Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Coagulation Factors
Summary of Coagulation Factors
Uploaded by
yepCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hematology - Steininger ReviewDocument30 pagesHematology - Steininger ReviewIssa AlejoNo ratings yet
- TCCC-MP Test Answer Key 140602Document16 pagesTCCC-MP Test Answer Key 140602samfarmer333100% (2)
- Blood Biochemistry 2 (2021)Document29 pagesBlood Biochemistry 2 (2021)anis izzatiNo ratings yet
- Normal Hemostasis (Coagulation System)Document5 pagesNormal Hemostasis (Coagulation System)Kathryn Cyrel DuranNo ratings yet
- Hemost. & Coag - PhysiologyDocument71 pagesHemost. & Coag - PhysiologyariniNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument67 pagesHemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, Makassarnurliah armandNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis: Mechanisms of Blood CoagulationDocument2 pagesHemostasis: Mechanisms of Blood CoagulationAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis 2024Document39 pagesHemostasis 2024Fahmi AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument55 pagesHemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarMJ PutraNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Hemostasis & Koagulasi (Prof. Dr. Mansyur Arif, PH.D, SP - PK (K) )Document55 pagesMekanisme Hemostasis & Koagulasi (Prof. Dr. Mansyur Arif, PH.D, SP - PK (K) )ikram hanafiNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument65 pagesHemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarShibaNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 Reviewer (Midterms)Document20 pagesHema 2 Reviewer (Midterms)Rachel Marie M. Gania100% (1)
- Overcoming Protein Instability Problems During Fusion Protein CleavageDocument5 pagesOvercoming Protein Instability Problems During Fusion Protein CleavageAsmaNo ratings yet
- Haemostasis Foundation 1-October 2010Document51 pagesHaemostasis Foundation 1-October 2010cute_sakura_03No ratings yet
- L.i.1.konsep HemostasisDocument9 pagesL.i.1.konsep Hemostasisenoayuningsih zegaNo ratings yet
- Blood Coagulation SystemDocument46 pagesBlood Coagulation SystemFedrik Monte Kristo LimbongNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and CoagulationDocument16 pagesHemostasis and CoagulationRezaTiansahNo ratings yet
- HEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayDocument3 pagesHEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayGianna SablanNo ratings yet
- Aspek Laboratorium Kelainan HemostasisDocument48 pagesAspek Laboratorium Kelainan HemostasisriskypiradeNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and PlateletsDocument5 pagesCoagulation and PlateletsisahNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis/ Coagulation: Platelet AggregationDocument42 pagesHemostasis/ Coagulation: Platelet Aggregation크리스찰이No ratings yet
- Part 2 HematologyDocument42 pagesPart 2 Hematology크리스찰이No ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Physiology of HemostasisDocument2 pagesChapter 4. Physiology of HemostasisDumapis RichardNo ratings yet
- Hema Prelim MergedDocument112 pagesHema Prelim MergedRich Darlene Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- Review of The Molecular Basis of Coagulation Cell 1988Document14 pagesReview of The Molecular Basis of Coagulation Cell 1988tugcag.dumlupinarNo ratings yet
- Fisio Hemostasis Unmal 2019Document69 pagesFisio Hemostasis Unmal 2019Betseba NataliaNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis: Rahajuningsih D. Setiabudy Department of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of IndonesiaDocument37 pagesHemostasis: Rahajuningsih D. Setiabudy Department of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of IndonesiastellatrsNo ratings yet
- Kastur IDocument38 pagesKastur IKasturi MohantyNo ratings yet
- REVALIDA COMPRE HEMA2LAB MIXING STUDIES UnivSantoTomasDocument4 pagesREVALIDA COMPRE HEMA2LAB MIXING STUDIES UnivSantoTomasJemimah CainoyNo ratings yet
- Hematologi Pharmacolog: Hemostasis and Blood Coagulation CascadeDocument19 pagesHematologi Pharmacolog: Hemostasis and Blood Coagulation CascadeDivina ArenaNo ratings yet
- 028 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) Heparin - Mechanism of Action, Indications, ADRâ ™S, ContraindicationsDocument5 pages028 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) Heparin - Mechanism of Action, Indications, ADRâ ™S, ContraindicationsOliver Jacobe100% (1)
- HemostasisDocument57 pagesHemostasisGiorgi TamazashviliNo ratings yet
- 1.diagrams - GP & BloodDocument16 pages1.diagrams - GP & BloodPriya SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Platelets and HemostasisDocument13 pagesPlatelets and HemostasisDhanush SatheeshNo ratings yet
- 10-Platelet Structure and Function PDFDocument21 pages10-Platelet Structure and Function PDFAnil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 - Prelim Topic 2 - Platelet Ultrastructure, Function and KineticsDocument7 pagesHema 2 - Prelim Topic 2 - Platelet Ultrastructure, Function and KineticsLowenstein JenzenNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis Substituition and Mixing StudiesDocument13 pagesHemostasis Substituition and Mixing StudiesjosereyescclNo ratings yet
- Role of Platelets in Hemostasis and Their DisordersDocument45 pagesRole of Platelets in Hemostasis and Their DisordersrohantheirNo ratings yet
- Clase 9Document41 pagesClase 9mikela silvaNo ratings yet
- The Coagulation CascadeDocument8 pagesThe Coagulation Cascade8pvz96ktd9No ratings yet
- Midterm Secondary Hemostasis 1Document3 pagesMidterm Secondary Hemostasis 1Who KnowsNo ratings yet
- Bleeding: 1. Vessel Wall 2. Platelets 3. Coagulation Protein 4. Anticoagulant Protein 5. Fibrinolytic SystemDocument5 pagesBleeding: 1. Vessel Wall 2. Platelets 3. Coagulation Protein 4. Anticoagulant Protein 5. Fibrinolytic Systemsarguss14100% (3)
- ThromboelastographyDocument39 pagesThromboelastographyMarcelliaNo ratings yet
- Secondary HemostasisDocument26 pagesSecondary Hemostasisirishgopez24No ratings yet
- 3-17-08 Whitehill PDFDocument47 pages3-17-08 Whitehill PDFSindile MchunuNo ratings yet
- PitavastatinDocument46 pagesPitavastatinSeLecToR ck LeeNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Coagulation: Miklós MolnárDocument67 pagesHemostasis and Coagulation: Miklós MolnárHamzaNo ratings yet
- Coagulation of BloodDocument16 pagesCoagulation of BloodMoner ManushNo ratings yet
- Expression Vector, Baculovirus Expression Vector: Promila Sheoran Ph.D. Biotechnology GJU S&T HisarDocument18 pagesExpression Vector, Baculovirus Expression Vector: Promila Sheoran Ph.D. Biotechnology GJU S&T HisarYooobsan Nii barriitiNo ratings yet
- Platelet Adhesion Aids in Platelet Activation Which Vasoconstriction (Reduces Blood Flow) To StopDocument13 pagesPlatelet Adhesion Aids in Platelet Activation Which Vasoconstriction (Reduces Blood Flow) To StopLian ChanNo ratings yet
- 33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileDocument40 pages33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Hemostatic DisordersDocument7 pagesHemostasis and Hemostatic DisordersBlitzen BusaingNo ratings yet
- Nucleus - Structure and FunctionDocument36 pagesNucleus - Structure and FunctionMUHAMMAD SHAYANNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Concept MapDocument3 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation Concept MapphoebjaetanNo ratings yet
- Coagulation TestsDocument1 pageCoagulation TestsUWIMANA Jean ClaudeNo ratings yet
- Acute Care Biomarkers - V1Document1 pageAcute Care Biomarkers - V1Muniba NasimNo ratings yet
- Platelets: o Serotonin, ADP & ATP o Destroyed by RESDocument7 pagesPlatelets: o Serotonin, ADP & ATP o Destroyed by RESEunice AndradeNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Pituitary and Thyroid Disorders On Haemostasis, Potential Clinical ImplicationsDocument12 pagesThe Effects of Pituitary and Thyroid Disorders On Haemostasis, Potential Clinical ImplicationsTamara Silva FabresNo ratings yet
