Professional Documents
Culture Documents
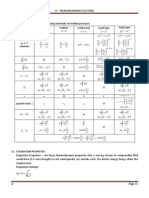
ρ dV C dt ρ F W: For liquid phase
ρ dV C dt ρ F W: For liquid phase
Uploaded by
Selly The SpiceOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ρ dV C dt ρ F W: For liquid phase
ρ dV C dt ρ F W: For liquid phase
Uploaded by
Selly The SpiceCopyright:
Available Formats
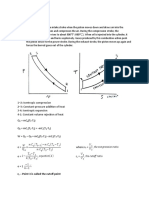
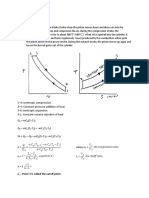
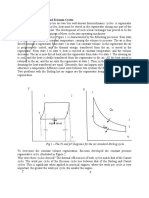
Q5
Assumptions:
- LPG is pure component of propane
- Liquid in tank is perfectly mixed
- Heat is added at a rate Q to maintain the pressure with evaporating liquid at rate Wv(kg/hr)
- Gas is withdrawn from top at volumetric flowrate of Fv
- negligible mass loss from tank
For liquid phase
total continuity equation
ρ dV C
=ρ F0 −W V
dt
Energy equation
ρ dV LU L
=ρ0 F0 h0 +W V H L +Q
dt
Vapor pressure from Antoine equation
V B
ln P =A−
T +C
For vapor phase
total continuity equation
d ρV V V
=W V −ρV FV
dt
Energy equation
d ρV V V U
=W V H L −ρV F V H V
dt
State
M PV
ρV =
RT
For a stable system, equation and variable must be equal.
Hence, volume of tank, V =V V +V L
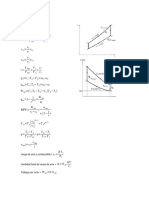
Q11
Lowest root = -0.4153
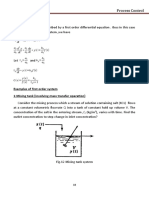
Q14
a) to derive dynamic models
Assume density of all streams are constant
Total mass balance in the tank
d ρV
= ρQ 1+ ρQ 2- ρQ 3
dt
dV
= Q 1+ Q 2- Q 3
dt
Solute balance
Inlet-outlet= accumulation
d C3 V
Q 1 C 1 +Q 2 C 2−Q 3 C3 =
dt
Assuming perfect mixing, concentration in tank is equal to concentration of outlet stream
Because volume is constant
dV
=0
dt
0= Q 1+ Q 2- Q 3
Q 1+ Q 2= Q 3
d C3 V
Q 1 C 1 +Q 2 C 2−Q 3 C3 =
dt
C 3=C
dC
Q 1 C 1 +Q 2 C 2−Q 3 C=V
dt
Integrating from time 0 to t
t c (t )
∫ ⅆt=v ∫ Q C + QdcC −Q C
0 c ( 0) 1 1 2 2 3
Q 1 ,C 1 ,Q 2 ,C 2are constant
V (Q 1 C 1+Q 2 C2 −Q 3 C ( t ) )
=- ln
Q 3 (Q¿¿ 1 C1 +Q 2 C 2−Q 3 C ( 0 ) ) ¿
−Q3 t
V
(Q1 C1 +Q2 C2−Q3 C ( t ))
e =
(Q¿¿ 1C 1 +Q2 C 2−Q3 C ( 0 ) )¿
¿¿
Q3 C ( t ) =( Q1 C 1 +Q2 C 2 )−¿ ¿
Hence, rearrange to get concentration at time, t
−Q3 t
( Q 1 C 1 +Q 2 C 2 ) ( Q1 C 1+Q2 C2 ) V
C ( t )= − −Q 3 C ( 0 ) e
Q3 Q3
b) at steady state, to find C 3
dC 3
=0
dt
( Q1 C 1+Q 2 C 2)
C 3=
Q3
Substitute the values to find C 3,
25 ( 2 ) +10(1.5)
C 3=
3.5
= 18.57mg/m 3
You might also like
- Seborg - Process Dynamics and Control 4th Ed 2017 Solutions PDFDocument572 pagesSeborg - Process Dynamics and Control 4th Ed 2017 Solutions PDFWilliam Manase89% (9)
- Solution Manual For Process Dynamics and Control 4th Edition - Dale Seborg, Thomas EdgarDocument34 pagesSolution Manual For Process Dynamics and Control 4th Edition - Dale Seborg, Thomas EdgarMphahlele Keletso67% (3)
- HW5 SolDocument11 pagesHW5 Solondutz33% (3)
- Power Cycles 1 - 1 PDFDocument6 pagesPower Cycles 1 - 1 PDFclarkmaxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Section B - Non-Numerical SolutionsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Section B - Non-Numerical Solutionslight2618No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Section B - Non-Numerical SolutionsDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - Section B - Non-Numerical SolutionsFaris NaufalNo ratings yet
- Fluids FormulasDocument2 pagesFluids Formulasteresapulga6100% (1)
- Solution: 1. Refer Eq. (6.28)Document4 pagesSolution: 1. Refer Eq. (6.28)kajal mishrsNo ratings yet
- Updated Question1Document2 pagesUpdated Question1azqa khalidNo ratings yet
- محاضرة رقم 15Document2 pagesمحاضرة رقم 15دريد فاضلNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 First Law-Closed System ProblemsDocument11 pagesUnit 2 First Law-Closed System Problemspiravi66No ratings yet
- Lecture - 11 - Second LawDocument10 pagesLecture - 11 - Second LawMihai MirceaNo ratings yet
- Paper Thermo Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesPaper Thermo Mechanical EngineeringAdif HerawanNo ratings yet
- Unit One and ThreeDocument32 pagesUnit One and ThreeGAURAV RATHORENo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document115 pagesChapter 6heryj12No ratings yet
- RC Circuits: Example 1. Very Simple RC Circuit: A Capacitor C, Charged To An Initial Voltage VDocument3 pagesRC Circuits: Example 1. Very Simple RC Circuit: A Capacitor C, Charged To An Initial Voltage VNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Pat-Iv Subjective (Summit Batches) : (Physics)Document2 pagesSolutions To Pat-Iv Subjective (Summit Batches) : (Physics)blue_l1No ratings yet
- Useful Equations For ME2121 (Part 1)Document5 pagesUseful Equations For ME2121 (Part 1)bleejunanNo ratings yet
- Process Control Assignment Roll No-492IC07Document13 pagesProcess Control Assignment Roll No-492IC07akulNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 7 - First LawDocument9 pagesLecture - 7 - First LawMihai MirceaNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow Through Nozzles and Diffusers: V DT V D V VDocument14 pagesCompressible Flow Through Nozzles and Diffusers: V DT V D V VCamilo SantacruzNo ratings yet
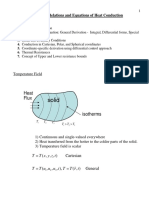
- UO2016F Slide 1 - Basic Relations and Equations of Heat ConductionDocument20 pagesUO2016F Slide 1 - Basic Relations and Equations of Heat ConductionSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics IDocument8 pagesThermodynamics IFerdaus Hasan BappiNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control Seborg 2nd Ch02 PDFDocument20 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control Seborg 2nd Ch02 PDFsdrtfgNo ratings yet
- Carnot CycleDocument10 pagesCarnot CycleSande NasNo ratings yet
- Plant Selection:: Figure1: Process DiagramDocument12 pagesPlant Selection:: Figure1: Process DiagramChisom ChubaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Ito Na PreDocument8 pagesPrelim Ito Na PreJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Heat Engines: First Law: Perfect GasDocument21 pagesHeat Engines: First Law: Perfect GasMagdy RiadNo ratings yet
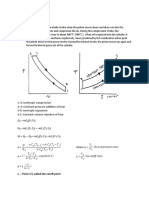
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument8 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesThermodynamicssamir boseNo ratings yet
- D - Thermodynamics 1 - REVIEWDocument1 pageD - Thermodynamics 1 - REVIEWallovidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17Document10 pagesLesson 17Tran NhanNo ratings yet
- Formelsamling 2009Document18 pagesFormelsamling 2009dunderdunderNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyExam2018 11Document1 pagePhilosophyExam2018 11Kokipro KokiproNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument5 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument7 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Unsteady Isothermal C STRDocument3 pagesUnsteady Isothermal C STRcansuNo ratings yet
- Equation Thermal Diesel CycleDocument2 pagesEquation Thermal Diesel CycleZakyKikyNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSIONDocument16 pagesCONCLUSIONlado prakasaNo ratings yet
- TER201 Lecture 6Document66 pagesTER201 Lecture 6lnxxNo ratings yet
- mC ΔT ρ v C ΔT ρ A hC ΔT ρ v C Δ Z (TDocument2 pagesmC ΔT ρ v C ΔT ρ A hC ΔT ρ v C Δ Z (TMohammad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document3 pagesLecture 7دريد فاضلNo ratings yet
- Evidence Consolidation ActivityDocument60 pagesEvidence Consolidation ActivityAlonso GalvisNo ratings yet
- Stirling and EricssonDocument7 pagesStirling and EricssonAJ SiosonNo ratings yet
- Home Work of Process ControlDocument5 pagesHome Work of Process ControlIqra SafdarNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThermodynamicsMonique OrugaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7. Vacuum Technology: 7-1. Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument12 pagesLecture 7. Vacuum Technology: 7-1. Kinetic Theory of Gases최종윤No ratings yet
- Volumetric PropertiesDocument36 pagesVolumetric PropertiesRohan BhilkarNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument8 pagesFormulasTecnoLife BaltoNo ratings yet
- SVPWM PDFDocument25 pagesSVPWM PDFLeroy Lionel SonfackNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Aerodynamics in CarsDocument20 pagesAerodynamics in CarsSagar KnNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument42 pagesLinear MomentumFady MichealNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Training Unit Operations and Training Manual FinalDocument107 pagesRefrigeration Training Unit Operations and Training Manual FinalDaniel James MurilloNo ratings yet
- Hanbell MPV Valve Spec SheetDocument1 pageHanbell MPV Valve Spec SheetDũng LêNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica StennerDocument2 pagesFicha Tecnica StennerJordany JimenezNo ratings yet
- Insight:: Ductile Iron, Green Sand CastingDocument4 pagesInsight:: Ductile Iron, Green Sand CastingM PankajNo ratings yet
- Pump Le400 Roy LmiDocument4 pagesPump Le400 Roy LmiShesharam ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Fresh Water GeneratorDocument131 pagesAlfa Laval Fresh Water GeneratorOvidiu Petcu80% (5)
- PDFDocument139 pagesPDFAnonymous ItzBhUGoi100% (2)
- Cyclone Recovery SystemsDocument13 pagesCyclone Recovery SystemsDaniela MateiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Joshua Micole Felizarta, LPTDocument25 pagesChemical Kinetics: Joshua Micole Felizarta, LPTArvin SayotoNo ratings yet
- 1st MeetingDocument15 pages1st MeetingPrakashHanumanthappaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Test and Production Separation Production Separation PresentationDocument73 pagesWelcome To The Test and Production Separation Production Separation PresentationhamdiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- CBB3024 FlowsheetingDocument66 pagesCBB3024 Flowsheetingfatiehah93No ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: Project No: Date: Sheet No.:1 1 Computed By: SubjectDocument1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet: Project No: Date: Sheet No.:1 1 Computed By: SubjectfebousNo ratings yet
- Ab/Abd Air Boosters & SystemsDocument10 pagesAb/Abd Air Boosters & SystemsMok YukNo ratings yet
- (°F) (Psi (G) ) (Psi (G) ) (Galus/Min) (KG/H) (CP) (Psi (A) )Document5 pages(°F) (Psi (G) ) (Psi (G) ) (Galus/Min) (KG/H) (CP) (Psi (A) )Elias EliasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - The Bernoulli EquationDocument53 pagesLecture 6 - The Bernoulli EquationThatayamodimo KebueNo ratings yet
- BS 5955-6Document21 pagesBS 5955-6Fenner ElectromechanicalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties of Fluids Revision NotesDocument37 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties of Fluids Revision NotesSachin BishtNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Directional DrillingDocument15 pagesHorizontal Directional Drillingoconnorr8133% (3)
- Design of Sedimentation TankDocument9 pagesDesign of Sedimentation TankHans Hans SadzNo ratings yet
- Regulators 92CTDocument16 pagesRegulators 92CTAlberto CastellanosNo ratings yet
- WSSI-part 2Document73 pagesWSSI-part 2Abdisa Legese100% (1)
- Pumping TestDocument80 pagesPumping Testdagutaku0% (1)
- R410A Non Inverter: Ceiling Concealed SeriesDocument2 pagesR410A Non Inverter: Ceiling Concealed SeriesAyda Johari100% (1)
- Boiler Types and ClassificationsDocument26 pagesBoiler Types and ClassificationshardikNo ratings yet
- Double Pipe Heat Exchanger DesignDocument10 pagesDouble Pipe Heat Exchanger DesignRhumi ELfver ShawolNo ratings yet
- WO - No Valve Type Size X Class Item Name MaterialDocument24 pagesWO - No Valve Type Size X Class Item Name MaterialAliasgarNo ratings yet