Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku Notes
Flavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku Notes
Uploaded by
Ronald BeasleyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Special Operations Forces Medical HandbookFrom EverandSpecial Operations Forces Medical HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Presentation On Dengue FeverDocument31 pagesPresentation On Dengue FeverDrMuhammad Ishfaq HabibNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiologyteddydeclines1483% (18)
- John Jay Immunization FormDocument3 pagesJohn Jay Immunization FormIsam BoukattayaNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Dengue 29052021Document43 pagesInfeksi Dengue 29052021Feby JuwitaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Document31 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Sheryl ElitaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Virus: DescriptionDocument12 pagesDengue Virus: Descriptionpedia blue bookNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemmorhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Document64 pagesDengue Hemmorhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Sheryl ElitaNo ratings yet
- DENGUEDocument14 pagesDENGUEAnaluciaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Didactics Dengue - 2Document75 pagesPedia Didactics Dengue - 2Joy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Dengue Insight DR Amit Johari Edited 2020Document82 pagesDengue Insight DR Amit Johari Edited 2020Vedehi BansalNo ratings yet
- Denguefever 180705234058Document2 pagesDenguefever 180705234058PLDT HOMENo ratings yet
- DHF - CDCDocument105 pagesDHF - CDCpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever & DHFDocument32 pagesDengue Fever & DHFWilliam Bunga DatuNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever & DHFDocument32 pagesDengue Fever & DHFArdan SafitraNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document11 pagesGroup 2Maya Hani MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Arthropod-Borne Viruses (Arboviruses) : Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)Document2 pagesArthropod-Borne Viruses (Arboviruses) : Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)MonicaNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument67 pagesDengueRafaela LennyNo ratings yet
- DR AfableDocument25 pagesDR AfableJohnny DeeNo ratings yet
- Dengue JimshDocument19 pagesDengue JimshRatul SealNo ratings yet
- Project On ManagmentDocument32 pagesProject On ManagmentRinkuNo ratings yet
- Management of Dengue FeverDocument31 pagesManagement of Dengue FeverDaniel RajNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa Dan Penatalaksanaan: Demam Berdarah DengueDocument48 pagesDiagnosa Dan Penatalaksanaan: Demam Berdarah DengueFahmi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Patofisiologi: Penularan Melalui Gigitan NyamukDocument1 pageDengue Fever Patofisiologi: Penularan Melalui Gigitan NyamukDinda RensiNo ratings yet
- Updated Management of Dengue, ImrulDocument73 pagesUpdated Management of Dengue, ImrulFaheem Ul HasanNo ratings yet
- Top Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingDocument3 pagesTop Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Dengue: Demam Berdarah Dengue Demam DengueDocument62 pagesInfeksi Virus Dengue: Demam Berdarah Dengue Demam DengueMarwi VinaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYAngela Jane MadristaNo ratings yet
- Who Dengue Classification and Differentials ModuleDocument14 pagesWho Dengue Classification and Differentials ModuleKevin AgbonesNo ratings yet
- How To Manage Vector-Borne Viral Disease As General Practitioner in Primary Health Care? (Dengue-Chikungunya-Zika Infection)Document83 pagesHow To Manage Vector-Borne Viral Disease As General Practitioner in Primary Health Care? (Dengue-Chikungunya-Zika Infection)fida amalinaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Presentation (KEMU)Document90 pagesDengue Presentation (KEMU)MuhammadTalhaNo ratings yet
- Dengue PathophysioDocument4 pagesDengue PathophysioHonhon MacasaquitNo ratings yet
- Dengue (3-8-2015)Document45 pagesDengue (3-8-2015)vishnuNo ratings yet
- Dengue AutosavedDocument12 pagesDengue AutosavedMaricris PallarNo ratings yet
- Demam Berdarah Dengue Pada Anak: MustaringDocument70 pagesDemam Berdarah Dengue Pada Anak: MustaringpipitNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Schematic DiagramDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Schematic DiagramTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Arthropod-Borne Virus 1-RirisDocument37 pagesArthropod-Borne Virus 1-Ririslutfia papitaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEKenrick Randell IbanaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Diagnosis: Ratna Setia AsihDocument24 pagesDengue Diagnosis: Ratna Setia AsihsanelyristiNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)Document37 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)sitizulfahhNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Pathophysiology and Its ManagementDocument2 pagesDengue Fever Pathophysiology and Its ManagementTeresita AvilesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatingDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatinggizelleNo ratings yet
- Pedia Tickler Update 2017Document2 pagesPedia Tickler Update 2017Tani BokNo ratings yet
- Dengue SlideDocument48 pagesDengue SlideKurouSakiNo ratings yet
- Demam Berdarah DengueDocument44 pagesDemam Berdarah DengueLastry Wardani100% (2)
- R. P. Vashist, Consultant Public HealthDocument26 pagesR. P. Vashist, Consultant Public Healthmaharshi mNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinDocument68 pagesDr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinSourav NathNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhage Fever 2Document49 pagesDengue Hemorrhage Fever 2chhaiden100% (3)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologylylasherliaNo ratings yet
- Dengue, Chikungunya Yellow Fever: Dr. Saida SharminDocument48 pagesDengue, Chikungunya Yellow Fever: Dr. Saida SharminBishwajit BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- DHF - CDC Utk DiprintDocument72 pagesDHF - CDC Utk DiprintpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Either Silent or Switched OffDocument67 pagesEither Silent or Switched OffPankaj Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Dengue VirusDocument2 pagesDengue VirusImee Claire PacisNo ratings yet
- Alert Medical Series: USMLE Alert I, II, IIIFrom EverandAlert Medical Series: USMLE Alert I, II, IIIRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Ideal Lymphedema Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide For Effective Lymphedema Management And Treatment With Nutritious RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Lymphedema Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide For Effective Lymphedema Management And Treatment With Nutritious RecipesNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Reactions PDFDocument3 pagesHypersensitivity Reactions PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Goku Notes: Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (Bunyaviruses, Arenaviruses, Filoviruses) - Dra. Ma. Ellery MendezDocument5 pagesGoku Notes: Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (Bunyaviruses, Arenaviruses, Filoviruses) - Dra. Ma. Ellery MendezRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesImmunology PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Influenza PDFDocument5 pagesInfluenza PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Borrelia and Leptospira Lecturer: Dra. Ferrer: Goku NotesDocument3 pagesBorrelia and Leptospira Lecturer: Dra. Ferrer: Goku NotesRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Goku Notes: Anaerobes Lecturer: Dr. LimDocument3 pagesGoku Notes: Anaerobes Lecturer: Dr. LimRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Hepatotrophic Viruses PDFDocument9 pagesHepatotrophic Viruses PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosDocument20 pagesOpportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Vaccines Research PaperDocument16 pagesVaccines Research PaperHana Pung100% (1)
- Update On COVID 19 Projections 2021.12.07 English 1Document18 pagesUpdate On COVID 19 Projections 2021.12.07 English 1Toronto StarNo ratings yet
- Bullous PemphigoidDocument21 pagesBullous PemphigoidChe Ainil ZainodinNo ratings yet
- MYCOFAST-RevolutioN-ATB Direct Brochure EN 2019-10Document2 pagesMYCOFAST-RevolutioN-ATB Direct Brochure EN 2019-10Lilia ZidouniNo ratings yet
- Deficiency of C8 Case Study NotesDocument2 pagesDeficiency of C8 Case Study NotesIan SibalNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology, Infectious Diseases, Parasitology & Tropical Diseases Notes 4Document165 pagesEpidemiology, Infectious Diseases, Parasitology & Tropical Diseases Notes 4Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- Reaksi AnafilaksisDocument34 pagesReaksi AnafilaksisPutri Reno IntanNo ratings yet
- Immunology Worksheet1Document4 pagesImmunology Worksheet1Caviles, Jasmin S.No ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH Programs PDFDocument24 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH Programs PDFMiss GNo ratings yet
- E ColiDocument8 pagesE Colihariprem26No ratings yet
- Rotavirus PresentationDocument8 pagesRotavirus Presentationapi-352899639No ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument4 pagesSystemic Lupus ErythematosushalaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214250923002007 MainDocument2 pages1 s2.0 S2214250923002007 MainsafitrinadiawahyuNo ratings yet
- Worksheet #3 VOCABULARYDocument2 pagesWorksheet #3 VOCABULARYAngel Angeleri-priftis.No ratings yet
- International Journal of Green and Herbal Chemistry: Anti Ageing Drugs in AyurvedaDocument14 pagesInternational Journal of Green and Herbal Chemistry: Anti Ageing Drugs in AyurvedaananthakumarNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline: APR 14, 2021 Dr. Michelle BuelaDocument5 pagesTopic Outline: APR 14, 2021 Dr. Michelle BuelaSGD5Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- BMC Infectious Diseases, 11 (1), P. 248.: Daftar PustakaDocument8 pagesBMC Infectious Diseases, 11 (1), P. 248.: Daftar PustakaAndi MagfirahNo ratings yet
- Blood - MCQDocument13 pagesBlood - MCQstuffNo ratings yet
- Linfatic System HeelDocument4 pagesLinfatic System HeelPablo Matas Soria100% (1)
- Lab No. Age/Gender Coll. On Name Reg. On Ref. Dr. Approved On 16/aug/2021 03:05PM Rpt. Centre Printed OnDocument1 pageLab No. Age/Gender Coll. On Name Reg. On Ref. Dr. Approved On 16/aug/2021 03:05PM Rpt. Centre Printed OnPratik GargNo ratings yet
- Ear Infections: These Include Otitis Externa, Otitis Media, MastoiditisDocument32 pagesEar Infections: These Include Otitis Externa, Otitis Media, Mastoiditisjohn mwambuNo ratings yet
- qt5xh555x9 NosplashDocument13 pagesqt5xh555x9 NosplashMARTINA CESARINA EDITH GUILLERMO ROMANNo ratings yet
- CfE2 S 74 Alexander Fleming PowerPoint English Ver 2Document14 pagesCfE2 S 74 Alexander Fleming PowerPoint English Ver 2Device 922No ratings yet
- Abzyme 2Document4 pagesAbzyme 2Rimpa PalNo ratings yet
- K011191138 - Vica Herza - Kesmas BDocument4 pagesK011191138 - Vica Herza - Kesmas BVica HerzaNo ratings yet
- TETANUSDocument15 pagesTETANUSLovely Michaela CaberioNo ratings yet
- Severeulcerative Colitis Associated With Coombs Positive Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Treated With InfliximabDocument4 pagesSevereulcerative Colitis Associated With Coombs Positive Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Treated With InfliximabIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- JCM 08 01283 v2Document44 pagesJCM 08 01283 v2Ambika SuwalNo ratings yet
- Chibueze Afugbuom Case 3Document2 pagesChibueze Afugbuom Case 3Chibueze AfugbuomNo ratings yet
Flavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku Notes
Flavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku Notes
Uploaded by
Ronald BeasleyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku Notes
Flavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku Notes
Uploaded by
Ronald BeasleyCopyright:
Available Formats
Goku Notes
Flavivirus DENGUE VIRUS
Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos
Causes dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever
I. Powerpoint Transmitted by mosquitoes
Has 4 serotypes (DEN- 1, 2, 3, 4)
FLAVIVIRIDAE
Aedes aegypti
>68 viruses
Spherical Dengue transmitted by infected female mosquito.
Enveloped Primarily a daytime feeder
Single stranded RNA Lives around human habitation
Cross related Lays eggs and produces larvae preferentially in
artificial containers with clean stagnant water
Flaviviruses
Clinical Presentations
Yellow fever virus
Dengue viruses Undifferentiated fever – may be the most common
St. Louis encephalitis virus presentation
Zika virus Classic dengue fever
West Nile virus Dengue hemorrhagic fever
Murray Valley encephalitis virus, tick- Dengue shock syndrome
borne encephalitis viruses and others
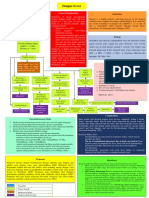
Clinical Characteristics of Dengue Fever
YELLOW FEVER Fever
Headache
Vector: Aedes aegypti Muscle and joint pain
Latin America, Carribean, Africa Nausea/vomiting
Inapparent to severe infection (jaundice, Rash
hemorrhage, albuminuria) Hemorrhagic manifestations
Hepatic necrosis, Councilman and Torres bodies
Hemorrhagic Manifestations of Dengue Fever
Diagnosis
Skin hemorrhages – petechiae, purpura,
Cell culture ecchymoses
Serology Gum bleeding
PCR Nose bleeding
Immunohistochemistry GIT bleeding – hematemesis, melena,
hematochezia
Treatment Hematuria
Increased menstrual flow
Supportive
Tourniquet Test
Prevention
Inflate a blood pressure cuff to a point midway
Live attenuated 17D Vaccine between systolic and diastolic pressure for 5
minutes.
Positive test – 20 or more petechiae per 1 inch2
2
(6.25 cm )
Goku Notes Page 1
Goku Notes
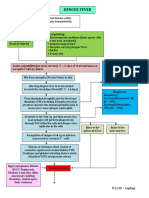
4 Necessary Criteria for Dengue Fever Warning Signs for Dengue Shock
Fever, or recent history of acute
fever Alarm Signals:
Hemorrhagic manifestations 4 Criteria for DHF:
Low platelet count (100,000/mm3 or Severe
less) abdominal pain
Fever
Objective evidence of “leaky Prolonged
Hemorrhagic
capillaries” vomiting
manifestations
Abrupt change
Excessive
Elevated hematocrit (20% or more from fever to
capillary
over the baseline) hypothermia
permeability
Low albumin Change in the
≤ 100,000/mm3
Pleural or other effusions level of
platelets
consciousness
(irritability or
Clinical Case Definition for Dengue Shock somnolence)
Syndrome
Initial Warning
4 Criteria for DHF Signals:
Evidence of circulatory failure Disappearance
manifested indirectly by all of the of fever
following: Drop in
platelets
Rapid and weak pulse Increase in
Narrow pulse pressure (≤20 hematocrit
mmHg) or hypotension for age When patients
Cold, clammy skin develop DSS:
Altered mental status
3-6 days after
Frank shock is direct evidence of onset of
circulatory failure. symptoms
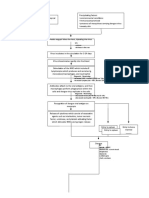
Clinical Evaluation in Dengue Fever
Blood Pressure Laboratory Tests in Dengue Fever
Evidence of bleeding on skin and other sites
Hydration status Clinical Laboratory Tests
Evidence of increased vascular permeability –
pleural effusions, ascites CBC – WBC, platelets, hematocrit
Tourniquet test Albumin
Liver function tests
Urine – check for microscopic hematuria
Goku Notes Page 2
Goku Notes
Dengue Specific Tests Diagnosis
Virus isolation CSF analysis
Serology EEG
IgM ELISA
Laboratory Methods for Dengue Diagnosis NT
HI
Virus isolation to determine the serotype of infecting CF
virus PCR
IgM ELISA for serologic diagnosis
Dengue NS1 antigen test – positive during viremic Treatment
(febrile) phase
Supportive
Management
Prevention
No hemorrhagic manifestations and patient is well
hydrated – home treatment Available locally
Hemorrhagic manifestations or hydration borderline Chimeric vaccine with 17D yellow fever virus
– consider hospitalization backbone containing prM and env genes from JEV
Warning signs (even without profound shock) or
DSS – hospitalize ZIKA VIRUS
Mosquito Barriers First discovered in 1947 and named after the Zika
forest in Uganda
Only needed until fever subsides, to prevent Aedes In 1952, the first human cases of Zika virus disease
aegypti mosquitoes from biting patients and were detected and since then, outbreaks of Zika
acquiring the virus have probably occurred in many locations.
Keep patient in screened sickroom or under In May 2015, the Pan American Health Organization
mosquito net. issued an alert regarding the first confirmed Zika
virus infection in Brazil and in Feb. 1, 2016, the
Prevention WHO declared Zika virus a public health emergency
of international concern.
Public Education Local transmission has been reported in many other
Vector control countries.
Dengue quadrivalent recombinant (chimeric) vaccine
(given at 0, 6 month schedule) from 9-45 years old Transmission
JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS Transmitted to human primarily through the bite of
infected Aedes mosquito
Single serotype Nonhuman and human primates are likely the main
5 genotypes based on E protein reservoirs of the virus, and anthroponotic (human to
Asia including SEA vector to human) transmission occurs during
Cycle: birds outbreaks.
Culex mosquitoes (Culex tritaeniorhynchus) – swine, Perinatal, in utero, and possible sexual and
humans, horses transfusion transmission events have also been
99% subclinical reported.
Lethargy, behavioral changes, motor abnormalities Zika virus RNA has been identified in asymptomatic
blood donors during an outgoing outbreak.
Goku Notes Page 3
Goku Notes
Features Flaviviruses
1 in 5 people infected becomes symptomatic. Yellow fever virus
Clinical findings are acute onset of fever with Dengue viruses
maculopapular rash, arthralgia, conjunctivitis, St. Louis encephalitis virus
myalgia and headache. Zika virus
Clinical illness is usually mild with symptoms lasting West Nile virus
for several days to a week. Murray Valley encephalitis virus, tick-
Severe disease requiring hospitalization is borne encephalitis viruses and others
uncommon and case fatality is low.
No vaccine and specific treatment available yet
Investigators are looking at the possible association Hepatitis C is considered a flavivirus.
between Zika virus and a reported increase in the
number of babies born with microcephaly. YELLOW FEVER
There have been cases of Guillain Barre syndrome
reported in patients following Zika virus infection. A historical illness
In the early part of the last century, it is already a
Diagnosis diagnosed illness.
It is common in Latin America and parts of Africa.
1st week after onset of symptoms – diagnosed by It is vector transmitted like a lot of flaviviruses.
reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction The vector is the Aedes aegypti which is also the
(RT-PCR) on serum vector for Dengue virus.
Virus specific IgM and neutralizing antibodies It causes a lot of inapparent infections but when
typically develop toward the end of the first week of infection tends to be severe, the patient develops
illness. jaundice due to liver involvement (reason why it was
Cross-reaction with related flaviviruses (e.g. dengue called Yellow fever).
and yellow fever) is common and may be difficult to Hemorrhage is also common together with renal
discern. involvement.
RT-PCR and virus isolation can be performed on Hepatic necrosis, when a biopsy is done,
other body fluids (e.g. urine, amniotic fluid, semen, Councilman and Torres bodies are seen on the
saliva which are transmitted to lab cold or frozen). stained smear.
Diagnosis is through culture, serology and PCR.
II. Recording There is no treatment for Yellow fever but it is
preventable.
FLAVIVIRUSES OFWs should be vaccinated with Yellow fever
vaccine from the Bureau of Quarantine especially if
There are now more than 70 Flaviviruses and these they are bound for Africa or Latin America.
are RNA viruses which are very small and are round,
spherical in shape and they possess an envelope DENGUE
like the flu viruses.
They consist of a single stranded RNA like most It is caused by 4 serotypes of the dengue virus
RNA viruses and they tend to be cross related to (DEN- 1, 2, 3, 4).
each other. Previously called Breakbone fever and Philippine
When a person gets infected with a certain flavivirus, Hemorrhagic fever
the antibodies developed against that particular virus Infection with a certain serotype may confer
tend to cross react with another type of flavivirus. protection for that particular serotype but it lasts only
for a short period of time.
A patient can be infected with 4 serotypes of dengue
in his life.
Goku Notes Page 4
Goku Notes
Infection is dependent on the prevalent serotype Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
order during the time when infection developed.
It is transmitted by Aedes aegypti and it is common There is a rise in temperature, initially very high,
in tropical areas which are heavily populated. which continues to rise further and falls gradually
It is not common in Russia, Europe or the northern within 3-7 days.
part of Africa due to their cold climate. It leads to Dengue shock syndrome sometimes.
It is seen mostly in Asia and in the northern tip of Generally more benign than the other group but they
Australia. are caused by the same virus.
In Mexico, it is also seen. There is neurologic involvement and severe dengue
In US, the illness is occasionally seen near the gulf correlates with severe viremia and production of
because it is near the tropical areas and it also cytokines
correlates with the vector density. This is the body’s immune response to severe
Female mosquitoes are the only ones which bite dengue.
humans because male mosquitoes feed on plants.
Aedes aegypti mosquitoes are daytime feeders as Dengue Shock Syndrome
opposed to Culex and Anopheles mosquitoes which
are night time feeders. Clinical Characteristics of Dengue Fever
They live around human inhabitations. (distinct signs)
They can be found in areas where there are lots of
houses, predominantly urban areas. Fever
They are not common in the mountains. Headache
This vector does not have a long flight range. Muscle and joint pain
It cannot fly a long distance. Nausea/vomiting
It tends to go from house to house. Rash –not always present
They tend to breed in human inhabitations. Hemorrhagic manifestations
They lay larvae and eggs in clean, stagnant water.
Waters found in clean containers, tires, plants and
rooftops serve as a medium for laying eggs. Hemorrhagic Manifestations of Dengue
They do not breed in dirty canals. Fever
The first infection of dengue is mild.
The second infection is more symptomatic but cases Skin hemorrhages – petechiae,
of first infection can be severe. purpura, ecchymoses
Generally it is estimated that out of 100 people who Gum bleeding
gets the virus, only about 25 may show symptoms. Nose bleeding – very common
GIT bleeding – hematemesis, melena,
Clinical Presentations hematochezia which can lead to
significant blood loss
Undifferentiated fever which is flu like in nature Hematuria (bleeding occurs in
Unless specific testing is done, it will not be thought kidneys)
of as dengue. Increased menstrual flow
Classic Dengue Fever Tourniquet Test
Another classic presentation is the biphasic fever Inflate a blood pressure cuff to a point midway
where the patient has a rise in temperature, then for between systolic and diastolic pressure for 5
about 2-3 days it goes down then goes up again minutes.
after 1 day. If systolic is 100 or 110 and diastolic is 70, inflate the
They develop a rash and symptoms develop cuff at 90 for 5 minutes.
anytime during this phase.
Goku Notes Page 5
Goku Notes
2
Positive test – 20 or more petechiae per 1 inch Course of Dengue Fever
(6.25 cm2)
Not specific for dengue Starts with a very high fever
Cases of severe dengue can have a negative Fever becomes continues and goes down between
tourniquet test especially if they are coming with day 3 to day 7.
shock or hypotension. Fever can be as short as 3 days.
During the times when the patient is febrile there is
New Classification for Dengue Fever viremia and there is virus in the blood.
They also have lack of appetite, headache,
Dengue without Warning Signs anorexia, abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle and joint
Dengue with Warning Signs pain and there can already be a positive tourniquet
Severe Dengue test.
Patient looks flushed and reddish.
Criteria for Severe Dengue Fever Sometimes, maculopapular rashes are seen similar
to other viral exanthems.
4 Necessary Criteria for Dengue Fever When the fever is going down, platelet count falls.
As the fever goes down, decline in platelet count is
Fever, or recent history of acute fever seen.
Hemorrhagic manifestations – a positive Soon after the decline in platelet count, plasma
tourniquet test may suffice starts to leak out of the capillaries.
3
Low platelet count (100,000/mm or less) There will now be rising hematocrit levels.
Objective evidence of “leaky capillaries” Patient can go into shock from the time that the
fever went down up to about 2 days after.
Elevated hematocrit (20% or more over Some people mistake that the patient already
the baseline) recovered because the fever has already gone
Low albumin – due to leakage of down.
plasma The patient does not necessarily bleed but can die
Pleural or other effusions of shock due to plasma loss.
Those that bleed oftentimes have a preceding
In severe dengue, plasma goes out of the blood shock.
vessels due to the inflammation on the blood vessel If the patient is not given fluids the patient can die of
wall, they leak out plasma so the blood becomes fluid loss.
concentrated. Patients may have rash when he has fever but a lot
If it is not replaced with fluid, patient will die of of patients do not have rash.
hypotension and shock. There can also be rash when the patient is
This is dengue shock syndrome. recovered already and it is called Herman rash.
rd
Plasma leaks out and goes to the 3 space and These are itchy and tend to be more on the lower
patient can have ascites or pleural effusion. extremities but sometimes also seen on the upper
If there is pleural effusion in a patient with dengue, it extremities.
is severe dengue because there is an evidence of If this is seen in a patient, the patient is probably
leaky capillaries. nearing recovery.
The most common sign of leaky capillary in severe There are 2 types of rash, one that can develop
dengue is a rise in the hematocrit of the patient. during the fever and one that can develop as the
The most common site for pleural effusion in dengue patient is nearing recovery.
is the right pleural space. There can be rapid pulse, narrowed pulse pressure
and cold clammy skin as signs of shock.
Goku Notes Page 6
Goku Notes
Clinical Evaluation Albumin
Liver function tests – the virus can affect the liver
Blood pressure monitoring other than hematocrit Urine – check for microscopic hematuria
monitoring Culture is difficult and takes a long time
When the systolic and diastolic BP is narrow or Serology
come near each other, if fluids are not given, the BP
will narrow further, and when it continues to narrow, Laboratory Methods for Dengue Diagnosis
the patient will have hypotension and shock.
Together with narrowing of the pulse pressure, it can Virus isolation to determine the serotype of infecting
be a determinant of how strong the pulse is. virus
If the pulse is weak, the patient has a narrow pulse IgM ELISA for serologic diagnosis
pressure. Dengue NS1 (non-structural 1) antigen test –
The skin gets cold and clammy. positive during viremic (febrile) phase because what
They also have decreased urine output which is a is being detected in NS1 is antigen for the virus
sign of diminished intravascular volume. itself.
If the virus is no longer present in the blood it will be
Clinical Evaluation in Dengue Fever
negative.
It is negative when the patient is in shock.
Blood Pressure
It will be negative when the patient is about to be
Evidence of bleeding on skin and
discharged.
other sites
IgM ELISA – is positive in day 4 or 5 of illness
Hydration status – patient can die of
IgG ELISA
dehydration
ELISA testing may have cross reaction with other
Evidence of increased vascular
flaviviruses.
permeability – pleural effusions,
ascites
Management
Tourniquet test
No hemorrhagic manifestations and patient is well
hydrated – home treatment, adequate fluid intake
Warning Signals:
Hemorrhagic manifestations or hydration borderline
– consider hospitalization
Severe abdominal pain
Warning signs (even without profound shock) or
Prolonged vomiting
DSS – hospitalize
Abrupt change from fever to
hypothermia Treatment
Change in the level of consciousness
(irritability or somnolence)
There is no treatment.
Organ involvement Give fluids with paracetamol.
Liver failure Avoid Ibuprofen because it can cause bleeding.
Renal failure It can also do damage in dehydration.
Usually sets in when there is drop of
Stick to Paracetamol with right doses because it can
fever, decrease in platelet and
damage the liver if given too much.
increase in hematocrit.
Monitor BP, hematocrit, level of consciousness and
urine output.
Laboratory Tests in Dengue Fever Blood products are only given when there is
significant bleeding.
Clinical Laboratory Tests There is no need to give platelets.
CBC – WBC, platelets, hematocrit
Goku Notes Page 7
Goku Notes
Mosquito Barriers Prevention
Needed until the fever subsides Available locally
Rooms of the patients should be screened. Chimeric vaccine with 17D yellow fever virus
backbone containing prM and env genes from JEV
Prevention is inserted
Vaccine is derived from yellow fever
Public Education Given in 2 doses from 9 months to 17 years (1 year
Vector control apart, 1 primary dose and 1 booster)
Dengue quadrivalent recombinant (chimeric) vaccine 18 and above – only one dose of the vaccine
(given at 0, 6 and 12 month schedule) from 9-45
years old ZIKA VIRUS
JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS First discovered in 1947 and is named after the Zika
forest in Uganda
Single serotype In 1952, the first human cases of Zika virus disease
Most common cause of encephalitis in Asia were detected and since then, outbreaks of Zika
Vector borne have probably occurred in many locations.
5 genotypes based on E protein Not famous in the Philippines
Culex mosquitoes (Culex tritaeniorhynchus) is the In May 2015, the Pan American Health Organization
vector which is common in rural areas – bites swine, issued an alert regarding the first confirmed Zika
humans, horses virus infection in Brazil and in Feb. 1, 2016, the
The virus is transferred when the mosquitoes bite WHO declared Zika virus a public health emergency
birds (waterbirds specifically with long necks and of international concern because it spread to certain
long legs) parts of Latin America.
Humans can be bitten and can be infected but Local transmission has been reported in many other
viremia level is low. countries.
No human to human transmission through mosquito
bites Transmission
99% subclinical
Lethargy, behavioral changes, motor abnormalities Transmitted to human primarily through the bite of
infected Aedes mosquito
Nonhuman and human primates are likely the main
Diagnosis reservoirs of the virus, and anthroponotic (human to
vector to human) transmission occurs during
CSF analysis outbreaks.
EEG Main reservoirs are monkeys as well as humans.
IgM ELISA on the CSF Perinatal, in utero, and possible sexual and
IgG in the blood and see if it is a 4 fold rising titer transfusion transmission events have also been
from the serum 2 weeks later reported.
Nuclear testing Zika virus RNA has been identified in asymptomatic
HI blood donors during an outgoing outbreak.
CF
PCR Features
Treatment 1 in 5 people infected becomes symptomatic.
Clinical findings are acute onset of fever with
Supportive maculopapular rash, arthralgia, conjunctivitis,
myalgia and headache.
Goku Notes Page 8
Goku Notes
Clinical illness is usually mild with symptoms lasting
for several days to a week.
Severe disease can occur.
Severe disease requiring hospitalization is
uncommon and case fatality is low.
No vaccine and specific treatment available yet
Investigators are looking at the possible association
between Zika virus and a reported increase in the
number of babies born with microcephaly.
There have been cases of Guillain Barre syndrome
(ascending symmetric type of paralysis) reported in
patients following Zika virus infection.
Diagnosis
st
3 days to 1 week after onset of symptoms –
diagnosed by reverse transcriptase polymerase
chain reaction (RT-PCR) on serum
Virus specific IgM and neutralizing antibodies
typically develop toward the end of the first week of
illness.
Cross-reaction with related flaviviruses (e.g. dengue
and yellow fever) is common and may be difficult to
discern.
RT-PCR and virus isolation can be performed on
other body fluids (e.g. urine, amniotic fluid, semen,
saliva which are transmitted to lab cold or frozen).
END
Special thanks to KTRC for the rcording and
ppt pictures.