- Blood Faed Haemostasis 3 Coagulation Tests Intro To Bleeding Disorders Full PDFDocument46 pagesBlood Faed Haemostasis 3 Coagulation Tests Intro To Bleeding Disorders Full PDFAsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsFrom EverandCell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsAnne RidleyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)Document1 pageCharacteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)yepNo ratings yet
- Basella Rubra Biological Stain: Health Benefits of Basella (Vine Spinach)Document3 pagesBasella Rubra Biological Stain: Health Benefits of Basella (Vine Spinach)yepNo ratings yet
- WaloDocument67 pagesWaloyepNo ratings yet
- Instructions MPH Data: A. Process Workflow and AccountabilityDocument57 pagesInstructions MPH Data: A. Process Workflow and AccountabilityyepNo ratings yet
- Bachelor in Science of Medical Technology Central Luzon Doctors' Hospital Educational Institution S.Y. 2018 - 2019Document7 pagesBachelor in Science of Medical Technology Central Luzon Doctors' Hospital Educational Institution S.Y. 2018 - 2019yepNo ratings yet
- PA41 - R14001B - Clinical Chemistry SummaryDocument3 pagesPA41 - R14001B - Clinical Chemistry SummaryyepNo ratings yet
- Sa Kabilang MedyasDocument31 pagesSa Kabilang MedyasyepNo ratings yet
- Multiplication: Grade 3Document27 pagesMultiplication: Grade 3yepNo ratings yet
- ChinilinDocument37 pagesChinilinyepNo ratings yet
- Citizens Charter 2018Document77 pagesCitizens Charter 2018yepNo ratings yet
- Special Staining Cytochemistry: BY Zenaida Capistrano-Cajucom, RMT, Ma - Ed.Mgt, FpametDocument93 pagesSpecial Staining Cytochemistry: BY Zenaida Capistrano-Cajucom, RMT, Ma - Ed.Mgt, FpametyepNo ratings yet
- Gestational and Placental Disorders: Ovary Pregnancy Results From TheDocument4 pagesGestational and Placental Disorders: Ovary Pregnancy Results From TheyepNo ratings yet
- Alorica WAH Expectations Supplement RJBDocument3 pagesAlorica WAH Expectations Supplement RJByepNo ratings yet
- Appendix C ComputationDocument2 pagesAppendix C ComputationyepNo ratings yet
- WaloDocument67 pagesWaloyepNo ratings yet
- Bring My Device (BMD) Policy (Philippine Employees)Document4 pagesBring My Device (BMD) Policy (Philippine Employees)yepNo ratings yet
- Penis: Male Genital System and Lower Urinary TractDocument21 pagesPenis: Male Genital System and Lower Urinary TractyepNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document2 pagesScience 2yepNo ratings yet
- Opioids and Law EnforcementDocument16 pagesOpioids and Law EnforcementNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug ExcretionDocument61 pages8 Drug ExcretionAhmed YTNo ratings yet
- Literature Reviews Literature Review - 1 AimDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviews Literature Review - 1 AimShashank Cooled RanaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology by Elagouri MohammedDocument31 pagesGastroenterology by Elagouri MohammedStylesh GuRlyNo ratings yet
- HipertensiDocument28 pagesHipertensidokteraanNo ratings yet
- IQVIA Institute Biosimilar Shared Savings Programs in Europe 12-22 ForwebDocument44 pagesIQVIA Institute Biosimilar Shared Savings Programs in Europe 12-22 Forwebخالد العشريNo ratings yet
- ISR NG Chun Ruh2Document1 pageISR NG Chun Ruh2Yasmine SlhNo ratings yet
- Sotalol Drug CardDocument2 pagesSotalol Drug CardJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument6 pagesCaseMadhulika Sharma0% (1)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument4 pagesFundamentals of NursingMaricel DuposNo ratings yet
- Psikiatri Mantap UnlockedDocument100 pagesPsikiatri Mantap UnlockedFuad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Curofy Best ECG CasesDocument26 pagesCurofy Best ECG Casescnshariff@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Bahan LatihanDocument247 pagesBahan LatihanDasep DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Historypharmacopoeia 180817063405 PDFDocument111 pagesPharmacy Historypharmacopoeia 180817063405 PDFchandra sekhar gowra0% (1)
- Childhood Seizure DisordersDocument57 pagesChildhood Seizure DisordersashuNo ratings yet
- 10 DOH Approved MedicineDocument3 pages10 DOH Approved MedicineRonel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Formularium PDFDocument16 pagesFormularium PDFDewayu NanaNo ratings yet
- Aromatherapy As Complementary Medicine: Amira Ahmed Kamal El-Din El-AnssaryDocument13 pagesAromatherapy As Complementary Medicine: Amira Ahmed Kamal El-Din El-AnssarySava VijakNo ratings yet
- Clinical PharmacyDocument26 pagesClinical PharmacyboyapallymeghanaNo ratings yet
- AmebiasisDocument16 pagesAmebiasisNagendra NayakNo ratings yet
- Norgesic CMIDocument15 pagesNorgesic CMITechtureGNo ratings yet
- Requirements For Opening A Drugstore PDFDocument2 pagesRequirements For Opening A Drugstore PDFPsyar Lysa Javier67% (3)
- Delusional Disorder Case Study Psych ClinDocument13 pagesDelusional Disorder Case Study Psych Clinapi-655682809No ratings yet
- 9 Pharmacokinetics WorkbookDocument16 pages9 Pharmacokinetics WorkbookClayson BuftonNo ratings yet
- Biologics and Related Drugs - Definitions Naming and ExamplesDocument6 pagesBiologics and Related Drugs - Definitions Naming and ExamplesevacawleyNo ratings yet
- James Hupp, Head, Neck and Orofacial Infections. 2016-60-67Document11 pagesJames Hupp, Head, Neck and Orofacial Infections. 2016-60-67Hukjvccx JjyfdxxvbNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (Arb) Comparison ChartDocument1 pageAngiotensin Receptor Blocker (Arb) Comparison Chartanindia wardhani100% (1)
- Produk Lob Wajib ApotekDocument12 pagesProduk Lob Wajib ApotekQatrunnada Klinik PratamaNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Cannabis CBD Pharma With Role of Biotechnology Hydroponic in IndiaDocument1 pageNext Generation Cannabis CBD Pharma With Role of Biotechnology Hydroponic in Indiamanas sewa aashramNo ratings yet
Summary of Coagulation Factors
Summary of Coagulation Factors
Uploaded by
yepOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Coagulation Factors
Summary of Coagulation Factors
Uploaded by
yepCopyright:
Available Formats
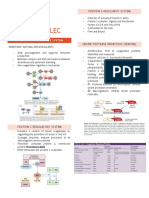
COAGULATON FACTOR
FACTOR SOURCE PATHWAY DESCRIPTION FUNCTION
I fibrinogen Liver Common Plasma Glycoprotein Adhesive protein which
340 kDa aids in fibrin clot
formation
II Prothrombin Liver common Vit K dependent; serine Presence in the activated
protease; 72 kDa form and main enzyme of
coag
III Tissue Secreted by damaged Extrinsic & Intrinsic Known as lipoprotein initiator of
factor/thromboplastin cells and platelets thromboplastin; extrinsic pathway
37 kDa
IV Calcium Bone and Gut Entire process Require for coag factors Metal cation which is
to bind to phospholipid; important in coag
mechanism
V Labile Factor/ Liver and platelet Intrinsic and Extrinsic 330 kDa Cofactor for the
Proaccelerin activation of prothrombin
to thrombin
(prothrombinase
complex)
VI
VII Stable factor/ Platelet and endothelium Extrinsic Vit K dependent serine With tissue factor,
proconvertin protease; initiates extrinsic
50 kDa pathway (F IX & X)
VIII liver Intrinsic 330 kDa Cofactor for intrinsic
Antihemophilic Factor activation of factor X
(which is form tenase
complex)
IX Plasma liver Intrinsic Vit K dependent; serine Activated form is the
Thromboplastin protease; 50 kDa enzyme for intrinsic
Component/ christmas activator of factor X
factor (forms tenase complex
with factor VIII)
X Stuart Prower Factor liver Intrinsic and Extrinsic Vit K dependent serine Activated form is the
protease; 58.9 kDA enzyme for final common
pathway of prothrombin
(forms prothrombinase
complex with factor V)
XI Plasma liver Intrinsic 160 kDa; serine protease Activates intrinsic
Thromboplastin activator of factor IX
Antecedent
XII Hageman Factor/ liver Intrinsic (activates 80 kDa; serine protease Initiates activated partial
Glass Factor plasmin) thromboplastin time
(aPTT) based intrinsic
pathway; activates factor
XI, VII and Prekellikrein
XIII Fibrin-stabilizing liver Retards fibrinolysis 320 kDa; Cross-link Transamidase which
Factor fibrin cross-links fibrin clot
Summary of Coagulation Factors
factors explanation
Contact group PK, HMWK, XII, XI Factors involved in initiation of
intrinsic pathway
Prothrombin group II, VII, IX, X Vitamin K–dependent factors.
Fibrinogen group I, V, VIII, XIII Factors acted on by thrombin (V,
VIII, & XIII are activated; I is
converted to fibrin). All are high
molecular weight proteins.
Factors in extrinsic pathway TF, VII
Factors in intrinsic pathway PK, HMWK, XII, XI, IX, VIII
Factors in common pathway X, V, II, I
Extrinsic tenase complex VIIa/TF Acts on X.
Intrinsic tenase complex IXa/VIIIa Acts on X.
Prothrombinase complex Xa/Va Acts on prothrombin
Factor VIII complex VIII:C & von Willebrand factor VIII:C is the procoagulant; VWF
(VWF) is the carrier protein
Produced in liver All
Require vitamin K for II, VII, IX, X
synthesis
Affected by Coumadin II, VII, IX, X All that require vitamin K.
(warfarin) Warfarin is a vitamin K
antagonist.
Consumed during clotting I, II, V, VIII, XIII Not present in serum.
Labile factors V, VIII
You might also like
- Hematology - Steininger ReviewDocument30 pagesHematology - Steininger ReviewIssa AlejoNo ratings yet
- TCCC-MP Test Answer Key 140602Document16 pagesTCCC-MP Test Answer Key 140602samfarmer333100% (2)
- Blood Biochemistry 2 (2021)Document29 pagesBlood Biochemistry 2 (2021)anis izzatiNo ratings yet
- Normal Hemostasis (Coagulation System)Document5 pagesNormal Hemostasis (Coagulation System)Kathryn Cyrel DuranNo ratings yet
- Hemost. & Coag - PhysiologyDocument71 pagesHemost. & Coag - PhysiologyariniNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument67 pagesHemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, Makassarnurliah armandNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis: Mechanisms of Blood CoagulationDocument2 pagesHemostasis: Mechanisms of Blood CoagulationAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis 2024Document39 pagesHemostasis 2024Fahmi AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument55 pagesHemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarMJ PutraNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Hemostasis & Koagulasi (Prof. Dr. Mansyur Arif, PH.D, SP - PK (K) )Document55 pagesMekanisme Hemostasis & Koagulasi (Prof. Dr. Mansyur Arif, PH.D, SP - PK (K) )ikram hanafiNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument65 pagesHemostatic Physiology: Mansyur Arif Dept. of Clinical Pathology Fac - of Medicine, Hasanuddin University, MakassarShibaNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 Reviewer (Midterms)Document20 pagesHema 2 Reviewer (Midterms)Rachel Marie M. Gania100% (1)
- Overcoming Protein Instability Problems During Fusion Protein CleavageDocument5 pagesOvercoming Protein Instability Problems During Fusion Protein CleavageAsmaNo ratings yet
- Haemostasis Foundation 1-October 2010Document51 pagesHaemostasis Foundation 1-October 2010cute_sakura_03No ratings yet
- L.i.1.konsep HemostasisDocument9 pagesL.i.1.konsep Hemostasisenoayuningsih zegaNo ratings yet
- Blood Coagulation SystemDocument46 pagesBlood Coagulation SystemFedrik Monte Kristo LimbongNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and CoagulationDocument16 pagesHemostasis and CoagulationRezaTiansahNo ratings yet
- HEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayDocument3 pagesHEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayGianna SablanNo ratings yet
- Aspek Laboratorium Kelainan HemostasisDocument48 pagesAspek Laboratorium Kelainan HemostasisriskypiradeNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and PlateletsDocument5 pagesCoagulation and PlateletsisahNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis/ Coagulation: Platelet AggregationDocument42 pagesHemostasis/ Coagulation: Platelet Aggregation크리스찰이No ratings yet
- Part 2 HematologyDocument42 pagesPart 2 Hematology크리스찰이No ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Physiology of HemostasisDocument2 pagesChapter 4. Physiology of HemostasisDumapis RichardNo ratings yet
- Hema Prelim MergedDocument112 pagesHema Prelim MergedRich Darlene Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- Review of The Molecular Basis of Coagulation Cell 1988Document14 pagesReview of The Molecular Basis of Coagulation Cell 1988tugcag.dumlupinarNo ratings yet
- Fisio Hemostasis Unmal 2019Document69 pagesFisio Hemostasis Unmal 2019Betseba NataliaNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis: Rahajuningsih D. Setiabudy Department of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of IndonesiaDocument37 pagesHemostasis: Rahajuningsih D. Setiabudy Department of Clinical Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of IndonesiastellatrsNo ratings yet
- Kastur IDocument38 pagesKastur IKasturi MohantyNo ratings yet
- REVALIDA COMPRE HEMA2LAB MIXING STUDIES UnivSantoTomasDocument4 pagesREVALIDA COMPRE HEMA2LAB MIXING STUDIES UnivSantoTomasJemimah CainoyNo ratings yet
- Hematologi Pharmacolog: Hemostasis and Blood Coagulation CascadeDocument19 pagesHematologi Pharmacolog: Hemostasis and Blood Coagulation CascadeDivina ArenaNo ratings yet
- 028 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) Heparin - Mechanism of Action, Indications, ADRâ ™S, ContraindicationsDocument5 pages028 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) Heparin - Mechanism of Action, Indications, ADRâ ™S, ContraindicationsOliver Jacobe100% (1)
- HemostasisDocument57 pagesHemostasisGiorgi TamazashviliNo ratings yet
- 1.diagrams - GP & BloodDocument16 pages1.diagrams - GP & BloodPriya SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Platelets and HemostasisDocument13 pagesPlatelets and HemostasisDhanush SatheeshNo ratings yet
- 10-Platelet Structure and Function PDFDocument21 pages10-Platelet Structure and Function PDFAnil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 - Prelim Topic 2 - Platelet Ultrastructure, Function and KineticsDocument7 pagesHema 2 - Prelim Topic 2 - Platelet Ultrastructure, Function and KineticsLowenstein JenzenNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis Substituition and Mixing StudiesDocument13 pagesHemostasis Substituition and Mixing StudiesjosereyescclNo ratings yet
- Role of Platelets in Hemostasis and Their DisordersDocument45 pagesRole of Platelets in Hemostasis and Their DisordersrohantheirNo ratings yet
- Clase 9Document41 pagesClase 9mikela silvaNo ratings yet
- The Coagulation CascadeDocument8 pagesThe Coagulation Cascade8pvz96ktd9No ratings yet
- Midterm Secondary Hemostasis 1Document3 pagesMidterm Secondary Hemostasis 1Who KnowsNo ratings yet
- Bleeding: 1. Vessel Wall 2. Platelets 3. Coagulation Protein 4. Anticoagulant Protein 5. Fibrinolytic SystemDocument5 pagesBleeding: 1. Vessel Wall 2. Platelets 3. Coagulation Protein 4. Anticoagulant Protein 5. Fibrinolytic Systemsarguss14100% (3)
- ThromboelastographyDocument39 pagesThromboelastographyMarcelliaNo ratings yet
- Secondary HemostasisDocument26 pagesSecondary Hemostasisirishgopez24No ratings yet
- 3-17-08 Whitehill PDFDocument47 pages3-17-08 Whitehill PDFSindile MchunuNo ratings yet
- PitavastatinDocument46 pagesPitavastatinSeLecToR ck LeeNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Coagulation: Miklós MolnárDocument67 pagesHemostasis and Coagulation: Miklós MolnárHamzaNo ratings yet
- Coagulation of BloodDocument16 pagesCoagulation of BloodMoner ManushNo ratings yet
- Expression Vector, Baculovirus Expression Vector: Promila Sheoran Ph.D. Biotechnology GJU S&T HisarDocument18 pagesExpression Vector, Baculovirus Expression Vector: Promila Sheoran Ph.D. Biotechnology GJU S&T HisarYooobsan Nii barriitiNo ratings yet
