Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics Representators
Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics Representators
Uploaded by
Manja ĆetkovićCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureDocument9 pagesLab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureFloyd SeremNo ratings yet
- Phillipose, M.T. P. 0-23Document17 pagesPhillipose, M.T. P. 0-23MAYAKKANNAN G100% (2)
- Day 2Document15 pagesDay 2saifali986254No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom AlgaeDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdom AlgaeKhùśh NäùłákhāNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationketakiNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesPlant Kingdommariamfernandes6No ratings yet
- CH 3Document6 pagesCH 3Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledsrishtiNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomAanchal PandeyNo ratings yet
- 9.algaeDocument5 pages9.algaeMukbsNo ratings yet
- 9.algaeDocument5 pages9.algaeMukbsNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Belwal Chandrashkear ChethanDocument6 pagesCH 3 Belwal Chandrashkear ChethanShivammaNo ratings yet
- Chlorophyta & EuglenophytaDocument17 pagesChlorophyta & EuglenophytaNia AnandaNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Microorganisms: Part 2: Eucaryotic MicrobesDocument26 pagesDiversity of Microorganisms: Part 2: Eucaryotic MicrobesSri Widia NingsihNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdomrautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Classification of Algae - FritchDocument4 pagesClassification of Algae - Fritchsharina NNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Plant KingdomDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Plant KingdomYashiNo ratings yet
- Zbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Document15 pagesZbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Ashok ParasharNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesPlant KingdomAMLAAN 10CNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Quick NotesDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdom Quick NotesDevesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages3 Plant KingdomitzanandNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 PLANT KINGDOMDocument8 pagesCh-3 PLANT KINGDOMKrishna SenapatiNo ratings yet
- .Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesDocument10 pages.Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy NotesDocument13 pagesPlant Taxonomy NotesMikaela MendozaNo ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesII ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- 1.4.1 Eukaryotes - Fungi, Algae, Protozoan - Structure, ClassificationDocument31 pages1.4.1 Eukaryotes - Fungi, Algae, Protozoan - Structure, Classificationjumbergy01No ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument34 pagesAlgaeAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom PowernotesDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdom Powernotessheikhanzar643No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom - Handwritten Notes 02Document9 pagesPlant Kingdom - Handwritten Notes 02rkamini995No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWrajatbharti830No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomArnavNo ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument53 pagesAlgaeDeepika KVNo ratings yet
- KINGDOM Plantae + Algae For StudentsDocument8 pagesKINGDOM Plantae + Algae For Studentsraahat soniNo ratings yet
- Higher Secondary Botany Short Notes DR Anil HssliveDocument15 pagesHigher Secondary Botany Short Notes DR Anil Hsslivetobyviru2255No ratings yet
- Botany Taxonomy SummaryDocument12 pagesBotany Taxonomy SummaryVINCENT IMPERIALNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom ChartDocument1 pagePlant Kingdom ChartTanya SiyagNo ratings yet
- Most Amazing LMR Plant Kingdom..Document5 pagesMost Amazing LMR Plant Kingdom..anoushkalvy2510No ratings yet
- Laboratory Notes For BIO 1003Document7 pagesLaboratory Notes For BIO 1003kedahn9No ratings yet
