Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems On Mathematical Model
Problems On Mathematical Model
Uploaded by
Roshini FelixOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems On Mathematical Model
Problems On Mathematical Model
Uploaded by
Roshini FelixCopyright:
Available Formats
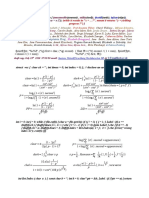
6. On average one call arrives every 5 seconds.
During a period of 10 seconds, what is the probability that:
1. No call arrives?
2. One call arrives?
3. Two call arrives?
4. More than two calls arrive?
μ = 10/5 =2
Where μ = 2
x
μ
P ( x )= e− μ
x!
0
2
P ( 0 )= e−2
0! 1. P (0) = 0.135
1
2 −2 2. P (1) = 0.270
P (1 ) = e
1!
22 −2 3. P(2)= 0.270
P (2 )= e
2!
4. P( >2) =1- P(0) - P(1) - P(2)
= 1- 0.135 - 0.270 - 0.270
= 0.325
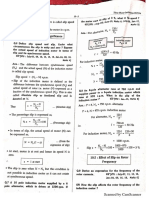
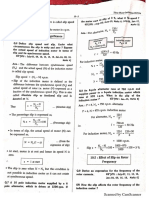
7.In a telephone system the average call duration is 2 minutes. A call has already lasted 4 minutes. What is the
probability that:
1. The call will last at least another 4 minutes?
2. The call will end within the next 4 minutes?
The probability is independent of the time which as already elapsed
−4/2
P (T ≥ t) = e−t / h = 𝑒 = 0.135
The call will end within the next 4 minutes
P (T ≤ t) = 1− P (T ≥ t) = 1− 0.135 = 0.865
You might also like
- A1 Solu 3490w19 4Document6 pagesA1 Solu 3490w19 4Patricia CortezziNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 24thfeb Morning ShiftDocument14 pagesMathematics 24thfeb Morning ShiftLalu kuttyNo ratings yet
- التحليل المركب د. باسم فراسينDocument139 pagesالتحليل المركب د. باسم فراسينmhmdsaedhudieb2004No ratings yet
- Permutations and Combinations: MathematicsDocument9 pagesPermutations and Combinations: MathematicsGURUMARUTHI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier TransformDocument10 pagesFast Fourier TransformAnonymous sDiOXHwPPjNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier TransformDocument10 pagesFast Fourier TransformAnonymous sDiOXHwPPjNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier TransformDocument10 pagesFast Fourier TransformAnonymous sDiOXHwPPjNo ratings yet
- P (X=r) = µ = E (x) = λ σ² = var (x) = λ: λ = on average receive 3 calls in an hour λ = average 4 accidents in 3 daysDocument6 pagesP (X=r) = µ = E (x) = λ σ² = var (x) = λ: λ = on average receive 3 calls in an hour λ = average 4 accidents in 3 daysHui YingNo ratings yet
- PR Obl Em2. 1:: Homework-2Document15 pagesPR Obl Em2. 1:: Homework-2Red BxNo ratings yet
- MATH2222 Homework 3Document9 pagesMATH2222 Homework 3Isaac LeongNo ratings yet
- EE-202 Exam I February 6, 2008: NameDocument10 pagesEE-202 Exam I February 6, 2008: NameBoilerhelproomNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan G10 Day 4 PROOF BY MATHEMATICAL INDUCTIONDocument4 pagesLesson Plan G10 Day 4 PROOF BY MATHEMATICAL INDUCTIONGINA LIZA CANAMANo ratings yet
- Math4575 HW Chapter7Document6 pagesMath4575 HW Chapter7李王仁No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Anonymous j817fgpimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document30 pagesLecture 12PradiptoNo ratings yet
- Solution CS161 Spring 12 Homework 8Document4 pagesSolution CS161 Spring 12 Homework 8Anikien AdinaNo ratings yet
- Jeemains Entranceexam 2019 (8thapril Morning) SolutionsDocument21 pagesJeemains Entranceexam 2019 (8thapril Morning) SolutionsTanish KumarNo ratings yet
- td3 Analyse1 Info CorrectionDocument18 pagestd3 Analyse1 Info CorrectionImy MezNo ratings yet
- Full Test 2 PDFDocument36 pagesFull Test 2 PDFanup vermaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document4 pagesExercise 1Khalil El LejriNo ratings yet
- P P P P P: Mathematical InductionDocument6 pagesP P P P P: Mathematical InductionTakaNo ratings yet
- Markov Chains - Processos EstocásticosDocument24 pagesMarkov Chains - Processos EstocásticosSarahNo ratings yet
- Properties of The Exponential DistributionDocument13 pagesProperties of The Exponential DistributionClaudio Amaury C. JiménezNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyDocument6 pagesMassachusetts Institute of TechnologykurozoulNo ratings yet
- Fourier AnalysisDocument28 pagesFourier AnalysisSourav Chandra DasNo ratings yet
- University of Toronto ECE-345: Algorithms and Data Structures Solutions To Midterm Examination (Fall 2013)Document2 pagesUniversity of Toronto ECE-345: Algorithms and Data Structures Solutions To Midterm Examination (Fall 2013)Haotian YinNo ratings yet
- Qweqwe 123123Document8 pagesQweqwe 123123Chng Yong XienNo ratings yet
- IOE516 - Stochastic Processes II Homework Set 2 - Suggested SolutionsDocument6 pagesIOE516 - Stochastic Processes II Homework Set 2 - Suggested SolutionsAloke ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- IOQM Paper With Solution Part BDocument5 pagesIOQM Paper With Solution Part BManya ShahNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: Induction and RecursionDocument23 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: Induction and RecursionAdilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4mhafifi 2011No ratings yet
- 4211618chapter - 31 Probability DistributionDocument40 pages4211618chapter - 31 Probability DistributionK SantoshNo ratings yet
- Prob-Four Couples SittingDocument2 pagesProb-Four Couples Sittingxaviour111No ratings yet
- mth202 Lecture21-RecursionDocument10 pagesmth202 Lecture21-Recursioncontact.webwrapperNo ratings yet
- On The Periodic Continued Radicals of 2 and Generalization For Vieta's ProductDocument19 pagesOn The Periodic Continued Radicals of 2 and Generalization For Vieta's Productmarius mirceaNo ratings yet
- 2024 ORTI Term - 2 Maths AssignmentDocument6 pages2024 ORTI Term - 2 Maths AssignmentanakoluziphoNo ratings yet
- Recursion LectureDocument16 pagesRecursion Lecturemhmdmfsr07No ratings yet
- CS1020: D S A I: 1. Big-O ComplexityDocument7 pagesCS1020: D S A I: 1. Big-O ComplexityAnish SonytvNo ratings yet
- QF204 Additional Examples Week 10: Random Walk: 1 QuestionsDocument3 pagesQF204 Additional Examples Week 10: Random Walk: 1 QuestionsKhoaNamNguyenNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3 SolutionDocument5 pagesAssignment #3 SolutionAdil AliNo ratings yet
- Fall 2010 Final SolutionDocument11 pagesFall 2010 Final SolutionAndrew ZellerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Recursion, Recurrence Relations, and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument23 pagesChapter 3: Recursion, Recurrence Relations, and Analysis of AlgorithmsCLNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Section 2.2 On Today Test #1 On Chapters 1 (1.1-1.3,1.5-1.6), 2 (2.1-2.2, 2.4) On 2/13 WednesdayDocument4 pagesQuiz On Section 2.2 On Today Test #1 On Chapters 1 (1.1-1.3,1.5-1.6), 2 (2.1-2.2, 2.4) On 2/13 Wednesdaygoflux pwnsNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics, University of Zagreb, 41000 Zagreb, CROATIADocument14 pagesDepartment of Mathematics, University of Zagreb, 41000 Zagreb, CROATIAKornelija MikšaNo ratings yet
- Disc Week 10Document15 pagesDisc Week 10Syed Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 SolutionsDocument9 pagesHomework 5 SolutionsAE ENo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument7 pagesDiscrete Mathematicslucas97jensenNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Order 4 Sequences: Faculty Research FairDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Order 4 Sequences: Faculty Research FairJulius Fergy RabagoNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci Numbers and Binet Formula: (An Introduction To Number Theory)Document27 pagesFibonacci Numbers and Binet Formula: (An Introduction To Number Theory)StarryGailSanchezNo ratings yet
- (Event) (Time N.T) : Stephanie FongDocument76 pages(Event) (Time N.T) : Stephanie FongssfofoNo ratings yet
- Aaoa-2 1 PDFDocument25 pagesAaoa-2 1 PDFMadeehah AatifNo ratings yet
- Mathematical InductionDocument13 pagesMathematical InductionBretana joanNo ratings yet
- IEOR 4106: Spring 2011 Solutions To Homework Assignment 7: Due On Tuesday, March 22Document5 pagesIEOR 4106: Spring 2011 Solutions To Homework Assignment 7: Due On Tuesday, March 22amyNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Lecture 2Document6 pagesCommunication Systems Lecture 2Mousa AltheleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 CountingDocument35 pagesChapter 5 Countingmtdeptrai430No ratings yet
- Direct Proofs: Proofs by Contradiction and by Mathematical InductionDocument11 pagesDirect Proofs: Proofs by Contradiction and by Mathematical InductionRouka Rouda ElAwadyNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Lesson 2Document2 pagesDiscrete Math Lesson 2Vinci Van MontielNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar MassesDocument7 pagesColligative Properties and Determination of Molar MassesRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- 15EC11T-BEEE-LESSON PLANNING FOR I Sem 2016-17Document7 pages15EC11T-BEEE-LESSON PLANNING FOR I Sem 2016-17Roshini FelixNo ratings yet
- 179 Swapna Shree ChemistryDocument6 pages179 Swapna Shree ChemistryRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Course PlainDocument7 pagesEmbedded System Course PlainRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- Course Plan: Government of KarnatakaDocument8 pagesCourse Plan: Government of KarnatakaRoshini Felix100% (1)
- Consumer Behaviour Module - 6 Ms. Archana VijayDocument2 pagesConsumer Behaviour Module - 6 Ms. Archana VijayRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- 15ec46p-Mc Lab-Course PlanDocument6 pages15ec46p-Mc Lab-Course PlanRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- Digital Switching System 10EC82 PDFDocument7 pagesDigital Switching System 10EC82 PDFRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- Sub WT Values For Different CasesDocument3 pagesSub WT Values For Different CasesRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Roshini FelixNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2020-04-28 08.27.45Document2 pagesNew Doc 2020-04-28 08.27.45Roshini FelixNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument1 pageEquationsRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- Scanned by CamscannerDocument2 pagesScanned by CamscannerRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- E AE N + Ae A) : 1. From Erlang Lost Call FormulaDocument2 pagesE AE N + Ae A) : 1. From Erlang Lost Call FormulaRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generators ProblemsDocument2 pagesSynchronous Generators ProblemsRoshini FelixNo ratings yet
- Module3-Telecommunications Traffic: IntroductionDocument26 pagesModule3-Telecommunications Traffic: IntroductionRoshini FelixNo ratings yet