Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subsequent Measurement:: Differ in Inventory Value
Subsequent Measurement:: Differ in Inventory Value
Uploaded by
Charina Jane Pascual0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views4 pagesThis document summarizes accounting principles for inventories. It discusses the scope of inventories, recognition principles, initial and subsequent measurement methods, and cost formulas. The key points are:
- Inventories include assets held for sale, in production, or for use in production. Common types are merchandise, work-in-process, and raw materials.
- Inventories are initially measured at cost, which includes purchase price less discounts and taxes. Manufacturing cost includes materials, labor, and overhead.
- Subsequent measurement methods include cost methods like FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average, as well as net realizable value which is the estimated selling price less completion and disposal costs.
Original Description:
Original Title
Inventories 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes accounting principles for inventories. It discusses the scope of inventories, recognition principles, initial and subsequent measurement methods, and cost formulas. The key points are:
- Inventories include assets held for sale, in production, or for use in production. Common types are merchandise, work-in-process, and raw materials.
- Inventories are initially measured at cost, which includes purchase price less discounts and taxes. Manufacturing cost includes materials, labor, and overhead.
- Subsequent measurement methods include cost methods like FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average, as well as net realizable value which is the estimated selling price less completion and disposal costs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views4 pagesSubsequent Measurement:: Differ in Inventory Value
Subsequent Measurement:: Differ in Inventory Value
Uploaded by
Charina Jane PascualThis document summarizes accounting principles for inventories. It discusses the scope of inventories, recognition principles, initial and subsequent measurement methods, and cost formulas. The key points are:
- Inventories include assets held for sale, in production, or for use in production. Common types are merchandise, work-in-process, and raw materials.
- Inventories are initially measured at cost, which includes purchase price less discounts and taxes. Manufacturing cost includes materials, labor, and overhead.
- Subsequent measurement methods include cost methods like FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average, as well as net realizable value which is the estimated selling price less completion and disposal costs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
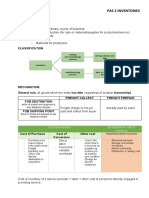
INVENTORIES - Variable – actual production
PAS 2 o Legal Test of Ownership in Transit
1. FOB Shipping Point – Buyer
Scope: 2. FOB Destination – Seller
1. Held for consumption 3. Freight Alongside (FAS) – Buyer
2. Held for sale – Merchandise inventory (merchandising) 4. Cost Insurance Freight (CIF) – Buyer
Finished goods inventory (manufacturing) 5. Ex-ship – Seller
3. Use in production – manufacturing o Special Sales
- Raw materials 1. Bill and hold – Buyer
- Work in process 2. Layaway Sales – Seller (ex: condominium – upon full payment – Buyer)
- Finished goods 3. Sale with a right of return – Seller
4. Sale on trial – Seller (ex: Spotify)
Outside the Scope: 5. Consigned Goods – Consignor
1. Commodity Brokers (IFRS 9) Subsequent Measurement:
2. Harvest Procedure (PAS 41) – Biological Procedure
o Cost – expressly provide that the cost of inventories shall be determined by
Recognition Principle: using either:
First In, First Out (FIFO) – the Both
goodsarefirst purchased are first sold.
1. Satisfy the scope - Periodic the same - at end
2. Probable that future economic benefits will flow to the entity. - Perpetual - every movement
3. Measurable
Inventories are assets held for sale in the ordinary course of business, Weighted Average
in the process of production for such sale or in the form of materials or - Periodic -> at end
supplies to be consumed in the production process or in the rendering Average Unit Cost = total cost of goods available for sale / total
of services. number of units available for sale
- Perpetual -> every movement Purchase and
Measurement; -> Moving Average Purchase Return
New Weighted Average Unit Cost = total cost of goods available
Initial Measurement; after every purchase and purchase returns / total units available for sale
Inventory Cost = new weighted average unit cost × unit on hand
o Purchased
1. Purchase Price Last In, First Out (LIFO) – the goods
Differ inlast purchased are first sold.
excluding: - Periodic inventory value - at end
- Interest – except if it classify under PAS 23 (Borrowing Cost) - Perpetual - every movement
- Recovery Tax (ex. VAT)
Specific Identification – specific cost are attributed to identify items
- Trade Discount – direct deduction; not recorded
of inventory.
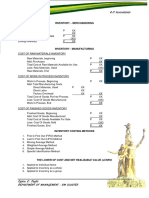
o Manufactured Cost of the Inventory = units on hand × actual unit cost
1. Raw materials - This method is appropriate for inventories that are
2. Direct labor segregated for a specific project and inventories that are
3. Factory overhead – Fixed – normal capacity – capitalized as inventory not ordinarily interchangeable.
- Excess – expense - May be used in either periodic and perpetual system
- The flow of the inventory cost correspond with actual Gross Profit Rate = Gross Profit / Sales (Based on sales)
physical flow of goods. Gross Profit Rate = Gross Profit / Cost (Based on Cost)
Standard Cost – predetermined products costs established on the * Excludes the sales discount and sales allowance.
basis of normal levels of materials and supplies, labor, efficiency Retail Inventory Method – measuring inventory of large number of
and capacity utilization. Cost Retail
- Standard cost method may be used for convenience if the Beginning X X
result approximate cost. Purchases X X
Relative Sales Price Method – cost is proportionate to selling price.
Freight-in X
o Net Realizable Value – estimated selling price in the ordinary course of Purchase returns (x) X
business less the estimated cost of completion and the estimated cost of Purchase allowance (x)
disposal. Transferred in X X
- Inventories shall be measured at the lower of cost and net
Transferred out (x) (x)
realizable value is now known as LCNRV.
Mark up X
Merchandise Inventory Raw Materials Work in Process Finished Goods Mark up cancel (x) Cost Ratio:
Estimation selling price X / / Total Goods Available for Sale X / X = x (Conservative)
Estimation cost to complete X / X Mark down X
Estimation cost to sell X / / Mark down cancel (x)
Replacement Cost / x X Total Goods Available for Sale X / X = x (Average)
Beginning (x) (x)
- Item by item basis = x (FIFO)
Total Goods Available for Sale X / X
Accounting for inventory writedown:
- Cost < NRV = Cost; No problem rapidly changing items with similar margin for which it is
Cost Ratio
impracticable to =use
TGAS
other@costing
Cost / TGAS
method. @ Retail (Selling Price)
- Cost > NRV = NRV; Impairment Loss, loss in inventory writedown. Conservative = Formula except writedowns/markdowns
Total Goods Available for Sale
Accounting for Impairment Loss: Average = Formula
- Reversal of impairment is up to the extent of loss. FIFO = Formula except beginning inventory
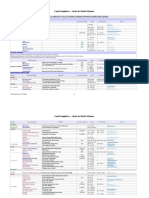
Direct Method Allowance Method Accounting Procedure:
- loss is buried in Cost of Goods Sold - loss is recognized Periodic System Perpetual System
- loss is presented as part of COGS Purchase of merchandise Purchases xx Inventory xx
* Gross Profit is the same in Direct and Allowance Method. on account Accounts Payable xx Accounts Payable xx
Payment of freight on the Freight In xx Inventory xx
Purchase Commitment – to purchase at specific price at future purchase Cash xx Cash xx
time or date. Return of merchandise Accounts Payable xx Accounts Payable xx
Gain – fixed price < Market = No Entry purchased to supplier Purchase Return xx Inventory xx
- fixed price > Market = Loss (Recognized) Sale of Merchandise on Accounts Receivable xx Accounts Receivable xx
account Sales xx Sales xx
o Estimation of Inventory – approximate value of inventory when it is not COGS xx
possible to take a physical count. Inventory xx
* loss * interim reports Return of merchandise sold Sales Return xx Sales Return xx
from customer Accounts Receivable xx Accounts Receivable xx
Gross Profit Method – ratio of cost of goods sold to net sales is Inventory xx
relatively constant from period to period. COGS xx
Adjustment of ending Inventory-end xx No Journal Entry
inventory Income Summary xx
closed to cost of goods sold result of normal shrinkage and
breakage of inventory.
abnormal and material shortage – other expense
o Trade discount
arrive at invoice price; charged to the buyer
not recorded
o Cash discount
purchase discount – buyer
sales discount – seller
o Methods of recording purchases
Gross method – purchases and payable are recorded at gross.
Net method – purchases and payable are recorded at net.
o Cost of inventories
cost of purchase
- it shall not include foreign exchange differences involving
a foreign currency.
- recognized as interest expense over the period.
cost of conversion
- cost directly related to the units of production.
- Fixed production overhead – indirect cost; remains
o Basic formula under the gross profit method constant regardless of the volume of production.
- Uncollected fixed overhead – expense when incurred.
Goods Available for Sale (GAS) xx
- Variable production overhead – indirect cost; varies
Less: Cost of Goods Sold xx
directly with the volume of production.
Ending Inventory xx
other cost
o Goods Available for Sale - incurred in bringing the inventories to their present
Beginning Inventory xx location and condition.
Add: Purchases xx - excluded and recognized as expense when:
Freight in xx - abnormal amounts
Total xx - storage cost (finished goods)
Less: Purchase return xx - storage cost (goods in process) – capitalized
Purchase allowance xx - administrative overheads
Purchase discount xx xx - distribution or selling costs
Goods Available for Sale xx o Gain on purchase commitment
classified as other income
Presentation and Disclosure: o Disclose to the financial statement
o Inventories amount of inventories or any writedown of inventories – expense
current assets amount of reversal of writedown – income
statement of financial position carrying amount of inventories pledge as security – liabilities
o Inventory shortage or overage o Agricultural, forest and mineral products
measured at net realizable value
sale is assured under a forward contract or government guarantee.
homogeneous market exist and negligible risk of failure to sell
o Commodities of broker-traders
measured at fair-value less cost of disposal.
Broker-traders – who buy and sell commodities for others or on
their own account.
o Cost of goods sold
use of the gross profit rate
Net sales multiplied by cost ratio – based on sales
Net sales divided by sales ratio – based on cost
o Sales Allowance and sales discount
not deducted from sales
do not increase the physical inventory of goods
You might also like
- Elysian CycleDocument3 pagesElysian CycleMyrnil TilbeNo ratings yet
- Effect of Rebranding On The Customer Satisfaction of Foodpanda Bangladesh LimitedDocument56 pagesEffect of Rebranding On The Customer Satisfaction of Foodpanda Bangladesh LimitedSiam Farhan75% (4)
- Lookup Out LatestDocument717 pagesLookup Out Latestravidas2006100% (1)
- CHAPTER 16-Inventories: Far SummaryDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 16-Inventories: Far SummaryFuturamaramaNo ratings yet
- Far Notes For QualiDocument10 pagesFar Notes For QualiMergierose DalgoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Inventories Goods Includible in InventoryDocument4 pagesChapter 7: Inventories Goods Includible in InventoryAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Cost FlowDocument2 pagesInventory Cost FlowFe ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Far ManufDocument4 pagesFar ManufAshryle SalazarNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 and 11Document5 pagesChap 10 and 11Mary Claudette UnabiaNo ratings yet
- In-Class Exercise Chapte 6 Part 1 (24 Ed)Document5 pagesIn-Class Exercise Chapte 6 Part 1 (24 Ed)Thomas TermoteNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument12 pagesAccounting NotesKrystelle JalemNo ratings yet
- Pas 2 Inventories: Nature: DefinitionDocument3 pagesPas 2 Inventories: Nature: DefinitionKristalen ArmandoNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument3 pagesInventoriesNikki RañolaNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument6 pagesInventories: Financial Accounting and ReportingcolNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1 Notes Part 4Document10 pagesIntacc 1 Notes Part 4Crizelda BauyonNo ratings yet
- MA NotesDocument15 pagesMA NotesHershi TrinidadNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument9 pagesInventoriesDon John David100% (2)
- Materials and Supplies Awaiting Use in The Production ProcessDocument3 pagesMaterials and Supplies Awaiting Use in The Production ProcessMizumi IshiharaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For INVENTORIESDocument4 pagesAccounting For INVENTORIESMeludyNo ratings yet
- PAS 2 InventoriesDocument6 pagesPAS 2 Inventoriesgreat angelNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Product Cost and Variance AccountDocument9 pagesThe Difference Between Product Cost and Variance AccountIvory ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Introduction To Manufacturing Operations (New Account Titles The Financial Statements)Document3 pagesModule 7: Introduction To Manufacturing Operations (New Account Titles The Financial Statements)Ashitero YoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Inventories: CustomersDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Inventories: CustomersireneNo ratings yet
- COSTCON - Accounting For MaterialsDocument2 pagesCOSTCON - Accounting For MaterialsAcademic StuffNo ratings yet
- Costacc 7Document4 pagesCostacc 7parkjenaa09No ratings yet
- Module 5 - Inventories: Maritime Shipping TermsDocument4 pagesModule 5 - Inventories: Maritime Shipping TermsAva RodriguesNo ratings yet
- ACC 203 Module 4 PAS 2 Inventories PAS 41 Biological AssetsDocument15 pagesACC 203 Module 4 PAS 2 Inventories PAS 41 Biological AssetsKirsty SicamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6kareem abozeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document16 pagesChapter 6kareem abozeedNo ratings yet
- Inventories 2024Document27 pagesInventories 2024Charish Ann SimbajonNo ratings yet
- Far 6813 - Inventory Cost Flow Lower of Cost or Net Realizable Value (LCNRV)Document2 pagesFar 6813 - Inventory Cost Flow Lower of Cost or Net Realizable Value (LCNRV)Kent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- Inventories NotesDocument2 pagesInventories NotesMikaela LacabaNo ratings yet
- 161 12 PAS 2 InventoriesDocument2 pages161 12 PAS 2 InventoriesRegina Gregoria SalasNo ratings yet
- Pas 2Document5 pagesPas 2ilexNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerCINDY BALANONNo ratings yet
- Aaca Chap 12Document3 pagesAaca Chap 12Eidel PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - IND AS 2 InventoriesDocument18 pagesChapter 3 - IND AS 2 InventoriesAmbati Madhava ReddyNo ratings yet
- INVENTORIESDocument28 pagesINVENTORIESLourdios EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument2 pagesIntacc ReviewerCassandra CeñidoNo ratings yet
- 2 Inventory Cost Flow Intermediate Accounting ReviewerDocument3 pages2 Inventory Cost Flow Intermediate Accounting ReviewerDalia ElarabyNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 10 InventoryDocument1 pageCFAS Chapter 10 InventoryKaren CaelNo ratings yet
- 4.0 COMPLETE INVENTORIES - StudentsDocument14 pages4.0 COMPLETE INVENTORIES - StudentsTyron TayloNo ratings yet
- 2 Accounting For MaterialsDocument8 pages2 Accounting For MaterialsRonn Robby RosalesNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 - PAS 2 InventoriesDocument7 pagesGROUP 2 - PAS 2 InventoriesNhicoleChoiNo ratings yet
- Presentation4.1 - Audit of Inventories, Cost of Sales and Other Related AccountsDocument37 pagesPresentation4.1 - Audit of Inventories, Cost of Sales and Other Related AccountsRoseanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Scope: Allocation of Fixed Production OverheadsDocument8 pagesScope: Allocation of Fixed Production OverheadsjayveeNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument7 pagesInventoriesRomlan Akman DuranoNo ratings yet
- Accounting For InventoryDocument30 pagesAccounting For Inventorydmkinga617No ratings yet
- Pas 2Document2 pagesPas 2Ella MaeNo ratings yet
- PAS 2 50% CompleteDocument8 pagesPAS 2 50% CompleteALJON-KHAN CHUANo ratings yet
- s2 Aud2 PrelimDocument17 pagess2 Aud2 PrelimDanielNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting - Exam SheetDocument2 pagesFinancial Reporting - Exam SheetMaría Mercedes RedondoNo ratings yet
- Cfas - InventoriesDocument6 pagesCfas - InventoriesYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting de Leon Chapter 7 SUMMARYDocument7 pagesCost Accounting de Leon Chapter 7 SUMMARYHarrietNo ratings yet
- 121 Prelims ReviewerDocument6 pages121 Prelims Reviewerjohnmichaelaspe1234No ratings yet
- Assignment 1571213755 SmsDocument15 pagesAssignment 1571213755 SmsRahul Kumar Sharma 17No ratings yet
- FormulasDocument12 pagesFormulasMathivanan NatarajNo ratings yet
- A. Identify The Units in Ending InventoryDocument6 pagesA. Identify The Units in Ending InventoryYevhenii VdovenkoNo ratings yet
- Inventories: PERIODIC SYSTEM-physical Counting of Goods OnDocument4 pagesInventories: PERIODIC SYSTEM-physical Counting of Goods OnGirl Lang AkoNo ratings yet
- Assertions (OROCA CAVE)Document2 pagesAssertions (OROCA CAVE)Victoria V. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pas 2 InventoriesDocument12 pagesPas 2 InventoriesLETIGIO, RHEANA ROSE M.100% (1)
- InventoriesDocument3 pagesInventoriesZance JordaanNo ratings yet
- NSTP EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesNSTP EntrepreneurshipCharina Jane Pascual100% (1)
- Pascual, Maria Charina Jane A. BSA 1-12 Mr. Tubay: 16 Personality TestDocument1 pagePascual, Maria Charina Jane A. BSA 1-12 Mr. Tubay: 16 Personality TestCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- NSTP EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesNSTP EntrepreneurshipCharina Jane Pascual100% (1)
- Accounts ReceivableDocument2 pagesAccounts ReceivableCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- It's Cool Supplies: Purchase JournalDocument10 pagesIt's Cool Supplies: Purchase JournalCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Interest Is Equal To The Amount Paid: Case 1Document3 pagesTransfer of Interest Is Equal To The Amount Paid: Case 1Charina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- I. Economics and Its NatureDocument5 pagesI. Economics and Its NatureCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- 50 Bonds PayableDocument6 pages50 Bonds PayableCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Doubtful AccountsDocument1 pageEstimation of Doubtful AccountsCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- Cash AND Cash Equiva Note S Recei Vabl Acco Unts Recei Vabl Invent Ories Prop Erty, Plan T and Equip Loan S Recei Vabl Invest Ment in AssociDocument1 pageCash AND Cash Equiva Note S Recei Vabl Acco Unts Recei Vabl Invent Ories Prop Erty, Plan T and Equip Loan S Recei Vabl Invest Ment in AssociCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- The Transformation Process Can BeDocument3 pagesThe Transformation Process Can BeCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- It's Cool Supplies Purchases JournalDocument11 pagesIt's Cool Supplies Purchases JournalCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- Angelina FacewashDocument17 pagesAngelina Facewashfiza akhterNo ratings yet
- SM Advantage Card (SMAC)Document4 pagesSM Advantage Card (SMAC)Jykyll PaulNo ratings yet
- STR Bba 5 Sem Summer Training ProjectDocument75 pagesSTR Bba 5 Sem Summer Training Projectanamika vermaNo ratings yet
- Hello Panda 10 GR Brand KnowledgeDocument25 pagesHello Panda 10 GR Brand KnowledgeTsf RizqyNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project Report ON Big Bazaar: Under The Guidance ofDocument46 pagesSummer Internship Project Report ON Big Bazaar: Under The Guidance ofSunil Kumar TNo ratings yet
- W5 - Session 10 Marketing Management PDFDocument22 pagesW5 - Session 10 Marketing Management PDFZaky Abdurrasyid MNo ratings yet
- Loreal 4psDocument2 pagesLoreal 4psMohit NavalkhaNo ratings yet
- Plastic MoneyDocument42 pagesPlastic MoneyAnonymous So5qPSnNo ratings yet
- The RattrapDocument18 pagesThe RattraprajniNo ratings yet
- Used-Case Study of Walmart Customer Queuing Management ProcessDocument9 pagesUsed-Case Study of Walmart Customer Queuing Management ProcessHtetThinzarNo ratings yet
- CATC DL Ch06 E Commerce FundamentalsDocument16 pagesCATC DL Ch06 E Commerce Fundamentals01-11-09 ธีรายุ ฟื้นหัวสระNo ratings yet
- Resume of SheryleenwilliamsDocument2 pagesResume of Sheryleenwilliamsapi-28577818No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 1 - Module 1-Lesson 1: Relevance of The CourseDocument16 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 1 - Module 1-Lesson 1: Relevance of The Courselea banting67% (3)
- Marketing Management Module 3Document14 pagesMarketing Management Module 3Sharon Cadampog MananguiteNo ratings yet
- Report On Marketing Chanel Analysis: Presented byDocument15 pagesReport On Marketing Chanel Analysis: Presented byNaij ahmedNo ratings yet
- Consumer and Business Buyer BehaviorDocument4 pagesConsumer and Business Buyer BehaviorAzizah Dwi PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Rural & Agricultural Marketing NotesDocument30 pagesRural & Agricultural Marketing NotesDivaxNo ratings yet
- PPOM Test 2Document2 pagesPPOM Test 2Fairooz AliNo ratings yet
- Seven Eleven JapanDocument14 pagesSeven Eleven JapanJuan Sebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Anti Laws of Luxury: Submitted By: Akshay Khanna MBA (M&S) Section-A A-44Document11 pagesAnti Laws of Luxury: Submitted By: Akshay Khanna MBA (M&S) Section-A A-44alpana chawlaNo ratings yet
- Lowe'S - Brand Strategy AnalysisDocument10 pagesLowe'S - Brand Strategy AnalysisLouis JacquotNo ratings yet
- 26 03 2021 Bicycle SuppliersDocument18 pages26 03 2021 Bicycle SuppliersCharlie WaitesNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN OP HENDRI DecemberDocument45 pagesLAPORAN OP HENDRI DecemberSiti QoryatiNo ratings yet
- Chap 16: Personal Selling & Sales Promotion: Linh Tran, Hanoi University Nov 23, 2020Document16 pagesChap 16: Personal Selling & Sales Promotion: Linh Tran, Hanoi University Nov 23, 2020Vân HoàngNo ratings yet
- SBI Elite Card JanuaryDocument3 pagesSBI Elite Card Januaryamarayugandhar94No ratings yet
- Sales Training - Your Price Is RightDocument3 pagesSales Training - Your Price Is RightSuvidha SNo ratings yet
- Final City Council LetterDocument4 pagesFinal City Council LetterZvnnyv1019No ratings yet