo ratings yet
- Legislative Oppression - Restricting Gestational Surrogacy ToDocument45 pagesLegislative Oppression - Restricting Gestational Surrogacy ToDrake Lawrence FuentabellaNo ratings yet
- Biology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational ServicesDocument2,088 pagesBiology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational Servicesteamindian gamersNo ratings yet
- CH8 Sacred Sex, Virgin and Wedding NightDocument14 pagesCH8 Sacred Sex, Virgin and Wedding NightTheVeiledGarden50% (2)
- 7th Grade Science StandardsDocument2 pages7th Grade Science Standardsapi-250657038No ratings yet
- Sexual-Contract Open Relationships PDFDocument6 pagesSexual-Contract Open Relationships PDFDarlene KasterNo ratings yet
- A Complete Beginner's Guide To Breast SexDocument2 pagesA Complete Beginner's Guide To Breast SexZahid EmuNo ratings yet
- SpermatozoaDocument7 pagesSpermatozoaSilvin Ezra AmoraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology RevisionDocument88 pagesIGCSE Biology RevisionAlex Parkinson100% (3)
- Scie5 Q2 Mod2 ChangesThatOccurDuringPuberty v3Document17 pagesScie5 Q2 Mod2 ChangesThatOccurDuringPuberty v3DanielMatsunagaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Insemination ManualDocument54 pagesArtificial Insemination ManualSteve Cris SanchezNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesDocument55 pagesReproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesTay Kai xin (Ahs)No ratings yet
- Erotic MassageDocument4 pagesErotic MassagesuzyNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument3 pagesArgumentative EssayMax ZinNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Inheritance PatternDocument22 pagesCell Division and Inheritance PatternSheraz ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Revision Work Sheet 2023-THIRD LANGUAGE-HINDIDocument6 pagesRevision Work Sheet 2023-THIRD LANGUAGE-HINDIadhihNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive System ReviewerJewel Arcega PartoNo ratings yet
- Kineme PhiliaDocument1 pageKineme PhiliaILAO, Danica S.No ratings yet
- Sci PPT Q2 WK 2 Day 1-5Document74 pagesSci PPT Q2 WK 2 Day 1-5mary antonette pagalNo ratings yet
- Stages of Children Development ShantellDocument7 pagesStages of Children Development ShantellShantell ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument30 pagesClass NotesdayakarsyamNo ratings yet
- July 9... CXC BiologyDocument58 pagesJuly 9... CXC BiologyShantay BurtonNo ratings yet
- Module in Science 6 - Reproduction of Non-Vascular PlantsDocument20 pagesModule in Science 6 - Reproduction of Non-Vascular PlantsMAYETTE PAYABANNo ratings yet
- SurrogacyDocument9 pagesSurrogacySangita HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument38 pagesQ4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionPhan MhiveNo ratings yet
- 04 - 2reproduction in ProtozoaDocument5 pages04 - 2reproduction in ProtozoaDipankar RoyNo ratings yet
- 7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13Document2 pages7th Chapter - Reproduction in Plants - Summative Assessment II 2012-13WillSmith100% (1)
- ST SCI 10 wk1-2Document3 pagesST SCI 10 wk1-2Ivygrace NabitadNo ratings yet