Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics School
Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics School
Uploaded by
Alok KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Medical Terminology For Health Professions Spiral Bound Version Mindtap Course List 9Th Edition Ehrlich Full ChapterDocument68 pagesMedical Terminology For Health Professions Spiral Bound Version Mindtap Course List 9Th Edition Ehrlich Full Chapterjames.radford791100% (7)
- Cognitive Psychology and Its Implications 8th Edition Anderson Test BankDocument20 pagesCognitive Psychology and Its Implications 8th Edition Anderson Test BankJacobFoxgipbn95% (19)
- Histology Final ExamDocument33 pagesHistology Final ExamAlok Kumar75% (4)
- Kaznmu SyllabusDocument15 pagesKaznmu SyllabusAlok Kumar100% (1)
- S6 - Q2 - DLPS - Week 1 To 5Document302 pagesS6 - Q2 - DLPS - Week 1 To 5Dom MartinezNo ratings yet
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument5 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Fish N FrogDocument23 pagesRespiration in Fish N FrogHazirah HussinNo ratings yet
- For Stud Less 11Document15 pagesFor Stud Less 11xtomx1904No ratings yet
- Tus 2013 NisanDocument22 pagesTus 2013 NisanAsma MajidiNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly 23-24 Grade 5 - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly 23-24 Grade 5 - Answer KeyshamshadNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organs PDFTanzila SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense OrgansDocument20 pagesSelina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense OrgansDeepakNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument43 pagesBasicxakos16766No ratings yet
- Tus 2013 EylulDocument21 pagesTus 2013 EylulAsma MajidiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EBB 2023Document46 pagesQuestion Bank EBB 2023Muhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansDocument19 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansParardha DharNo ratings yet
- Exam Biology f4Document2 pagesExam Biology f4fardowsomoalimhassanNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: Pattern 2012)Document114 pagesNeuroanatomy: Pattern 2012)Devsya DodiaNo ratings yet
- Tus 2014 EylulDocument24 pagesTus 2014 EylulAsma MajidiNo ratings yet
- Terminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)Document8 pagesTerminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)KES SCIENCE FYJC PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-10 at 11.40.36 AMDocument67 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-10 at 11.40.36 AMAnchal LohanaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Chapter 3-Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesBiology: Chapter 3-Human Anatomy and PhysiologyMaahrukh Shifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - WS - X-24-25Document4 pagesNervous System - WS - X-24-25shnc1801No ratings yet
- Test, Questions and Clinical - Cases in NeurologyDocument111 pagesTest, Questions and Clinical - Cases in NeurologyPurwa Rane100% (1)
- Biology Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesBiology Sense OrgansasdasdNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Year 1Document8 pagesOphthalmology Year 1Malak Al ShammariNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System-Dr54gvs6Document26 pagesThe Skeletal System-Dr54gvs6Abdo HusseinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test BankDocument38 pagesPrinciples of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bankaidenqpepe100% (17)
- Principles of Animal Physiology 3Rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Animal Physiology 3Rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full Chapter PDFAndrewRobinsonixez100% (12)
- CHAPTER 11 Nervous System Spinal Cord PRETEST With AnswersDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 11 Nervous System Spinal Cord PRETEST With AnswersanaflaviaaguiarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Document33 pagesLab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Катерина ЛяшинаNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine and Nervous SystemTashi OngNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 - Rev Worksheet 1 (23-24) Answer KeyDocument5 pagesGrade 5 - Rev Worksheet 1 (23-24) Answer KeyshamshadNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz - NervesDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz - NervesChantel AceveroNo ratings yet
- XBHA2103 (Human Anatomy & Physiology) - Lab Sheet Jan 2022Document23 pagesXBHA2103 (Human Anatomy & Physiology) - Lab Sheet Jan 2022zulhusniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Seeleys Anatomy Physiology 12th by Vanputte DownloadDocument49 pagesTest Bank For Seeleys Anatomy Physiology 12th by Vanputte DownloadBenjaminWilsongaco100% (22)
- Tutorial 7 - Cranial N and ANS-teacherDocument4 pagesTutorial 7 - Cranial N and ANS-teacherL HYNo ratings yet
- APPSY Past PPR PDFDocument93 pagesAPPSY Past PPR PDFHafsa KhalidNo ratings yet
- Week 2 WS-Body Cavities and RegionsDocument2 pagesWeek 2 WS-Body Cavities and RegionsGHEIST INC.No ratings yet
- PM291 ErrataDocument10 pagesPM291 ErrataServal GideonNo ratings yet
- 6 - Embryology - PASS - MRCOG 2017Document22 pages6 - Embryology - PASS - MRCOG 2017emadhishamaburawiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank instant download all chapterDocument27 pagesPrinciples of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank instant download all chaptercaslaanttu58100% (4)
- Download Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank all chaptersDocument37 pagesDownload Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank all chaptersanilocrusz100% (6)
- Important QuestionsDocument38 pagesImportant Questionsas3941asNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full ChapterDocument37 pages(Download PDF) Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full Chapterrodaleyovesh0100% (8)
- 185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorDocument60 pages185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorMostafa Montaser100% (5)
- Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesEssentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Marieb Solutions Manualdipolarramenta7uyxw100% (26)
- Question Paper - Vetm 2002 - December - Final Examination - 2020-21Document10 pagesQuestion Paper - Vetm 2002 - December - Final Examination - 2020-21TheBoss 20No ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument4 pagesMIDTERMArchon BanzonNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Mid-Term ReviewDocument61 pagesOphthalmology Mid-Term ReviewMax TraderNo ratings yet
- Cells, Human Reproduction and HeredityDocument28 pagesCells, Human Reproduction and HeredityYuenHei KwokNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationDocument24 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationhelloNo ratings yet
- Anatomi, Fisiologi Mata Serta Overview RZDocument44 pagesAnatomi, Fisiologi Mata Serta Overview RZEuginia Yosephine100% (1)
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQUmair SaudNo ratings yet
- Diploma Pharmacy First Year - Hap - MCQSDocument13 pagesDiploma Pharmacy First Year - Hap - MCQSAnitha Mary Dambale92% (36)
- Biology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 5Document6 pagesBiology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 5Kamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Neuroscience: Lecture 3: Windows To The BrainDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Computational Neuroscience: Lecture 3: Windows To The BrainNAGAVARSHININo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 8Document5 pagesLab Exercise 8Yeong-Ja KwonNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy MCQ2Document5 pagesNeuroanatomy MCQ2michaelkingtz01No ratings yet
- Neuro DambiDocument51 pagesNeuro DambiKerim SabicNo ratings yet
- Anaphy NervousDocument6 pagesAnaphy NervousArcher RiegoNo ratings yet
- AzadDocument2 pagesAzadrifat iqbalNo ratings yet
- Nlknpast AppDocument7 pagesNlknpast AppUCL SportsNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Grade X Biology PT2Document4 pagesPractice Paper Grade X Biology PT2setidi1975No ratings yet
- 2 5273733825283753522 PDFDocument5 pages2 5273733825283753522 PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- ENT Atf-93-131Document10 pagesENT Atf-93-131Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- The List of Exam Test Items in The Discipline "Molecular Biology" For The 1st Year Students, Specialty "General Medicine", 2019-2020 Academic YearDocument17 pagesThe List of Exam Test Items in The Discipline "Molecular Biology" For The 1st Year Students, Specialty "General Medicine", 2019-2020 Academic YearAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- 1st Midterm Control PDFDocument13 pages1st Midterm Control PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- 13-Theme - Practice - For Student of IndiaDocument2 pages13-Theme - Practice - For Student of IndiaAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Department Informatics With Biophysics Course Methodical Recommendations EditionDocument5 pagesDepartment Informatics With Biophysics Course Methodical Recommendations EditionAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- (29final) 1125angl FinalDocument133 pages(29final) 1125angl FinalAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Phy123 PDFDocument2 pagesPhy123 PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Histology With AnsDocument166 pagesHistology With AnsAlok Kumar0% (1)
- 2 Part - Test MHKDocument36 pages2 Part - Test MHKAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- State Exam Questions +Document29 pagesState Exam Questions +Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Part - Test MHKDocument33 pages1 Part - Test MHKAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Trauma MarrowDocument5 pagesThoracic Trauma MarrowAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS GM 2019-20 EnglishDocument63 pagesSYLLABUS GM 2019-20 EnglishAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical SkillsDocument1 pagePractical SkillsAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- 399 Bob StatementDocument1 page399 Bob StatementAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical Task 1Document1 pagePractical Task 1Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Ashiq CH 16Document3 pagesAshiq CH 16Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous and Re Ex OvulatorsDocument14 pagesSpontaneous and Re Ex OvulatorsFazal Akbar KhaliliNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY CHAPTER 8 Form 4Document21 pagesBIOLOGY CHAPTER 8 Form 4husnäNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Collections.Document335 pagesScience Form 3 Collections.Fazil JayNo ratings yet
- SBI3U Chapter 10 Self-QuizDocument6 pagesSBI3U Chapter 10 Self-QuizJannette JaneNo ratings yet
- Local Media5742365695864783121Document13 pagesLocal Media5742365695864783121Brian Voyd RebitoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesCirculatory SystemAlizaNo ratings yet
- Aad Abdomen WorksheetDocument15 pagesAad Abdomen WorksheetAchNo ratings yet
- Coronary CirculationDocument33 pagesCoronary CirculationAayushman YadavNo ratings yet
- Science 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesScience 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDyaan TrajicoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesLecture 1 Respiratory SystemArnelNo ratings yet
- Blood Disorders LimmerEducationDocument1 pageBlood Disorders LimmerEducationrehaan662No ratings yet
- CiullabbDocument71 pagesCiullabbMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Bony Pelvis and Fetal Skull: Dr. Iman Yousif AbdulmalekDocument46 pagesAnatomy of The Female Bony Pelvis and Fetal Skull: Dr. Iman Yousif AbdulmalekSnap SnhhNo ratings yet
- 15 - HomeostasisDocument13 pages15 - HomeostasisMuhammad TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma Power PointDocument44 pagesBronchial Asthma Power Pointjohnbech07No ratings yet
- RBC Morph Ulka 2Document69 pagesRBC Morph Ulka 2Rushi WalgudeNo ratings yet
- Massive Haemorrhage: P Donnelly B FergusonDocument18 pagesMassive Haemorrhage: P Donnelly B FergusonRizqiNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Cell TheoryDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Cell TheoryPercival RiegoNo ratings yet
- Feyer 2020 WvngoshawkDocument13 pagesFeyer 2020 WvngoshawkAgnieszka CzujkowskaNo ratings yet
- SOX Science5 Q2 M2of7Document18 pagesSOX Science5 Q2 M2of7Neil Joy Felomino Basa-LepalemNo ratings yet
- Biologi Kertas 1 Percubaan SPM 2012 MRSM K (Myschoolchildren - Com)Document42 pagesBiologi Kertas 1 Percubaan SPM 2012 MRSM K (Myschoolchildren - Com)Preedep BaradidathanNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord EOR - 163162 - 284 - 18220 - v1Document16 pagesUmbilical Cord EOR - 163162 - 284 - 18220 - v1Secret ImamNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3 - Fisiologi Sistem Muskuloskeletal (Dr. Adelia Handoko)Document36 pagesKuliah 3 - Fisiologi Sistem Muskuloskeletal (Dr. Adelia Handoko)Linda ayuNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesParts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryAnonymous giver100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants-2Document4 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants-2aditya kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 8th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 8th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFhuonghuyen2cp9ez100% (15)
- Nomina AnatomicaDocument4 pagesNomina AnatomicaIoana Purice100% (1)
Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics School
Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics School
Uploaded by
Alok KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics School
Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics School
Uploaded by
Alok KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
«С.Ж.
АСФЕНДИЯРОВ АТЫНДАҒЫ ҰЛТТЫҚ МЕДИЦИНА УНИВЕРСИТЕТІ» КЕАҚ
NCJSC«ASFENDIYAROVNATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY»
Edition: 1
Department of Normal Anatomy Methodical instruction
Page1of6
Methodical instruction for the 1st year students of the General Medicine and
Pediatrics School
Theme of the lesson: Anatomy and topography of the sensory organs. Organ of
vision.Eyeball. Auxiliary structures of the eye, optic (II) nerve, oculomotor (III) nerve,
block (IV) nerve, abducent (VI) nerve: nuclei, branches. The organ of hearing and
balance.Vestibulo-cochlear (VIII) nerve.Organs of smell and taste. Olfactory (I) nerve.
Option 1
Task 1.Test questions (with one or with several correct answers).
Each question - 5 points. Maximum - 35 points
1.Cortical end of the olfactory analyzer 4. Layers of eye:
A) calcarinesulcus A) fibrous
B) frontallobe B) mucous
C) occipitallobe C) vascular
D) parietallobe D) retina
E) para-hippocampalgyrus, uncus E) muscular
2. Anatomical formations of outer ear: 5. Fibrous layer of eye includes:
A) auricula A) adventitia
B) cavitas tympani B) iris
C) meatusacusticusexternus C) cornea
D) membrana tympani D) tenon capsule
E) ossiculaauditus E) sclera
3. Muscles acting on pupil: 6. The eyeball choroid includes:
A) m. sphincter pupillae A) tenon capsule
B) m. stapedius B) choroid
C) m. dilatator pupillae C) retina
D) m. tensor tympani D) ciliary body
E) m. risorius E) iris
7. What pass through superior orbital
fissure?
A) III pair
B) IV pair
C) VІ pair
D) I pair
E) II pair
Developer Teacher Ohanova M.I.
«С.Ж.АСФЕНДИЯРОВ АТЫНДАҒЫ ҰЛТТЫҚ МЕДИЦИНА УНИВЕРСИТЕТІ» КЕАҚ
NCJSC«ASFENDIYAROVNATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY»
Edition: 1
Department of Normal Anatomy Methodical instruction
Page2of6
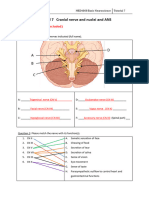
Task 2.There are 5 steps in the picture. 1 step - 7 points. Maximum 35 points
1 What is the anatomical formation? 1
2 What is the anatomical formation? 2
3 What is the anatomical formation? 3
4 What is the anatomical formation? 4
5 What is the anatomical formation? 5
Task 3.The situational tasks solution. For the correct solution of one task - 15 points.
Maximum 30 points
Task 1. The patient complains to the neurologist about an impaired coordination of
movements. When examination focal damage of the pons nuclei is revealed, including
olive nucleus, which is an intermediate balance nucleus.
Question: What cranial nerves nuclei are located in pons, determine its topography.
Task 2. A Patient complains of the upper eyelid prolapse (ptosis), dilated pupil
(mydriasis), divergent strabismus, double vision.
Question: What cranial nerve function is impaired in this patient?
Developer Teacher Ohanova M.I.
«С.Ж.АСФЕНДИЯРОВ АТЫНДАҒЫ ҰЛТТЫҚ МЕДИЦИНА УНИВЕРСИТЕТІ» КЕАҚ
NCJSC«ASFENDIYAROVNATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY»
Edition: 1
Department of Normal Anatomy Methodical instruction
Page3of6
Methodical instruction for the 1st year students of the General Medicine and
Pediatrics School
Theme of the lesson: Anatomy and topography of the sensory organs. Organ of
vision.Eyeball. Auxiliary structures of the eye, optic (II) nerve, oculomotor (III) nerve,
block (IV) nerve, abducent (VI) nerve: nuclei, branches. The organ of hearing and
balance.Vestibulo-cochlear (VIII) nerve.Organs of smell and taste. Olfactory (I) nerve.
Option 2
Task 1.Test questions (with one or with several correct answers).
Each question - 5 points. Maximum - 35 points
1. Ciliary muscle function C) m. rectus medialis
A) changes the lenscurvature D) m. rectus inferior
B) rotateseyeball E) m. rectus superior
C) changes the pupildiameter
D) closes eyelids 5. Three retinal neurons
E) wrinkles brow A) basal cells
B) multipolar cells
2.The muscles that move eye up: C) rods and cones
A) inferior rectus D) bipolar cells
B) inferior oblique E) lipid cells
C) transverse muscle
D) superior rectus 6. Photosensitive retinal visual cells
E) superior oblique A) fibroblast
B) myocytes
3. The muscles acting on the auditory C) rods and cones
ossicles: D) ganglion cells
A) m .sphincter pupillae E) pigment cells
B) m. stapedius
C) m. dilatator pupillae 7. The anatomical formations of middle
D) m. tensor tympani ear:
E) m. risorius A) auricula
B) cavitas tympani
4.What eyeball muscle damage leads to C) meatusacusticusexternus
diplopia: D) membrana tympani
A) m. obliquus inferior E) ossiculaauditus
B) m. obliquus superior
Developer Teacher Ohanova M.I.
«С.Ж.АСФЕНДИЯРОВ АТЫНДАҒЫ ҰЛТТЫҚ МЕДИЦИНА УНИВЕРСИТЕТІ» КЕАҚ
NCJSC«ASFENDIYAROVNATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY»
Edition: 1
Department of Normal Anatomy Methodical instruction
Page4of6
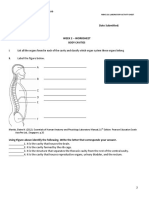
Task 2.There are 5 steps in the picture. 1 step - 7 points. Maximum 35 points
1 What is the eye layer №1
2 Name the nerve №2
3 What is the visual analyzer cortical
center №3
4 What is the subcortical center of
vision №4
5 What is this №5
Task 3. The situational tasks solution. For the correct solution of one task - 15 points.
Maximum 30 points
Task 1. The patient complains of double vision in the eyes when looking down and
limiting the mobility of the eyeball down.
Question: What nerve is affected in this patient?
Task 2. In the 5 years old patient with oculomotor nerve damage a triad of symptoms is
described: drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis), dilated pupil (mydriasis), exotropia.
Question: Give anatomical justification for the listed symptoms appearance in this
patient.
Developer Teacher Ohanova M.I.
«С.Ж.АСФЕНДИЯРОВ АТЫНДАҒЫ ҰЛТТЫҚ МЕДИЦИНА УНИВЕРСИТЕТІ» КЕАҚ
NCJSC«ASFENDIYAROVNATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY»
Edition: 1
Department of Normal Anatomy Methodical instruction
Page5of6
Methodical instruction for the 1st year students of the General Medicine and
Pediatrics School
Theme of the lesson: Anatomy and topography of the sensory organs. Organ of vision.
Eyeball. Auxiliary structures of the eye, optic (II) nerve, oculomotor (III) nerve, block
(IV) nerve, abducent (VI) nerve: nuclei, branches. The organ of hearing and
balance.Vestibulo-cochlear (VIII) nerve. Organs of smell and taste. Olfactory (I) nerve.
Option 3
Task 1.Test questions (with one or with several correct answers).
Each question - 5 points. Maximum - 35 points
1. Anatomical formations of the internal D) ciliary body
ear: E) retina
A) auricula
B) cavitas tympani 5. The olfactory analyzer receptor is:
C) labyrinthusosseus А) Corti's organ of the inner ear
D) labyrinthusmembranaceus В) ampoule crest, spots of saccule and
E) ossiculaauditus utricle of inner ear
С) specific cells in mucous membrane of
2. Cortical end of the visual analyzer superior nasal concha
A) inferior temporal gyrus D) rods
B) superior temporal gyrus E) cones
C) calcarine sulcus
D) postcentralgyrus 6. Olfactory and abducent nerves are
E) precentralgyrus pairs of cranial nerves:
A) I
3. The auditory analyzer receptor is: B) VI
А) Corti's organ of inner ear C) X
В) ampoule crest, spots of saccule and D) XIII
utricle of inner ear E) IX
С) specific cells in mucous membrane of
superior nasal concha 7. Optic, trochlea and oculomotor nerve
D) rods are pairs of cranial nerves
E) cones A) II
B) IV
4.Eyeball membrane containing dilator C) III
and sphincterof a pupil D) XIII
A) sclera E) IX
B) cornea
C) iris
Developer Teacher Ohanova M.I.
«С.Ж.АСФЕНДИЯРОВ АТЫНДАҒЫ ҰЛТТЫҚ МЕДИЦИНА УНИВЕРСИТЕТІ» КЕАҚ
NCJSC«ASFENDIYAROVNATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY»
Edition: 1
Department of Normal Anatomy Methodical instruction
Page6of6
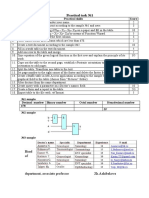
Task 2.There are 5 steps in the picture. 1 step - 7 points. Maximum 35 points
1 What is the anatomical formation? №1
2 What is the anatomical formation? №2
3 What is the anatomical formation? №3
4 What is the anatomical formation? №4
5 What is the anatomical formation? №5
Task 3. The situational tasks solution. For the correct solution of one task - 15 points.
Maximum 30 points
Task 1. In cases of the auricle structure violation otoplasty is performed, which
involves surgery of the auricle cartilage and soft tissues. Otoplasty is aesthetic and
reconstructive. The first changes only the auricle shape, the second has more difficult
task - the creation of a completely or partially missing auricle.
Question: Describe the auricle structure.
Task 2. On examination the patient has a converging strabismus and complaints of
double vision.
Question: What nerve is affected in the patient?
Developer Teacher Ohanova M.I.
You might also like
- Medical Terminology For Health Professions Spiral Bound Version Mindtap Course List 9Th Edition Ehrlich Full ChapterDocument68 pagesMedical Terminology For Health Professions Spiral Bound Version Mindtap Course List 9Th Edition Ehrlich Full Chapterjames.radford791100% (7)
- Cognitive Psychology and Its Implications 8th Edition Anderson Test BankDocument20 pagesCognitive Psychology and Its Implications 8th Edition Anderson Test BankJacobFoxgipbn95% (19)
- Histology Final ExamDocument33 pagesHistology Final ExamAlok Kumar75% (4)
- Kaznmu SyllabusDocument15 pagesKaznmu SyllabusAlok Kumar100% (1)
- S6 - Q2 - DLPS - Week 1 To 5Document302 pagesS6 - Q2 - DLPS - Week 1 To 5Dom MartinezNo ratings yet
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument5 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Fish N FrogDocument23 pagesRespiration in Fish N FrogHazirah HussinNo ratings yet
- For Stud Less 11Document15 pagesFor Stud Less 11xtomx1904No ratings yet
- Tus 2013 NisanDocument22 pagesTus 2013 NisanAsma MajidiNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly 23-24 Grade 5 - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly 23-24 Grade 5 - Answer KeyshamshadNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organs PDFTanzila SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense OrgansDocument20 pagesSelina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense OrgansDeepakNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument43 pagesBasicxakos16766No ratings yet
- Tus 2013 EylulDocument21 pagesTus 2013 EylulAsma MajidiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EBB 2023Document46 pagesQuestion Bank EBB 2023Muhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansDocument19 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansParardha DharNo ratings yet
- Exam Biology f4Document2 pagesExam Biology f4fardowsomoalimhassanNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: Pattern 2012)Document114 pagesNeuroanatomy: Pattern 2012)Devsya DodiaNo ratings yet
- Tus 2014 EylulDocument24 pagesTus 2014 EylulAsma MajidiNo ratings yet
- Terminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)Document8 pagesTerminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)KES SCIENCE FYJC PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-10 at 11.40.36 AMDocument67 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-10 at 11.40.36 AMAnchal LohanaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Chapter 3-Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesBiology: Chapter 3-Human Anatomy and PhysiologyMaahrukh Shifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - WS - X-24-25Document4 pagesNervous System - WS - X-24-25shnc1801No ratings yet
- Test, Questions and Clinical - Cases in NeurologyDocument111 pagesTest, Questions and Clinical - Cases in NeurologyPurwa Rane100% (1)
- Biology Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesBiology Sense OrgansasdasdNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Year 1Document8 pagesOphthalmology Year 1Malak Al ShammariNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System-Dr54gvs6Document26 pagesThe Skeletal System-Dr54gvs6Abdo HusseinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test BankDocument38 pagesPrinciples of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bankaidenqpepe100% (17)
- Principles of Animal Physiology 3Rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Animal Physiology 3Rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full Chapter PDFAndrewRobinsonixez100% (12)
- CHAPTER 11 Nervous System Spinal Cord PRETEST With AnswersDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 11 Nervous System Spinal Cord PRETEST With AnswersanaflaviaaguiarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Document33 pagesLab Manual - Cranial Nerves - Atlas - Part - 1Катерина ЛяшинаNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine and Nervous SystemTashi OngNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 - Rev Worksheet 1 (23-24) Answer KeyDocument5 pagesGrade 5 - Rev Worksheet 1 (23-24) Answer KeyshamshadNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz - NervesDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz - NervesChantel AceveroNo ratings yet
- XBHA2103 (Human Anatomy & Physiology) - Lab Sheet Jan 2022Document23 pagesXBHA2103 (Human Anatomy & Physiology) - Lab Sheet Jan 2022zulhusniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Seeleys Anatomy Physiology 12th by Vanputte DownloadDocument49 pagesTest Bank For Seeleys Anatomy Physiology 12th by Vanputte DownloadBenjaminWilsongaco100% (22)
- Tutorial 7 - Cranial N and ANS-teacherDocument4 pagesTutorial 7 - Cranial N and ANS-teacherL HYNo ratings yet
- APPSY Past PPR PDFDocument93 pagesAPPSY Past PPR PDFHafsa KhalidNo ratings yet
- Week 2 WS-Body Cavities and RegionsDocument2 pagesWeek 2 WS-Body Cavities and RegionsGHEIST INC.No ratings yet
- PM291 ErrataDocument10 pagesPM291 ErrataServal GideonNo ratings yet
- 6 - Embryology - PASS - MRCOG 2017Document22 pages6 - Embryology - PASS - MRCOG 2017emadhishamaburawiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank instant download all chapterDocument27 pagesPrinciples of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank instant download all chaptercaslaanttu58100% (4)
- Download Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank all chaptersDocument37 pagesDownload Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank all chaptersanilocrusz100% (6)
- Important QuestionsDocument38 pagesImportant Questionsas3941asNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full ChapterDocument37 pages(Download PDF) Principles of Animal Physiology 3rd Edition Moyes Test Bank Full Chapterrodaleyovesh0100% (8)
- 185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorDocument60 pages185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorMostafa Montaser100% (5)
- Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesEssentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Marieb Solutions Manualdipolarramenta7uyxw100% (26)
- Question Paper - Vetm 2002 - December - Final Examination - 2020-21Document10 pagesQuestion Paper - Vetm 2002 - December - Final Examination - 2020-21TheBoss 20No ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument4 pagesMIDTERMArchon BanzonNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Mid-Term ReviewDocument61 pagesOphthalmology Mid-Term ReviewMax TraderNo ratings yet
- Cells, Human Reproduction and HeredityDocument28 pagesCells, Human Reproduction and HeredityYuenHei KwokNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationDocument24 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationhelloNo ratings yet
- Anatomi, Fisiologi Mata Serta Overview RZDocument44 pagesAnatomi, Fisiologi Mata Serta Overview RZEuginia Yosephine100% (1)
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQUmair SaudNo ratings yet
- Diploma Pharmacy First Year - Hap - MCQSDocument13 pagesDiploma Pharmacy First Year - Hap - MCQSAnitha Mary Dambale92% (36)
- Biology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 5Document6 pagesBiology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 5Kamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Neuroscience: Lecture 3: Windows To The BrainDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Computational Neuroscience: Lecture 3: Windows To The BrainNAGAVARSHININo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 8Document5 pagesLab Exercise 8Yeong-Ja KwonNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy MCQ2Document5 pagesNeuroanatomy MCQ2michaelkingtz01No ratings yet
- Neuro DambiDocument51 pagesNeuro DambiKerim SabicNo ratings yet
- Anaphy NervousDocument6 pagesAnaphy NervousArcher RiegoNo ratings yet
- AzadDocument2 pagesAzadrifat iqbalNo ratings yet
- Nlknpast AppDocument7 pagesNlknpast AppUCL SportsNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Grade X Biology PT2Document4 pagesPractice Paper Grade X Biology PT2setidi1975No ratings yet
- 2 5273733825283753522 PDFDocument5 pages2 5273733825283753522 PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- ENT Atf-93-131Document10 pagesENT Atf-93-131Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- The List of Exam Test Items in The Discipline "Molecular Biology" For The 1st Year Students, Specialty "General Medicine", 2019-2020 Academic YearDocument17 pagesThe List of Exam Test Items in The Discipline "Molecular Biology" For The 1st Year Students, Specialty "General Medicine", 2019-2020 Academic YearAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- 1st Midterm Control PDFDocument13 pages1st Midterm Control PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- 13-Theme - Practice - For Student of IndiaDocument2 pages13-Theme - Practice - For Student of IndiaAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Department Informatics With Biophysics Course Methodical Recommendations EditionDocument5 pagesDepartment Informatics With Biophysics Course Methodical Recommendations EditionAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- (29final) 1125angl FinalDocument133 pages(29final) 1125angl FinalAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Phy123 PDFDocument2 pagesPhy123 PDFAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Histology With AnsDocument166 pagesHistology With AnsAlok Kumar0% (1)
- 2 Part - Test MHKDocument36 pages2 Part - Test MHKAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- State Exam Questions +Document29 pagesState Exam Questions +Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Part - Test MHKDocument33 pages1 Part - Test MHKAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Trauma MarrowDocument5 pagesThoracic Trauma MarrowAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS GM 2019-20 EnglishDocument63 pagesSYLLABUS GM 2019-20 EnglishAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical SkillsDocument1 pagePractical SkillsAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- 399 Bob StatementDocument1 page399 Bob StatementAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical Task 1Document1 pagePractical Task 1Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Ashiq CH 16Document3 pagesAshiq CH 16Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous and Re Ex OvulatorsDocument14 pagesSpontaneous and Re Ex OvulatorsFazal Akbar KhaliliNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY CHAPTER 8 Form 4Document21 pagesBIOLOGY CHAPTER 8 Form 4husnäNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Collections.Document335 pagesScience Form 3 Collections.Fazil JayNo ratings yet
- SBI3U Chapter 10 Self-QuizDocument6 pagesSBI3U Chapter 10 Self-QuizJannette JaneNo ratings yet
- Local Media5742365695864783121Document13 pagesLocal Media5742365695864783121Brian Voyd RebitoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesCirculatory SystemAlizaNo ratings yet
- Aad Abdomen WorksheetDocument15 pagesAad Abdomen WorksheetAchNo ratings yet
- Coronary CirculationDocument33 pagesCoronary CirculationAayushman YadavNo ratings yet
- Science 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesScience 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDyaan TrajicoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesLecture 1 Respiratory SystemArnelNo ratings yet
- Blood Disorders LimmerEducationDocument1 pageBlood Disorders LimmerEducationrehaan662No ratings yet
- CiullabbDocument71 pagesCiullabbMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Bony Pelvis and Fetal Skull: Dr. Iman Yousif AbdulmalekDocument46 pagesAnatomy of The Female Bony Pelvis and Fetal Skull: Dr. Iman Yousif AbdulmalekSnap SnhhNo ratings yet
- 15 - HomeostasisDocument13 pages15 - HomeostasisMuhammad TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma Power PointDocument44 pagesBronchial Asthma Power Pointjohnbech07No ratings yet
- RBC Morph Ulka 2Document69 pagesRBC Morph Ulka 2Rushi WalgudeNo ratings yet
- Massive Haemorrhage: P Donnelly B FergusonDocument18 pagesMassive Haemorrhage: P Donnelly B FergusonRizqiNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Cell TheoryDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Cell TheoryPercival RiegoNo ratings yet
- Feyer 2020 WvngoshawkDocument13 pagesFeyer 2020 WvngoshawkAgnieszka CzujkowskaNo ratings yet
- SOX Science5 Q2 M2of7Document18 pagesSOX Science5 Q2 M2of7Neil Joy Felomino Basa-LepalemNo ratings yet
- Biologi Kertas 1 Percubaan SPM 2012 MRSM K (Myschoolchildren - Com)Document42 pagesBiologi Kertas 1 Percubaan SPM 2012 MRSM K (Myschoolchildren - Com)Preedep BaradidathanNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord EOR - 163162 - 284 - 18220 - v1Document16 pagesUmbilical Cord EOR - 163162 - 284 - 18220 - v1Secret ImamNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3 - Fisiologi Sistem Muskuloskeletal (Dr. Adelia Handoko)Document36 pagesKuliah 3 - Fisiologi Sistem Muskuloskeletal (Dr. Adelia Handoko)Linda ayuNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesParts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryAnonymous giver100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants-2Document4 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants-2aditya kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 8th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 8th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFhuonghuyen2cp9ez100% (15)
- Nomina AnatomicaDocument4 pagesNomina AnatomicaIoana Purice100% (1)