Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macro Reviewer Chapter 3
Macro Reviewer Chapter 3
Uploaded by
peachOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Macro Reviewer Chapter 3
Macro Reviewer Chapter 3
Uploaded by
peachCopyright:
Available Formats
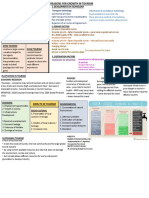
CHAPTER 3 ARTS, SCIENCES, TECHNOLOGY,
MEDICINE, CULTURE, MUSIC AND EVEN
THE TOURISM SYSTEM
POLITICS
BASIC APPROACHES TO THE STUDY OF
7. Systems Approach
TOURISM
-BRING TOGETHER DIFFERENT
1. Institutional Approach
COMPONENTS OR PARTS THAT ARE
-BUSINESS SIDE OF TOURISM. SOMEHOW LINKED TO EACH OTHER BY
INSTITUTIONS THAT OPERATE UNDER COMMON PRINCIPLE/GROUP. IT
THE TOURISM INDUSTRY SUCH AS SIMPLIFIES COMPLEX IDEAS AND
TRAVEL AGENCIES, HOTELS, AIRLINES PRESENT THEM IN AN
ETC. RISK FACTORS AND OPERATIONAL ORGANIZED/SYNTHESIZED MANNER
METHODS
8. Geographical or Demographic Approach
2. Historical Approach
-ENVIRONMENT AND THE
-DEVELOPMENTAL MANNER. OBSERVES CHARACTERISTICS OF PEOPLE. RURAL
THE INDUSTRY AS IT STARTS AND OR URBAN SETTING, MOUNTAINOUS
EVEOLVES THROUGH TIME OR COASTAL, DEVELOPING, HIGLY
DEVELOPED OR UNDERDEVELOPED.
3. Managerial Approach EDUCATIONAL ATTAINMENT, AGE
-MANAGEMENT ACTIVITIES LIKE GROUP, POPULATION SIZE
PLANNING, RESEARCH, ADVERTISING, 9. Product Approach
PRICING, CONTROL AND OTHER
OPERATIONS -PRODUCT OF TOURISM, COMPONENTS
AND COMPATIBILITY TO TOURISTS
4. Economic Approach PREFEFENCES. COMPONENTS INCLUDES
-CONTRIBUTION OF TOURISM TO THE THE 5 A’s
NATIONAL ECONOMY IS MEASURED
AND MONITORED. ECONOMIC
DEVELOPMENT AND FINANCES
5. Sociological Approach
-HOST-GUEST INTERACTIONS.
BEHAVIOUR OF TOURISTS, COMMUNITY
THAT RECEIVES THE TOURISTS AND
EFFECTS OF VISITORS TO COMMUNITY.
IMPACT OF TOURISM TO THE
COMMUNITY BASED ON BEHAVIOUR,
HABITS, TRADITIONS AND CUSTOMS
6. Interdisciplinary Approach
-FUSION OF DIFFERENT FIELDS THAT
CROSS AND BROUGHT TOGETHER IN
ORDER TO BRING ABOUT TOURISM.
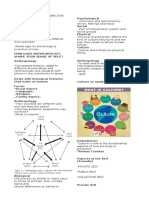
LEIPER’S MODEL: THE TOURISM MODEL Discomfort reliability
Attractions
Stopover points
Security
Tourist Destination Regions (TDRs)
Features and Conditions
Attractions
Accessibility
Tolerance
Security
Life-support and comfort systems
Explanation: Cost and benefit advantage
TGRs are the places where trips begin, where Information diffusion
people who will later be described or counted
GOELDNER & RITCHIE’S FRAMEWORK ON THE
as tourists start their journey.
TOURISM SYSTEM
TR This is an intermediate zone where the
-A complex diagram that detailed the different
principal travel activity of tourism occurs,
components and the relationships of the
distinct from visit activity in destinations.
tourism phenomenon
An efficient TR is a path where access is easy
Components of Tourism Phenomenon
for large numbers of travelers.
Tourists
TDR A person chooses to stay a while in order
to experience some feature or characteristic. Natural resources and environment
Transit Routes (TR) Built environment
Factors affecting tourism as per Leiper: Operating sectors
Travel Time Public and private sector
Fares and other travel costs Catalyst, planning, development,
promotion and management
Availability of a carrier and other transport
organizations
facilities
Capacity
Frequency of services on public carriers
Changes in transit
You might also like
- 116791-Chapter 2 - Preliminary Site AssessmentDocument11 pages116791-Chapter 2 - Preliminary Site AssessmentVENA LANDERO100% (1)
- Leipersmodeloftourismsystem PDFDocument11 pagesLeipersmodeloftourismsystem PDFAjay MatiedaNo ratings yet
- L5 Tourism EconomicsDocument93 pagesL5 Tourism EconomicsPaul BallesteroNo ratings yet
- The Tourism and Hospitality Network and Supply Components: Category IDocument8 pagesThe Tourism and Hospitality Network and Supply Components: Category Isuby100% (5)
- Project An Monitoring Tool 1Document3 pagesProject An Monitoring Tool 1Rames Ely GJ100% (2)
- List of Pestel Characteristics: PoliticalDocument8 pagesList of Pestel Characteristics: PoliticalFiz Arman100% (1)
- Weavetech Case (HR)Document5 pagesWeavetech Case (HR)K.Akshay Pai0% (3)
- Unit 1 Lesson 3Document12 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 3Bj Apostol QuejaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Tourism PlanningDocument4 pagesBarriers To Tourism PlanningApril GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tourism PlanningDocument14 pagesTourism PlanningFROYLAND TIPACTIPACNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Macro7Document7 pagesReviewer Macro7Glen joseph SerranoNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Hyplex Module Micro Perspective of Tourism and HospitalityDocument14 pagesPrelim - Hyplex Module Micro Perspective of Tourism and HospitalityMarj BinondoNo ratings yet
- Guest". Comes From The Word "Hospice", An Old FrenchDocument20 pagesGuest". Comes From The Word "Hospice", An Old FrenchAudrey RNo ratings yet
- Guest". Comes From The Word "Hospice", An Old FrenchDocument19 pagesGuest". Comes From The Word "Hospice", An Old FrenchAudrey RNo ratings yet
- 1-Basic Concepts in Tourism Planning and DevelopmentDocument40 pages1-Basic Concepts in Tourism Planning and DevelopmentAngelhee A PlacidoNo ratings yet
- Tourism Unit1Document84 pagesTourism Unit1Rewatraj PokhrelNo ratings yet
- MTTM Complete SyllabusDocument29 pagesMTTM Complete SyllabusSumit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document17 pagesUnit 7Mahak ShivhareNo ratings yet
- Sustainable MidtermDocument6 pagesSustainable MidtermJulienne DumaelNo ratings yet
- SustainabilityDocument7 pagesSustainabilityadrian espanoNo ratings yet
- Macro-Perspective in Tourism and Hospitality Module 3Document22 pagesMacro-Perspective in Tourism and Hospitality Module 3Benjo Manzano QuidulitNo ratings yet
- The Tourism Industry: 7.1 Tour OperatorsDocument25 pagesThe Tourism Industry: 7.1 Tour OperatorsProGaming pgNo ratings yet
- Technology, Innovation, Sustainability, and Governance of Recreation and Other Sectors of The Tourism IndustryDocument8 pagesTechnology, Innovation, Sustainability, and Governance of Recreation and Other Sectors of The Tourism IndustryAnne VarquezNo ratings yet
- 12.tourism Notes 1Document216 pages12.tourism Notes 1Karan PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Baggio-Tour AnalDocument20 pagesBaggio-Tour Analelgriniyassine3No ratings yet
- The Traveling Public and Tourism Promoters: ChaptersDocument34 pagesThe Traveling Public and Tourism Promoters: Chaptersnazim aliNo ratings yet
- Tourism Industry - Structure and ComponentsDocument21 pagesTourism Industry - Structure and ComponentsJohanna “Han Na” AcibronNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Tourism To Hospitality: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document9 pagesThe Relationship of Tourism To Hospitality: Study Guide For Module No. 3Marlyn MabalotNo ratings yet
- MTTM 101Document241 pagesMTTM 101Titem Ashenafi BertaNo ratings yet
- THC 212 T2 C.R.1Document1 pageTHC 212 T2 C.R.1Erica Lenn VillagraciaNo ratings yet
- Attributes That Influence Resort Attractiveness: A Case Study of Selected Kimberley ResortsDocument21 pagesAttributes That Influence Resort Attractiveness: A Case Study of Selected Kimberley ResortsGihrene EspadaNo ratings yet
- Destination ManagementDocument10 pagesDestination ManagementDana AlsarawaniNo ratings yet
- Tourism Planning: Micro Perspective of Tourism and HospitalityDocument33 pagesTourism Planning: Micro Perspective of Tourism and HospitalityMalou NuevoNo ratings yet
- Destination Planning Concepts: Kavya Vinay I 08 I M2 I GectDocument10 pagesDestination Planning Concepts: Kavya Vinay I 08 I M2 I Gectkavya vinayNo ratings yet
- Commercial Air Travel Safer Transport & Shorter Travelling Time Rise of Budget Airlines Expansion of Air Routes and AgreementsDocument2 pagesCommercial Air Travel Safer Transport & Shorter Travelling Time Rise of Budget Airlines Expansion of Air Routes and AgreementsLIM JUN YOU RVHS STU 2018No ratings yet
- Commercial Air Travel Safer Transport & Shorter Travelling Time Rise of Budget Airlines Expansion of Air Routes and AgreementsDocument2 pagesCommercial Air Travel Safer Transport & Shorter Travelling Time Rise of Budget Airlines Expansion of Air Routes and AgreementsLIM JUN YOU RVHS STU 2018No ratings yet
- Micro and Macro EnvironmentsDocument8 pagesMicro and Macro EnvironmentsShumon Hamid100% (1)
- Managing Visitor Impact: Sustainable Tourism & Hospitality Assessment & DevelopmentDocument15 pagesManaging Visitor Impact: Sustainable Tourism & Hospitality Assessment & DevelopmentJUN GERONANo ratings yet
- Economic Impacts Carrying CapacityDocument8 pagesEconomic Impacts Carrying CapacityAnvesh VakadiNo ratings yet
- Tourism Network SystemDocument15 pagesTourism Network SystemFrance Marie Aberin Raguini-Tacadena100% (2)
- CONCEPT of SUSTAINABLE TOURISMDocument22 pagesCONCEPT of SUSTAINABLE TOURISManamejico. clarcNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document16 pagesUnit 6Cathy MNo ratings yet
- Scope and Sectors of The Tourism IndustryDocument5 pagesScope and Sectors of The Tourism IndustryCazandra Natalie JuanitezNo ratings yet
- Elements of TourismDocument3 pagesElements of TourismGhazala ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Tour PolicyDocument4 pagesReviewer Tour PolicyRuth AguilarNo ratings yet
- Tourism Network and Supply Components: The TravelerDocument9 pagesTourism Network and Supply Components: The TravelerAngela MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Tourism Transport'S Development in Economic GrowthDocument10 pagesThe Role of Tourism Transport'S Development in Economic Growthfarxod mamatovNo ratings yet
- Source of Tourism Product InformationDocument13 pagesSource of Tourism Product InformationRudailyn SolivaNo ratings yet
- Managing Visitor ImpactsDocument31 pagesManaging Visitor ImpactsNini Montefalco100% (1)
- Sihtm Destination MGT PresentationDocument10 pagesSihtm Destination MGT PresentationErica CostaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Tourism ReviewerDocument3 pagesSustainable Tourism ReviewerRechelle VillartaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Tourism Infrastructure Planning: A Gis Based ApproachDocument11 pagesSustainable Tourism Infrastructure Planning: A Gis Based ApproachCarlos PuigdomenechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tourism and Hospitality Network and Supply ComponentsDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Tourism and Hospitality Network and Supply ComponentsApril AlbayNo ratings yet
- Tpad ReviewerDocument12 pagesTpad ReviewerCarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Tourism and Information TechnologyDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Tourism and Information TechnologyAdonna Mari D. MATUTINONo ratings yet
- Dta10143 - Topic 4Document19 pagesDta10143 - Topic 4cotek cunNo ratings yet
- Landscape Planning For Tourism in Natural Areas - Case of CourtallamDocument51 pagesLandscape Planning For Tourism in Natural Areas - Case of CourtallamLekshmi ShunnmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document14 pagesUnit 8Tourism and Hospitality ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Impactsof Tourism Industryon Host CommunityDocument11 pagesThe Impactsof Tourism Industryon Host Communitynasywa candrikaNo ratings yet
- Tour Guiding and Escorting ModuleDocument106 pagesTour Guiding and Escorting ModuleMikhaelaNo ratings yet
- Definition, Dimensions Determinants of Tourism Impacts: Learning OutcomeDocument17 pagesDefinition, Dimensions Determinants of Tourism Impacts: Learning OutcomeJUN GERONANo ratings yet
- TM15 - Tourism PlatformsDocument19 pagesTM15 - Tourism PlatformsXye BreyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Reviewer Chapter 3Document2 pagesUnderstanding The Self Reviewer Chapter 3peachNo ratings yet
- Intro To Cruise Line Chapter 4 ReviewerDocument3 pagesIntro To Cruise Line Chapter 4 ReviewerpeachNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Reviewer Chapter 2Document2 pagesUnderstanding The Self Reviewer Chapter 2peach100% (1)
- Historical Development Unit Topics: TH THDocument3 pagesHistorical Development Unit Topics: TH THpeachNo ratings yet
- Report (Sculpture Materials)Document32 pagesReport (Sculpture Materials)triziasisonNo ratings yet
- (2022, Review, Saran) 3D Printing of Composite Materials - A Short ReviewDocument5 pages(2022, Review, Saran) 3D Printing of Composite Materials - A Short ReviewNam Huu TranNo ratings yet
- Personal Information: Single / Male / Indonesia / Purwakarta Passport / - / C2940195Document5 pagesPersonal Information: Single / Male / Indonesia / Purwakarta Passport / - / C2940195Muhammad RaihanNo ratings yet
- PPCoN 2169-2000Document113 pagesPPCoN 2169-2000Minh Hong PhamNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument7 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogKatrina Baldas Kew-isNo ratings yet
- Manage Prescribed Load List (PLL) AR0008 C: InstructionsDocument5 pagesManage Prescribed Load List (PLL) AR0008 C: InstructionsAmazinmets07No ratings yet
- OSB Error HandlingDocument45 pagesOSB Error Handlingabhishek_acharya_13100% (1)
- Winnie Leung: Summary of SkillsDocument2 pagesWinnie Leung: Summary of Skillsapi-248493924No ratings yet
- TvtgurpsnewDocument94 pagesTvtgurpsnewKevin HutchingsNo ratings yet
- C Quick GuideDocument34 pagesC Quick Guidemmarin1982No ratings yet
- September 2005 Limpkin Call Oklawaha Valley Audubon SocietyDocument4 pagesSeptember 2005 Limpkin Call Oklawaha Valley Audubon SocietyOklawaha Valley Audubon SocietyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Activities PrintDocument514 pagesFundamentals Activities PrintTOP NOTCHNo ratings yet
- Phys - Exam - May 2014-ZagazigDocument8 pagesPhys - Exam - May 2014-ZagazigWael ElsawyNo ratings yet
- 364.7T-02 (11) Evaluation and Minimization of Bruising (Microcracking) in Concrete Repair (TechNote)Document3 pages364.7T-02 (11) Evaluation and Minimization of Bruising (Microcracking) in Concrete Repair (TechNote)YaserNo ratings yet
- Surgical TreatmentDocument4 pagesSurgical TreatmentRobertRaduNo ratings yet
- 4 Lec AJ Culture Fall2023Document50 pages4 Lec AJ Culture Fall2023muhammad zohaibNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science - Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument17 pagesGrade 7 Science - Characteristics of Living ThingsPathmanathan Nadeson100% (1)
- Bondage in Jane AustenDocument13 pagesBondage in Jane AustensoodhamungurNo ratings yet
- Clark C33D - MotorDocument24 pagesClark C33D - MotorEstefanio figueiredoNo ratings yet
- This Article Needs Additional Citations For VerificationDocument3 pagesThis Article Needs Additional Citations For Verificationsamina taneNo ratings yet
- Material: ASTM A395 Ductile Iron or ASTM A105 Forged Steel: ID H TDocument1 pageMaterial: ASTM A395 Ductile Iron or ASTM A105 Forged Steel: ID H T1mmahoneyNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities: How Brands Can Succeed in Rural IndiaDocument9 pagesChallenges and Opportunities: How Brands Can Succeed in Rural Indiapriyanka mohanNo ratings yet
- Zaremby - BKRVW - Turner's European Intellectual History - TNC - 2015.11Document3 pagesZaremby - BKRVW - Turner's European Intellectual History - TNC - 2015.11Alvino-Mario FantiniNo ratings yet
- 05 Light Is LifeDocument10 pages05 Light Is Lifetenbears m.100% (2)
- A STUDY ON Fundamental & Technical AnalysisDocument86 pagesA STUDY ON Fundamental & Technical AnalysisKeleti Santhosh100% (1)
- Please Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceDocument2 pagesPlease Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceSaipraveen PerumallaNo ratings yet
- Correlational Relationship of Nursing Professional Subjects and Board Exam Performance of Isabela State University-Echague November 2022 Nursing Licensure Examination TakersDocument20 pagesCorrelational Relationship of Nursing Professional Subjects and Board Exam Performance of Isabela State University-Echague November 2022 Nursing Licensure Examination TakersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet