Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Logarithms: Laws of Logarithm
Logarithms: Laws of Logarithm
Uploaded by
Arabella Sanchez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views8 pages1. The document discusses various mathematical topics including logarithms, progressions, trigonometry, and formulas.
2. Geometric progressions are defined with equations relating subsequent terms to the common ratio. Arithmetic progressions are defined with equations relating terms to the initial term and common difference.
3. Trigonometric functions are introduced with definitions of angle measures in degrees, radians, and gradians. Reference angles and trigonometric identities are also mentioned.
Original Description:
math
Original Title
math formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses various mathematical topics including logarithms, progressions, trigonometry, and formulas.
2. Geometric progressions are defined with equations relating subsequent terms to the common ratio. Arithmetic progressions are defined with equations relating terms to the initial term and common difference.
3. Trigonometric functions are introduced with definitions of angle measures in degrees, radians, and gradians. Reference angles and trigonometric identities are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views8 pagesLogarithms: Laws of Logarithm
Logarithms: Laws of Logarithm
Uploaded by
Arabella Sanchez1. The document discusses various mathematical topics including logarithms, progressions, trigonometry, and formulas.
2. Geometric progressions are defined with equations relating subsequent terms to the common ratio. Arithmetic progressions are defined with equations relating terms to the initial term and common difference.
3. Trigonometric functions are introduced with definitions of angle measures in degrees, radians, and gradians. Reference angles and trigonometric identities are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
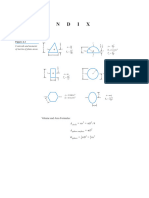
DISCRIMINANT GEOMETRIC PROGRESSION
LOGARITHMS B2-4ac 1.an = a1 * rn-1
n−1
D= 0 ,- REAL AND EQUAL 2.S= a(1−r )
Log822=1.486 MANTISSA D>0 and perfect square
UNEQUAL AND RATIONAL
- REAL, 1−r
3.Geometric Mean = a2 √ a 1 a 3
D>0, and not perfect square- REAL, a1
4.Infinite =
UNEQUAL AND IRRATIONAL 1−r
CHARACTERISTIC D<0 – COMPLEX AND IMAGINARY 2 a1 a 3
LOGARITHM 5.Harmonic Mean :
BASE a1 +a3
a2+ b2 +c 2
6. Quadratic Mean =
√ 4
LAWS OF LOGARITHM TERM WITH y
BINOMIAL THEOREM
r
MEAN PROPORTIONAL
a x
1. log a + log b= log ab n−r r
x
= b
or x= √ ab
2. log a – log b = log (a/b) nCr x y
Rth Term
log a
3. logb a = n C r−1 x n−r +1 y r −1 FOURTH PROPORTIONAL
log b
4. (log a)b = b log a a c bc
5. logx1 = 0
Coefficient of the Next Term =
b x
or x=
a
C=
6. logaab= b ¿
Coefficient of Previous Term∗Exponent of x of previous term ¿
X= logaN Exponent of THIRD
y of the P .PROPORTIONAL
T +¿ 1
2
a c
Ax= N = or x= b
b x a
QUADRATIC FORMULA ARITHMETIC PROGRESSION COIN PROBLEMS
1. an = am +(n-m)d
x=
−b ± √ b2−4 ac n
PENNY - 0.01
2a 2. S= (a1 + an )
2 NICKEL – 0.05
n
3. S= 2
(2 a1 +(n-1)d) DIME – 0.10
SUM OF ROOTS = -B/A
PRODUCT OF ROOTS = C/A 4. Arithmetic Mean =
a1+ a
3 QUARTER- 0.25
2
an = nth term HALF- 0.50
S = sum
d = common difference
DIGIT PROBLEMS TRIGONOMETRY REFERENCE ANGLES
10t + u : 2 Digit ANGLE MEASURES Q 1= θ =φ
100h + 10t + u : 3 Digit
CLOCK PROBLEMS Q 2= θ =(180−φ)
M =
60 H ± 2θ 1 Revolution:360 Degrees Q 3= θ =(φ−180)
11 2 π Radians Q4= θ =(360-φ
RATE / MOTION PROBLEMS
D= (R-C)T → Against /Upstream 400 Gradians
Coterminal Angle
D= (R+C)T → With/Downstream 6400 Mils θ= β
Meeting = D1+D2 + k(360)
Overtaking= d1=d2
Meeting (circular)= d1-d2
TYPES OBLIQUE TRIANGLE
PROPORTION AND VARIATION Null : 0 SINE LAW
mean Acute: less than 90 a b c
a:b=c:d
= =
sinA sinB sinC
Right: 90
extremes
Obtuse :Greater than 90 but less
than 180. COSINE LAW
WORK PROBLEMS Straight :exactly 180 a 2=b 2+c 2-2bccosA
1. Given rate working alone and/or time
together Reflex : Greater than 180 but b 2=a 2+c 2-2accosB
timetogether less than 360 c 2=b 2+a 2-2abcosA
Job done = ∑ rate working alone Perigon : One revolution: 360
2. Using man – hour Analysis TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTIES
1 job done = constant man-hr
Angle Pairs 1. Reciprocal Identities
∠ A+∠ B = 90 → sin(θ) = 1/csc(θ)
cos(θ) = 1/sec(θ)
COMPLEMENTARY tan(θ) = 1/cot(θ)
2. Pythagorean Identities
∠ A+∠ B = 180→
sin2 u+cos 2 u= 1
SUPPLEMENTARY 1+ tan 2 u = sec 2 u
∠ A+∠ B = 360 → 1+¿ cot 2 u = csc 2 u
3. Function of Negative Angles
sin(-u)= -sin(u) ; cos(-u) = cos(u)
EXPLEMENTARY tan(-u)= -tan(u) ; cot(-u) = -cot(u)
sec (-u)= sec(u) ; csc(-u) = -csc(u)
ADDITION FORMULAS OTHER TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITY 3. Given Two sides and
Included Angle
1
ab sin θ
2
4. Given Two Angles and
Included Sides
x2 sinθ sinα
2 sinβ
SUBTRACTION FORMULAS COFUNCTION IDENTITY 5. Circle inside a
sinθ= cos(90-θ) triangle
sec θ = csc (90-θ ) Rs
6. Circle outside a
tan θ = cot (90-θ )
triangle
CALCULATOR NOTATION abc
WRITTEN : sin 2y 4r
Calculator: sin (y)2
WRITTEN : sin y 2
7. Triangle with Escribed
Calculator : sin( y 2)
Circle
r(s-a)
DOUBLE ANGLE FORMULA AREA OF TRIANGLE SPHERICAL
1.With Known base and height
1 TRIGONOMETRY
Area = 2 bh 1 Minute of Arc = 1 nautical
2. With known Three Sides Mile
(Heron’s Formula ) 1 Nautical Mile = 6080 ft.
1 Nautical Mile =1.1516 Statue
Mile
1 Statue Mile = 5280 ft.
1 Knot = 1 Nautical Mile/
hr.
SPHERICAL TRIANGLE 5. Area of Pentagarm
Laws of Cosines for sides 3. Polygon Circumscribing a
Circle
A= 1.123 r 2
cos a = cosb cosc + sinb
nr 2 tan ¿)
sinc cosA 6. Area of Hexagram
4. Polygon Given Length of
cos b = cosa cosc + sina Side √ 3 r2
sinc cosB n x2
cos c = cosa cosb + sina 180
4 tan
sinb cosC n
Area of Spherical AREA AND PERIMETER OF REG. POLYGON PARABOLLIC SEGMENT
1. GIVEN APTHEM AND PERIMETER 1.Area
Triangle 1
pr 2
π r2 E 2 A= bh
A= : Where E= 3
180 2. Given apothem and number of sides
(A+B+C)-180 180
2.Spandrel
nr 2(tan ¿
n
3. Given Length and Number of Sides 1
A = bh
3
nx 2 180
(cot )
4 n
PLANE AND SOLID GEOMETRY ELLIPSE
1.Sum of Interior Angle 1. AREA
(n-2)*180 4. Given Radius of A= πab
2.Number of Diagonals Circumscribing Circle 2. Circumference
n 2
2
(n−3)
A= nR
(sin
360
) First Approximation
2 n o C= π ¿)
3.Polygon Inscribed in a
Circle Better Approximation
360
n R2 360 P= 2 nr (sin ) = π |3(a+b)-√(a+3 b)(3 a+b)
sin ( ¿ n
2 n |
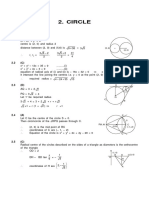
CIRCLE SPECIAL PLANE CURVES 4. Cycloid
1. LEMINISCATE Equation in Parametric Form :
1.Area
Equation in Rectangular Form x=a (θ−sinθ)
π r 2 = in terms of radius
2 (( x ¿ ¿ 2+ y 2) ¿ = a 2( x ¿ ¿ 2− y 2)¿ y=a(1−cosθ)
πD = in terms of Equation in Polar Form Area of One Arc
4
Diameter r 2 = a 2 cos 2 θ 3 π a2
Angle θ Arc Length of One Arc
2.Circumference of a Circle
= 45o = 8a
C=2 πr Total Area
3.Length of an Arc Distance Between two cusps
A= 2 a2
s=rθ D= 2 aπ
5.Area of Circular Sector 2. THREE LEAVED ROSE
1 1 2 Equation in polar form
r s or r θ
r =asin3 θ
2 2
Formula for n –
6.Area of Circular Segment leaved Rose
Case I r =acosnθ
Asector -Atriangle Total Area
1 2 πa 2
r ¿ -sinθ ¿
2 4
Case II 3.Four Leaved Rose
Asector + Atriangle Equation in Polar Form
1 2 r =asin2 θ
r ¿ +sin∝¿
2 For n – Leave Rose
r =asin¿ )
Total area
πa 2
2
7.Epicycloid 10. Astroid – A hypocycloid with four cusps
Equation in Rectangular Form
Parametric Equation 2 2 2
a+ b 3 3 = 3
x=(a+b) cos θ−bcos ( )θ x +y a
b Equation In Parametric Form
a+b x=a cos 3 θ
y=(a+ b)sinθ−bsin( )θ
b y=a sin3 θ
Area Bounded
3 2
πa
8
Arc Length (Total)
6a
8.Cardiod (An epicycloid of one 11. Trochoid
cusps) Parametric Equations
Equation in polar form X= aθ−bsinθ
r =2 a(1+cosθ) Y= a−bcosθ
Area Bounded by the Curve Three Possible Cases
6 π a2 b<a = Curtate cycloid
Arc Length of Curve b>a = Prolate cycloid
16a b=a = cycloid
9.Tractrix 12. Spiral of
Equation in Parametric
Form Archimedes
θ
x=a (ln cot −cosθ) Equation in Polar
2
y=a sinθ Form
r =aθ
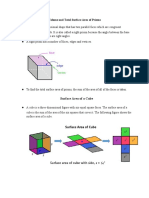