- Protistans (English Version)Document8 pagesProtistans (English Version)Brian Adam MJfansNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassDocument4 pagesBiological ClassVaibhav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Part 1 4Document3 pagesPlant Kingdom Part 1 4Mahesh DodkeNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument40 pagesKingdom PlantaeSelvaraju ParthibhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDivyansha Sharma100% (1)
- Shaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolDocument62 pagesShaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- 2 Biological Classification-Sample Notes 2021Document2 pages2 Biological Classification-Sample Notes 2021Pranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Tree of LifeDocument3 pagesKingdom Plantae Tree of LifekathluqNo ratings yet
- Basis of Classification: Plant TaxonomyDocument4 pagesBasis of Classification: Plant TaxonomyEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Bio 111 LecDocument50 pagesBio 111 LecFlorence PalomarNo ratings yet
- Taxanomy - TableDocument1 pageTaxanomy - TableJue Vee LimNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom NotesDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdom NotesAmythNo ratings yet
- Week Two Biology SS1Document12 pagesWeek Two Biology SS1Oseni MuibaNo ratings yet
- General Characters of AlgaeDocument50 pagesGeneral Characters of AlgaeAnilNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument34 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma Acidarmanusjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- 1.4domain Eukarya: Kingdom ProtistaDocument42 pages1.4domain Eukarya: Kingdom ProtistaaixyaehNo ratings yet
- Brown AlgaeDocument19 pagesBrown AlgaelaluwimaNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument4 pagesBiological ClassificationYashwanthNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plant KingdomDocument31 pages3 - Plant KingdomYuvaraj100% (1)
- Iesc 107Document18 pagesIesc 107Sunnu BabyNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 Module 5 Reduced FileDocument12 pagesScience7 Q2 Module 5 Reduced FileKei SparksNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Enhanvement in Food Production PDFDocument15 pagesStrategies For Enhanvement in Food Production PDFKRUPAASREENo ratings yet
- Energy, Ecology and Environment (ESL 330) : Course InstructorsDocument12 pagesEnergy, Ecology and Environment (ESL 330) : Course InstructorsEthan HuntNo ratings yet
- A Brief Account of Territorial Behaviour in AnimalsDocument7 pagesA Brief Account of Territorial Behaviour in AnimalsKapil SharmaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- FromAntsGrizzlies Transcript FilmDocument5 pagesFromAntsGrizzlies Transcript FilmRennik McCaigNo ratings yet
- Animal Description WorksheetDocument3 pagesAnimal Description WorksheetSneider Cardona100% (1)
- A. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCDocument1 pageA. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCHannah 晗❾No ratings yet
- Cell Wall and Cell Membrane 23rd AugustDocument7 pagesCell Wall and Cell Membrane 23rd AugustRanjan SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingDocument9 pagesA Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingMaria Angela Caisapanta PachecoNo ratings yet
- Soil FungiDocument22 pagesSoil Fungidwana148100% (1)
- Documentation and Reflection Paper Format of 'TREE-PARENTING' ProjectDocument6 pagesDocumentation and Reflection Paper Format of 'TREE-PARENTING' ProjectJohn LopezNo ratings yet
- Wildlife ActDocument42 pagesWildlife ActEmiaNo ratings yet
- Plant Leaves: Pha 611 Lec Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyDocument44 pagesPlant Leaves: Pha 611 Lec Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyLlang LleavNo ratings yet
- Algae Botany 2021 B.Sc. 1st YrDocument4 pagesAlgae Botany 2021 B.Sc. 1st YrPET BOTANY 2021No ratings yet
- Lepidocyclina Sp. ,: A. Foraminifera Besar 1Document11 pagesLepidocyclina Sp. ,: A. Foraminifera Besar 1lidia aprilitaNo ratings yet
- Cpp-Biology-Class 8-Phase 1Document3 pagesCpp-Biology-Class 8-Phase 1NischalNo ratings yet
- Sanyam and VipashaDocument10 pagesSanyam and VipashaAnonymous zy3rAYHNo ratings yet
