Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparison of Common Hematological Disorders
Comparison of Common Hematological Disorders
Uploaded by
Tharani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 page1) Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) typically affects children and occurs after a bloody diarrhea illness caused by Shiga toxin-producing E. coli. It involves microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury.
2) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) usually affects young adults and can be triggered by HIV. It is caused by a deficiency of ADAMTS13 protease leading to platelet clumping in small blood vessels.
3) Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) can occur in children or adults. It presents as isolated thrombocytopenia after ruling out other causes through
Original Description:
here
Original Title
Common_Hematological_Disorders
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) typically affects children and occurs after a bloody diarrhea illness caused by Shiga toxin-producing E. coli. It involves microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury.
2) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) usually affects young adults and can be triggered by HIV. It is caused by a deficiency of ADAMTS13 protease leading to platelet clumping in small blood vessels.
3) Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) can occur in children or adults. It presents as isolated thrombocytopenia after ruling out other causes through
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 pageComparison of Common Hematological Disorders
Comparison of Common Hematological Disorders
Uploaded by
Tharani1) Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) typically affects children and occurs after a bloody diarrhea illness caused by Shiga toxin-producing E. coli. It involves microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury.
2) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) usually affects young adults and can be triggered by HIV. It is caused by a deficiency of ADAMTS13 protease leading to platelet clumping in small blood vessels.
3) Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) can occur in children or adults. It presents as isolated thrombocytopenia after ruling out other causes through
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
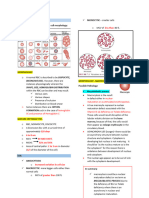
Comparison of Common Hematological Disorders
Trombotic Thrombocytopenic Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Purpura (TTP) Purpura (ITP)
It affects "children" It affects "Young adults" It occurs in "children or adults"
It occurs after bloody diarrheal illness - Usually idiopathic. Thrombocytopenia may be the initial
(Previous infection) - Maybe triggered by HIV infection. presentation of HIV or HCV infection
Due to infection with : Hereditary or acquired autoantibody to ITP is usually diagnosed after
ADAMTS13, a plasma protease that excluding other possible causes of
Shiga toxin produced by a strain of cleaves von Willebrand factor (vWF) off thrombocytopenia based on :
E.coli (01 57:H7). the endothelial surface. History
Pathophysiology Examination
- Shiga toxin initially invades and CBC and peripheral smear
destroys colonic epithelial lining, - As ADAMTS13 1evels fall (due to
antibody), vWF multimers accumulate If all other causes of thrombocytopenia
producing bloody diarrhea
on the endothelial wall, trapping excluded, the most appropriate next
Followed by: systemic vascular
platelets at areas of high shearing force step is :
endothelial injury and subsequent
(eg, small arterioles, capillaries) and testing for HIV and hepatitis C virus
platelet microthrombi formation,
leading to the formation of thrombi.
which leads to thrombocytopenia
If test is negative :
and schistocytes as they flow
Bone marrow biopsy
through small vessels.
Presentation
Neurological changes (weird patient / - No splenomegaly or stigmata of
Abdominal pain + bloody diarrhea headache/confusion/Coma/stroke with liver disease
normal CNS examination) + Fever - No fever, palatal petechiae,
cervical lymphadenopathy or
+ triad of : splenomegaly (No EBV infection)
1- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia :
- RBC count
- Haptoglobin / LDH
- Indirect bilirubin
- Mild ALT/ AST No anemia (normal Hb)
Most appropriate next step is :
Peripheral blood smear:
show signs of intravascular hemolysis (eg, schistocytes, triangle cells)
2- Thrombocytopenia :
- Bleeding time Isolated thrombocytopenia
- Normal PT/ PTT (Normal coagulation studies)
3- Acute kidney injury :
Clinically : Laboratory:
- Hematuria - Creatinine No acute kidney injury
- Poor urine output - BUN
- Edema - Proteinuria
Treatment
Treatment is supportive Treatment is emergent (life-threatening) :
- Fluid/electrolyte management Treatment of the underlying infection
1- Plasma exchange
- Blood transfusions can affect the platelet count.
2- Glucocorticoids are often added.