Goku Notes Page 9
You might also like
- Special Operations Forces Medical HandbookFrom EverandSpecial Operations Forces Medical HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Presentation On Dengue FeverDocument31 pagesPresentation On Dengue FeverDrMuhammad Ishfaq HabibNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiologyteddydeclines1483% (18)
- John Jay Immunization FormDocument3 pagesJohn Jay Immunization FormIsam BoukattayaNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Dengue 29052021Document43 pagesInfeksi Dengue 29052021Feby JuwitaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Document31 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Sheryl ElitaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Virus: DescriptionDocument12 pagesDengue Virus: Descriptionpedia blue bookNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemmorhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Document64 pagesDengue Hemmorhagic Fever: Dr. Dwi Lingga Utama, Spa (K)Sheryl ElitaNo ratings yet
- DENGUEDocument14 pagesDENGUEAnaluciaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Didactics Dengue - 2Document75 pagesPedia Didactics Dengue - 2Joy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Dengue Insight DR Amit Johari Edited 2020Document82 pagesDengue Insight DR Amit Johari Edited 2020Vedehi BansalNo ratings yet
- Denguefever 180705234058Document2 pagesDenguefever 180705234058PLDT HOMENo ratings yet
- DHF - CDCDocument105 pagesDHF - CDCpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever & DHFDocument32 pagesDengue Fever & DHFWilliam Bunga DatuNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever & DHFDocument32 pagesDengue Fever & DHFArdan SafitraNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document11 pagesGroup 2Maya Hani MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Arthropod-Borne Viruses (Arboviruses) : Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)Document2 pagesArthropod-Borne Viruses (Arboviruses) : Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)MonicaNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument67 pagesDengueRafaela LennyNo ratings yet
- DR AfableDocument25 pagesDR AfableJohnny DeeNo ratings yet
- Dengue JimshDocument19 pagesDengue JimshRatul SealNo ratings yet
- Project On ManagmentDocument32 pagesProject On ManagmentRinkuNo ratings yet
- Management of Dengue FeverDocument31 pagesManagement of Dengue FeverDaniel RajNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa Dan Penatalaksanaan: Demam Berdarah DengueDocument48 pagesDiagnosa Dan Penatalaksanaan: Demam Berdarah DengueFahmi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Patofisiologi: Penularan Melalui Gigitan NyamukDocument1 pageDengue Fever Patofisiologi: Penularan Melalui Gigitan NyamukDinda RensiNo ratings yet
- Updated Management of Dengue, ImrulDocument73 pagesUpdated Management of Dengue, ImrulFaheem Ul HasanNo ratings yet
- Top Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingDocument3 pagesTop Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Dengue: Demam Berdarah Dengue Demam DengueDocument62 pagesInfeksi Virus Dengue: Demam Berdarah Dengue Demam DengueMarwi VinaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYAngela Jane MadristaNo ratings yet
- Who Dengue Classification and Differentials ModuleDocument14 pagesWho Dengue Classification and Differentials ModuleKevin AgbonesNo ratings yet
- How To Manage Vector-Borne Viral Disease As General Practitioner in Primary Health Care? (Dengue-Chikungunya-Zika Infection)Document83 pagesHow To Manage Vector-Borne Viral Disease As General Practitioner in Primary Health Care? (Dengue-Chikungunya-Zika Infection)fida amalinaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Presentation (KEMU)Document90 pagesDengue Presentation (KEMU)MuhammadTalhaNo ratings yet
- Dengue PathophysioDocument4 pagesDengue PathophysioHonhon MacasaquitNo ratings yet
- Dengue (3-8-2015)Document45 pagesDengue (3-8-2015)vishnuNo ratings yet
- Dengue AutosavedDocument12 pagesDengue AutosavedMaricris PallarNo ratings yet
- Demam Berdarah Dengue Pada Anak: MustaringDocument70 pagesDemam Berdarah Dengue Pada Anak: MustaringpipitNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Schematic DiagramDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Schematic DiagramTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Arthropod-Borne Virus 1-RirisDocument37 pagesArthropod-Borne Virus 1-Ririslutfia papitaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEKenrick Randell IbanaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Diagnosis: Ratna Setia AsihDocument24 pagesDengue Diagnosis: Ratna Setia AsihsanelyristiNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)Document37 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Supervised By: Dr. Pulung M. Silalahi, Sp.A Created: Siti Zulfah (1102014255)sitizulfahhNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Pathophysiology and Its ManagementDocument2 pagesDengue Fever Pathophysiology and Its ManagementTeresita AvilesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatingDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatinggizelleNo ratings yet
- Pedia Tickler Update 2017Document2 pagesPedia Tickler Update 2017Tani BokNo ratings yet
- Dengue SlideDocument48 pagesDengue SlideKurouSakiNo ratings yet
- Demam Berdarah DengueDocument44 pagesDemam Berdarah DengueLastry Wardani100% (2)
- R. P. Vashist, Consultant Public HealthDocument26 pagesR. P. Vashist, Consultant Public Healthmaharshi mNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinDocument68 pagesDr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinSourav NathNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhage Fever 2Document49 pagesDengue Hemorrhage Fever 2chhaiden100% (3)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologylylasherliaNo ratings yet
- Dengue, Chikungunya Yellow Fever: Dr. Saida SharminDocument48 pagesDengue, Chikungunya Yellow Fever: Dr. Saida SharminBishwajit BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- DHF - CDC Utk DiprintDocument72 pagesDHF - CDC Utk DiprintpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Either Silent or Switched OffDocument67 pagesEither Silent or Switched OffPankaj Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Dengue VirusDocument2 pagesDengue VirusImee Claire PacisNo ratings yet
- Alert Medical Series: USMLE Alert I, II, IIIFrom EverandAlert Medical Series: USMLE Alert I, II, IIIRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Ideal Lymphedema Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide For Effective Lymphedema Management And Treatment With Nutritious RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Lymphedema Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide For Effective Lymphedema Management And Treatment With Nutritious RecipesNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Reactions PDFDocument3 pagesHypersensitivity Reactions PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Goku Notes: Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (Bunyaviruses, Arenaviruses, Filoviruses) - Dra. Ma. Ellery MendezDocument5 pagesGoku Notes: Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (Bunyaviruses, Arenaviruses, Filoviruses) - Dra. Ma. Ellery MendezRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesImmunology PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Influenza PDFDocument5 pagesInfluenza PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Borrelia and Leptospira Lecturer: Dra. Ferrer: Goku NotesDocument3 pagesBorrelia and Leptospira Lecturer: Dra. Ferrer: Goku NotesRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Goku Notes: Anaerobes Lecturer: Dr. LimDocument3 pagesGoku Notes: Anaerobes Lecturer: Dr. LimRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Hepatotrophic Viruses PDFDocument9 pagesHepatotrophic Viruses PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosDocument20 pagesOpportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Vaccines Research PaperDocument16 pagesVaccines Research PaperHana Pung100% (1)
- Update On COVID 19 Projections 2021.12.07 English 1Document18 pagesUpdate On COVID 19 Projections 2021.12.07 English 1Toronto StarNo ratings yet
- Bullous PemphigoidDocument21 pagesBullous PemphigoidChe Ainil ZainodinNo ratings yet
- MYCOFAST-RevolutioN-ATB Direct Brochure EN 2019-10Document2 pagesMYCOFAST-RevolutioN-ATB Direct Brochure EN 2019-10Lilia ZidouniNo ratings yet
- Deficiency of C8 Case Study NotesDocument2 pagesDeficiency of C8 Case Study NotesIan SibalNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology, Infectious Diseases, Parasitology & Tropical Diseases Notes 4Document165 pagesEpidemiology, Infectious Diseases, Parasitology & Tropical Diseases Notes 4Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- Reaksi AnafilaksisDocument34 pagesReaksi AnafilaksisPutri Reno IntanNo ratings yet
- Immunology Worksheet1Document4 pagesImmunology Worksheet1Caviles, Jasmin S.No ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH Programs PDFDocument24 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH Programs PDFMiss GNo ratings yet
- E ColiDocument8 pagesE Colihariprem26No ratings yet
- Rotavirus PresentationDocument8 pagesRotavirus Presentationapi-352899639No ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument4 pagesSystemic Lupus ErythematosushalaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214250923002007 MainDocument2 pages1 s2.0 S2214250923002007 MainsafitrinadiawahyuNo ratings yet
- Worksheet #3 VOCABULARYDocument2 pagesWorksheet #3 VOCABULARYAngel Angeleri-priftis.No ratings yet
- International Journal of Green and Herbal Chemistry: Anti Ageing Drugs in AyurvedaDocument14 pagesInternational Journal of Green and Herbal Chemistry: Anti Ageing Drugs in AyurvedaananthakumarNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline: APR 14, 2021 Dr. Michelle BuelaDocument5 pagesTopic Outline: APR 14, 2021 Dr. Michelle BuelaSGD5Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- BMC Infectious Diseases, 11 (1), P. 248.: Daftar PustakaDocument8 pagesBMC Infectious Diseases, 11 (1), P. 248.: Daftar PustakaAndi MagfirahNo ratings yet
- Blood - MCQDocument13 pagesBlood - MCQstuffNo ratings yet
- Linfatic System HeelDocument4 pagesLinfatic System HeelPablo Matas Soria100% (1)
- Lab No. Age/Gender Coll. On Name Reg. On Ref. Dr. Approved On 16/aug/2021 03:05PM Rpt. Centre Printed OnDocument1 pageLab No. Age/Gender Coll. On Name Reg. On Ref. Dr. Approved On 16/aug/2021 03:05PM Rpt. Centre Printed OnPratik GargNo ratings yet
- Ear Infections: These Include Otitis Externa, Otitis Media, MastoiditisDocument32 pagesEar Infections: These Include Otitis Externa, Otitis Media, Mastoiditisjohn mwambuNo ratings yet
- qt5xh555x9 NosplashDocument13 pagesqt5xh555x9 NosplashMARTINA CESARINA EDITH GUILLERMO ROMANNo ratings yet
- CfE2 S 74 Alexander Fleming PowerPoint English Ver 2Document14 pagesCfE2 S 74 Alexander Fleming PowerPoint English Ver 2Device 922No ratings yet
- Abzyme 2Document4 pagesAbzyme 2Rimpa PalNo ratings yet
- K011191138 - Vica Herza - Kesmas BDocument4 pagesK011191138 - Vica Herza - Kesmas BVica HerzaNo ratings yet
- TETANUSDocument15 pagesTETANUSLovely Michaela CaberioNo ratings yet
- Severeulcerative Colitis Associated With Coombs Positive Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Treated With InfliximabDocument4 pagesSevereulcerative Colitis Associated With Coombs Positive Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Treated With InfliximabIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- JCM 08 01283 v2Document44 pagesJCM 08 01283 v2Ambika SuwalNo ratings yet
- Chibueze Afugbuom Case 3Document2 pagesChibueze Afugbuom Case 3Chibueze AfugbuomNo ratings yet