Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CB - Assignment-Aditi Gupta
CB - Assignment-Aditi Gupta
Uploaded by
Aditi Gupta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views5 pagesThe Howard-Sheth Model proposes three levels of consumer decision making: extensive problem solving when consumers have no information, limited problem solving when consumers have some knowledge, and habitual response when consumers are familiar with brands. The model identifies four major sets of variables that influence consumer decisions: inputs like marketing, media, and social stimuli; perceptual and learning constructs like goals and preferences; outputs like attention and intentions; and exogenous variables like personality and time pressure. While pioneering, critics note the model does not sufficiently account for societal and religious influences on decision making.
Original Description:
Model
Original Title
CB- Assignment-Aditi Gupta
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Howard-Sheth Model proposes three levels of consumer decision making: extensive problem solving when consumers have no information, limited problem solving when consumers have some knowledge, and habitual response when consumers are familiar with brands. The model identifies four major sets of variables that influence consumer decisions: inputs like marketing, media, and social stimuli; perceptual and learning constructs like goals and preferences; outputs like attention and intentions; and exogenous variables like personality and time pressure. While pioneering, critics note the model does not sufficiently account for societal and religious influences on decision making.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views5 pagesCB - Assignment-Aditi Gupta
CB - Assignment-Aditi Gupta
Uploaded by
Aditi GuptaThe Howard-Sheth Model proposes three levels of consumer decision making: extensive problem solving when consumers have no information, limited problem solving when consumers have some knowledge, and habitual response when consumers are familiar with brands. The model identifies four major sets of variables that influence consumer decisions: inputs like marketing, media, and social stimuli; perceptual and learning constructs like goals and preferences; outputs like attention and intentions; and exogenous variables like personality and time pressure. While pioneering, critics note the model does not sufficiently account for societal and religious influences on decision making.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
NAME: Aditi Gupta
Roll no.: Ms18Ms501012
Q: Explain the components and working of HSM in brief
A:
John Howard and Jagadish Sheth put forward the Howard
Sheth model of consumer behavior in 1969, in their
publication entitled, ‘The Theory of buyer Behaviour’.
The Howard Sheth Model is a sophisticated integration of the
various social, psychological and marketing influences on
consumer choice into a coherent sequence of information
processing. It aims not only to explain consumer behavior in
terms of cognitive functioning but to provide an empirically
testable depiction of such behavior and its outcomes (Howard
1977).
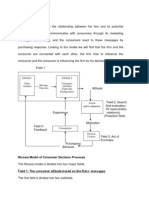
The logic of the Howard Sheth model of consumer behavior
summarize like this. There are inputs in the form of Stimuli.
There are outputs beginning with attention to a given stimulus
and ending with purchase. In between the inputs and the
outputs there are variables affecting perception and learning.
These variables are termed ‘hypothetical’ since they cannot be
directly measured at the time of occurrence.
The Howard Sheth model of consumer behavior suggests
three levels of decision making:
The first level describes the extensive problem solving. At
this level the consumer does not have any basic information or
knowledge about the brand and he does not have any
preferences for any product. In this situation, the consumer
will seek information about all the different brands in the
market before purchasing.
The second level is limited problem solving. This situation
exists for consumers who have little knowledge about the
market, or partial knowledge about what they want to
purchase. In order to arrive at a brand preference some
comparative brand information is sought.
The third level is a habitual response behavior. In this level
the consumer knows very well about the different brands and
he can differentiate between the different characteristics of
each product, and he already decides to purchase a particular
product.
According to the Howard Sheth model of consumer behavior
there are four major sets of variables; namely:
Inputs: These input variables consist of three distinct
types of stimuli (information sources) in the
consumer’s environment. The marketer in the form of
product or brand information furnishes physical brand
characteristics (significative stimuli) and verbal or
visual product characteristics (symbolic stimuli).
There are impersonal sources like mass media
communication and advertising, over which the firm
has no control. However, the information sources also
include sales and service personnel who can add and
help the marketing efforts of the firm. The third type is
provided by the consumer’s social environment
(family, reference group, and social class). This social
source is personal and the company/marketer has no
control over this source. All three types of stimuli
provide inputs concerning the product class or specific
brands to the specific consumer.
Perceptual and Learning Constructs: The central part
of the model deals with the psychological variables
involved when the consumer is contemplating a
decision. Some of the variables are perceptual in
nature, and are concerned with how the consumer
receives and understands the information from the
input stimuli and other parts of the model. For
example, stimulus ambiguity happened when the
consumer does not understand the message from the
environment. Perceptual bias occurs if the consumer
distorts the information received so that it fits his or
her established needs or experience. Learning
constructs category, consumers’ goals, information
about brands, criteria for evaluation alternatives,
preferences and buying intentions are all included. The
proposed interaction In between the different variables
in the perceptual and learning constructs and other sets
give the model its distinctive advantage.
Outputs: The outputs are the results of the perceptual
and learning variables and how the consumers will
response to these variables (attention, brand
comprehension, attitudes, and intention).
Exogenous(External) variables: Exogenous variables
are not directly part of the decision-making process.
However, some relevant exogenous variables include
the importance of the purchase, consumer personality
traits, religion, and time pressure.
The decision-making process, which Howard-Sheth Model
tries to explain, takes place at three Inputs stages:
Significance, Symbolic and Social stimuli. In both
significative and symbolic stimuli, the model emphasizes on
material aspects such as price and quality. These stimuli are
not applicable in every society. While in social stimuli the
model does not mention the basis of decision-making in this
stimulus, such as what influence the family decision? This
may differ from one society to another.
Finally, no direct relation was drawn on the role of religion in
influencing the consumer’s decision-making processes.
Religion was considered as external factor with no real
influence on consumer, which give the model obvious
weakness in anticipation the consumer decision
Most scholars agree that the study of consumer behavior was
advanced and given an impetus by Howard Sheth Model. The
major advantage and strength of the model lied in the
precision with which a large number of variables have been
linked in the working relationships to cover most aspects of
the purchase decision and the effective utilization of
contribution from the behavioral sciences.
You might also like
- A Theory of Buyer BehaviourDocument3 pagesA Theory of Buyer BehaviourRevanth Kumar50% (2)
- Howard Seth ModalDocument10 pagesHoward Seth ModalgnmadaviNo ratings yet
- Howard Shet ModelDocument4 pagesHoward Shet ModelGirija mirjeNo ratings yet
- B2B ProjectDocument6 pagesB2B ProjectGayathry SureshNo ratings yet
- Howard and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument2 pagesHoward and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourGauri sharmaNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth ModelDocument5 pagesHoward Sheth Modelrahul viju100% (1)
- Chapter 02 NanduniDocument20 pagesChapter 02 NanduniNeluka vishuddhiNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviorDocument7 pagesModels of Consumer BehaviorAnuj BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviorDocument14 pagesModels of Consumer Behaviorrahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth ModelDocument4 pagesHoward Sheth ModelDipjyoti TalukdarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Models & ApplicationsDocument42 pagesConsumer Behaviour Models & ApplicationsSiddhi MahaddalkarNo ratings yet
- Nicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially PredispositionDocument6 pagesNicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially Predispositionanon_80127205No ratings yet
- Howard ShethDocument5 pagesHoward Shethjmpnv007No ratings yet
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR Didi Kartik Make inDocument8 pagesCONSUMER BEHAVIOUR Didi Kartik Make inVashu KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior (The Selective Perception)Document4 pagesConsumer Behavior (The Selective Perception)Islam Samier100% (1)
- Reading 3 - CB ModelsDocument5 pagesReading 3 - CB Modelsmohitvarshney725No ratings yet
- Unit 4 CBDocument13 pagesUnit 4 CBAnilBahugunaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Alissandrei Ann LacuataDocument92 pagesPrepared By: Alissandrei Ann LacuataJamaica Sañez TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth and Nicosia ModelsDocument4 pagesHoward Sheth and Nicosia ModelskkNo ratings yet
- C.B AssignmentDocument8 pagesC.B AssignmentNipun ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismDocument41 pagesConsumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismShwetaBajiraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3shikhsNo ratings yet
- ARTICLEDocument16 pagesARTICLEShivam GhalmeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document23 pagesUnit 2Bhuvaneswari ANo ratings yet
- Chapter - IDocument74 pagesChapter - IsmsrickyNo ratings yet
- Product Psychology Sociology Socialanthropology EconomicsDocument5 pagesProduct Psychology Sociology Socialanthropology EconomicsAbhimanyu KotwalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour: Mini Project On Howard Seth ModelDocument10 pagesConsumer Behaviour: Mini Project On Howard Seth ModelLokesh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Study On Consumer Behavior For Pest Control Management Services in LucknowDocument45 pagesStudy On Consumer Behavior For Pest Control Management Services in LucknowavnishNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards Foods and ChipsDocument41 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards Foods and ChipsRaj Singh100% (1)
- Consumer PerceptionDocument4 pagesConsumer Perceptionusingh_58No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior On Public Private Bank 1Document53 pagesConsumer Behavior On Public Private Bank 1gsdurai.mba2725No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior 1Document19 pagesConsumer Behavior 1SURAJNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Consumer Behaviour ModelsDocument30 pagesUnit-2 Consumer Behaviour ModelsUmang GoelNo ratings yet
- Main Projects Lingam 15.5.2015Document59 pagesMain Projects Lingam 15.5.2015Naresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior ModelsDocument9 pagesConsumer Behavior ModelsShiney RajanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour ModelsDocument50 pagesConsumer Behaviour ModelsSunil PatelNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument87 pagesConsumer BehaviourDaksh AryanNo ratings yet
- CB ModelsDocument37 pagesCB ModelspraveenaNo ratings yet
- Piyush Consumer BehaviourDocument19 pagesPiyush Consumer BehaviourNehal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument5 pagesConsumer BehaviourManinder Singh KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Cia-1 CBDocument14 pagesCia-1 CBAnuraag KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth Model NotesDocument5 pagesHoward Sheth Model NotesarunvisaalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Report 1Document35 pagesConsumer Behavior Report 1adeelngNo ratings yet
- Tata NanoDocument70 pagesTata Nanoanibanerjee15No ratings yet
- Please Read: A Personal Appeal From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy WalesDocument5 pagesPlease Read: A Personal Appeal From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy WalesPashminaDoshiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFDocument22 pagesConsumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFPrashant TripathiNo ratings yet
- ModelDocument22 pagesModelArchana DeepakNo ratings yet
- ModelDocument22 pagesModelArchana DeepakNo ratings yet
- CB Notes by ShreyashDocument13 pagesCB Notes by ShreyashAkshat VyasNo ratings yet
- What Is Consumer Behavior in MarketingDocument2 pagesWhat Is Consumer Behavior in MarketingAbdul Mannan ButtNo ratings yet
- Tourism and Consumer BehaviorDocument27 pagesTourism and Consumer BehaviorChristopher CuvinNo ratings yet
- Review LitDocument9 pagesReview LitBablu JamdarNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chapter 5Document3 pagesSummary of Chapter 5Argie CatambacanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Consumer Buying BehavioursreeramNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Consumer Buying BehaviourakiyashrajNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Is The Study of How People Buy, What They BuyDocument9 pagesConsumer Behavior Is The Study of How People Buy, What They BuyPushpendra Trivedi100% (1)
- Consumer Pyscology-An Introduction and Its Brief HistoryDocument7 pagesConsumer Pyscology-An Introduction and Its Brief HistoryHritik SinghNo ratings yet
- List of BanksDocument8 pagesList of BanksAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cybercrime & Security: BY:-Aditi GuptaDocument16 pagesCybercrime & Security: BY:-Aditi GuptaAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime and Security: Pratik Raj Mishra B.Tech-CSEDocument12 pagesCyber Crime and Security: Pratik Raj Mishra B.Tech-CSEAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report BRM-1Document43 pagesFinal Project Report BRM-1Aditi Gupta100% (1)
- CYBER Crime & Security: BY:-Aditi GuptaDocument16 pagesCYBER Crime & Security: BY:-Aditi GuptaAditi Gupta100% (1)
- Dos Attack BasicsDocument3 pagesDos Attack BasicsAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Emerging Trends in Marketing, Analyzing Competitors, Industry Concept of CompetitionDocument8 pagesSubmitted By:: Emerging Trends in Marketing, Analyzing Competitors, Industry Concept of CompetitionAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Young Adults Learning Executive Function Skills by Playing Focused Video GamesDocument8 pagesYoung Adults Learning Executive Function Skills by Playing Focused Video GamesCamiloNo ratings yet
- 20130306210342kuliah 2a - Learning Theoies Piaget, Bruner, VygoskyDocument64 pages20130306210342kuliah 2a - Learning Theoies Piaget, Bruner, VygoskyIka Zalikha BNo ratings yet
- Reading An Example of Classroom-Based Action Research - N/ADocument3 pagesReading An Example of Classroom-Based Action Research - N/AEmily BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Across The Curriculum 1409 PDFDocument40 pagesCritical Thinking Across The Curriculum 1409 PDFHassan LemzaouakNo ratings yet
- Shada Zhafira - Tugas Sieve Tray 2Document8 pagesShada Zhafira - Tugas Sieve Tray 2Shada ZhafiraNo ratings yet
- Axiology A. Definition of AxiologyDocument6 pagesAxiology A. Definition of AxiologyDiya FitriNo ratings yet
- General Capabilities - CCT - Learning ContinuumDocument2 pagesGeneral Capabilities - CCT - Learning Continuumapi-340721646No ratings yet
- Leslie L. Paguio BSN 4-C Instruction: Read The Lecture On CONFLICT MANAGEMENT and Write An ESSAYDocument2 pagesLeslie L. Paguio BSN 4-C Instruction: Read The Lecture On CONFLICT MANAGEMENT and Write An ESSAYLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1.3. Who Is A Benildean Critical and Creative ThinkerDocument2 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1.3. Who Is A Benildean Critical and Creative ThinkerlamegothNo ratings yet
- Reflection of The Demo TeachingDocument2 pagesReflection of The Demo Teachingqwerty100% (5)
- 20-09-2019 What Is AbilityDocument2 pages20-09-2019 What Is AbilityRizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Teaching vs. Facilitating: Mercè Bernaus Mbernaus@uab - EsDocument16 pagesTeaching vs. Facilitating: Mercè Bernaus Mbernaus@uab - EsBernard Vincent Guitan MineroNo ratings yet
- Monden Student Success Plan SSPDocument2 pagesMonden Student Success Plan SSPapi-304732665No ratings yet
- NLP TheoriesDocument3 pagesNLP TheoriesAriol ZereNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Biography of John Amos Comenius: Science For Young Children KAK3023Document7 pages1.0 Biography of John Amos Comenius: Science For Young Children KAK3023Laili AhmadNo ratings yet
- IELTS Exam Preparation - General Reading Passage 18Document4 pagesIELTS Exam Preparation - General Reading Passage 18HOPENo ratings yet
- Intended Learning Outcomes: After Studying This Chapter, You Should Be Able To Do TheDocument4 pagesIntended Learning Outcomes: After Studying This Chapter, You Should Be Able To Do Thejestoni alvezNo ratings yet
- Cheryl F. Fischer: Supervision of InstructionDocument18 pagesCheryl F. Fischer: Supervision of InstructionAnne Atienza GarciaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual DisabilitiesDocument1 pageIntellectual Disabilitiesapi-558321133No ratings yet
- RPH Week 4 2022 (Fazlina) 1Document16 pagesRPH Week 4 2022 (Fazlina) 1fazlina harunNo ratings yet
- Human Activity RecognizationDocument8 pagesHuman Activity RecognizationNIckNo ratings yet
- Division of Biñan City: Self - Learning ModuleDocument9 pagesDivision of Biñan City: Self - Learning ModuleBayoyong NhsNo ratings yet
- OB Final Exam12Document2 pagesOB Final Exam12Aye TubeNo ratings yet
- Learning Style InventoryDocument9 pagesLearning Style InventoryAashna DuggalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Acrostic PoemsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Acrostic Poemsapi-534368950No ratings yet
- Strategies For Lesson PlanningDocument14 pagesStrategies For Lesson PlanningVince NavarezNo ratings yet
- PART III Lesson 1 Learning To Be A Better StudentDocument30 pagesPART III Lesson 1 Learning To Be A Better StudentMelvin Pogi138No ratings yet
- Neuroscience Brain RelatedDocument10 pagesNeuroscience Brain RelateddgavrileNo ratings yet
- The Cognition of Comics: What "Comics" Can Tell Us About The MindDocument2 pagesThe Cognition of Comics: What "Comics" Can Tell Us About The MindPixel CobrizoNo ratings yet
- The Learning Styles Learning StylesDocument4 pagesThe Learning Styles Learning StylesMARY JEANINA ALBANo ratings yet