- Platelet Adhesion Aids in Platelet Activation Which Vasoconstriction (Reduces Blood Flow) To StopDocument13 pagesPlatelet Adhesion Aids in Platelet Activation Which Vasoconstriction (Reduces Blood Flow) To StopLian ChanNo ratings yet
- 33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileDocument40 pages33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Hemostatic DisordersDocument7 pagesHemostasis and Hemostatic DisordersBlitzen BusaingNo ratings yet
- Nucleus - Structure and FunctionDocument36 pagesNucleus - Structure and FunctionMUHAMMAD SHAYANNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Concept MapDocument3 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation Concept MapphoebjaetanNo ratings yet
- Coagulation TestsDocument1 pageCoagulation TestsUWIMANA Jean ClaudeNo ratings yet
- Acute Care Biomarkers - V1Document1 pageAcute Care Biomarkers - V1Muniba NasimNo ratings yet
- Platelets: o Serotonin, ADP & ATP o Destroyed by RESDocument7 pagesPlatelets: o Serotonin, ADP & ATP o Destroyed by RESEunice AndradeNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Pituitary and Thyroid Disorders On Haemostasis, Potential Clinical ImplicationsDocument12 pagesThe Effects of Pituitary and Thyroid Disorders On Haemostasis, Potential Clinical ImplicationsTamara Silva FabresNo ratings yet
- Blood Faed Haemostasis 3 Coagulation Tests Intro To Bleeding Disorders Full PDFDocument46 pagesBlood Faed Haemostasis 3 Coagulation Tests Intro To Bleeding Disorders Full PDFAsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsFrom EverandCell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsAnne RidleyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)Document1 pageCharacteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)yepNo ratings yet
- Basella Rubra Biological Stain: Health Benefits of Basella (Vine Spinach)Document3 pagesBasella Rubra Biological Stain: Health Benefits of Basella (Vine Spinach)yepNo ratings yet
- WaloDocument67 pagesWaloyepNo ratings yet
- Instructions MPH Data: A. Process Workflow and AccountabilityDocument57 pagesInstructions MPH Data: A. Process Workflow and AccountabilityyepNo ratings yet
- Bachelor in Science of Medical Technology Central Luzon Doctors' Hospital Educational Institution S.Y. 2018 - 2019Document7 pagesBachelor in Science of Medical Technology Central Luzon Doctors' Hospital Educational Institution S.Y. 2018 - 2019yepNo ratings yet
- PA41 - R14001B - Clinical Chemistry SummaryDocument3 pagesPA41 - R14001B - Clinical Chemistry SummaryyepNo ratings yet
- Sa Kabilang MedyasDocument31 pagesSa Kabilang MedyasyepNo ratings yet
- Multiplication: Grade 3Document27 pagesMultiplication: Grade 3yepNo ratings yet
- ChinilinDocument37 pagesChinilinyepNo ratings yet
- Citizens Charter 2018Document77 pagesCitizens Charter 2018yepNo ratings yet
- Special Staining Cytochemistry: BY Zenaida Capistrano-Cajucom, RMT, Ma - Ed.Mgt, FpametDocument93 pagesSpecial Staining Cytochemistry: BY Zenaida Capistrano-Cajucom, RMT, Ma - Ed.Mgt, FpametyepNo ratings yet
- Gestational and Placental Disorders: Ovary Pregnancy Results From TheDocument4 pagesGestational and Placental Disorders: Ovary Pregnancy Results From TheyepNo ratings yet
- Alorica WAH Expectations Supplement RJBDocument3 pagesAlorica WAH Expectations Supplement RJByepNo ratings yet
- Appendix C ComputationDocument2 pagesAppendix C ComputationyepNo ratings yet
- WaloDocument67 pagesWaloyepNo ratings yet
- Bring My Device (BMD) Policy (Philippine Employees)Document4 pagesBring My Device (BMD) Policy (Philippine Employees)yepNo ratings yet
- Penis: Male Genital System and Lower Urinary TractDocument21 pagesPenis: Male Genital System and Lower Urinary TractyepNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document2 pagesScience 2yepNo ratings yet
- Opioids and Law EnforcementDocument16 pagesOpioids and Law EnforcementNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug ExcretionDocument61 pages8 Drug ExcretionAhmed YTNo ratings yet
- Literature Reviews Literature Review - 1 AimDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviews Literature Review - 1 AimShashank Cooled RanaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology by Elagouri MohammedDocument31 pagesGastroenterology by Elagouri MohammedStylesh GuRlyNo ratings yet
- HipertensiDocument28 pagesHipertensidokteraanNo ratings yet
- IQVIA Institute Biosimilar Shared Savings Programs in Europe 12-22 ForwebDocument44 pagesIQVIA Institute Biosimilar Shared Savings Programs in Europe 12-22 Forwebخالد العشريNo ratings yet
- ISR NG Chun Ruh2Document1 pageISR NG Chun Ruh2Yasmine SlhNo ratings yet
- Sotalol Drug CardDocument2 pagesSotalol Drug CardJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument6 pagesCaseMadhulika Sharma0% (1)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument4 pagesFundamentals of NursingMaricel DuposNo ratings yet
- Psikiatri Mantap UnlockedDocument100 pagesPsikiatri Mantap UnlockedFuad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Curofy Best ECG CasesDocument26 pagesCurofy Best ECG Casescnshariff@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Bahan LatihanDocument247 pagesBahan LatihanDasep DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Historypharmacopoeia 180817063405 PDFDocument111 pagesPharmacy Historypharmacopoeia 180817063405 PDFchandra sekhar gowra0% (1)
- Childhood Seizure DisordersDocument57 pagesChildhood Seizure DisordersashuNo ratings yet
- 10 DOH Approved MedicineDocument3 pages10 DOH Approved MedicineRonel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Formularium PDFDocument16 pagesFormularium PDFDewayu NanaNo ratings yet
- Aromatherapy As Complementary Medicine: Amira Ahmed Kamal El-Din El-AnssaryDocument13 pagesAromatherapy As Complementary Medicine: Amira Ahmed Kamal El-Din El-AnssarySava VijakNo ratings yet
- Clinical PharmacyDocument26 pagesClinical PharmacyboyapallymeghanaNo ratings yet
- AmebiasisDocument16 pagesAmebiasisNagendra NayakNo ratings yet
- Norgesic CMIDocument15 pagesNorgesic CMITechtureGNo ratings yet
- Requirements For Opening A Drugstore PDFDocument2 pagesRequirements For Opening A Drugstore PDFPsyar Lysa Javier67% (3)
- Delusional Disorder Case Study Psych ClinDocument13 pagesDelusional Disorder Case Study Psych Clinapi-655682809No ratings yet
- 9 Pharmacokinetics WorkbookDocument16 pages9 Pharmacokinetics WorkbookClayson BuftonNo ratings yet
- Biologics and Related Drugs - Definitions Naming and ExamplesDocument6 pagesBiologics and Related Drugs - Definitions Naming and ExamplesevacawleyNo ratings yet
- James Hupp, Head, Neck and Orofacial Infections. 2016-60-67Document11 pagesJames Hupp, Head, Neck and Orofacial Infections. 2016-60-67Hukjvccx JjyfdxxvbNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (Arb) Comparison ChartDocument1 pageAngiotensin Receptor Blocker (Arb) Comparison Chartanindia wardhani100% (1)
- Produk Lob Wajib ApotekDocument12 pagesProduk Lob Wajib ApotekQatrunnada Klinik PratamaNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Cannabis CBD Pharma With Role of Biotechnology Hydroponic in IndiaDocument1 pageNext Generation Cannabis CBD Pharma With Role of Biotechnology Hydroponic in Indiamanas sewa aashramNo ratings yet