Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Staffing The Engineering Organization
Staffing The Engineering Organization
Uploaded by
Reden LopezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Staffing The Engineering Organization
Staffing The Engineering Organization
Uploaded by
Reden LopezCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 5
STAFFING THE ENGINEERING ORGANIZATION
What is staffing?
Staffing is the process of acquiring, deploying, and retaining a workforce of sufficient
quantity and quality to create positive impacts on the organization’s effectiveness. (Heneman and
Judge, 2005).
Objectives:
Establish a basic ground of what staffing.
Identify and appreciate the basic process of staffing and its benefits.
Develop staffing techniques in order to be an efficient engineer manager.
Address company issues with an effective staffing management application.
The goal of staffing ….
Is to match people with jobs so that the realization of the organization’s objectives will
be facilitated.
As an Engineer Manager… One must be concerned with putting the right persons in various
positions within his area of concern.
As an Engineer Manager… There is great responsibility in assuring that the right persons are
assigned to positions that fit their qualifications.
The 8 steps in staffing process
1. Human resource planning
2. Recruitment
3. Selection
4. Induction and Orientation
5. Training and development
6. Performance Appraisal
7. Employment decision
8. Separations
1. Human resource planning
Human resource planning is first step in staffing and is defined as the on- going process
of systematic planning to achieve optimum use of an organization's most valuable asset -
its human resources. The objective of human resource planning is to ensure the best fit
between employees and jobs, while avoiding manpower shortages or surpluses.
The 3 Key Elements of Human Resource Planning
1. Forecasting – is an assessment of future human resource needs in relation
to the current capabilities of the organization.
Methods of Forecasting:
Time series methods
Explanatory or casual method
Monitoring methods
2. Programming - which means translating the forecasted human resource
needs to personnel objectives and goals.
3. Evaluation and control – which refers to monitoring human resource
action plans and evaluating their success.
2. Recruitment
Recruitment refers to attracting qualified persons to apply for vacant positions in
the company so that those who are best suited to serve the company may be selected.
Source of applicants:
Organizations current employees
Referrals from employees
Recruitment firms
Newspaper advertisement
Schools
Competitors
Internet
3. Selection
Selection refers to the act of choosing from those that are available the
individuals most likely to succeed on the job. The purpose of selection is to evaluate each
candidate and to pick the most suited for the position available. Selection procedures may
be simple or complex depending on the cost of a wrong decision. If the management
picks the wrong person and the subsequent effect to the organization is negligible, then
the selection process is made simple. Subsequently, when the position under
consideration involves special skills, a more elaborate selection process is undertaken.
Ways of Determining Qualifications of Candidate
a. Application blanks. The application blanks provides information about the
persons characteristics such as age, marital status, address, education,
background, experience, and special interest. After reading the application blank,
the evaluator will have some basis on whether or not to proceed further in
evaluating the applicant.
b. References. References are those written by previous employees, co- workers,
teachers, club officers, etc. there statement may provide some vital information on
the character of the applicant.
c. Interviews. Information may be gathered in an interview by asking a series of
relevant questions to the job candidate.
d. Testing. This involves an evaluation of the future behaviour or performance of an
individual.
i. Psychological test – Is an objective, standard measure of a sample
behaviour it is classified into: aptitude test, performance test, personality
test, interest test.
ii. Physical examination - a type of test given to assess the physical healthy
of an applicant.
4. Induction and Orientation
The employee is informed about his duties, responsibilities, and responsibilities.
Induction •Socialization process Orientation.
5. Training and Development
Training refers to the learning that is provided in order to improve performance
on the present job.
General types of training
Training Programs for non-managers
o Training and educational programs for executive.
Training Programs for Nonmanagers
o On-the-job training
o Vestibule
o Apprenticeship
o Special Course Managers
o In-basket
o Management games
o Case studies
o Role-playing
o Behavior modeling
o Sensitivity training
o Transaction analysis
Benefit of Training
Build up confidence
Improves morale of employees
Build trust of the employee
6. Performance Appraisal
Is the act of evaluating the employee.
8th ways of appraising the employee
i. Rating scale method
ii. Essay method
iii. Management by objective method
iv. Assessment center method
v. Checklist method
vi. Work standard method
vii. Ranking method
viii. Critical-incident method
7. Employment Decision
a. Monetary Reward – this are given to employees whose performance is at par or
above standard requirements.
b. Promotion – this refers to a movement by a person into a position of higher pay
and greater responsibilities and which is given to a reward for competence and
ambition.
c. Transfer – this is the movement of the person to a different job at the same or
similar level of responsibility in the organization.
d. Demotion – this is a movement from one position to another which has less pay
or responsibility attached to it. This is also a form of punishment.
8. Separation
a. Voluntary - it is the will of the employee to resign and he must notify the
company weeks before he resign.
b. Involuntary – or termination is the last option that the manager exercises
when employees performance is poor or when an employee violates the rules
and regulation of the company.
You might also like
- Engineering Management Chapter 5Document29 pagesEngineering Management Chapter 5Janea ChrisNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior and Performance Appraisal 2Document20 pagesOrganizational Behavior and Performance Appraisal 2Ceazar Justine Fulugan100% (3)
- Staffing The Engineering OrganizationDocument29 pagesStaffing The Engineering OrganizationMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Stages of The Employment Cycle.xDocument8 pagesStages of The Employment Cycle.xMary Grace SarenoNo ratings yet
- Staffing The Engineering Organization - : Group 5 - Bsce 3EDocument38 pagesStaffing The Engineering Organization - : Group 5 - Bsce 3EJohn Rhey AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Performance Management and Rewards Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesModule 6: Performance Management and Rewards Learning OutcomesElla MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument19 pagesStaffingbernalesdanica0102No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 StaffingDocument23 pagesChapter 6 StaffingLatha VarugheseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Engineering ManagementDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Engineering ManagementJohn Philip Molina NuñezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Functions of Management - CDE - 1Document55 pagesCHAPTER 3 Functions of Management - CDE - 1Kathleen EspineliNo ratings yet
- Em Kinn NGG GinsDocument6 pagesEm Kinn NGG Ginsarvin paruliNo ratings yet
- Indira School of Business Studies, Pune.: Human Resources ManagementDocument8 pagesIndira School of Business Studies, Pune.: Human Resources ManagementAnkita ShettyNo ratings yet
- MS Unit - IiiDocument24 pagesMS Unit - IiiDinesh SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Ch-6 StaffingDocument12 pagesCh-6 StaffingShashwat SammyNo ratings yet
- Int. To MGT Chapter SixDocument27 pagesInt. To MGT Chapter SixmisganabbbbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Eneman20Document5 pagesChapter 5-Eneman20Reynald John PastranaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 NotesDocument2 pagesModule 6 Notesthe lousy donutNo ratings yet
- Functions of Human Resource Management1Document7 pagesFunctions of Human Resource Management1Marvee ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 9 and 10Document21 pagesCHAPTER 8 9 and 10Jemima TapioNo ratings yet
- Staffing The Engineering OrganizationDocument32 pagesStaffing The Engineering OrganizationAbegail Ada Calayo MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of Human Resource Management: 3. Job AnalysisDocument12 pagesNature and Scope of Human Resource Management: 3. Job AnalysisSankar RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Universitry of Mysore: C-1: AssignmentDocument10 pagesUniversitry of Mysore: C-1: AssignmentVenkateshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management StaffingDocument25 pagesEngineering Management StaffingCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Performance Appraisal: MeaningDocument33 pagesUnit 5 Performance Appraisal: Meaning20-1023 Indumathi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Staffing Chester Dela CruzDocument32 pagesStaffing Chester Dela CruzangeloNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon State College Bulan CampusDocument5 pagesSorsogon State College Bulan CampusJung JiahNo ratings yet
- Org and Mngt-Week 10Document7 pagesOrg and Mngt-Week 10Caroline VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Handouts Chapter 5 8Document7 pages2nd Quarter Handouts Chapter 5 8kathlen mae marollanoNo ratings yet
- Staffing Quarter 2 Week 9 ExpectationsDocument5 pagesStaffing Quarter 2 Week 9 ExpectationsRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- 1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1Document35 pages1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1JNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Nature and Scope of HRM: 1.1 Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Nature and Scope of HRM: 1.1 Introduction To Human Resource Managementbeing selfNo ratings yet
- CH - 4Document17 pagesCH - 4etebark h/michaleNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Directing: StaffingDocument16 pagesUnit IV Directing: StaffingSwetha DurairajNo ratings yet
- Staffing Function of ManagementDocument31 pagesStaffing Function of ManagementBridget Nicole BordeosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To TopicDocument56 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To TopicSagar ShipraNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 6 Business-Studies Revision NotesDocument11 pagesClass 12 Chapter 6 Business-Studies Revision NotesShanel VazNo ratings yet
- Staffing: Tirsolito C. Salvador PUP CBA 2019-2020Document47 pagesStaffing: Tirsolito C. Salvador PUP CBA 2019-2020Tams AngelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 StaffingDocument34 pagesChapter 5 Staffingedward0% (1)
- Unit Iv Management ConceptsDocument25 pagesUnit Iv Management ConceptsRAMESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - ES 313Document10 pagesModule 5 - ES 313Vincent Czar CabiliNo ratings yet
- CHP 0 Fundamental of HRM-TNDDocument27 pagesCHP 0 Fundamental of HRM-TNDMd. Atiqul Hoque NiloyNo ratings yet
- Performances Appraisal: Development DiscussionDocument16 pagesPerformances Appraisal: Development Discussion2009silmshady6709No ratings yet
- STAFFINGDocument24 pagesSTAFFINGseia deirahNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 PresentationDocument61 pagesGROUP 8 Presentationjosh jaroNo ratings yet
- Designing The Managerial Job: Selection and RecruitmentDocument31 pagesDesigning The Managerial Job: Selection and Recruitmentrakum81No ratings yet
- Person at The Right Job.: Human Aspects of OrganizingDocument5 pagesPerson at The Right Job.: Human Aspects of OrganizingdummyNo ratings yet
- Definition of Staffing and Steps inDocument10 pagesDefinition of Staffing and Steps inEfean KimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managementchapter 5Document9 pagesIntroduction To Managementchapter 5Abdulhafiz AbdiNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument33 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAbhinandan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Vergara R1Document5 pagesVergara R1Jannie Leila VergaraNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument6 pagesStaffingUsman AhmedNo ratings yet
- #6 StaffingDocument25 pages#6 StaffingJoanna Garcia100% (1)
- Specialized Lesson 5 - Staffing (2nd QTR)Document3 pagesSpecialized Lesson 5 - Staffing (2nd QTR)JullianaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 StaffingDocument33 pages3.3 Staffingfranguejohnkenneth8No ratings yet
- MGT111 Module-5Document16 pagesMGT111 Module-5jian.ryccNo ratings yet
- System (CCPS) Is One That StoresDocument7 pagesSystem (CCPS) Is One That StoresJoanne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document5 pagesLesson 5JOHN IRVIN TAERNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Staffing Chapter 4 YohannesDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Management Staffing Chapter 4 YohannesDave DaveNo ratings yet
- How to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsFrom EverandHow to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsNo ratings yet
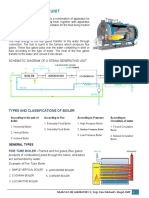
- Chapter 2: Fuels and CombustionDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Fuels and CombustionReden LopezNo ratings yet
- MLAB 3 - BoilerDocument3 pagesMLAB 3 - BoilerReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Liability of Technical Men NavarsDocument9 pagesLiability of Technical Men NavarsReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Bataan Peninsula State University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageBataan Peninsula State University: Republic of The PhilippinesReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power Plant (Case Problem) : Answers: (A) 267.4°F, (B) 29.7Mbtu/H, (C) 187,120 LBM/H, (D) 10.8 PercentDocument1 pageGeothermal Power Plant (Case Problem) : Answers: (A) 267.4°F, (B) 29.7Mbtu/H, (C) 187,120 LBM/H, (D) 10.8 PercentReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument22 pagesAlgebra FormulasReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Example Design ProblemDocument1 pageCooling Load Example Design ProblemReden LopezNo ratings yet
- ReturnLabel PDFDocument1 pageReturnLabel PDFReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Returnlabel: To Seller Address: FromDocument1 pageReturnlabel: To Seller Address: FromReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Thesis Edit and CriticDocument76 pagesThesis Edit and CriticReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Ac Midterm Part 1 Key AnswersDocument1 pageAc Midterm Part 1 Key AnswersReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Meic - 511: Fluidsim ComponentsDocument11 pagesMeic - 511: Fluidsim ComponentsReden LopezNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Scope and LimitationsDocument3 pages1.5 Scope and LimitationsReden LopezNo ratings yet
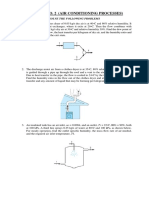
- Activity No. 2 (Air Conditioning Processes) : Solve The Following ProblemsDocument2 pagesActivity No. 2 (Air Conditioning Processes) : Solve The Following ProblemsReden LopezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial SectorsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Financial SectorsAaryan dev RastogiNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis Using Camel Model-A Study of Select Private BanksDocument10 pagesPerformance Analysis Using Camel Model-A Study of Select Private BanksLIKHITHA RNo ratings yet
- Factories Act, 1948 - Mcqs With Factories Act, 1948 - Mcqs With Answers - Part I Answers - Part IDocument8 pagesFactories Act, 1948 - Mcqs With Factories Act, 1948 - Mcqs With Answers - Part I Answers - Part IA2 Sir Fan PageNo ratings yet
- Kindle Vs Book VishalDocument8 pagesKindle Vs Book VishalVishalNo ratings yet
- ERP - SIIE - Bighrissen - Cherkaoui - VF - 2011Document6 pagesERP - SIIE - Bighrissen - Cherkaoui - VF - 2011Asmaa El OuardiNo ratings yet
- Molykote® Longterm 2 Plus Datasheet EngDocument2 pagesMolykote® Longterm 2 Plus Datasheet EngAlaa HassanNo ratings yet
- An Evaluation of The Challenges Facing Tra On Revenue Collection in Tanzania A Case of Kariakoo Tax RegionDocument5 pagesAn Evaluation of The Challenges Facing Tra On Revenue Collection in Tanzania A Case of Kariakoo Tax RegionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Forest Hills LogisticsDocument14 pagesForest Hills LogisticsSaiNo ratings yet
- NCD3Document300 pagesNCD3lenkapradipta_2000No ratings yet
- The Effect of Cosmetic Packaging DesignDocument13 pagesThe Effect of Cosmetic Packaging DesignVo Minh Thu (Aptech HCM)No ratings yet
- Company Profile - Medisol Placements Pvt. LTDDocument4 pagesCompany Profile - Medisol Placements Pvt. LTDshamsshajahanNo ratings yet
- DPR - Charsadda - 2 April 2023Document5 pagesDPR - Charsadda - 2 April 2023Usman JilaniNo ratings yet
- Far110 Quiz 1 Inventory & Suspense Ac January 2022 QDocument2 pagesFar110 Quiz 1 Inventory & Suspense Ac January 2022 QINTAN NOOR AMIRA ROSDINo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Mechanical Overspeed Trip Devices: InsightDocument2 pagesSteam Turbine Mechanical Overspeed Trip Devices: InsightManoj Singh100% (1)
- The Smithsonian Agreement VigencyDocument4 pagesThe Smithsonian Agreement Vigencyjamuel portilloNo ratings yet
- DR Pooja Mishra 2Document27 pagesDR Pooja Mishra 2Samer AliNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1&2Document21 pagesPresentation 1&2salvadorNo ratings yet
- PT GAJAH TUNGGAL TBK PDFDocument96 pagesPT GAJAH TUNGGAL TBK PDFKholila Mutia SafitriNo ratings yet
- Depends InsuranceDocument3 pagesDepends Insurancevasuakm8No ratings yet
- Apr Manual V 3Document175 pagesApr Manual V 3rohit guptNo ratings yet
- ACCCOB2 - Exercise 5Document6 pagesACCCOB2 - Exercise 5neo leeNo ratings yet
- Emami LTD.: General OverviewDocument5 pagesEmami LTD.: General Overviewflash vszoomNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Free Market Foundation - FINALDocument9 pagesCase Study - Free Market Foundation - FINALjjruttiNo ratings yet
- MECO Lecture2Document14 pagesMECO Lecture2saif ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- PR CP Report T & DDocument100 pagesPR CP Report T & DIranshah MakerNo ratings yet
- Adjusters Registration Form 13 - 0Document4 pagesAdjusters Registration Form 13 - 0lacatancopycentreNo ratings yet
- Itr-1 Sahaj Indian Income Tax Return: Acknowledgement Number: Assessment Year: 2019-20Document6 pagesItr-1 Sahaj Indian Income Tax Return: Acknowledgement Number: Assessment Year: 2019-20rk49103No ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour in Sport 2017Document263 pagesOrganizational Behaviour in Sport 2017Güngör BoroNo ratings yet
- Alyssa JonesDocument7 pagesAlyssa Jonesapi-454019927No ratings yet
- Concept of Human Resource Management: Presented By: Rupesh NyaupaneDocument26 pagesConcept of Human Resource Management: Presented By: Rupesh NyaupaneEng MatanaNo ratings yet