1. Cube b) Right Circular Cylinder
Total Surface Area
6 a2
Lateral Surface Area
Volume Ch
a2 2 πrh
Volume
Space Diagonal Bh
√3a π r2 h
Face Diagonal
√2 a
2. Rectangular 3. Prism
Parallelepiped
Area of Rectangular
Parellelepiped
2(ab+bc+ac)
Volume
Abc
Space Diagonal
d = √ a2 +b 2+ c2
4. Cylinder
a) Oblique Cylinder
Lateral surface Area
2 πrL
2 πrhcscθ
Volume
Bh
π r 2 ( Lsinθ)
You might also like
- Geometry Formulas All Gathered On One Easy Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGeometry Formulas All Gathered On One Easy Cheat Sheetnatashkan100% (2)
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisesDocument4 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisessreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Thinking Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Thinking Lesson Planapi-284504897No ratings yet
- MS Answer Key - CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts (Revised)Document158 pagesMS Answer Key - CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts (Revised)adar100% (1)
- Math in Our World - Module 3.1Document10 pagesMath in Our World - Module 3.1Gee Lysa Pascua Vilbar100% (1)
- AP Calculus AB Review Chapter 1Document21 pagesAP Calculus AB Review Chapter 1Preeti RatnamNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAlgebra 2 Lesson Planapi-534016621No ratings yet
- Service Tower Problem - Solutions: Adapted From Module 2: Worksheet 6 in Precalculus: Pathways To CalculusDocument5 pagesService Tower Problem - Solutions: Adapted From Module 2: Worksheet 6 in Precalculus: Pathways To Calculusapi-287216602100% (1)
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDocument5 pagesAP Calculus BC Study GuideJohn MoonNo ratings yet
- 8$20 AreaDocument26 pages8$20 AreaBaskaran SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathDocument70 pagesDiscrete MathAkanshaJainNo ratings yet
- Hs Geometry PDFDocument26 pagesHs Geometry PDFapi-255155256No ratings yet
- Abstract Algebra For Beginners - BeachyDocument177 pagesAbstract Algebra For Beginners - Beachycantor2000100% (1)
- Mass PointDocument5 pagesMass PointPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry (From: Applications of Trigonometry in Real LifeDocument6 pagesTrigonometry (From: Applications of Trigonometry in Real LifeLavishGulatiNo ratings yet
- Ratio & ProportionDocument8 pagesRatio & ProportionMbatutesNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: 7. Set TheoryDocument10 pagesBasic Concepts: 7. Set Theoryreeta ramNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument8 pagesDiscrete MathematicsLightcavalierNo ratings yet
- A Guide For Making ProofsDocument11 pagesA Guide For Making Proofsgule88No ratings yet
- Study BooksDocument6 pagesStudy BooksAster PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series No CommentsDocument33 pagesSequences and Series No CommentsSam Shah100% (1)
- Logarithms PDFDocument43 pagesLogarithms PDFFly I canNo ratings yet
- End Use Certificate - Blanket CertDocument1 pageEnd Use Certificate - Blanket CertsirjamlesNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDFDocument16 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDFValery Liz0% (1)
- Winter HW 2015 Math HL G12Document9 pagesWinter HW 2015 Math HL G12MishaZetov100% (1)
- MATH2412 Dot ProductDocument7 pagesMATH2412 Dot ProductmjdaleneziNo ratings yet
- Mock AP Exam 3 Review - MC ProblemsDocument36 pagesMock AP Exam 3 Review - MC ProblemsMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- The Chinese Remainder TheoremDocument9 pagesThe Chinese Remainder Theoremna_hariprsadNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras Theorem LessonDocument5 pagesPythagoras Theorem Lessononek1edNo ratings yet
- Calculus 5th Ed - Deborah Hughes-Hallet - Chap18-SolsDocument58 pagesCalculus 5th Ed - Deborah Hughes-Hallet - Chap18-SolsHector NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Goldbach Conjecture Proof Miles MathisDocument4 pagesGoldbach Conjecture Proof Miles MathisRobertoNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Rational Root TheoremDocument15 pages3.3 Rational Root TheoremJoseph S. Palileo Jr.No ratings yet
- Trig Quiz 1-A Sample Answer KeyDocument2 pagesTrig Quiz 1-A Sample Answer KeysdenoyerNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Nut ShellDocument6 pagesLinear Algebra Nut ShellSoumen Bose100% (1)
- A Brief History of GeometryDocument29 pagesA Brief History of GeometryDie A Muslimah100% (1)
- Proof TheoryDocument93 pagesProof TheoryWillNo ratings yet
- Abstract Algebra Cheat Sheet PDFDocument5 pagesAbstract Algebra Cheat Sheet PDFZsofia PopNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Question Paper Set GDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 7 Mathematics Question Paper Set GaaNo ratings yet
- Gases and Atmospheric ChemistryDocument10 pagesGases and Atmospheric ChemistryKatheeja MusatheekNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of College Geometry 2nd Ed. - E. M. HemmerlingDocument240 pagesFundamentals of College Geometry 2nd Ed. - E. M. HemmerlingPetro Cnel100% (1)
- Mathematics is Beautiful: Suggestions for people between 9 and 99 years to look at and exploreFrom EverandMathematics is Beautiful: Suggestions for people between 9 and 99 years to look at and exploreNo ratings yet
- Free Trigonometry Tutorials and ProblemsDocument9 pagesFree Trigonometry Tutorials and ProblemsMicheal JordanNo ratings yet
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions - 0Document116 pagesExponential and Logarithmic Functions - 0Rommel CruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Taylor's Theorem PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 10 Taylor's Theorem PDFTu ShirotaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Graph TheoryDocument32 pagesAn Introduction To Graph TheoryTitei PaulNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsDocument15 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsLymenson BoongalingNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming ExamplesDocument2 pagesDynamic Programming ExamplesHunegnaw MelkamuNo ratings yet
- Area Bounded by A CurveDocument15 pagesArea Bounded by A CurveRajesh MarkNo ratings yet
- Growth and DecayDocument38 pagesGrowth and DecayMarvin LabajoNo ratings yet
- Hands On GeometryDocument9 pagesHands On Geometrytina_cardone1No ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Fall'20Document6 pagesLinear Algebra Fall'20rNo ratings yet
- Advanced CalculusDocument210 pagesAdvanced CalculusElliot Lu100% (2)
- Attacking Problems in Logarithms and Exponential FunctionsFrom EverandAttacking Problems in Logarithms and Exponential FunctionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Additional Mathematics Summary NotesDocument3 pagesAdditional Mathematics Summary NotesDavid Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Figure A.1 (Centroids and Moment of Inertia)Document1 pageFigure A.1 (Centroids and Moment of Inertia)Raziel Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Formulae 2Document5 pagesFormulae 2ajay penumalaNo ratings yet
- Txbook AppendixDocument12 pagesTxbook AppendixSai PranayNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document11 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4THINES REVI100% (12)
- Acoustics QuestionsDocument6 pagesAcoustics QuestionsArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument1 pageGeneral ChemistryArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Interview Guides: Help Desk Job DutiesDocument7 pagesInterview Guides: Help Desk Job DutiesArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Mock BoardDocument2 pagesMathematics Mock BoardArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics: First Failure AnnunciatorsDocument2 pagesIndustrial Electronics: First Failure AnnunciatorsArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Group Study Team OliverDocument3 pagesGroup Study Team OliverArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Radar Sytem With Liquid Crystal DisplayDocument3 pagesUltrasonic Radar Sytem With Liquid Crystal DisplayArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines DocuDocument3 pagesTransmission Lines DocuArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Day 2 PDFDocument64 pagesDay 2 PDFArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Xerox Exam 2nd Sem 2016 - 2017Document152 pagesXerox Exam 2nd Sem 2016 - 2017Arabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Comp UletDocument4 pagesComp UletArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument42 pagesDC MotorsArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine LawDocument33 pagesSine and Cosine LawBretana joanNo ratings yet
- Isometric Projection Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesIsometric Projection Tutorial Questionsjimmy johnNo ratings yet
- Fractals and TessellationsDocument57 pagesFractals and Tessellationsyazz100% (2)
- Balotario de TrigonometriaDocument2 pagesBalotario de TrigonometriaRamonEustaquioCaroBayonaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: - To Model Problems Using Linear Equations VocabularyDocument8 pagesObjectives: - To Model Problems Using Linear Equations Vocabularyapi-503409471No ratings yet
- Quiz Volume of Cylinders Cones and SpheresDocument5 pagesQuiz Volume of Cylinders Cones and SpheresdeagggNo ratings yet
- Xi Mathematics Practical ActivityDocument30 pagesXi Mathematics Practical ActivityAdarsh Kumar PadhanNo ratings yet
- Transformations Challenge Exam QuestionsDocument16 pagesTransformations Challenge Exam QuestionsShaaminiNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: NAME - SCOREDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: NAME - SCOREMarites James - LomibaoNo ratings yet
- CurvesDocument118 pagesCurvesAmitabha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Geometry PretestDocument3 pagesOlympiad Geometry PretestSatya RanjanNo ratings yet
- Circle (Solution)Document11 pagesCircle (Solution)ayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- ANGLEDocument37 pagesANGLEAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- MCOph 7 H UD7 PT 1 TXPDCW 4Document19 pagesMCOph 7 H UD7 PT 1 TXPDCW 4sivashnivaasagamNo ratings yet
- Geometry (RaMOthon) Complete RevisionDocument38 pagesGeometry (RaMOthon) Complete RevisionsaiNo ratings yet
- SMO 2007 Senior SolutionDocument12 pagesSMO 2007 Senior Solutionwmdsg50% (2)
- CEET416 - Reverse CurvesDocument3 pagesCEET416 - Reverse Curvespipeds100% (7)
- 2003QDocument3 pages2003QDương Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- TSA Andvolume of SolidsDocument14 pagesTSA Andvolume of SolidsJairNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Extra Exercises 3.1: Pythagoras' TheoremDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Extra Exercises 3.1: Pythagoras' TheoremPh DeNo ratings yet
- Torch of Life Academy High School Department 1 Quarter Period Geometry Quiz 3Document3 pagesTorch of Life Academy High School Department 1 Quarter Period Geometry Quiz 3Ean FagarNo ratings yet
- Math Sample Paper Class 8Document10 pagesMath Sample Paper Class 8RudraNo ratings yet
- Cls Jeead-18-19 Xiii Mat Target-3 Set-1 Chapter-9Document96 pagesCls Jeead-18-19 Xiii Mat Target-3 Set-1 Chapter-9Minee's KitchenNo ratings yet
- 511 Mat - 2018 PDFDocument7 pages511 Mat - 2018 PDFHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Brilliant Public School, Sitamarhi: IX - Maths Chapter NotesDocument67 pagesBrilliant Public School, Sitamarhi: IX - Maths Chapter Notessihg JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Centroid and Moments of InertiaDocument11 pagesCentroid and Moments of InertiaSheenah TelanNo ratings yet
- Simo CLASS 10Document4 pagesSimo CLASS 10suraj varma100% (1)
- CIKK Geometry Begin With Play Van HieleDocument16 pagesCIKK Geometry Begin With Play Van HieleAnastase KatalinNo ratings yet
- 01-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper-1Document7 pages01-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper-1SUB MOH MAYA HAI100% (1)