Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preventive Dentistry 3
Preventive Dentistry 3
Uploaded by
khaled alahmadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dermatology Essentials 2nd Ed 2022Document1,514 pagesDermatology Essentials 2nd Ed 2022MARTINA MARIA INSUA CASTRO100% (2)
- Nursing Fundamentals Test 1 Study GuideDocument15 pagesNursing Fundamentals Test 1 Study GuideJasmin VasquezNo ratings yet
- Dental Lab CommunicationDocument3 pagesDental Lab Communicationkhaled alahmad100% (1)
- TLE-G-7 - 8-Module-2-Household-Services - Week 2-5 - PRACTICE-OCCUPATIONAL-HEALTH-AND-SAFETY-PROCEDURESDocument35 pagesTLE-G-7 - 8-Module-2-Household-Services - Week 2-5 - PRACTICE-OCCUPATIONAL-HEALTH-AND-SAFETY-PROCEDURESRina Vianney De Leon100% (7)
- Themes - Overview - iOS Human Interface GuidelinesDocument3 pagesThemes - Overview - iOS Human Interface Guidelineskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- PBHE 501 Final Exam AnswersDocument4 pagesPBHE 501 Final Exam Answerswilcox_446121292100% (2)
- Spine PDFDocument7 pagesSpine PDFDRAHMEDFAHMYORTHOCLINIC100% (1)
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudySophia Loraine Dorone Jesura100% (1)
- Dr. Hadeyah Lecture 1 - Community Dentstry Introduction (Document11 pagesDr. Hadeyah Lecture 1 - Community Dentstry Introduction (Omar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Community Dentistry: Done By: D. Sanaa Noori AliDocument34 pagesCommunity Dentistry: Done By: D. Sanaa Noori Aliنور الحلوهNo ratings yet
- Introduction Public HealthDocument76 pagesIntroduction Public Healthnathanielge19No ratings yet
- Lec.1community Dentistry4thDocument7 pagesLec.1community Dentistry4thمحمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:bishow Dangal Roll No:seven 7 1) Problem 1Document4 pagesSubmitted By:bishow Dangal Roll No:seven 7 1) Problem 1BishowNo ratings yet
- Community Dental HealthDocument16 pagesCommunity Dental HealthsriharidinoNo ratings yet
- Scope and Objectives of Dental Health EducationDocument11 pagesScope and Objectives of Dental Health Education9raja4No ratings yet
- Plan For Integrated CommunityDocument22 pagesPlan For Integrated CommunityKingtone RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Seba Saqer - 20180482 - Public HealthDocument18 pagesSeba Saqer - 20180482 - Public HealthSaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Seba Saqer - 20180482 Puplic HealthDocument9 pagesSeba Saqer - 20180482 Puplic HealthSaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Community Lecture 1Document30 pagesCommunity Lecture 1منتظر العميديNo ratings yet
- Planning and EvaluationDocument28 pagesPlanning and Evaluationvdtjqm8y4nNo ratings yet
- NUSG 117 Project Paper: West Negros CollegeDocument6 pagesNUSG 117 Project Paper: West Negros CollegeJack FrostNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: School Dental Health ProgramDocument6 pagesShort Notes: School Dental Health ProgramGanesh Pavan Kumar KarriNo ratings yet
- Comdent II Lec Day 2Document5 pagesComdent II Lec Day 2Nica FernandezNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of InterventionDocument21 pagesDesign and Implementation of InterventionSamit RajanNo ratings yet
- Discussion - Program PlanningDocument2 pagesDiscussion - Program PlanningRuri DSNo ratings yet
- NRSG 780 - Health Promotion and Population Health: Module 8: Program Planning Essentials and ModelsDocument12 pagesNRSG 780 - Health Promotion and Population Health: Module 8: Program Planning Essentials and ModelsjustdoyourNo ratings yet
- DCP4B Manal (4) Health EconomicsDocument52 pagesDCP4B Manal (4) Health Economicsnancy alsharuNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of InterventionDocument21 pagesDesign and Implementation of InterventionSamit RajanNo ratings yet
- Community Dentistry Ii: Planning - It Is A Decision About A Course of ActionDocument8 pagesCommunity Dentistry Ii: Planning - It Is A Decision About A Course of ActionMark Anthony C. MalubagNo ratings yet
- Doh 125Document40 pagesDoh 125ovov711No ratings yet
- What - Is - Research (Dragged) 7Document1 pageWhat - Is - Research (Dragged) 7jifod18255No ratings yet
- GRP Guidelines On Health Promotion Evaluation enDocument16 pagesGRP Guidelines On Health Promotion Evaluation enTri SubiantoroNo ratings yet
- Community Health ProgramDocument43 pagesCommunity Health ProgramBsoom .iNo ratings yet
- Public Health - Module 1Document11 pagesPublic Health - Module 1bishalkumarharijan4No ratings yet
- 3........ Developing Plan For HP Intervention - 21Document23 pages3........ Developing Plan For HP Intervention - 21farajhiNo ratings yet
- Generalized Model For Program Planning1Document18 pagesGeneralized Model For Program Planning1Hafid JuniorNo ratings yet
- PMCV Finalreport RWoodwardKron 23feb14Document27 pagesPMCV Finalreport RWoodwardKron 23feb14M Arshad Iqbal HarralNo ratings yet
- Anubhav - Assignment FLCDocument14 pagesAnubhav - Assignment FLCTREESANo ratings yet
- Health Promotion Session 3 - 115525 - 122725Document22 pagesHealth Promotion Session 3 - 115525 - 122725allanfocus91No ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Ii NUR204: Population Groups and Community As Clients)Document31 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Ii NUR204: Population Groups and Community As Clients)ZairaNo ratings yet
- Dental Public Health Lecture SeriesDocument25 pagesDental Public Health Lecture SeriesChris TayNo ratings yet
- Entry Reentry, Allied, and Alternative Careers An IWLC Working Group ReportDocument2 pagesEntry Reentry, Allied, and Alternative Careers An IWLC Working Group ReportMega Arti UtamiNo ratings yet
- D. Ali NCD-1 (Muhadharaty)Document80 pagesD. Ali NCD-1 (Muhadharaty)علي موسى مهديNo ratings yet
- Community Oral Health Improvement ProcessDocument28 pagesCommunity Oral Health Improvement Processapi-738333066No ratings yet
- Nursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and Community MIDTERMDocument6 pagesNursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and Community MIDTERMjillmonicadaquipil7No ratings yet
- Precede Proceed Model ExampleDocument8 pagesPrecede Proceed Model ExampleHealthcare reality checkNo ratings yet
- Social Influence Strategies for Environmental Behavior Change: Second EditionFrom EverandSocial Influence Strategies for Environmental Behavior Change: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Precede Procede ModelDocument14 pagesPrecede Procede Modelエド パジャロン100% (1)
- 6ncm102 Developing Hltcare Plan 1Document41 pages6ncm102 Developing Hltcare Plan 1Mark Justin LealNo ratings yet
- Performance Measures For Mental Healthcare in Singapore: CommentaryDocument6 pagesPerformance Measures For Mental Healthcare in Singapore: Commentarypaijosuseno2242No ratings yet
- KKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK M N N N N N NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNDocument12 pagesKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK M N N N N N NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNEuston ChinharaNo ratings yet
- Health Planning - PSM Made EasyDocument6 pagesHealth Planning - PSM Made EasyChristiana OnyinyeNo ratings yet
- Health Education Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument44 pagesHealth Education Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDayapan MPC100% (1)
- Dhyg 415 Study Guide Yezi Pang - 1Document117 pagesDhyg 415 Study Guide Yezi Pang - 1api-473128642No ratings yet
- Unov/ Unodc Call For Proposals Drug Abuse Prevention Centre (DAPC) GrantsDocument15 pagesUnov/ Unodc Call For Proposals Drug Abuse Prevention Centre (DAPC) GrantsNehemiah ChipatoNo ratings yet
- Public Policy & Program Eveluation Lec 01Document29 pagesPublic Policy & Program Eveluation Lec 01Zainab Tariq AliNo ratings yet
- Planning Health Education/ Promotion ProgramDocument39 pagesPlanning Health Education/ Promotion ProgramSamie SephieNo ratings yet
- Department of Masters On Business Administration: Prepared By: Natnael Ebrahim Advisor Name: Shimeles Asfaw (Ass - Prof)Document21 pagesDepartment of Masters On Business Administration: Prepared By: Natnael Ebrahim Advisor Name: Shimeles Asfaw (Ass - Prof)natnael ebrahimNo ratings yet
- Steps in Community Health Nursing ProcessDocument3 pagesSteps in Community Health Nursing ProcessJoemay Belle CabanelaNo ratings yet
- Elective Final ModuleDocument5 pagesElective Final ModuleDember Mor TaugNo ratings yet
- PFE ProjectDocument4 pagesPFE ProjectRoopal BeheraNo ratings yet
- Social Policy and Administration: Eldoret Technical Training Institute - Lodwar CampusDocument30 pagesSocial Policy and Administration: Eldoret Technical Training Institute - Lodwar CampusshaniceodongoNo ratings yet
- Assignment May 11Document5 pagesAssignment May 11MARY FORTUNE MAE RAMONESNo ratings yet
- At Mod 3 InfoDocument119 pagesAt Mod 3 InfoDave KokNo ratings yet
- ToolDocument10 pagesToolArjun SabuNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument46 pagesHealth EducationKobby AmoahNo ratings yet
- Eng KG2 - U4 S4 What Happens When It's WindyDocument9 pagesEng KG2 - U4 S4 What Happens When It's Windykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Eng KG2 - U4 S6 What Happens When It's WindyDocument6 pagesEng KG2 - U4 S6 What Happens When It's Windykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Headache 2Document11 pagesHeadache 2khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Periodontology Couse SpecsDocument4 pagesPeriodontology Couse Specskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Perio ProjectDocument26 pagesPerio Projectkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- HeadachesDocument19 pagesHeadacheskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Headache LectureDocument57 pagesHeadache Lecturekhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- New Classification PerioDocument15 pagesNew Classification Periokhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and ParathyroidDocument33 pagesThyroid and Parathyroidkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- OMED 324 - Oral Medicine: Program: Department Offering The Course: Level / SemesterDocument4 pagesOMED 324 - Oral Medicine: Program: Department Offering The Course: Level / Semesterkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: 3 Dentistry Number: 38 Price: 500Document13 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: 3 Dentistry Number: 38 Price: 500khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Tooth Loss222222Document8 pagesTooth Loss222222khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Effect of Teeth Loss On Oro-Facial Environment: Done By: Khaled Hamed Alabd Alahmad ID: 201502300Document8 pagesEffect of Teeth Loss On Oro-Facial Environment: Done By: Khaled Hamed Alabd Alahmad ID: 201502300khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counseling in DentistryDocument8 pagesGenetic Counseling in Dentistrykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Endodontics IIIDocument40 pagesEndodontics IIIkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Communication With Dental LaboratoryDocument16 pagesCommunication With Dental Laboratorykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Treatment of A Class IV Anterior Fracture: AestheticsDocument3 pagesTreatment of A Class IV Anterior Fracture: Aestheticskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Morphological Difference Between Primary and Permanent TeethDocument13 pagesClinical Significance of Morphological Difference Between Primary and Permanent Teethkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counseling in DentistryDocument8 pagesGenetic Counseling in Dentistrykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Removable Partial DentureDocument40 pagesRemovable Partial Denturekhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Endo 5th AssignmentDocument3 pagesEndo 5th Assignmentkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Iphone ResolutionsDocument3 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Iphone Resolutionskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Career Opportunities: Dentistry Offers Stimulating Career OptionsDocument4 pagesCareer Opportunities: Dentistry Offers Stimulating Career Optionskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Ethical IssuesDocument13 pagesEthical Issueskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Outcomes of Vocal Hygiene Program in Facilitating VocalDocument13 pagesOutcomes of Vocal Hygiene Program in Facilitating VocalCRISTIAN FERNANDO MEJIA SOLISNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEW OF Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesOVERVIEW OF Public Health Nursing in The Philippinesjanina myka100% (1)
- Toxoplasmosis Serologic Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageToxoplasmosis Serologic Testing AlgorithmHanny Prasetiana YuriantiNo ratings yet
- Corynebacterium Dyphtheriae: Corynebacterium Diphtheria Is A Pathogenic Gram Positive Bacillus Causing DiphtheriaDocument3 pagesCorynebacterium Dyphtheriae: Corynebacterium Diphtheria Is A Pathogenic Gram Positive Bacillus Causing DiphtheriaknedhNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) RecordsDocument2 pagesCoronavirus (COVID-19) RecordstinaruthNo ratings yet
- The Immune System Defense Against Disease Study GuideDocument52 pagesThe Immune System Defense Against Disease Study GuidemaddoxNo ratings yet
- 1-h PyloriDocument14 pages1-h Pyloriademabdella38No ratings yet
- Health Related VisitsDocument31 pagesHealth Related VisitsSirAdjeteyNo ratings yet
- Health Coaching Quality FrameworkDocument22 pagesHealth Coaching Quality FrameworkGONDHES CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo Mother CareDocument24 pagesKangaroo Mother CareAjeesh100% (1)
- Cosmetic: Anterior Cervicoplasty in The Male PatientDocument9 pagesCosmetic: Anterior Cervicoplasty in The Male PatientIsaac SomohanoNo ratings yet
- Debate SpeechDocument2 pagesDebate SpeechBianca AsisNo ratings yet
- Advances in Intracranial HemorrhageDocument15 pagesAdvances in Intracranial HemorrhageJorge GonzalesNo ratings yet
- IPAQ - AUTOMATIC REPORT - KuisionerDocument20 pagesIPAQ - AUTOMATIC REPORT - KuisionerTri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Handbook ApitherapyDocument60 pagesHandbook ApitherapyengrezgarNo ratings yet
- Uses of Farm AnimalsDocument9 pagesUses of Farm AnimalsMohammed Nabeel MujtahidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Historical Development of Society SocietyDocument120 pagesUnit 1. Historical Development of Society Societyyangi dokaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading, Exercise 1-SOLVEDDocument4 pagesIELTS Reading, Exercise 1-SOLVEDcwpartuNo ratings yet
- Probiotics and Prebiotics in Animal Health and Food Safety PDFDocument275 pagesProbiotics and Prebiotics in Animal Health and Food Safety PDFIonela Hotea100% (2)
- A3 TopicDocument2 pagesA3 TopicNoel AñascoNo ratings yet
- AAI Pathology of Hematologic MalignanciesDocument2 pagesAAI Pathology of Hematologic MalignanciesHappy Singh100% (1)
- Adenoidectomy and Tosillectomy MethodsDocument5 pagesAdenoidectomy and Tosillectomy MethodsBkas GrgNo ratings yet
- Herboxa Nutrition Launched Lungwort All-Natural Dietary Supplement That Supports Lung FunctionDocument3 pagesHerboxa Nutrition Launched Lungwort All-Natural Dietary Supplement That Supports Lung FunctionPR.comNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology and Venipuncture Nosocomial InfectionDocument55 pagesPharmacology and Venipuncture Nosocomial InfectionArvic Pascua MaltizoNo ratings yet
- JOELDocument8 pagesJOELJoel ArumbakanNo ratings yet
- Balt International Product CatalogueDocument21 pagesBalt International Product CatalogueTấn Sang TrươngNo ratings yet
Preventive Dentistry 3
Preventive Dentistry 3
Uploaded by
khaled alahmadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Preventive Dentistry 3
Preventive Dentistry 3
Uploaded by
khaled alahmadCopyright:
Available Formats
o Public Health Practice:
- Public health dentistry: It’s a discipline that considers the total community as the
patient. Thus, it’s concerned with the oral health of all members of the society.
Example: Fluoridation programs. When successfully implemented in a
community, all will gain the protective benefit against dental caries.
o Similarities Between Private & Public Health Practice:
Private Practice Public Health Practice
Examination Survey
Diagnosis Analysis
Treatment Planning Program Planning
Treatment Program Operation
Payment for Services Financing
Evaluation Appraisal
o Private Practice: Careful examination & history Accurate diagnosis of problem
Treatment is planned to address the problem (cost of treatment/approved)
Service is provided and paid Subsequent visits provide evaluation of treatment
o Public Health Practice:
- Methods employed in dental public health practice parallel those of the private
practitioner, but involve the total community instead of the individual.
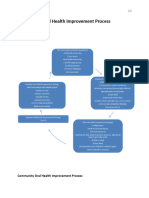
A- Survey: Nature and extent of a dental problem must be determined.
Example: The level of dental caries in a subgroup of children in a community may
be considered for study.
- The magnitude of the problem is assessed by screening examinations of the children
in target population. We are measuring and quantifying the condition based on
scientific principles (Dental Indices).
B- Analysis: Once the information is collected through a survey analysis of data to
answer certain questions.
1- What is the extent of the problem?
2- Are there appropriate solutions available to solve the problem?
statistical analysis transform information into a useful form.
C- Program planning: Survey Analysis process Problem is identified and its scope
is determined
- To assure success, all aspects should be considered.
- Communication is made with concerned individuals and organizations.
Example: To provide dental care for children, we must:
- Contact the parents of children
- Arrange transportation to where care will be provided
- Obtain agreements from practitioners to provide care for children.
D- Program Operation: Once carefully planned Program is implemented
- Even in a well-planned program, problems tend to occur and continuous surveillance
is necessary.
Examples are: Dental health education, disease prevention, or clinical services.
E- Financing: It’s usually provided by appropriate governmental agencies.
F- Appraisal: It’s the continuous evaluation to:
- Assess the effect of the program
- Measure the success/lack of the program
- Consider modifications that might improve the program.
You might also like
- Dermatology Essentials 2nd Ed 2022Document1,514 pagesDermatology Essentials 2nd Ed 2022MARTINA MARIA INSUA CASTRO100% (2)
- Nursing Fundamentals Test 1 Study GuideDocument15 pagesNursing Fundamentals Test 1 Study GuideJasmin VasquezNo ratings yet
- Dental Lab CommunicationDocument3 pagesDental Lab Communicationkhaled alahmad100% (1)
- TLE-G-7 - 8-Module-2-Household-Services - Week 2-5 - PRACTICE-OCCUPATIONAL-HEALTH-AND-SAFETY-PROCEDURESDocument35 pagesTLE-G-7 - 8-Module-2-Household-Services - Week 2-5 - PRACTICE-OCCUPATIONAL-HEALTH-AND-SAFETY-PROCEDURESRina Vianney De Leon100% (7)
- Themes - Overview - iOS Human Interface GuidelinesDocument3 pagesThemes - Overview - iOS Human Interface Guidelineskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- PBHE 501 Final Exam AnswersDocument4 pagesPBHE 501 Final Exam Answerswilcox_446121292100% (2)
- Spine PDFDocument7 pagesSpine PDFDRAHMEDFAHMYORTHOCLINIC100% (1)
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudySophia Loraine Dorone Jesura100% (1)
- Dr. Hadeyah Lecture 1 - Community Dentstry Introduction (Document11 pagesDr. Hadeyah Lecture 1 - Community Dentstry Introduction (Omar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Community Dentistry: Done By: D. Sanaa Noori AliDocument34 pagesCommunity Dentistry: Done By: D. Sanaa Noori Aliنور الحلوهNo ratings yet
- Introduction Public HealthDocument76 pagesIntroduction Public Healthnathanielge19No ratings yet
- Lec.1community Dentistry4thDocument7 pagesLec.1community Dentistry4thمحمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:bishow Dangal Roll No:seven 7 1) Problem 1Document4 pagesSubmitted By:bishow Dangal Roll No:seven 7 1) Problem 1BishowNo ratings yet
- Community Dental HealthDocument16 pagesCommunity Dental HealthsriharidinoNo ratings yet
- Scope and Objectives of Dental Health EducationDocument11 pagesScope and Objectives of Dental Health Education9raja4No ratings yet
- Plan For Integrated CommunityDocument22 pagesPlan For Integrated CommunityKingtone RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Seba Saqer - 20180482 - Public HealthDocument18 pagesSeba Saqer - 20180482 - Public HealthSaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Seba Saqer - 20180482 Puplic HealthDocument9 pagesSeba Saqer - 20180482 Puplic HealthSaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Community Lecture 1Document30 pagesCommunity Lecture 1منتظر العميديNo ratings yet
- Planning and EvaluationDocument28 pagesPlanning and Evaluationvdtjqm8y4nNo ratings yet
- NUSG 117 Project Paper: West Negros CollegeDocument6 pagesNUSG 117 Project Paper: West Negros CollegeJack FrostNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: School Dental Health ProgramDocument6 pagesShort Notes: School Dental Health ProgramGanesh Pavan Kumar KarriNo ratings yet
- Comdent II Lec Day 2Document5 pagesComdent II Lec Day 2Nica FernandezNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of InterventionDocument21 pagesDesign and Implementation of InterventionSamit RajanNo ratings yet
- Discussion - Program PlanningDocument2 pagesDiscussion - Program PlanningRuri DSNo ratings yet
- NRSG 780 - Health Promotion and Population Health: Module 8: Program Planning Essentials and ModelsDocument12 pagesNRSG 780 - Health Promotion and Population Health: Module 8: Program Planning Essentials and ModelsjustdoyourNo ratings yet
- DCP4B Manal (4) Health EconomicsDocument52 pagesDCP4B Manal (4) Health Economicsnancy alsharuNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of InterventionDocument21 pagesDesign and Implementation of InterventionSamit RajanNo ratings yet
- Community Dentistry Ii: Planning - It Is A Decision About A Course of ActionDocument8 pagesCommunity Dentistry Ii: Planning - It Is A Decision About A Course of ActionMark Anthony C. MalubagNo ratings yet
- Doh 125Document40 pagesDoh 125ovov711No ratings yet
- What - Is - Research (Dragged) 7Document1 pageWhat - Is - Research (Dragged) 7jifod18255No ratings yet
- GRP Guidelines On Health Promotion Evaluation enDocument16 pagesGRP Guidelines On Health Promotion Evaluation enTri SubiantoroNo ratings yet
- Community Health ProgramDocument43 pagesCommunity Health ProgramBsoom .iNo ratings yet
- Public Health - Module 1Document11 pagesPublic Health - Module 1bishalkumarharijan4No ratings yet
- 3........ Developing Plan For HP Intervention - 21Document23 pages3........ Developing Plan For HP Intervention - 21farajhiNo ratings yet
- Generalized Model For Program Planning1Document18 pagesGeneralized Model For Program Planning1Hafid JuniorNo ratings yet
- PMCV Finalreport RWoodwardKron 23feb14Document27 pagesPMCV Finalreport RWoodwardKron 23feb14M Arshad Iqbal HarralNo ratings yet
- Anubhav - Assignment FLCDocument14 pagesAnubhav - Assignment FLCTREESANo ratings yet
- Health Promotion Session 3 - 115525 - 122725Document22 pagesHealth Promotion Session 3 - 115525 - 122725allanfocus91No ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Ii NUR204: Population Groups and Community As Clients)Document31 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Ii NUR204: Population Groups and Community As Clients)ZairaNo ratings yet
- Dental Public Health Lecture SeriesDocument25 pagesDental Public Health Lecture SeriesChris TayNo ratings yet
- Entry Reentry, Allied, and Alternative Careers An IWLC Working Group ReportDocument2 pagesEntry Reentry, Allied, and Alternative Careers An IWLC Working Group ReportMega Arti UtamiNo ratings yet
- D. Ali NCD-1 (Muhadharaty)Document80 pagesD. Ali NCD-1 (Muhadharaty)علي موسى مهديNo ratings yet
- Community Oral Health Improvement ProcessDocument28 pagesCommunity Oral Health Improvement Processapi-738333066No ratings yet
- Nursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and Community MIDTERMDocument6 pagesNursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and Community MIDTERMjillmonicadaquipil7No ratings yet
- Precede Proceed Model ExampleDocument8 pagesPrecede Proceed Model ExampleHealthcare reality checkNo ratings yet
- Social Influence Strategies for Environmental Behavior Change: Second EditionFrom EverandSocial Influence Strategies for Environmental Behavior Change: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Precede Procede ModelDocument14 pagesPrecede Procede Modelエド パジャロン100% (1)
- 6ncm102 Developing Hltcare Plan 1Document41 pages6ncm102 Developing Hltcare Plan 1Mark Justin LealNo ratings yet
- Performance Measures For Mental Healthcare in Singapore: CommentaryDocument6 pagesPerformance Measures For Mental Healthcare in Singapore: Commentarypaijosuseno2242No ratings yet
- KKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK M N N N N N NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNDocument12 pagesKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK M N N N N N NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNEuston ChinharaNo ratings yet
- Health Planning - PSM Made EasyDocument6 pagesHealth Planning - PSM Made EasyChristiana OnyinyeNo ratings yet
- Health Education Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument44 pagesHealth Education Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDayapan MPC100% (1)
- Dhyg 415 Study Guide Yezi Pang - 1Document117 pagesDhyg 415 Study Guide Yezi Pang - 1api-473128642No ratings yet
- Unov/ Unodc Call For Proposals Drug Abuse Prevention Centre (DAPC) GrantsDocument15 pagesUnov/ Unodc Call For Proposals Drug Abuse Prevention Centre (DAPC) GrantsNehemiah ChipatoNo ratings yet
- Public Policy & Program Eveluation Lec 01Document29 pagesPublic Policy & Program Eveluation Lec 01Zainab Tariq AliNo ratings yet
- Planning Health Education/ Promotion ProgramDocument39 pagesPlanning Health Education/ Promotion ProgramSamie SephieNo ratings yet
- Department of Masters On Business Administration: Prepared By: Natnael Ebrahim Advisor Name: Shimeles Asfaw (Ass - Prof)Document21 pagesDepartment of Masters On Business Administration: Prepared By: Natnael Ebrahim Advisor Name: Shimeles Asfaw (Ass - Prof)natnael ebrahimNo ratings yet
- Steps in Community Health Nursing ProcessDocument3 pagesSteps in Community Health Nursing ProcessJoemay Belle CabanelaNo ratings yet
- Elective Final ModuleDocument5 pagesElective Final ModuleDember Mor TaugNo ratings yet
- PFE ProjectDocument4 pagesPFE ProjectRoopal BeheraNo ratings yet
- Social Policy and Administration: Eldoret Technical Training Institute - Lodwar CampusDocument30 pagesSocial Policy and Administration: Eldoret Technical Training Institute - Lodwar CampusshaniceodongoNo ratings yet
- Assignment May 11Document5 pagesAssignment May 11MARY FORTUNE MAE RAMONESNo ratings yet
- At Mod 3 InfoDocument119 pagesAt Mod 3 InfoDave KokNo ratings yet
- ToolDocument10 pagesToolArjun SabuNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument46 pagesHealth EducationKobby AmoahNo ratings yet
- Eng KG2 - U4 S4 What Happens When It's WindyDocument9 pagesEng KG2 - U4 S4 What Happens When It's Windykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Eng KG2 - U4 S6 What Happens When It's WindyDocument6 pagesEng KG2 - U4 S6 What Happens When It's Windykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Headache 2Document11 pagesHeadache 2khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Periodontology Couse SpecsDocument4 pagesPeriodontology Couse Specskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Perio ProjectDocument26 pagesPerio Projectkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- HeadachesDocument19 pagesHeadacheskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Headache LectureDocument57 pagesHeadache Lecturekhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- New Classification PerioDocument15 pagesNew Classification Periokhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and ParathyroidDocument33 pagesThyroid and Parathyroidkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- OMED 324 - Oral Medicine: Program: Department Offering The Course: Level / SemesterDocument4 pagesOMED 324 - Oral Medicine: Program: Department Offering The Course: Level / Semesterkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: 3 Dentistry Number: 38 Price: 500Document13 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: 3 Dentistry Number: 38 Price: 500khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Tooth Loss222222Document8 pagesTooth Loss222222khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Effect of Teeth Loss On Oro-Facial Environment: Done By: Khaled Hamed Alabd Alahmad ID: 201502300Document8 pagesEffect of Teeth Loss On Oro-Facial Environment: Done By: Khaled Hamed Alabd Alahmad ID: 201502300khaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counseling in DentistryDocument8 pagesGenetic Counseling in Dentistrykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Endodontics IIIDocument40 pagesEndodontics IIIkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Communication With Dental LaboratoryDocument16 pagesCommunication With Dental Laboratorykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Treatment of A Class IV Anterior Fracture: AestheticsDocument3 pagesTreatment of A Class IV Anterior Fracture: Aestheticskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Morphological Difference Between Primary and Permanent TeethDocument13 pagesClinical Significance of Morphological Difference Between Primary and Permanent Teethkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counseling in DentistryDocument8 pagesGenetic Counseling in Dentistrykhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Removable Partial DentureDocument40 pagesRemovable Partial Denturekhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Endo 5th AssignmentDocument3 pagesEndo 5th Assignmentkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Iphone ResolutionsDocument3 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Iphone Resolutionskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Career Opportunities: Dentistry Offers Stimulating Career OptionsDocument4 pagesCareer Opportunities: Dentistry Offers Stimulating Career Optionskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Ethical IssuesDocument13 pagesEthical Issueskhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Outcomes of Vocal Hygiene Program in Facilitating VocalDocument13 pagesOutcomes of Vocal Hygiene Program in Facilitating VocalCRISTIAN FERNANDO MEJIA SOLISNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEW OF Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesOVERVIEW OF Public Health Nursing in The Philippinesjanina myka100% (1)
- Toxoplasmosis Serologic Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageToxoplasmosis Serologic Testing AlgorithmHanny Prasetiana YuriantiNo ratings yet
- Corynebacterium Dyphtheriae: Corynebacterium Diphtheria Is A Pathogenic Gram Positive Bacillus Causing DiphtheriaDocument3 pagesCorynebacterium Dyphtheriae: Corynebacterium Diphtheria Is A Pathogenic Gram Positive Bacillus Causing DiphtheriaknedhNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) RecordsDocument2 pagesCoronavirus (COVID-19) RecordstinaruthNo ratings yet
- The Immune System Defense Against Disease Study GuideDocument52 pagesThe Immune System Defense Against Disease Study GuidemaddoxNo ratings yet
- 1-h PyloriDocument14 pages1-h Pyloriademabdella38No ratings yet
- Health Related VisitsDocument31 pagesHealth Related VisitsSirAdjeteyNo ratings yet
- Health Coaching Quality FrameworkDocument22 pagesHealth Coaching Quality FrameworkGONDHES CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo Mother CareDocument24 pagesKangaroo Mother CareAjeesh100% (1)
- Cosmetic: Anterior Cervicoplasty in The Male PatientDocument9 pagesCosmetic: Anterior Cervicoplasty in The Male PatientIsaac SomohanoNo ratings yet
- Debate SpeechDocument2 pagesDebate SpeechBianca AsisNo ratings yet
- Advances in Intracranial HemorrhageDocument15 pagesAdvances in Intracranial HemorrhageJorge GonzalesNo ratings yet
- IPAQ - AUTOMATIC REPORT - KuisionerDocument20 pagesIPAQ - AUTOMATIC REPORT - KuisionerTri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Handbook ApitherapyDocument60 pagesHandbook ApitherapyengrezgarNo ratings yet
- Uses of Farm AnimalsDocument9 pagesUses of Farm AnimalsMohammed Nabeel MujtahidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Historical Development of Society SocietyDocument120 pagesUnit 1. Historical Development of Society Societyyangi dokaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading, Exercise 1-SOLVEDDocument4 pagesIELTS Reading, Exercise 1-SOLVEDcwpartuNo ratings yet
- Probiotics and Prebiotics in Animal Health and Food Safety PDFDocument275 pagesProbiotics and Prebiotics in Animal Health and Food Safety PDFIonela Hotea100% (2)
- A3 TopicDocument2 pagesA3 TopicNoel AñascoNo ratings yet
- AAI Pathology of Hematologic MalignanciesDocument2 pagesAAI Pathology of Hematologic MalignanciesHappy Singh100% (1)
- Adenoidectomy and Tosillectomy MethodsDocument5 pagesAdenoidectomy and Tosillectomy MethodsBkas GrgNo ratings yet
- Herboxa Nutrition Launched Lungwort All-Natural Dietary Supplement That Supports Lung FunctionDocument3 pagesHerboxa Nutrition Launched Lungwort All-Natural Dietary Supplement That Supports Lung FunctionPR.comNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology and Venipuncture Nosocomial InfectionDocument55 pagesPharmacology and Venipuncture Nosocomial InfectionArvic Pascua MaltizoNo ratings yet
- JOELDocument8 pagesJOELJoel ArumbakanNo ratings yet
- Balt International Product CatalogueDocument21 pagesBalt International Product CatalogueTấn Sang TrươngNo ratings yet