- Dialysis
Differential diagnosis
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia & Thrombocytopenia can also be seen in : Henoch-Schonlein purpura
- DIC Abnormal coagulation studies. lgA-mediated small vessels vasculitis
following URI in children causing :
(While in HUS & TTP Normal coagulation studies) 1. Palpable purpura 2. Arthralgias
3. Abdominal pain 3. Renal disease
Normal: platelet count & coagulation
studies
You might also like
- BOC Study Guide Sixth EditionDocument377 pagesBOC Study Guide Sixth EditionBjörn Daamo88% (25)
- Anemia Pregnancy ACOG 2021.Document10 pagesAnemia Pregnancy ACOG 2021.Laura Daniela Murillo100% (2)
- C. Delay Hanging The Blood and Notify The HCPDocument31 pagesC. Delay Hanging The Blood and Notify The HCPmyNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Bleeding NeonateDocument51 pagesApproach To A Bleeding NeonateJosmy JosephNo ratings yet
- HematoonkologiDocument38 pagesHematoonkologiUnggul YudhaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders - SarahDocument17 pagesBleeding Disorders - SarahkhaledNo ratings yet
- The Specialist: Consultation WithDocument8 pagesThe Specialist: Consultation WithsarabisimonaNo ratings yet
- PATH - Bleeding Disorders (7p)Document7 pagesPATH - Bleeding Disorders (7p)Omar HamwiNo ratings yet
- Bleeding and Coagulation Disorders: DR Nidhi Chaurasia JR-1 MDS PedodonticsDocument66 pagesBleeding and Coagulation Disorders: DR Nidhi Chaurasia JR-1 MDS PedodonticsDrNidhi Krishna100% (1)
- 7.hematology Oncology RDocument48 pages7.hematology Oncology Ranas barakahNo ratings yet
- Pathology Bleeding DisordersDocument67 pagesPathology Bleeding DisordersMarcelliaNo ratings yet
- (2005) AAP Thrombocytopenia in ChildhoddDocument11 pages(2005) AAP Thrombocytopenia in ChildhoddFabiola Vania FeliciaNo ratings yet
- ThrombocytopeniaDocument49 pagesThrombocytopeniaMaria EnjelinaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument35 pagesBleeding Disorderskholoud220100% (3)
- Abnormal Bleeding IN Children: DR Barnabas Atwiine Paediatric Haematologist and Oncologist MustDocument48 pagesAbnormal Bleeding IN Children: DR Barnabas Atwiine Paediatric Haematologist and Oncologist MustSsenyonga DominicNo ratings yet
- Systemic VasculitidesDocument124 pagesSystemic VasculitidesshahikamunaferNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders: Vascular AbnormalitiesDocument21 pagesBleeding Disorders: Vascular AbnormalitiesFirman AmalNo ratings yet
- 3032 Full PDFDocument12 pages3032 Full PDFcinosure1No ratings yet
- PSGNDocument23 pagesPSGNalpha mae beltranNo ratings yet
- Kappler 2017Document23 pagesKappler 2017Alex CroNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis Coaching NotesDocument45 pagesHemostasis Coaching NotesBen SabladaNo ratings yet
- Whydoesmypatienthave Thrombocytopenia?: Ellice Y. Wong,, Michal G. RoseDocument22 pagesWhydoesmypatienthave Thrombocytopenia?: Ellice Y. Wong,, Michal G. RoseLilasNo ratings yet
- Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic PurpuraDocument7 pagesAcute Immune Thrombocytopenic PurpuraMoeses MoesesNo ratings yet
- 3 Hemostasis, Hemorrhagic Diathesis and ThrombosisDocument55 pages3 Hemostasis, Hemorrhagic Diathesis and ThrombosisSuman MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura-NouDocument61 pagesImmune Thrombocytopenic Purpura-NouDM XyzNo ratings yet
- 116 - Disorders of HemostasisDocument13 pages116 - Disorders of HemostasisMuliyamanNo ratings yet
- Thrombocytopenia Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: DR Ahmad Abu Al-Samen MDDocument17 pagesThrombocytopenia Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: DR Ahmad Abu Al-Samen MDmohNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DiseasesDocument2 pagesHematologic Diseasessun shineNo ratings yet
- AV UWorld EOs (Rough Draft) - Data - QID LandscapeDocument139 pagesAV UWorld EOs (Rough Draft) - Data - QID LandscapeFeroz RaZa SoomrOo100% (2)
- Patho - Platelets AtfDocument19 pagesPatho - Platelets AtfGaurav ThapaNo ratings yet