- Cupressus Sempervirens (Mediterranean Cypress) - CABI CompendiumDocument14 pagesCupressus Sempervirens (Mediterranean Cypress) - CABI CompendiumJoshua LindgrenNo ratings yet
- Drosophila: (White vs. Bar)Document9 pagesDrosophila: (White vs. Bar)api-302938634No ratings yet
- Assigment Unit 6 and Unit 20Document5 pagesAssigment Unit 6 and Unit 20Galuh ChanNo ratings yet
- Combining Pure-Line and Cross-Bred Information in Poultry BreedingDocument6 pagesCombining Pure-Line and Cross-Bred Information in Poultry BreedingRvk NairNo ratings yet
- 1B3 Pond Ecosystem Reading PDFDocument2 pages1B3 Pond Ecosystem Reading PDFhendrywNo ratings yet
- Scope and SequenceDocument1 pageScope and SequenceBabNo ratings yet
- Relationships Among OrganismsDocument47 pagesRelationships Among OrganismsFirasat SultanNo ratings yet
- (Journal) Pediatrics Clinics of North America. Volume 53. Number 6 (2006) PDFDocument249 pages(Journal) Pediatrics Clinics of North America. Volume 53. Number 6 (2006) PDFEnrique TrvjilloNo ratings yet
- Beed 16 Multigrade DLPDocument10 pagesBeed 16 Multigrade DLPDesyrie Joy Soriano DirayNo ratings yet
- 1718 1st DCP Project Sheet 8 Biology - OKDocument8 pages1718 1st DCP Project Sheet 8 Biology - OKMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics Representators
Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics Representators
Uploaded by
Manja ĆetkovićOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics Representators
Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics Representators
Uploaded by
Manja ĆetkovićCopyright:
Available Formats
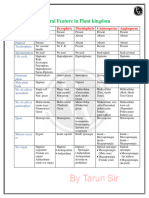
Types of Algae and
Characteristics Representators
their pigments
Euglenophyta
-Unicellular organisms
(Euglenoids)
that are able to move
Phacus
-They lack a cell wall
Chlorophyll a Euglena
but they have an
and b Trachelomonas
elastic pellicle around
Carotenoids
them instead
Xanthophylls
-Vegetative
Phacus reproduction
Diatomea, -Mostly unicellular,
Bacillariophyta they rarely form
(Diatoms) colonies and can be
found in different Asterionella
Chlorophyll a shapes Fragilaria
and c -They have a strong Cymbella
Carotenoids cell wall made out of
Xanthophylls silicium
Asterionella -Asexual and sexual
reproduction
Paeophyta
(Brownalgae)
-Giant kelp forms thick Fucus
Chlorophyll a underwater forests Laminaria
and c -Asexual and sexual Microcystis
Carotenoids reproduction
Xanthophylls Fucus
Chlorophyta -Unicellular and often
(Greenalgae) form colonies
-They can live in fresh
Chlorophyll a and saltwater as well
Spirogyra
and b as out of it.
Chlorococcus
Carotenoids -Green Algae are
Chlamydomonas
Xanthophylls predecessors of most
land plants
-Vegetative, asexual
Spirogyra
and sexual
reproduction
Rhodophyta (Red algae)
Chlorophyll a -Multicellular algae
and d They live at a depth of Gelidium
Carotenoids 250m Coralline
Xanthophylls -Vegetative, sexual Batrachospermum
Phycobilin blue and asexual
and red reproduction
Gelidium
You might also like
- Lab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureDocument9 pagesLab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureFloyd SeremNo ratings yet
- Phillipose, M.T. P. 0-23Document17 pagesPhillipose, M.T. P. 0-23MAYAKKANNAN G100% (2)
- Day 2Document15 pagesDay 2saifali986254No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom AlgaeDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdom AlgaeKhùśh NäùłákhāNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationketakiNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesPlant Kingdommariamfernandes6No ratings yet
- CH 3Document6 pagesCH 3Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledsrishtiNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomAanchal PandeyNo ratings yet
- 9.algaeDocument5 pages9.algaeMukbsNo ratings yet
- 9.algaeDocument5 pages9.algaeMukbsNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Belwal Chandrashkear ChethanDocument6 pagesCH 3 Belwal Chandrashkear ChethanShivammaNo ratings yet
- Chlorophyta & EuglenophytaDocument17 pagesChlorophyta & EuglenophytaNia AnandaNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Microorganisms: Part 2: Eucaryotic MicrobesDocument26 pagesDiversity of Microorganisms: Part 2: Eucaryotic MicrobesSri Widia NingsihNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdomrautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Classification of Algae - FritchDocument4 pagesClassification of Algae - Fritchsharina NNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Plant KingdomDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Plant KingdomYashiNo ratings yet
- Zbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Document15 pagesZbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Ashok ParasharNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesPlant KingdomAMLAAN 10CNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Quick NotesDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdom Quick NotesDevesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages3 Plant KingdomitzanandNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 PLANT KINGDOMDocument8 pagesCh-3 PLANT KINGDOMKrishna SenapatiNo ratings yet
- .Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesDocument10 pages.Trashed-Plant Kingdom NotesAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy NotesDocument13 pagesPlant Taxonomy NotesMikaela MendozaNo ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesII ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- 1.4.1 Eukaryotes - Fungi, Algae, Protozoan - Structure, ClassificationDocument31 pages1.4.1 Eukaryotes - Fungi, Algae, Protozoan - Structure, Classificationjumbergy01No ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument34 pagesAlgaeAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom PowernotesDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdom Powernotessheikhanzar643No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom - Handwritten Notes 02Document9 pagesPlant Kingdom - Handwritten Notes 02rkamini995No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom Notes by Tarun Sir PWrajatbharti830No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomArnavNo ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument53 pagesAlgaeDeepika KVNo ratings yet
- KINGDOM Plantae + Algae For StudentsDocument8 pagesKINGDOM Plantae + Algae For Studentsraahat soniNo ratings yet
- Higher Secondary Botany Short Notes DR Anil HssliveDocument15 pagesHigher Secondary Botany Short Notes DR Anil Hsslivetobyviru2255No ratings yet
- Botany Taxonomy SummaryDocument12 pagesBotany Taxonomy SummaryVINCENT IMPERIALNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom ChartDocument1 pagePlant Kingdom ChartTanya SiyagNo ratings yet
- Most Amazing LMR Plant Kingdom..Document5 pagesMost Amazing LMR Plant Kingdom..anoushkalvy2510No ratings yet
- Laboratory Notes For BIO 1003Document7 pagesLaboratory Notes For BIO 1003kedahn9No ratings yet
- Protistans (English Version)Document8 pagesProtistans (English Version)Brian Adam MJfansNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassDocument4 pagesBiological ClassVaibhav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Part 1 4Document3 pagesPlant Kingdom Part 1 4Mahesh DodkeNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument40 pagesKingdom PlantaeSelvaraju ParthibhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDivyansha Sharma100% (1)
- Shaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolDocument62 pagesShaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- 2 Biological Classification-Sample Notes 2021Document2 pages2 Biological Classification-Sample Notes 2021Pranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Tree of LifeDocument3 pagesKingdom Plantae Tree of LifekathluqNo ratings yet
- Basis of Classification: Plant TaxonomyDocument4 pagesBasis of Classification: Plant TaxonomyEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Bio 111 LecDocument50 pagesBio 111 LecFlorence PalomarNo ratings yet
- Taxanomy - TableDocument1 pageTaxanomy - TableJue Vee LimNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom NotesDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdom NotesAmythNo ratings yet
- Week Two Biology SS1Document12 pagesWeek Two Biology SS1Oseni MuibaNo ratings yet
- General Characters of AlgaeDocument50 pagesGeneral Characters of AlgaeAnilNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument34 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma Acidarmanusjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- 1.4domain Eukarya: Kingdom ProtistaDocument42 pages1.4domain Eukarya: Kingdom ProtistaaixyaehNo ratings yet
- Brown AlgaeDocument19 pagesBrown AlgaelaluwimaNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument4 pagesBiological ClassificationYashwanthNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plant KingdomDocument31 pages3 - Plant KingdomYuvaraj100% (1)
- Iesc 107Document18 pagesIesc 107Sunnu BabyNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 Module 5 Reduced FileDocument12 pagesScience7 Q2 Module 5 Reduced FileKei SparksNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Enhanvement in Food Production PDFDocument15 pagesStrategies For Enhanvement in Food Production PDFKRUPAASREENo ratings yet
- Energy, Ecology and Environment (ESL 330) : Course InstructorsDocument12 pagesEnergy, Ecology and Environment (ESL 330) : Course InstructorsEthan HuntNo ratings yet
- A Brief Account of Territorial Behaviour in AnimalsDocument7 pagesA Brief Account of Territorial Behaviour in AnimalsKapil SharmaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant Cell - LatestAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- FromAntsGrizzlies Transcript FilmDocument5 pagesFromAntsGrizzlies Transcript FilmRennik McCaigNo ratings yet
- Animal Description WorksheetDocument3 pagesAnimal Description WorksheetSneider Cardona100% (1)
- A. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCDocument1 pageA. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCHannah 晗❾No ratings yet
- Cell Wall and Cell Membrane 23rd AugustDocument7 pagesCell Wall and Cell Membrane 23rd AugustRanjan SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingDocument9 pagesA Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingMaria Angela Caisapanta PachecoNo ratings yet
- Soil FungiDocument22 pagesSoil Fungidwana148100% (1)
- Documentation and Reflection Paper Format of 'TREE-PARENTING' ProjectDocument6 pagesDocumentation and Reflection Paper Format of 'TREE-PARENTING' ProjectJohn LopezNo ratings yet
- Wildlife ActDocument42 pagesWildlife ActEmiaNo ratings yet
- Plant Leaves: Pha 611 Lec Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyDocument44 pagesPlant Leaves: Pha 611 Lec Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyLlang LleavNo ratings yet
- Algae Botany 2021 B.Sc. 1st YrDocument4 pagesAlgae Botany 2021 B.Sc. 1st YrPET BOTANY 2021No ratings yet
- Lepidocyclina Sp. ,: A. Foraminifera Besar 1Document11 pagesLepidocyclina Sp. ,: A. Foraminifera Besar 1lidia aprilitaNo ratings yet
- Cpp-Biology-Class 8-Phase 1Document3 pagesCpp-Biology-Class 8-Phase 1NischalNo ratings yet
- Sanyam and VipashaDocument10 pagesSanyam and VipashaAnonymous zy3rAYHNo ratings yet
- Cupressus Sempervirens (Mediterranean Cypress) - CABI CompendiumDocument14 pagesCupressus Sempervirens (Mediterranean Cypress) - CABI CompendiumJoshua LindgrenNo ratings yet
- Drosophila: (White vs. Bar)Document9 pagesDrosophila: (White vs. Bar)api-302938634No ratings yet
- Assigment Unit 6 and Unit 20Document5 pagesAssigment Unit 6 and Unit 20Galuh ChanNo ratings yet
- Combining Pure-Line and Cross-Bred Information in Poultry BreedingDocument6 pagesCombining Pure-Line and Cross-Bred Information in Poultry BreedingRvk NairNo ratings yet
- 1B3 Pond Ecosystem Reading PDFDocument2 pages1B3 Pond Ecosystem Reading PDFhendrywNo ratings yet
- Scope and SequenceDocument1 pageScope and SequenceBabNo ratings yet
- Relationships Among OrganismsDocument47 pagesRelationships Among OrganismsFirasat SultanNo ratings yet
- (Journal) Pediatrics Clinics of North America. Volume 53. Number 6 (2006) PDFDocument249 pages(Journal) Pediatrics Clinics of North America. Volume 53. Number 6 (2006) PDFEnrique TrvjilloNo ratings yet
- Beed 16 Multigrade DLPDocument10 pagesBeed 16 Multigrade DLPDesyrie Joy Soriano DirayNo ratings yet
- 1718 1st DCP Project Sheet 8 Biology - OKDocument8 pages1718 1st DCP Project Sheet 8 Biology - OKMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet