Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
Влада Хоружий0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThe cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels which work together to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart acts as a pump to force blood through the blood vessels, which form a closed system to transport blood and allow for gas, nutrient, and waste exchange between blood and body cells. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for survival as tissues need oxygen and nutrients delivered via circulation while removing waste.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels which work together to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart acts as a pump to force blood through the blood vessels, which form a closed system to transport blood and allow for gas, nutrient, and waste exchange between blood and body cells. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for survival as tissues need oxygen and nutrients delivered via circulation while removing waste.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageCardiovascular System
Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
Влада ХоружийThe cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels which work together to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart acts as a pump to force blood through the blood vessels, which form a closed system to transport blood and allow for gas, nutrient, and waste exchange between blood and body cells. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for survival as tissues need oxygen and nutrients delivered via circulation while removing waste.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is the portion of the circulatory system that
includes the heart and blood vessels. It moves the blood between the body
cells and the organs of the integumentary, digestive, respiratory, and urinary
systems that communicate with the external environment. The heart acts as a
pump that forces blood through the blood vessels. The blood vessels form a
closed system of ducts, which transports the blood and allows exchanges of
gases, nutrients, and wastes between the blood and the body cells.
A functional cardiovascular system is vital for survival, because without
circulation, the tissues lack a supply of oxygen and nutrients, and waste
substances accumulate.
Heart
The heart is a hollow, cone – shaped, muscular pump located within the
mediastinum of the thorax and resting upon the diaphragm.
The heart is bordered laterally by the lungs, posteriorly by the backbone,
and anteriorly by the sternum. Its base lies beneath the second rib.
Internally, the heart is divided into four hollow chambers. The upper
chambers, called atria have relatively thin walls and receive the blood from
veins. The lower chambers, the ventricles, force the blood out of the heart
into arteries.
The atrium and ventricle on the right side are separated from those on the
left by a septum. The atrium on each side communicates with its
corresponding ventricle through an opening called the atrioventricular
orifice, which is guarded by an atrioventricular valve (A-V valve).
The wall of the heart is composed of three distinct layers: an outer
epicardium, a middle myocardium, and an inner endocardium.
The epicardium functions as an outer protective layer. It is a serous
membrane that consists of connective tissue covered by epithelium, and it
includes blood capillaries, lymph capillaries, and nerve fibers.
The middle layer, or myocardium, is relatively thick and consists largely
of the cardiac muscle tissue responsible for forcing the blood out of the
heart chambers.
The inner layer, or endocardium, consists of epithelium and connective
tissue that contains many elastic and collagenous fibers. The connective
tissue also contains blood vessels and some specialized cardiac muscle
fibers called Purkinje fibers.
You might also like
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemDawn Santiago RNNo ratings yet
- The Heart 115921 Am - AaddcfDocument216 pagesThe Heart 115921 Am - AaddcfNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- .archANATOMY 11Document5 pages.archANATOMY 11najem2sonNo ratings yet
- BIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Document9 pagesBIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Jv Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Document60 pagesAcfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Bala GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument19 pagesHeart Anatomydeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- القلبDocument11 pagesالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.6Document5 pagesAnatomy Lec.6aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Copy2-The HeartDocument180 pagesCopy2-The HeartNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Semis ReviewerDocument18 pagesCardiovascular System Semis ReviewerReggie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Heartvanessaresullar100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartPTV SportsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy WordDocument4 pagesAnatomy Wordarezoo bahramiNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Overview and PositionDocument11 pagesThe Heart: Overview and PositionLil_QuinceNo ratings yet
- Circulatory (2) (Autosaved)Document37 pagesCirculatory (2) (Autosaved)Tesfanew SeteNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument27 pagesHeartJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemGodsend OparaNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORY 0 Lymphatic SystemDocument24 pagesCIRCULATORY 0 Lymphatic SystemMuskan TiwariNo ratings yet
- PHS 205 Cardiovascular SystemDocument33 pagesPHS 205 Cardiovascular Systemdivineraymond34No ratings yet
- Module 1 PDFDocument20 pagesModule 1 PDFAlup MjhayNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Sys Part 1Document10 pagesCardiovascular Sys Part 1LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument47 pagesCirculatory Systemeliassultan3No ratings yet
- HeartDocument45 pagesHeartlilac.poppy.48No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Circulatory SystemDocument157 pagesUnit 4 Circulatory SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemABDUL HANANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1Document22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1adedayodavid860No ratings yet
- Biology Project Human HeartDocument17 pagesBiology Project Human HeartdeepmanisharmaNo ratings yet
- The Heart - NotesDocument11 pagesThe Heart - NotesLast AccNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemYna MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsDocument33 pagesCardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsnoshNo ratings yet
- Austin CardiologyDocument15 pagesAustin CardiologyAustin Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument9 pagesThe Cardiovascular System The HeartMarjorie AbelgasNo ratings yet
- CVS Heart Complete PDFDocument364 pagesCVS Heart Complete PDFNabeel HamzaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDocument69 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of HeartRitu Arun Kaushik100% (2)
- The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory Systemnoemi feblesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Cardiovascular Systemtewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Cardiovascular System and The BloodDocument12 pagesLesson 1 Cardiovascular System and The BloodPathy LinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Sukri Tika Yuli Safrina Sughro Puji UtamiDocument10 pagesSukri Tika Yuli Safrina Sughro Puji UtamiRudy MunandarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesMarie ParksNo ratings yet
- Austin Journal of Clinical CardiologyDocument15 pagesAustin Journal of Clinical CardiologyAustin Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- The Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissueDocument4 pagesThe Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissuehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemChekaina Rain BaldomarNo ratings yet
- Syok Hipovolemik EnglishDocument25 pagesSyok Hipovolemik Englishatmarida 123No ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىDocument10 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 The Circulatory System - The HeartDocument14 pagesChapter 19 The Circulatory System - The HeartGary Bowen100% (1)
- Anatomy NstemiDocument3 pagesAnatomy NstemiSheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Heart Structure and FunctionsDocument3 pagesHeart Structure and FunctionsChristella KateNo ratings yet
- Group1 Presentation On The HeartDocument14 pagesGroup1 Presentation On The HeartchukwukerechimezirimNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System 1Document20 pagesCardiovascular System 1Prince YoungNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyNikka Aubrey Tegui-inNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument13 pagesCirculationshifaaurangzeb2No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Cardiovascular System EsparciaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To The Cardiovascular System EsparciaJohnferson S. BornalesNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument24 pagesThe HeartAnubhav MishraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Histology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Histology of The Cardiovascular SystemTasmiah HossainNo ratings yet
- HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesHUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY Cardiovascular SystemZaira MangalimanNo ratings yet
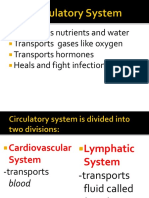
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet