Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Uploaded by
Inga ElenaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- American Language Hub 5 Students BookDocument186 pagesAmerican Language Hub 5 Students Bookbillhorn7793100% (1)
- My English Grammar Guide CompressDocument39 pagesMy English Grammar Guide CompressBenny LeeNo ratings yet
- Times: I Talk, )Document11 pagesTimes: I Talk, )mugiNo ratings yet
- Tense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNDocument2 pagesTense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNMirela MarinNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talked, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talked, )Seminarski Radovi Iz IstorijeNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentNorvin TreminioNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Eng Grammar Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesEng Grammar Parts of Speechsami karemNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument7 pagesTenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRajalakshmi Gajapathy100% (2)
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGiannina Ailén MusacchioNo ratings yet
- Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesAffirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsKavitha RajendranNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentClaudiaNo ratings yet
- გრამატიკაDocument3 pagesგრამატიკაgio903371No ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensescoquin8816No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 15, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 15, 2023sumanta biswasNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordslovely innocentNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple Presentmanchiraju raj kumarNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAdailton SamuelNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentBogdan ChișcababiiNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoprasannabandiNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: GrammarDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: GrammarGenesis Belen0% (1)
- 1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Document3 pages1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Adeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument10 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMina SamyNo ratings yet
- Tenses Cuadro ResumenDocument4 pagesTenses Cuadro ResumenGuillermo NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDiego GrañenaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesLucaNo ratings yet
- Guia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialDocument5 pagesGuia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialLizzy Yessenia Torres 11- 8 BCHNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDahliya DwitaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAngi BraileanuNo ratings yet
- Cours 2bac L en 04Document2 pagesCours 2bac L en 04hkuuiNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesOscar LunaNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument3 pagesInglesazoljamiaidounNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioDocument2 pagesTiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioelisaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsmllorenteNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarinela AnghelNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentSofiene GuedriNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesLiliia RakNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsanamariaNo ratings yet
- Verbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésDocument242 pagesVerbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésVioleta Patricia Molet100% (1)
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesRasta FariNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesMelinaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar OnlineDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar OnlineNasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentCristina ArdeleanNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAlfi Ramdhani PNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesMaria ArtilesNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument2 pagesTenseKlaudia TerjékNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key Wordsyadhi20No ratings yet
- ÖzetDocument2 pagesÖzetEnes PolatNo ratings yet
- Level 1Document1 pageLevel 1Melissa ReyesNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDocument9 pagesSimple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsSusila PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument6 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarkoNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJosé LiraNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRavi Teja AnneNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Italk, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: Italk, )Enes PolatNo ratings yet
- The Fun Way To Learn EnglishDocument7 pagesThe Fun Way To Learn EnglishPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference. c1 UnedDocument38 pagesGrammar Reference. c1 UnedCristina Gonzalez GarridoNo ratings yet
- This Table Illustrates The Tenses in A Simple Way: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesThis Table Illustrates The Tenses in A Simple Way: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRafik RafNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- Eating Out - Exercises 5 PDFDocument2 pagesEating Out - Exercises 5 PDFInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Going To The Supermarket (A2)Document2 pagesGoing To The Supermarket (A2)Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Future Tense Exercises Part 1Document2 pagesFuture Tense Exercises Part 1Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Advice For Exams - Exercises 0Document3 pagesAdvice For Exams - Exercises 0Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Olimpiada de Limba Engleză Etapa LocalăDocument4 pagesOlimpiada de Limba Engleză Etapa LocalăInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing 1-2 TestDocument2 pagesIELTS Writing 1-2 TestInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Solar System's First Interstellar Visitor Dazzles ScientistsDocument3 pagesSolar System's First Interstellar Visitor Dazzles ScientistsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Irregular VerbsDocument5 pagesIllustrated Irregular VerbsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Translating Cultural TermsDocument24 pagesTranslating Cultural TermsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Translating Culture Vs Cultural TranslationDocument8 pagesTranslating Culture Vs Cultural TranslationInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Exam Practice Speaking Section - Sample Task 1Document2 pagesProficiency Exam Practice Speaking Section - Sample Task 1Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Types of TestsDocument4 pagesTypes of TestsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Skills, Understanding The Main Idea MiddleundefinedJamestown PublishersundefinedDocument66 pagesComprehension Skills, Understanding The Main Idea MiddleundefinedJamestown PublishersundefinedKenan NabilNo ratings yet
- Your English Pal ESL Lesson Plan Friends Student v2Document4 pagesYour English Pal ESL Lesson Plan Friends Student v2Ágnes JassóNo ratings yet
- 1. Cẩm Bình-20-1-24- MĐ 421Document5 pages1. Cẩm Bình-20-1-24- MĐ 421Quan Dang HongNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Focus On The LearnerDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - Focus On The LearnerZaher Al-SaltiNo ratings yet
- Mini Dictionary of Irish SlangDocument2 pagesMini Dictionary of Irish SlangClaire F.No ratings yet
- 300 The Secret Life of Walter Mitty - WishDocument2 pages300 The Secret Life of Walter Mitty - WishAnthony NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of AdjectivesDocument5 pagesComparison of AdjectivesÖzen NeboğluNo ratings yet
- History of SanskritDocument502 pagesHistory of SanskritPranam Pranav100% (3)
- Hillary Schepps Senior ThesisDocument62 pagesHillary Schepps Senior ThesisjustlilyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document13 pagesUnit 3Ingrid BeltránNo ratings yet
- Noun ClausesDocument10 pagesNoun ClausesAna Maria Benavides MartinNo ratings yet
- Spellings Question Answers, PSC, UPSC, IBPS, SSC Previous PapersDocument13 pagesSpellings Question Answers, PSC, UPSC, IBPS, SSC Previous PapersalammehsudNo ratings yet
- Sentence Constituents PDFDocument14 pagesSentence Constituents PDFKiana Asumbrado CodillaNo ratings yet
- SEM 111 Weeks13-14 Language Learning Material Development (20230426095827)Document17 pagesSEM 111 Weeks13-14 Language Learning Material Development (20230426095827)Ramos Gedie MaeNo ratings yet
- 1 cs626 Intro 27jul22Document44 pages1 cs626 Intro 27jul22chandraNo ratings yet
- Anh 8Document276 pagesAnh 8duonglhaiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Mathematics For Grade 3Document19 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Mathematics For Grade 3Prexus Emz TaccadNo ratings yet
- 32877.TOC - CHO 3rd SemDocument9 pages32877.TOC - CHO 3rd SemMansi GargNo ratings yet
- Ariane CotDocument5 pagesAriane CotAriane Grace LopezNo ratings yet
- Lark Parser Readthedocs Io en LatestDocument90 pagesLark Parser Readthedocs Io en LatestDoble DBSNo ratings yet
- VERBOSDocument2 pagesVERBOSbiblionorenaNo ratings yet
- Presentation МетодичкаDocument22 pagesPresentation МетодичкаYour Public ProfileNo ratings yet
- Inglés - Prueba para Ingresar A IV° BachDocument12 pagesInglés - Prueba para Ingresar A IV° BachJuan Carlos Monzón ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Learning Theories-A Keen Perspective: December 2016Document3 pagesVocabulary Learning Theories-A Keen Perspective: December 2016Nafisatu Khoirun NisaNo ratings yet
- Spelling Bee Toolkit 3 5Document118 pagesSpelling Bee Toolkit 3 5PJ Rod100% (1)
- Random Choices - A PowerPoint Randomizer - TekhnologicDocument11 pagesRandom Choices - A PowerPoint Randomizer - TekhnologicABoseLopusoNo ratings yet
- Ruce - B.tech - Ru20 - Vi Semester - SyllabusDocument34 pagesRuce - B.tech - Ru20 - Vi Semester - SyllabusShaik azeezullahNo ratings yet
- HSG ANH 6 ĐỀ 2Document4 pagesHSG ANH 6 ĐỀ 2Nguyen Ngoc MinhNo ratings yet
- ADVERBSDocument27 pagesADVERBSCatherine MargarseNo ratings yet
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Uploaded by
Inga ElenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Uploaded by
Inga ElenaCopyright:
Available Formats
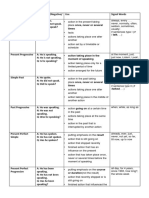
Table of English Tenses
tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
always, every …, never,
Simple A: He speaks. action in the present taking
normally, often, seldom,
Present N: He does not speak. place regularly, never or several sometimes, usually
Q: Does he speak? times if sentences type I (If
facts I talk, …)
actions taking place one after
another
action set by a timetable or
schedule
Present A: He is speaking. at the moment, just, just
action taking place in the
Progressive N: He is not speaking. now, Listen!, Look!, now,
Q: Is he speaking? moment of speaking right now
action taking place only for a
limited period of time
action arranged for the future
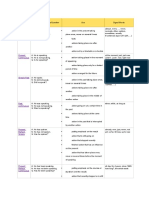
Simple A: He spoke. yesterday, 2 minutes ago,
action in the past taking
Past N: He did not speak. in 1990, the other day, last
Q: Did he speak? place once, never or several times Friday
actions taking place one after if sentence type II (If
another I talked, …)
action taking place in the
middle of another action
Past A: He was speaking. while, as long as
action going on at a certain
Progressive N: He was not speaking.
Q: Was he speaking? time in the past
actions taking place at the
same time
action in the past that is
interrupted by another action
Present A: He has spoken. already, ever, just, never,
putting emphasis on the result
Perfect N: He has not spoken. not yet, so far, till now, up
Simple Q: Has he spoken? action that is still going on to now
action that stopped recently
finished action that has an
influence on the present
action that has taken place
once, never or several times before
the moment of speaking
Present A: He has been speaking. all day, for 4 years, since
putting emphasis on
Perfect N: He has not been speaking. 1993, how long?, the
Progressive Q: Has he been speaking? the course or duration (not the whole week
result)
action that recently stopped
or is still going on
finished action that influenced
the present
Past A: He had spoken. already, just, never, not
action taking place before a
Perfect N: He had not spoken. yet, once, until that day
Simple Q: Had he spoken? certain time in the past if sentence type III (If
sometimes interchangeable I had talked, …)
with past perfect progressive
putting emphasis only on
the fact (not the duration)
Past A: He had been speaking. for, since, the whole day,
action taking place before a
Perfect N: He had not been speaking. all day
Progressive Q: Had he been speaking? certain time in the past
sometimes interchangeable
with past perfect simple
putting emphasis on
the duration or course of an action
Future I A: He will speak. in a year, next …,
action in the future that
Simple N: He will not speak. tomorrow
Q: Will he speak? cannot be influenced If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her,
spontaneous decision she will help you.)
assumption: I think,
assumption with regard to the
probably, perhaps
future
Future I A: He is going to speak. in one year, next week,
decision made for the future
Simple N: He is not going to speak. tomorrow
Q: Is he going to speak? conclusion with regard to the
(going to) future
Future I A: He will be speaking. in one year, next week,
action that is going on at a
Progressive N: He will not be speaking.
Q: Will he be speaking? tomorrow
certain time in the future
action that is sure to happen
in the near future
Future II A: He will have spoken. by Monday, in a week
action that will be finished at
Simple N: He will not have spoken.
Q: Will he have spoken? a certain time in the future
Future II A: He will have been speaking. for …, the last couple of
action taking place before a
Progressive N: He will not have been speaking. hours, all day long
Q: Will he have been speaking? certain time in the future
putting emphasis on
the course of an action
Conditional A: He would speak. if sentences type II
action that might take place
I Simple N: He would not speak. (If I were you, I would
Q: Would he speak? go home.)
Conditional A: He would be speaking.
action that might take place
I N: He would not be speaking.
Progressive Q: Would he be speaking? putting emphasis on
the course / duration of the action
Conditional A: He would have spoken. if sentences type III
action that might have taken
II Simple N: He would not have spoken. (If I had seen that, I would
Q: Would he have spoken? place in the past have helped.)
Conditional A: He would have been speaking.
action that might have taken
II N: He would not have been
Progressive speaking. place in the past
Q: Would he have been speaking? puts emphasis on
the course / duration of the action
You might also like
- American Language Hub 5 Students BookDocument186 pagesAmerican Language Hub 5 Students Bookbillhorn7793100% (1)
- My English Grammar Guide CompressDocument39 pagesMy English Grammar Guide CompressBenny LeeNo ratings yet
- Times: I Talk, )Document11 pagesTimes: I Talk, )mugiNo ratings yet
- Tense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNDocument2 pagesTense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNMirela MarinNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talked, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talked, )Seminarski Radovi Iz IstorijeNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentNorvin TreminioNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Eng Grammar Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesEng Grammar Parts of Speechsami karemNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument7 pagesTenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRajalakshmi Gajapathy100% (2)
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGiannina Ailén MusacchioNo ratings yet
- Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesAffirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsKavitha RajendranNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentClaudiaNo ratings yet
- გრამატიკაDocument3 pagesგრამატიკაgio903371No ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensescoquin8816No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 15, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 15, 2023sumanta biswasNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordslovely innocentNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple Presentmanchiraju raj kumarNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAdailton SamuelNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentBogdan ChișcababiiNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoprasannabandiNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: GrammarDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: GrammarGenesis Belen0% (1)
- 1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Document3 pages1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Adeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument10 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMina SamyNo ratings yet
- Tenses Cuadro ResumenDocument4 pagesTenses Cuadro ResumenGuillermo NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDiego GrañenaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesLucaNo ratings yet
- Guia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialDocument5 pagesGuia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialLizzy Yessenia Torres 11- 8 BCHNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDahliya DwitaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAngi BraileanuNo ratings yet
- Cours 2bac L en 04Document2 pagesCours 2bac L en 04hkuuiNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesOscar LunaNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument3 pagesInglesazoljamiaidounNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioDocument2 pagesTiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioelisaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsmllorenteNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarinela AnghelNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentSofiene GuedriNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesLiliia RakNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsanamariaNo ratings yet
- Verbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésDocument242 pagesVerbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésVioleta Patricia Molet100% (1)
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesRasta FariNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesMelinaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar OnlineDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar OnlineNasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentCristina ArdeleanNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAlfi Ramdhani PNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesMaria ArtilesNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument2 pagesTenseKlaudia TerjékNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key Wordsyadhi20No ratings yet
- ÖzetDocument2 pagesÖzetEnes PolatNo ratings yet
- Level 1Document1 pageLevel 1Melissa ReyesNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDocument9 pagesSimple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsSusila PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument6 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarkoNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJosé LiraNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRavi Teja AnneNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Italk, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: Italk, )Enes PolatNo ratings yet
- The Fun Way To Learn EnglishDocument7 pagesThe Fun Way To Learn EnglishPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference. c1 UnedDocument38 pagesGrammar Reference. c1 UnedCristina Gonzalez GarridoNo ratings yet
- This Table Illustrates The Tenses in A Simple Way: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesThis Table Illustrates The Tenses in A Simple Way: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRafik RafNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- Eating Out - Exercises 5 PDFDocument2 pagesEating Out - Exercises 5 PDFInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Going To The Supermarket (A2)Document2 pagesGoing To The Supermarket (A2)Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Future Tense Exercises Part 1Document2 pagesFuture Tense Exercises Part 1Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Advice For Exams - Exercises 0Document3 pagesAdvice For Exams - Exercises 0Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Olimpiada de Limba Engleză Etapa LocalăDocument4 pagesOlimpiada de Limba Engleză Etapa LocalăInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing 1-2 TestDocument2 pagesIELTS Writing 1-2 TestInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Solar System's First Interstellar Visitor Dazzles ScientistsDocument3 pagesSolar System's First Interstellar Visitor Dazzles ScientistsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Irregular VerbsDocument5 pagesIllustrated Irregular VerbsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Translating Cultural TermsDocument24 pagesTranslating Cultural TermsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Translating Culture Vs Cultural TranslationDocument8 pagesTranslating Culture Vs Cultural TranslationInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Exam Practice Speaking Section - Sample Task 1Document2 pagesProficiency Exam Practice Speaking Section - Sample Task 1Inga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Types of TestsDocument4 pagesTypes of TestsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Skills, Understanding The Main Idea MiddleundefinedJamestown PublishersundefinedDocument66 pagesComprehension Skills, Understanding The Main Idea MiddleundefinedJamestown PublishersundefinedKenan NabilNo ratings yet
- Your English Pal ESL Lesson Plan Friends Student v2Document4 pagesYour English Pal ESL Lesson Plan Friends Student v2Ágnes JassóNo ratings yet
- 1. Cẩm Bình-20-1-24- MĐ 421Document5 pages1. Cẩm Bình-20-1-24- MĐ 421Quan Dang HongNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Focus On The LearnerDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - Focus On The LearnerZaher Al-SaltiNo ratings yet
- Mini Dictionary of Irish SlangDocument2 pagesMini Dictionary of Irish SlangClaire F.No ratings yet
- 300 The Secret Life of Walter Mitty - WishDocument2 pages300 The Secret Life of Walter Mitty - WishAnthony NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of AdjectivesDocument5 pagesComparison of AdjectivesÖzen NeboğluNo ratings yet
- History of SanskritDocument502 pagesHistory of SanskritPranam Pranav100% (3)
- Hillary Schepps Senior ThesisDocument62 pagesHillary Schepps Senior ThesisjustlilyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document13 pagesUnit 3Ingrid BeltránNo ratings yet
- Noun ClausesDocument10 pagesNoun ClausesAna Maria Benavides MartinNo ratings yet
- Spellings Question Answers, PSC, UPSC, IBPS, SSC Previous PapersDocument13 pagesSpellings Question Answers, PSC, UPSC, IBPS, SSC Previous PapersalammehsudNo ratings yet
- Sentence Constituents PDFDocument14 pagesSentence Constituents PDFKiana Asumbrado CodillaNo ratings yet
- SEM 111 Weeks13-14 Language Learning Material Development (20230426095827)Document17 pagesSEM 111 Weeks13-14 Language Learning Material Development (20230426095827)Ramos Gedie MaeNo ratings yet
- 1 cs626 Intro 27jul22Document44 pages1 cs626 Intro 27jul22chandraNo ratings yet
- Anh 8Document276 pagesAnh 8duonglhaiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Mathematics For Grade 3Document19 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Mathematics For Grade 3Prexus Emz TaccadNo ratings yet
- 32877.TOC - CHO 3rd SemDocument9 pages32877.TOC - CHO 3rd SemMansi GargNo ratings yet
- Ariane CotDocument5 pagesAriane CotAriane Grace LopezNo ratings yet
- Lark Parser Readthedocs Io en LatestDocument90 pagesLark Parser Readthedocs Io en LatestDoble DBSNo ratings yet
- VERBOSDocument2 pagesVERBOSbiblionorenaNo ratings yet
- Presentation МетодичкаDocument22 pagesPresentation МетодичкаYour Public ProfileNo ratings yet
- Inglés - Prueba para Ingresar A IV° BachDocument12 pagesInglés - Prueba para Ingresar A IV° BachJuan Carlos Monzón ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Learning Theories-A Keen Perspective: December 2016Document3 pagesVocabulary Learning Theories-A Keen Perspective: December 2016Nafisatu Khoirun NisaNo ratings yet
- Spelling Bee Toolkit 3 5Document118 pagesSpelling Bee Toolkit 3 5PJ Rod100% (1)
- Random Choices - A PowerPoint Randomizer - TekhnologicDocument11 pagesRandom Choices - A PowerPoint Randomizer - TekhnologicABoseLopusoNo ratings yet
- Ruce - B.tech - Ru20 - Vi Semester - SyllabusDocument34 pagesRuce - B.tech - Ru20 - Vi Semester - SyllabusShaik azeezullahNo ratings yet
- HSG ANH 6 ĐỀ 2Document4 pagesHSG ANH 6 ĐỀ 2Nguyen Ngoc MinhNo ratings yet
- ADVERBSDocument27 pagesADVERBSCatherine MargarseNo ratings yet