Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Note PDF
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Note PDF
Uploaded by
TharaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Note PDF
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Note PDF
Uploaded by
TharaniCopyright:
Available Formats
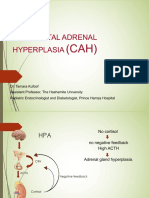
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Autosomal recessive defects in enzymes that are responsible for the production of cortisol Low levels of cortisol → lack of negative
feedback to the pituitary → ↑ ACTH → adrenal hyperplasia and increased synthesis of adrenal precursor steroids
21β-hydroxylase 11β-hydroxylase 17α-hydroxylase
95% of CAH 5% of CAH Rare
It converts : It converts : It converts :
Progesterone to 11-deoxycorticosterone to 17-hydroxyprogesterone to
Biochemistry 11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC) Corticosterone Androstenedione
17-hydroxyprogesterone to 11-deoxycortisol to
11-deoxycortisol Cortisol
Cortisol Decreased Decreased
Decreased
Aldosterone Decreased Although an increase in aldosterone would be expected in 17α-hydroxylase deficiency, ↑
DOC (which has aldosterone-like activity) inhibits renin and aldosterone production.
11- DOC Decreased Increased
Increased Decreased
Androgens
Female & male precocious puberty Female (1ry amenorrhea ) &
male Delayed puberty
Male Normal external genitalia at birth female external genitalia with
intraabdominal testes at birth
Female Male external genitalia along with a uterus and ovaries Normal external genitalia
Virilization, irregular menstrual cycles, infertility
Hypotension Hypertension
Blood pressure Because of salt-wasting associated It occurs despite hypoaldosteronism because DOC
with hypoaldosteronism possesses mineralocorticoid (aldosterone-like) activity.
and hypocortisolism
↑↑ 17-hydroxyprogesterone ↑ 17-hydroxyprogesterone ↓ 17-hydroxyprogesterone
Diagnostics ↓ DOC ↑↑ DOC ↑ DOC
↓ corticosterone ↓ corticosterone ↑↑ corticosterone
Additional laboratory Due to Hypoaldosteronism: Although aldosterone levels are Due to aldosterone-like activity
findings Hyponatremia decreased, DOC has some level of DOC :
All newborns in the US are Hyperkalemia, of mineralocorticoid activity Hypernatremia
screened for CAH by
Metabolic acidosis Electrolytes and pH are normal Hypokalemia
measuring :
17 hydroxyprogesterone Metabolic alkalosis
1) Lifelong glucocorticoid replacement therapy
Hydrocortisone in neonates and children
Prednisolone or dexamethasone in adolescents and adults
Treatment +
2) fludrocortisone therapy 2) Spironolactone to block mineralocorticoid receptors
3) Reduce dietary sodium intake
Types of 21B-CAH Classic form Non-Classic CAH
Severity Severe Mild
Onset of symptoms Early onset (during neonatal period or early infancy) Late onset (presents during late childhood/adulthood)
A) Salt-wasting type : Normal external genitalia at birth in
∼ 67% of all classic forms both genotypes
Clinical manifestations Males present 7–14 days after birth with failure Precocious puberty
to thrive, dehydration, vomiting, and shock Acne
Females present with ambiguous genitalia Infertility
B) Non-salt-wasting type (simple virilizing) : Females may also have irregular menstrual
∼ 33% of all classic forms cycles
No signs of shock
Males present with precocious puberty at 2–4 y
Females present with ambiguous genitalia
You might also like
- AtlasDocument56 pagesAtlasKolea HanganuNo ratings yet
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicDocument2 pagesHashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicPetraNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sex DevelopmentDocument5 pagesDisorders of Sex DevelopmentAnastasia KasapiNo ratings yet
- Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument11 pagesAmbiguous GenitaliadragondostNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adreal Hyperplasia and Testicular Feminization SyndromesDocument23 pagesCongenital Adreal Hyperplasia and Testicular Feminization SyndromesJunbek nov23No ratings yet
- White 2002Document16 pagesWhite 2002Esteban Martin Chiotti KaneshimaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal DisordersDocument56 pagesAdrenal DisordersKlyn Agagon GayodanNo ratings yet
- MT Laws Reviewer MidtermsDocument6 pagesMT Laws Reviewer MidtermsKyaru Fuentes100% (1)
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Definition and EtiologyDocument33 pagesCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Definition and Etiologylotp12No ratings yet
- Adrenogenital: Pregnancy and The SyndromeDocument4 pagesAdrenogenital: Pregnancy and The SyndromeEmi RahmanNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Presented By: Ahmad Fazwan JunaidiDocument16 pagesCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Presented By: Ahmad Fazwan JunaidiZakirNo ratings yet
- 17-Mrdi DLP-1Document114 pages17-Mrdi DLP-1Jawad Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- EhDocument3 pagesEhYusril MarhaenNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument46 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaSarahNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Health Outcomes in Adults With Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument47 pagesTreatment and Health Outcomes in Adults With Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaFadhilla FatmaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia:: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and ManagementDocument11 pagesCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia:: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Managementsabachannel456No ratings yet
- Peripheral Precocious Puberty Including Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Causes, Consequences, Management and OutcomesDocument15 pagesPeripheral Precocious Puberty Including Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Causes, Consequences, Management and OutcomesAbdurrahman HasanuddinNo ratings yet
- Adrenogenital Syndrome: Physical FindingsDocument2 pagesAdrenogenital Syndrome: Physical FindingschoobiNo ratings yet
- DSD Harjoedi Pedendo 19Document42 pagesDSD Harjoedi Pedendo 19bolabundarNo ratings yet
- Slides Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument43 pagesSlides Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaAsunción AncoNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex HormoneDocument22 pagesAdrenal Cortex HormoneYudistiraJefriRamadhanNo ratings yet
- 09-28-15 CAH Grand RoundsDocument55 pages09-28-15 CAH Grand Roundsnila sari batubaraNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument17 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaInani Nabila LahuriNo ratings yet
- First Aid For The OBS&GYN Clerkship CH 17 (Amenorrhea)Document9 pagesFirst Aid For The OBS&GYN Clerkship CH 17 (Amenorrhea)黃芳昌No ratings yet
- Casos EndocrinoDocument72 pagesCasos EndocrinoAlfredo JaureguiNo ratings yet
- MK CahDocument46 pagesMK CahMartini ListrikNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)Document17 pagesCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)Rastu MaharthaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument42 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasianeysaonlineNo ratings yet
- B. 10 Situation - Care of Client With Problems in Metabolism & Endocrine Functioning.Document7 pagesB. 10 Situation - Care of Client With Problems in Metabolism & Endocrine Functioning.SOLEIL LOUISE LACSON MARBAS100% (1)
- Nbs-Pedia Miterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesNbs-Pedia Miterms ReviewerChristian112233No ratings yet
- PPS Case 6Document2 pagesPPS Case 6Catrina FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCM107 ObstetricsDocument9 pagesNCM107 ObstetricsKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Pedia-Adrenal Gland DisordersDocument5 pagesPedia-Adrenal Gland DisordersEmerson QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Role of Lab in Diagnosing Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Ola H. ElgaddarDocument24 pagesRole of Lab in Diagnosing Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Ola H. ElgaddarOla ElgaddarNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument30 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaanrihmNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics UpdateDocument3 pagesPediatrics UpdateskNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia FT 2020Document49 pagesHypokalemia FT 2020ebkai98No ratings yet
- Endocrine NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine Notesrshannen19No ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument27 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaJunbek nov23No ratings yet
- April 6 Quiz Medical DR - Rajesh GubbaDocument141 pagesApril 6 Quiz Medical DR - Rajesh GubbaPraveenRajMNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument64 pagesObstetrics and GynecologyLyk TiglaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36 - Adrenocortical AgentsDocument3 pagesChapter 36 - Adrenocortical Agentskdayeon018No ratings yet
- IntersexnnDocument66 pagesIntersexnnSyahputraWibowoNo ratings yet
- Newborn Screening: Mental Retardation or Death If Left Congenital HypothyroidismDocument6 pagesNewborn Screening: Mental Retardation or Death If Left Congenital HypothyroidismMimie CaliNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesThe Endocrine SystemtumisobeNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Ilaban Mo Yan!!!!!! Lord, Help MeDocument17 pagesPart 2 Ilaban Mo Yan!!!!!! Lord, Help MeJoezer Gumangan VeranoNo ratings yet
- CAH-ABUAD NigeriaDocument47 pagesCAH-ABUAD NigeriaIghodaro IsokenNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument17 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaJeff CrocombeNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) : E25 Adrenogenital DisordersDocument6 pagesCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) : E25 Adrenogenital DisordersUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- FCK It Mahaba Vacant Kaya Gumawa NG Pharma Samplex-RatioDocument3 pagesFCK It Mahaba Vacant Kaya Gumawa NG Pharma Samplex-RatiofmlpletaNo ratings yet
- Week 14 Endocrine Disorders in PediatricsDocument6 pagesWeek 14 Endocrine Disorders in PediatricsWynahNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Adreno Genital SyndromeDocument29 pagesEndocrinology Adreno Genital SyndromeDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-04-26 at 12.52.44 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-04-26 at 12.52.44 PMRenadNo ratings yet
- General Biology Lesson 13Document13 pagesGeneral Biology Lesson 13GUCOR, LOVELY SHANE C.No ratings yet
- Endocrine New EditionDocument150 pagesEndocrine New Editiondigracia manatigaNo ratings yet
- Bachega 2012Document10 pagesBachega 2012Josue BarralNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho ReviseDocument10 pagesPa Tho ReviseCharl SembranoNo ratings yet
- CAH F1359 A4 BW FINAL Oct18Document3 pagesCAH F1359 A4 BW FINAL Oct18telefontest118No ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument4 pagesEndocrineMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- 1310 HaiderAdrenal Disorders Peds Board 2013Document21 pages1310 HaiderAdrenal Disorders Peds Board 2013Brandon LewisNo ratings yet
- Safety of Medications and Hormones UsedDocument12 pagesSafety of Medications and Hormones UsedandreNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Graves' Disease & PregnancyDocument19 pagesGraves' Disease & Pregnancyrajan kumar100% (1)
- Thyroid Function TestDocument21 pagesThyroid Function TestPat JacintoNo ratings yet
- Hematology: H. NO. 1-9-645, Vidyanagar, Adikmet Road, Near SBH, Hyderabad-500 044Document3 pagesHematology: H. NO. 1-9-645, Vidyanagar, Adikmet Road, Near SBH, Hyderabad-500 044Yours PharmacyNo ratings yet
- DynaMed Plus - Endocrine Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast CancerDocument50 pagesDynaMed Plus - Endocrine Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast CancerGamer MadaNo ratings yet
- TSH Conversion PDFDocument1 pageTSH Conversion PDFMarianNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evidence Lantus XR PDFDocument85 pagesClinical Evidence Lantus XR PDFPeter HoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) - TSH Levels TestDocument3 pagesThyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) - TSH Levels TestSANDHYASINI NAYAKNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Versi InggDocument18 pagesJurnal Versi InggAtika NajlaNo ratings yet
- TSWileyBio LongDocument2 pagesTSWileyBio LongWileyProtocolNo ratings yet
- Clinical Characterization of Patients WithDocument4 pagesClinical Characterization of Patients WithPaulo Eduardo CampanaNo ratings yet
- GDMDocument12 pagesGDMJennicaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Exam 3Document12 pagesEndocrine Exam 3Wynne EnglatieraNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument2 pagesReportAnkita GoyalNo ratings yet
- Sheehan Syndrome Sarina SchragerDocument3 pagesSheehan Syndrome Sarina Schragerfreddyop72No ratings yet
- (Template) Lab Report TemplateDocument16 pages(Template) Lab Report TemplateArunima 620006No ratings yet
- Oral Contraceptives PresentationDocument19 pagesOral Contraceptives PresentationJoshua DayeNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Is An Extreme Metabolic Hyperosmotiic Hyperglycemic State Is A LifeDocument2 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Is An Extreme Metabolic Hyperosmotiic Hyperglycemic State Is A LifeLyod BalagasayNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Pituitary HormonesDocument54 pagesPharmacology of Pituitary HormonesAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- CC2 Lab 13Document10 pagesCC2 Lab 13Junea SeeNo ratings yet
- Revalence of Thyroid Disorders in A Tertiary Care CenterDocument5 pagesRevalence of Thyroid Disorders in A Tertiary Care CenterAvisa Cetta CresmaNo ratings yet
- Total+Allowable+Error+Limits+Table+Example Rev20120725Document4 pagesTotal+Allowable+Error+Limits+Table+Example Rev20120725Meidina Siti HanifahNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning Project FinalDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning Project Finalapi-378401973No ratings yet
- Child With EndocrineDocument4 pagesChild With EndocrineSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Addison Disease (Adrenal Cortex)Document3 pagesAddison Disease (Adrenal Cortex)Edward XiamNo ratings yet
- Di and SiadhDocument15 pagesDi and SiadhSandra Martini SimmonsNo ratings yet
- AdrenalDocument9 pagesAdrenalNada MuchNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Management SystemDocument3 pagesDiabetes Management Systembeth2042No ratings yet
- Endocrine LabDocument15 pagesEndocrine Labapi-217439283No ratings yet