Professional Documents
Culture Documents
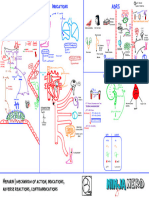
Adrenergic Agonist MAP
Adrenergic Agonist MAP
Uploaded by
Johnny BeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adrenergic Agonist MAP
Adrenergic Agonist MAP
Uploaded by
Johnny BeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Adrenergic
Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic Antagonist >>>
NEW SLIDE>>>>>
Direct-Acting Agonist Indirect Acting Agonist Mixed Action Agonist
Catecholamines Bind directly with Adrenergic receptors Non-Catecholamines Bind directly with Adrenergic receptors and
Facilitate release (displacement) of NE or displace NE from storage sites
inhibit reuptake of NE
Endogenous Synthetic
B2-Agonists (-ol) Dextoamphetamine / Methamphetamine
Ephedrine / Ephedra
Epinephrine Isoproternol MOA: Relaxes Bronchial smooth muscle
resulting in Bronchodilation MOA: Causes release oc Catecholamines (NE,
5HT, D) from pre-synaptic storage sites, MOA: direct acting a and B-agonist, also
inhibits their reuptake displaces NE from storage site
MOA: Released by Adrenal Medulla, agonist MOA: Non-selective agaonist at B1 and B2 Clincal: Asthma, COPD
at both a and B receptors (a1=a2; B1-B2) receptors (B1=B2) Clinical: ADHD, Narcolepsy, Obesity, Clinical: Ephedrine (1) Bronchospasms, (2)
Depression Nasal congestion, (3) HTON - temporarily
relieves SOB, tightness of chest and
Clinical: Bronchospasms, Anaphylactic Stimulates HR and contractility to maintain Monitor: Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
wheezing due to bronchial asthma
Shock, Cardiac Arrest, Anesthetic adjunct ( cardiac output (B1 stimulation increases SBP; and Pulmonary Function Tests (PFT) Adverse: CNS (insomnia, irritability, tremor,
prolongs duration of action) B2 stimulation decreases DBP), while also confusion, panic state, suicidal tendiencies,
causing Bronchodilation amphetamine psychosis / Dependence / HTN, Clinical: Ephedra: (1) Weight loss, (2) Energy
palpations / GI (NVD, anorexia) / Decreaseed booster, (3) Enhance Athletic performance
Increases cardiac output (increase SBP with Adverse: Cardiac (increase BP, Tachycardia),
growth rate (peds)
minimal decrease in DBP), Bronchodilation. Clinical: Bradyarrhythmias; Temporary use in CNS Stimulation (nervousness, restlessness),
At lower Dose: B2 vasodilation 3rd Degree AV block until Pacemaker Hypokalemia, Hyperglycemia Adverse: CNS (anxiety, insomnia), CV (HTN,
predominates, higher Dose: a1 insertion Contraindication: Pts with HTN, CV disease, Tachycardia), may interfere with detection
vasoconstriction predominates Hyperthyroidism, Glaucoma of amphetamines (false-positive)
Monitor: ECG Interactions: B-blockers (primarily non-
Adverse: CNS, anxiety, fear, tremor / selective Interactions: MAO-Inhibitors Interactions: a-blockers
Cardiac (HTN, Tachyarrhythmias), / Cerebral
Adverse: CNS (anxiety, fear, tremor),
Hemorrhage / Mydriasis / Hyperglycemia /
Cardiac (Tachyarrhythmias), Hyperglycemia Tyramine Pseudophedrine
Extravasation-tissue necrosis
Short-Acting B2-Agonist Long-Acting B2-Agonist
Interactions: COMT inhibitors may prolong
Dipivefrin
action, B-blockers result in physiologic
antagonism Drug Interactions! = not marketed MOA: Direct acting a and B-agonist (a>B)
Albuterol Arformoterol while also displacing NE from storage site
MOA: Prodrug metabolized to Epinephrine in Dobutamine MOA: enters nerve terminals and displaces
NE, which then acts on a-receptors Clinical: Relief of Nasal congestion
the eye that decreases IOP by contract radial
muscle that opens trabecular network to DOC for acute (or rescue) Respiratory relief ( Approved for COPD only
increase aqueous humor outflow COPD, Asthma) Found in fermented foods Adverse: Cardiac (HTN, Tachycardia),
MOA: Selective B1 agonist, Increase strength Illegally used as precursor to
of contraction (rate neutral) increase cardiac Formoterol methamphetamine, May interfere with urine
Clinical: Open-angle Glaucoma Levalbuterol Pts taking a mono amine oxidase inhibitors (
output (SBP increase) detection of amphetamine (false-positive)
MAOI) who eat Tyramine containing foods
Adverse: Mydriasis / Burning & Stinging can develop HTN crisis
Clinical: Increase Cardiac Output in Acute Interactions: a-blockers
Possesses a rapid onset (5 mins: 80% peak
Decompensated Heart Failure (ADHF)
R-isomer of Albuterol, purported to cause effect in 15 min) not approved for acute Cocaine (Class II)
NorEpinephrine
fewer side effects relief of asthmatic symptoms
Monitor: ECG
Metaproterenol Salmeterol
MOA: Agonist at both a and B receptors (a Adverse: CNS (Headache), Cardiac (A-fib) MOA: Inhibits reuptake of NE/EPI back into
effects >> B1>>B2) / Increased synaptic vesicles, blocks initiation or
Terbutaline
vasconstriction and increases inotropic conduction of the nerve impulse following
Interactions: COMT inhibitors may prolong local application
effect (rate-neutral due to reflex action, B-blockers result in physiologic Onset: 30 min for Asthma, 2 hrs for COPD
Bradycardia) to increase BP antagonism
Rarely used as Bronchodilator; Primarily used Indacterol Clinical: Topical anesthesia to accessible
Clinical: short-term Tx of shock ( to suppress Premature Birth mucouse membranes of oral, laryngeal, and
Hypotension) nasal cavities
Arrhythmia: Dopamine>>NorEpinephrine; no Approved for COPD only Adverse: CNS stimulation/depression,
mortality difference Cardio: Bradycardia (low dose),Tachycardia (
high dose), Vasoconstriction
Phenylephrine
Adverse: CNS (anxiety, fear, tremor),
Cardiac (HTN), Cerebral Hemorrhage (2nd Fatal Overdose: appx 1.2 gm; severe toxic
increase BP), Extravasation-tissue necrosis effects at even 20 mg
MOA: Synthetic a1-agonist, Increases BP,
Dilates Pupil, constricts engorged ocular,
Interactions: a-blockers (Physiological
nasal, and rectal vasculature to decrease
Antagonism) B-blockers (Exaggerated a
redness and congestion, shrinks hemorrhoids
response), Increase efficacy: MAO-inhibitor
and COMT inhibitor
Clinical: Tx of Hypotension/vascular failure
2nd to Shock, Mydriatic for EYE procedures,
Dopamine
Relief of eye redness, Hemorrhoids, and
Nasal congestion
MOA: Stimulates a, B, and Dopamine (D) Monitor: Increased BP
receptors depending on dose- a-receptors
increase BP at higher doses, B-receptors Adverse: Exravasation (IV)-tissue necrosis,
increase cardiac output (increase SBP with Hypertensive HA, Hypertensive patients,
minimal to DBP), D-receptors may increase Rebound congestion (nasal >3-5 days)
Renal perfusion increasing diuresis
Interactions: a-blockers, MAO-inhibitors
Clinical: Critical Care- low to moderate dose
for Cardiac and Septic Shock
Oxymetazoline
Alternative to NE, Arrhythmia: Dopamine>>
NE: no mortality difference, Low dose D
should NOT be used for Renal protection
MOA: a1 and a2 agonist, EYE drops or Nasal
spray produce vasoconstriction that
Monitor: ECG, Vitals, Urine output decreases blood flow resulting in decreased
ocular redness and nasal congestion
Adverse: CNS, anxiety, fear, tremor /
Cardiac (HTN, Tachyarrhythmias), / Cerebral Clinical: Ocular and Nasal vasoconstrictor (
Hemorrhage / Mydriasis / Hyperglycemia / relief of redness and congestion)
Extravasation-tissue necrosis
Adverse: Rebound hyperemia/congestion,
Interactions: a-blockers (physiological Ocular stinging/burning
antagonism), B-blockers (exaggerated a-
response), Increase efficacy: MAO-inhibitors
Midodrine
and COMT inhibitors
MOA: Prodrug that forms an active
metabolite, Desglymidodrine, an a1-agonist,
Causes vasoconstriction, increase BP
Clinical: Tx of symptomatic orthostatic
hypotension
Adverse: HTN, Bradycardia, Piloerection (
Goose bumps), Paresthesia (Skin sensations,
burning, prickling, itching, tingling)
Interactions: MAO-inhibitors
Clonidine
MOA: Stimulates a2 presynaptic receptors in
the brain stem (Central), Reduces
sympathetic outflow from CNS and
decreases Peripheral resistance, Renal
vascular resistance, HR, and BP
Clinical: HTN, ADHD (peds), Tourette (off-
label), Opioid withdrawal (off-label),
Nicotine withdrawal (off-label)
Caution: Do not discontinue long-term
Clonidine use suddenly
Adverse: CNS, Anticholinergic, Skin reactions
with transdermal, Sodium + Water retention,
may be given with diuretic
Interactions: May enhance AV-blocking
effect of B-blocker, Closely monitor HR
during treatment with B-blocker and
Clonidine. Withdraw B-blocker several days
before clonidine withdrawal, monitor BP
Brimonidine
MOA: Ocular a2-agonist, decreases aqueous
humor production
Clinical: Tx Glaucoma
Adverse: Ocular burning/stining
Mirabegron
MOA; B3-agonist that relaxes detrusor
muscle, increases bladder capacity
Clinical: Overactive bladder with symptoms
of urge urinary incontinence, urgency and
frequency
Adverse: Increase BP
Interactions: Anticholinergics for the
bladder (increases urinary retention)
Fenoldopam
MOA: D1-agonist binds with moderate
affinity to a2-receptors, Rapid acting
vasodilator, Decreases peripheral vascular
resistance and BP secondary to increased
renal blood flow, and natriuresis/diuresis
Clinical: Tx in Hospital, short-term (48hrs)
mgmt of Severe HTN, 6x more potent as
Dopamine in producing Renal Vasodilation
Adverse: HA, flushing, dizziness, N/V,
Tachycardia, Hypokelemia
You might also like
- A320 Family Maintenance Concept PosterDocument1 pageA320 Family Maintenance Concept PosterKamran Khan Tareen100% (1)
- RenalDocument1 pageRenalYezin Shamoon100% (1)
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- BFSDocument2 pagesBFSJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metals Test KitsDocument2 pagesHeavy Metals Test KitsosumexNo ratings yet
- Tooth TraumaDocument111 pagesTooth TraumaNavroop Kaur50% (2)
- Gen Path Case StudyDocument3 pagesGen Path Case Studydex7reme0% (1)
- Mind Map Sym&Parasym DrugsDocument2 pagesMind Map Sym&Parasym Drugsjitpinun.sNo ratings yet
- Angeline D. Alabastro, M.D.: CNS Pharmacology I: AntiepilepticsDocument10 pagesAngeline D. Alabastro, M.D.: CNS Pharmacology I: AntiepilepticsMiguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- Online Edition - Digital AccessDocument1 pageOnline Edition - Digital Access18aw2708No ratings yet
- All Charts Final Exam 1 PDFDocument294 pagesAll Charts Final Exam 1 PDFYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- Restaurant Risk MatrixDocument2 pagesRestaurant Risk MatrixScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Patient Data - 100Document1 pagePatient Data - 100pavankn0402No ratings yet
- Nifedi-Denk 20 Retard - Nifedipine 20mg Prolonged release tablet - PILDocument2 pagesNifedi-Denk 20 Retard - Nifedipine 20mg Prolonged release tablet - PILHamadou FadimatouNo ratings yet
- IRAC Modes of ActionDocument1 pageIRAC Modes of ActionsigitNo ratings yet
- Appendix 5 Hazmat Inventory SheetDocument1 pageAppendix 5 Hazmat Inventory Sheetaldrb hospitalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemTin Myat SweNo ratings yet
- Permanent Plus: Engine ControlDocument1 pagePermanent Plus: Engine ControlAlanNo ratings yet
- c15 ldn01610 SchematicDocument4 pagesc15 ldn01610 SchematicJacques Van Niekerk50% (2)
- Andrew J. Cutler - Valbenazine and DeutetrabenazineDocument1 pageAndrew J. Cutler - Valbenazine and DeutetrabenazineSanty P Vásconez CalderónNo ratings yet
- HPLC FenitoinaDocument32 pagesHPLC FenitoinaJhon Murga SNo ratings yet
- PMKP Juni-Desember 19Document256 pagesPMKP Juni-Desember 19Dini RizkyNo ratings yet
- c15 Main Schematic ECM PDFDocument4 pagesc15 Main Schematic ECM PDFWill ?No ratings yet
- Night Scan Powerlite ECDDocument2 pagesNight Scan Powerlite ECDSUNIL MISHRANo ratings yet
- Batteries: Color Code For Schematic LinesDocument2 pagesBatteries: Color Code For Schematic LinesIsaac NewtonNo ratings yet
- 23 - Preoperative Patient Assessment and ManagementDocument1 page23 - Preoperative Patient Assessment and ManagementHenrique MachadoNo ratings yet
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument1 pagePost-Traumatic Stress DisorderJoan MonzonesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Amala Wellness Guide SML 922d96d0 6f29 4b8c 856e b26ff73d360fDocument2 pagesAmala Wellness Guide SML 922d96d0 6f29 4b8c 856e b26ff73d360fdouglasknight2No ratings yet
- Neuroinflammation and Alzheimers Disease PosterDocument1 pageNeuroinflammation and Alzheimers Disease PosterVincent Mora GarcisNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument1 pageCase PresentationGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc.: ADVIA Centaur XP Version 1.0.EC and 1.0.ED Test DefinitionsDocument12 pagesSiemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc.: ADVIA Centaur XP Version 1.0.EC and 1.0.ED Test DefinitionsОлександрNo ratings yet
- De - Mavenclad - Actrims 2024 Cladrina p481Document1 pageDe - Mavenclad - Actrims 2024 Cladrina p481magdecanedaNo ratings yet
- Sample Matrix 1Document6 pagesSample Matrix 1eastNo ratings yet
- DQC24 Tableau Medicaments EN WEBDocument1 pageDQC24 Tableau Medicaments EN WEBcococooleNo ratings yet
- Ka1 Ebp 00a d7086 Iom Manual GCBDocument261 pagesKa1 Ebp 00a d7086 Iom Manual GCBLaura Callista AzahraNo ratings yet
- R&D Hazards Eval Form Ver 3.3Document13 pagesR&D Hazards Eval Form Ver 3.3dleggett5147No ratings yet
- C15 and C18 Industrial Engine Electrical System: View ADocument4 pagesC15 and C18 Industrial Engine Electrical System: View AOecox Cah Djadoel100% (2)
- PDF Hoja de Registro Anestesico Gava CompressDocument2 pagesPDF Hoja de Registro Anestesico Gava CompressEDITH NATHALY CUMBAJIN PANELUISANo ratings yet
- Fully Programmable. Ultra-Portable.: Made in ItalyDocument2 pagesFully Programmable. Ultra-Portable.: Made in ItalypsychpostersNo ratings yet
- 01 Control Structures PDFDocument22 pages01 Control Structures PDFJeff RobertNo ratings yet
- Biological PosterDocument1 pageBiological PosterAsad UllahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology] 03 Heparin - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology] 03 Heparin - KeyRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Combination Meter Combination Meter Combination MeterDocument1 pageCombination Meter Combination Meter Combination MeterDannyDDannyDNo ratings yet
- HIRADC - Pekerjaan 20 KV - PLTGU - Update 5 March 2018Document5 pagesHIRADC - Pekerjaan 20 KV - PLTGU - Update 5 March 2018ghieee100% (2)
- Dokumen - Tips Samsung GT E1200 SchematicsDocument7 pagesDokumen - Tips Samsung GT E1200 SchematicsHogir DoskyNo ratings yet
- ECU de 4 ConectoresDocument1 pageECU de 4 ConectoresHarold Rodriguez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Crt-Npc-Dmm-Hva-Dwg-Sd-Gn-33501 - Equipment Capacity Schedule 1-6Document1 pageCrt-Npc-Dmm-Hva-Dwg-Sd-Gn-33501 - Equipment Capacity Schedule 1-6Shah MuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Compare Vivix With Noni Xango MonavieDocument1 pageCompare Vivix With Noni Xango MonaviecustomhealthNo ratings yet
- DNA Repair Pathways PosterDocument1 pageDNA Repair Pathways Posterdyk2100% (1)
- Lanoxic Aps From Lanoxin DosageDocument4 pagesLanoxic Aps From Lanoxin Dosageelvie21No ratings yet
- M.4-1-001a - Mall Mechanical Services Panel Diagram P-CH-4THDocument1 pageM.4-1-001a - Mall Mechanical Services Panel Diagram P-CH-4THdiki anggriawanNo ratings yet
- Empagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Document2 pagesEmpagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Lord Carlo CabangalNo ratings yet
- ECT and A/T Indicator (1AZ-FSE) ECT and A/T Indicator (1AZ-FSE) ECT and A/T Indicator (1AZ-FSE)Document1 pageECT and A/T Indicator (1AZ-FSE) ECT and A/T Indicator (1AZ-FSE) ECT and A/T Indicator (1AZ-FSE)Luis100% (1)
- CD Radio Cassette-Corder: Specifications Troubleshooting PrecautionsDocument2 pagesCD Radio Cassette-Corder: Specifications Troubleshooting PrecautionsAliseNo ratings yet
- Oxaliplatin For Injection (Preservative-Free) 50 MG Per Vial and 100 MG Per Vial Package Leaflet - Taj PharmaDocument1 pageOxaliplatin For Injection (Preservative-Free) 50 MG Per Vial and 100 MG Per Vial Package Leaflet - Taj PharmaTAJ PHARMA — A Health Care ProviderNo ratings yet
- 994F Wheel Loader Electrical System: Cab Harness Connector and Component Location GridDocument4 pages994F Wheel Loader Electrical System: Cab Harness Connector and Component Location GridAlexis MikeNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster FungicidasDocument1 pageFrac Moa Poster Fungicidaskelvin horna guiopNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster March FRACDocument1 pageFrac Moa Poster March FRACEliana Garcia ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Homework Unit III N IVDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Homework Unit III N IVYazmin CoatlNo ratings yet
- Spectrum WhiteDocument1 pageSpectrum WhitethebigfishxNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: MathRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Inpatient Pocket Card SetDocument9 pagesInpatient Pocket Card SetJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Head / Hair Face Eyes Nose Oral / Throat Ears Neck: Physical Exam (Heent)Document1 pageHead / Hair Face Eyes Nose Oral / Throat Ears Neck: Physical Exam (Heent)Johnny BeeNo ratings yet
- GI Signs and SymptomsDocument40 pagesGI Signs and SymptomsJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Velocity-DIet 3.5.1Document75 pagesVelocity-DIet 3.5.1Johnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Ab Crunch Machine: Exercise DataDocument27 pagesAb Crunch Machine: Exercise DataJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- ArachnidsDocument1 pageArachnidsJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesDaftar PustakaDesyari SusantiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Screening Form - AgriSafe NetworkDocument4 pagesClinical Screening Form - AgriSafe NetworkAgriSafeNo ratings yet
- The Indian Journal of Pediatrics: OntentsDocument6 pagesThe Indian Journal of Pediatrics: OntentsPoldo ReinaldoNo ratings yet
- BuzzwordsDocument35 pagesBuzzwordstesta21100% (1)
- Pediatric Readiness Guidelines ChecklistDocument4 pagesPediatric Readiness Guidelines ChecklistsabirNo ratings yet
- Haematology and Biochemistry in Alpacas and Llamas: Red Blood CellsDocument6 pagesHaematology and Biochemistry in Alpacas and Llamas: Red Blood CellsDarwin Antezana De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20bDocument6 pagesChapter 20baexillisNo ratings yet
- Impulse Control DisordersDocument20 pagesImpulse Control DisordersKenth June GenobisNo ratings yet
- SNS 1 (Circulation)Document7 pagesSNS 1 (Circulation)Dheeraj Kumar100% (1)
- 1st Internal Assessment Examination. Dept of PhysiologyDocument2 pages1st Internal Assessment Examination. Dept of PhysiologyIshan KalraNo ratings yet
- Application of The MASCC and CISNE Risk-Strati Fication Scores To Identify Low-Risk Febrile Neutropenic Patients in The Emergency DepartmentDocument10 pagesApplication of The MASCC and CISNE Risk-Strati Fication Scores To Identify Low-Risk Febrile Neutropenic Patients in The Emergency DepartmentwiraNo ratings yet
- Lactated RingersDocument3 pagesLactated RingersE100% (5)
- Healthcare Insurance From A To Z - AnderzorgDocument86 pagesHealthcare Insurance From A To Z - AnderzorgJeremySitorusNo ratings yet
- Liberty University BIOL 101 Individual Assignment 3 Complete Solutions Correct Answers KeyDocument3 pagesLiberty University BIOL 101 Individual Assignment 3 Complete Solutions Correct Answers KeyLiberty0% (1)
- Thalidomide AssignmentDocument2 pagesThalidomide AssignmentMorganNo ratings yet
- ABC of Intensive CareDocument49 pagesABC of Intensive CareCurro MirallesNo ratings yet
- Psychological DisordersDocument6 pagesPsychological DisordersDiaиa DiazNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Autoimmune Diseases: Presented By, S.Nagaraj, M.Sc. 3 YearDocument51 pagesDiagnosis of Autoimmune Diseases: Presented By, S.Nagaraj, M.Sc. 3 YearAzhar Clinical Laboratory TubeNo ratings yet
- AcinobacterDocument2 pagesAcinobacterAllyson Layaoen CollierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ColostomyDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan ColostomyCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Herbal MedicineDocument5 pagesHerbal MedicineParth RathodNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Daily For Wed 05 Oct 2016 - WA Pharmacy Vax Success, End Med Review Cap Call, NSAID Heart Risk Link, Health AMPERSAND Beauty and Much MoreDocument4 pagesPharmacy Daily For Wed 05 Oct 2016 - WA Pharmacy Vax Success, End Med Review Cap Call, NSAID Heart Risk Link, Health AMPERSAND Beauty and Much MorepharmacydailyNo ratings yet
- Work Related Low Back Pain in Sedentary Railway Officials of The Age Group 30 To 60 Years at Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus Mumbai - A Survey StudyDocument30 pagesWork Related Low Back Pain in Sedentary Railway Officials of The Age Group 30 To 60 Years at Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus Mumbai - A Survey StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Case Study - MentalDocument13 pagesCase Study - Mentalapi-353370932No ratings yet
- Medication Safety PDFDocument95 pagesMedication Safety PDFMangayarkarasi ChandrakasanNo ratings yet
- Iv Drip IsoxilanDocument1 pageIv Drip IsoxilannierbobierNo ratings yet






































![Cardiovascular Pharmacology] 03 Heparin - Key](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/747791383/149x198/8cd3843a2c/1720070291?v=1)