- Disorder of PlateletsDocument27 pagesDisorder of PlateletsRoby KieranNo ratings yet
- Diseases Involving Blood Vessels of The KidneysDocument34 pagesDiseases Involving Blood Vessels of The KidneysAma SatharasingheNo ratings yet
- Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)Document61 pagesMyelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)Tusabe FredNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach of Bleeding Problems in Childhood: Novie Amelia ChozieDocument38 pagesClinical Approach of Bleeding Problems in Childhood: Novie Amelia ChoziebennyrolandnababanNo ratings yet
- Vascular DiseasesDocument9 pagesVascular DiseasesJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Inherited Disorders of Platelet Function,ITP and TTPDocument22 pagesInherited Disorders of Platelet Function,ITP and TTPYazanNo ratings yet
- (Stasi) How To Approach Thrombocytopenia PDFDocument7 pages(Stasi) How To Approach Thrombocytopenia PDFrodtobingNo ratings yet
- Hema Part 3 Final PDFDocument188 pagesHema Part 3 Final PDFH.B.ANo ratings yet
- Trombocytopenia Uniba 16-1-13Document32 pagesTrombocytopenia Uniba 16-1-13Dwiki Surya PrayogaNo ratings yet
- CoagulationDocument113 pagesCoagulationAmirhossein SheikhiNo ratings yet
- How To Approach A Patient With Bleeding?: ISTH Advanced Training Course, Portugal March 2014Document100 pagesHow To Approach A Patient With Bleeding?: ISTH Advanced Training Course, Portugal March 2014ramanNo ratings yet
- HematuriaDocument37 pagesHematuriaعبدالحكيم عمر عامر بن الزوعNo ratings yet
- Hippo EM Board Review - Renal & GU Written SummaryDocument15 pagesHippo EM Board Review - Renal & GU Written Summarykaylawilliam01No ratings yet
- Hanan Fathy Pediatric NephrologyDocument114 pagesHanan Fathy Pediatric NephrologydrhananfathyNo ratings yet
- 25-26 Vascular and Platelet Abnormalities &TMA FinalDocument34 pages25-26 Vascular and Platelet Abnormalities &TMA FinalAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- AML, CML, ALL, CLLDocument35 pagesAML, CML, ALL, CLLsanjibbhunia408No ratings yet
- Case Discussion: Huang Honghui Department of Hematology Ren Ji HospitalDocument29 pagesCase Discussion: Huang Honghui Department of Hematology Ren Ji HospitalronaldsacsNo ratings yet
- Hema Platelet DisordersDocument13 pagesHema Platelet DisordersJennie Grace MaloomNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument4 pagesBleeding DisordersRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- ThrombocytopeniaDocument9 pagesThrombocytopenia8pvz96ktd9No ratings yet
- Banan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiDocument32 pagesBanan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiSarahNo ratings yet
- Seminar 9-ITPDocument22 pagesSeminar 9-ITPanon_67984147No ratings yet
- Perdarahan Oleh Karena Gangguan Vaskular, ITP & Evan SyndromeDocument39 pagesPerdarahan Oleh Karena Gangguan Vaskular, ITP & Evan SyndromeEga FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Immune Thrombocytopenic PurpuraDocument28 pagesImmune Thrombocytopenic PurpuraFaheema Hasan YounusNo ratings yet
- TIPDocument20 pagesTIPpcarvallo18No ratings yet
- Causes of Thromboctyopenia &Document30 pagesCauses of Thromboctyopenia &Rishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Differential Diagnosis of Thrombotic MicroangiopathiesDocument32 pagesPathogenesis and Differential Diagnosis of Thrombotic MicroangiopathiesavgNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis Is The Complex Process of The Formation and Maturation of Blood CellsDocument35 pagesHematopoiesis Is The Complex Process of The Formation and Maturation of Blood CellsYary MayorNo ratings yet
- 2013 GuthMay8 SplenectomyDocument24 pages2013 GuthMay8 SplenectomyKNo ratings yet
- ThrombocytopeniaDocument9 pagesThrombocytopeniaamjad_muslehNo ratings yet
- Presenting Problem in Renal & Urinary Disease:: DysuriaDocument12 pagesPresenting Problem in Renal & Urinary Disease:: DysuriaKabirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Platelet DisorderDocument75 pagesQuantitative Platelet Disorderirishgopez24No ratings yet
- Donating Blood PersuasiveDocument3 pagesDonating Blood Persuasivepk khan100% (1)
- Mrs. V.dhana LakshmiDocument1 pageMrs. V.dhana LakshmiAnonymous lSZ9JVNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDocument12 pagesTransfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDiana Gabriela NinaNo ratings yet
- Blood Loss 2. Increased Destruction 3.impaired Red Cell ProductionDocument4 pagesBlood Loss 2. Increased Destruction 3.impaired Red Cell Productionjehangir zuberiNo ratings yet
- ABO BLOOD GROUP Part 1Document104 pagesABO BLOOD GROUP Part 1Taladua Cayla Grace O.No ratings yet
- A Comparison of Conventional Tube Test and Gel Technique in Evaluation of Direct Antiglobulin TestDocument5 pagesA Comparison of Conventional Tube Test and Gel Technique in Evaluation of Direct Antiglobulin TestYunita RapaNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Traceability and Uncertainty For Myt-3D, Myt-5D and Myt-CALDocument1 pageDeclaration of Traceability and Uncertainty For Myt-3D, Myt-5D and Myt-CALAna-Maria CroitoruNo ratings yet
- Bhutan National Standards BT ServicesDocument98 pagesBhutan National Standards BT ServicesDarla YsavelNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Expt # 3: Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProceduresDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Expt # 3: Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProceduresKriziaNo ratings yet
- 6.1.3 Quality Control of Blood ComponentsDocument4 pages6.1.3 Quality Control of Blood ComponentsBALAJINo ratings yet
- HaematologyDocument260 pagesHaematologydatitox100% (1)
- Capstone Project SlidesDocument24 pagesCapstone Project Slidesapi-545362109No ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2Document7 pagesRed Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2babael.zuher123No ratings yet
- Anemia GravisDocument35 pagesAnemia GravisMufthifina AulahaqNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology: Blood C/E (Complete, CBC)Document2 pagesDepartment of Hematology: Blood C/E (Complete, CBC)Abdul Karim Chaudhry0% (1)
- Editorial: Standardization of APTT Reagents For Heparin Therapy Monitoring: Urgent or Fading Priority?Document3 pagesEditorial: Standardization of APTT Reagents For Heparin Therapy Monitoring: Urgent or Fading Priority?Wiwing SetionoNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Practice Guidelines For Clinic and Laboratory PersonnelDocument98 pagesTransfusion Practice Guidelines For Clinic and Laboratory PersonnelZhayreal Zaki100% (1)
- Abo Blood Group System GeneticsDocument17 pagesAbo Blood Group System GeneticsSYED MUHAMMAD ALI100% (1)
- Virtual Blood Typing LabDocument1 pageVirtual Blood Typing Labapi-522349089No ratings yet
- Immunohematology and Blood BankingDocument9 pagesImmunohematology and Blood BankingMark Daniel LerioNo ratings yet
- Asbmt: Clinical Guide To ABO-Incompatible Allogeneic Stem Cell TransplantationDocument7 pagesAsbmt: Clinical Guide To ABO-Incompatible Allogeneic Stem Cell TransplantationMohana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Case Studies - MIC3002Document28 pagesCase Studies - MIC300217206404 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Electronic CrossmatchDocument4 pagesElectronic CrossmatchMano cempakaNo ratings yet
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences Jodhpur College of Nursing Practice TeachingDocument11 pagesAll India Institute of Medical Sciences Jodhpur College of Nursing Practice Teachingmaneesh senNo ratings yet
- Utoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: Reported By: Kathleen Chris G. Lapac MLS 3-ADocument11 pagesUtoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: Reported By: Kathleen Chris G. Lapac MLS 3-AABHINABA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Patient RBC PhenotypingDocument25 pagesPatient RBC PhenotypingKe XuNo ratings yet