Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Values: Core Values and Motivators For Leadership Roles
Values: Core Values and Motivators For Leadership Roles
Uploaded by
Markus LandingtonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Values: Core Values and Motivators For Leadership Roles
Values: Core Values and Motivators For Leadership Roles
Uploaded by
Markus LandingtonCopyright:
Available Formats
VALUES
CORE VALUES AND MOTIVATORS FOR LEADERSHIP
ROLES
Report for: Sam Poole
ID: UH634244
Date: 10.28.2019
Copyright 2016 by Hogan Assessment Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
Introduction
The Leadership Forecast Values Report describes your core values and goals and how they can affect your career. Values
are an essential part of your identity—they describe who you are, what you stand for, and the environments in which you
will flourish. Values powerfully shape the choices that you will make about work, play, and relationships; they will impact
your career in four ways.
1. Drivers: Your values are your key drivers—the things in life that motivate you. Values determine your aspirations and
symbolize what you strive for and hope to attain. Your values define what you desire in your work and life.
2. Fit.: Your values determine how well you will fit with any organizational culture. Organizational cultures typically
reflect the values of senior management. People are happy and productive in cultures that are consistent with their
values, and they are distressed and unhappy working in cultures defined by values that differ from their own.
3. Leadership Style and Culture: Your values reflect what you find rewarding and pay attention to or what you dislike
and avoid. Thus, your values define the behavior that you like and reward and the behavior that you ignore or dislike.
Consequently, your values shape the kind of culture that you, as a leader, will create for your staff and subordinates.
4. Unconscious Biases: Values influence the decisions you make—about people, projects, plans, and strategy. Values
filter perceptions of experience, especially about what is desirable or undesirable, good or bad. Values typically
operate outside conscious awareness and bias both thought and action.
Ways to Use this Information.
As you review this report, you may find that your values are inconsistent with your career or the demands placed on you
by your role in your current organization. In addition, your day-to-day behavior may not help, and sometimes may even
hinder, your ability to realize your career goals. You should not try to change your values if they don’t fit with your career
or organization. Rather, by becoming aware of your values and unconscious biases, you can begin to adapt your behavior
in ways that will create a more productive working situation for yourself and your team.
This report is based on your scores on the Motives, Values, Preferences Inventory (MVPI). The report summarizes your key
drivers, the kind of culture you will create as a leader, the organizational cultures that you will prefer (or should try to
avoid), the factors that may unconsciously bias your decision making, and possible strategies for minimizing your biases
and leading productively.
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 2
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
Ways to Use this Information.
The next page defines the ten MVPI scales and the following page presents a graphic representation of your values
profile. This is followed by the report, which describes the meaning and implications of your score on each scale along
the dimensions described above. Finally, the end of this report contains values-based development suggestions
designed to help you to increase your leadership effectiveness. Please note that scores between the 65th and 100th
percentile are considered high and represent goals towards which you strive on a daily basis. The higher the score, the
more important a value or driver is to you in your work and personal life. Scores between the 36th and 64th percentile are
average and represent values that are of mixed importance to you. In this range, you may find values that are pleasure
points in your life or values where you are fairly indifferent. Scores between the 0 and 35th percentile are considered low
and represent values that are not core drivers for you. The lower your score on a dimension in this report, the higher the
likelihood that you are indifferent to that value.
High and low scores on every scale have important implications for careers.
The information in this report will help you better understand yourself and your values-driven tendencies. Armed with
this information, you can capitalize on your strengths and minimize your tactical miscues. You can become more aware
of the culture that you create and use this information to interact more successfully with others in your organization. In a
competitive business environment, self-awareness and effective self-regulation are important assets that will allow you
to become a more successful leader.
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 3
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
Definitions
The Leadership Forecast Values Report is based on your scores on the ten scales of the MVPI. Those scales are defined
below.
Indifferent to Visibility vs. Wanting to be Noticed
RECOGNITION
Seeking fame, appreciation, and acknowledgment Low scorers are unconcerned about official
attention; high scorers seek the spotlight.
Indifferent to Achievement/Competition vs. Being Perceived as Influential
POWER
Driving to achieve results, control resources, and gain responsibility. Low scorers are willing to
follow; high scorers want to take charge and make a difference.
Serious and Self-disciplined vs. Fun Loving and Enjoyment Seeking
HEDONISM
Wanting fun, variety, and enjoyment in the workplace. Low scorers are restrained and self-
disciplined; High scorers are fun-loving and want to enjoy work.
Valuing Self-Help vs. Wanting to Help the Others
ALTRUISTIC
Wanting to help people who are struggling or in need. Low scorers believe in self-reliance; high
scorers selflessly extend help to others.
Independent vs. Wanting Social Contact
AFFILIATION
Seeking opportunities to build social networks and collaborate with people. Low scorers
prefer to work alone; high scorers search for interaction and social acceptance.
Valuing Progress and Change vs. History and Convention
TRADITION
Respecting structure, rules, and authority. Low scorers challenge the status quo and are open
to change; high scorers respect hierarchy, authority, and the ways of the past.
Risk Tolerant vs. Risk Averse
SECURITY
Wanting stability, structure, and order. Low scorers easily tolerate uncertainty and risk; high
scorers value defined clarity and predictability.
Indifferent to Financial Matters vs. Focused on Commercial Outcomes
COMMERCE
Seeking wealth and financial success. Low scorers have modest financial aspirations; high
scorers pay close attention to financial matters.
Practical vs. Creative
AESTHETICS
Creating work products with a focus on innovation, style, and appearance. Low scorers care
about functionality; high scorers care about creative self-expression and the look and feel of
their work.
Intuitive vs. Analytical
SCIENCE
Preferring a rational, objective approach to decision-making. Low scorers prefer quick,
intuitive decisions; high scorers prefer deliberate, data-based decisions.
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 4
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
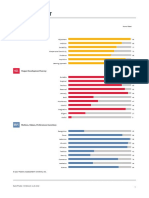
LEADERSHIP VALUES PROFILE
Scales
%
RECOGNITION
25
POWER
86
HEDONISM
98
ALTRUISTIC
95
AFFILIATION
94
TRADITION
41
SECURITY
35
COMMERCE
79
AESTHETICS
39
SCIENCE
80
LOW AVERAGE HIGH
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 5
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
RECOGNITION
Seeking fame, appreciation, and acknowledgment.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
25 • Avoid being the center of attention
• Be left alone to get on with your work
• Seek peace and quiet in the work environment
• Be a "silent contributor"
• Be seen as modest and unassuming
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Are calm and orderly
• Allow people to work independently
• Require limited team interactions and performance
• Avoid exuberant and noisy outbursts
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Publicly celebrate individual effort
• Encourage self-display
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Be muted, restrained, and relatively peaceful
• Value people who work and keep their heads down
• Minimize needless meetings and interactions
• Provide few rewards and praise only superior performance
• Assume people work for the intrinsic reward of doing a good job
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You may not notice when others want and need your attention
• You may assume that others know what you are thinking and, therefore, tend not to communicate
• You may make decisions without considering others’ needs for recognition
• You tend to think public recognition of performance is a waste of time
• You tend to prefer formal, scripted situations to spontaneous environments
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 6
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
POWER
Driving to achieve results, control resources, and gain responsibility.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
86 • Make an impact and get things done
• Be known for your accomplishments
• Create a legacy
• Be in charge of significant projects
• Have freedom of your actions
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Reward people who are bold and competitive
• Reward results with opportunities for advancement
• Empower people to get results
• Encourage individual initiative
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Fail to reward individual achievement
• Reward unproductive people
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Emphasize productivity and a drive for results
• Focus on ways to beat the competition
• Celebrate winners and winning
• Base rewards and promotions on merit, not politics
• Value innovation and creative problem solving
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You tend to frequently underestimate the competition
• You may refuse to acknowledge the possibility of failure
• You tend to prefer competition over cooperation
• You may not share success with your subordinates or team members
• You may be attracted to risky business propositions
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 7
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
HEDONISM
Wanting fun, variety, and enjoyment in the workplace.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
98 • Enjoy your life and your work
• Spend time with interesting people
• Innovate and create new solutions
• Work hard and play hard
• Explore new places and experiences
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Are fun loving and freewheeling
• Are comfortable with ambiguity or disorder
• Encourage you to work hard and play hard
• Provide chances for travel and entertainment
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Are excessively formal
• Emphasize procedures over results
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Be informal and open
• Take work and fun seriously
• Be flexible in policies, procedures, and protocol
• Emphasize results rather than methods
• Be moderately irreverent and limit testing
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You are likely to tolerate minor infractions of rules
• You may value change for its own sake
• You may dislike employees who can’t seem to have fun
• You are likely to make spontaneous and opportunistic decisions
• You tend to embrace novelty and eccentricity
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 8
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
ALTRUISTIC
Wanting to help people who are struggling or in need.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
95 • Meet people’s needs rather than increase profits
• Improve staff morale and well-being
• Do good for others
• Establish harmonious staff relations
• Motivate your staff to share your sense of social responsibility
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Care about and look after staff
• Have a public service agenda and mission
• Encourage volunteering
• Treat people with respect
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Appear to value profit over people
• Allow confrontation and rudeness
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Emphasize respect and consideration
• Accommodate individual needs
• Be democratic and solicit lots of input
• Be sensitive to issues of equity and fairness
• Maximize engagement and morale
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You may emphasize individual comfort over productivity
• You tend to believe that harmonious relations are more important than productivity
• You tend to undervalue the trait of self-reliance in your staff
• You may seek to promote social justice inside the building
• You tend to make decisions based on people’s feelings rather than data
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 9
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
AFFILIATION
Seeking opportunities to build social networks and collaborate with people.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
94 • Maximize interactions with others
• Work as part of group or team projects
• Experience variety and novelty in your work
• Seek out social acceptance and approval
• Maintain a large network of business contacts
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Rely on teams to accomplish work
• Require lots of interactions with people outside of the group
• Involve frequent meetings and public discussion
• Reward success for group, rather than individual, accomplishments
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Discourage face-to-face communication
• Require you to work alone
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Be team-based with flexible rules and roles
• Feature lots of meetings and opportunities to interact
• Provide spontaneous and flexible scheduling
• Provide lots of communication and feedback
• Discourage individual contributions
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You may prefer people to work together and cooperate
• You may encourage group based problem solving
• You may confuse activity (e.g., meetings and conversations) with productivity
• You may be an important catalyst for bringing diverse people together to collaborate
• You tend to believe that social interaction enhances productivity
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 10
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
TRADITION
Respecting structure, rules, and authority.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
41 • Question convention and authority
• Minimize external controls
• Seek novelty, change, and exploration
• Generate novel solutions to problems
• Pursue non-traditional work or careers
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Are democratic and consultative
• Challenge, innovate, and experiment
• Tolerate diversity
• Encourage initiative
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Are marked by authoritarian leadership
• Treat employees as expendable commodities
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Tend to be relaxed and informal
• Encourage spontaneity, openness, and initiative
• Value new ideas
• Seek interesting and novel projects
• Empower staff
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You tend to challenge authority
• You may dislike setting expectations for others
• You tend to be concerned with finding new ways to do things
• You may make decisions that promote autonomy and self-direction
• You may make decisions that reduce hierarchy
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 11
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
SECURITY
Wanting stability, structure, and order.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
35 • Find new challenges in life
• Have new experiences
• Be noticed by taking risks
• Explore novel ideas and new ways of doing things
• Test the ordinary limits
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Make decisions and move on
• Are fun, exciting, and even edgy
• Recruit colleagues who like risk and challenge
• Encourage spontaneous decision making
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Are routine and process-driven
• Discourage innovation and risk-taking
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Be experimental, lively, and bouncy
• Reward experimentation and risk taking
• Be flexible, quick, and nimble
• Have a bias toward action
• Be individualistic and sales oriented
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You may see change per se as the answer to problems
• You may make decisions based more on instinct than facts
• You may choose intuitively appealing actions and projects
• You tend to dislike cautious or defensive decision making
• You may interpret data in a creative, non-literal manner
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 12
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
COMMERCE
Seeking wealth and financial success.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
79 • Achieve wealth and fame
• Increase your compensation and net worth
• Gain power and control
• Win and beat the competition
• Create a legacy and be remembered
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Provide tangible rewards for performance
• Use metrics to evaluate performance
• Emphasize competition
• Have high aspirations
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Cannot define success
• Base rewards on seniority and not performance
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Value financial forecasting and cost benefit analysis
• Be alert for competitive threats
• Continuously evaluate productivity and performance
• Be intolerant of complacency
• Be driven by a sense of urgency
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You may see others as competitors
• You tend to see staff as a tool for your own success
• You may underestimate problems or threats
• You might be constantly searching for competitive advantage
• You might be averse to signs of sentimentality and tender-mindedness
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 13
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
AESTHETICS
Focusing on innovation, style, and appearance.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
39 • Make decisions based on established facts
• Deliver practical and workable solutions
• Translate vague ideas into practical reality
• Avoid seeming weak and indecisive
• Emphasize substance over style
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Are procedural and organized
• Work with tangible products and goals
• Are practical and action-oriented
• Have a practical, business-like orientation
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Are so fraught with emotion that nothing gets done
• Use style to obscure practicality
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Mistrust emotion and sentiment
• Emphasize functionality and minimize frills
• Minimize concern with design issues
• Make decisions based on facts rather than feelings
• Focus on outcomes over process
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You may not be especially interested in marketing issues
• You may have little interest in why something works
• You may show only mild concern with staff morale
• You may tend to avoid speculation and theoretical discussions
• You may focus on hard facts and prior experience
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 14
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
SCIENCE
Preferring a rational, objective approach to decision-making.
Drivers
You tend to be personally motivated by a desire to:
80 • Understand how things work
• Make data-based decisions
• Explore new technologies
• Find the right answers to problems
• Learn and stay up to date
Fit
You should be most comfortable working in environments that:
• Reward logic and rational analysis
• Support empirical inquiry
• Are modern and technology-savvy
• Encourage people to question authority
And you tend to dislike environments that:
• Favor faith-based decision making
• Fail to defend claims rationally
Leadership Style and Culture
As a leader, the culture you create tends to:
• Emphasize logic and rational problem solving
• Be argumentative
• Value being bright and being right
• Be picky about evidence
• Challenge others’ views and assertions
Unconscious Biases
You may not be aware of the following aspects of your leadership style:
• You may dislike concepts such as superstition, luck, or fate
• You may instinctively need to challenge received opinion
• You tend to prefer analysis over action
• You tend to distrust quick decisions
• You may resist gut-level judgments and individual experience
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 15
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
Development Opportunities
RECOGNITION
• Recognize that others need "pats on the back" more than you do
• Take an active interest in the performance of your staff; ask them for progress reports and tell them when they are
doing good work
• Outline explicitly your expectations for your team and each member of your staff
• Be tolerant of any accomplishments your staff may celebrate—even if you choose not to participate
POWER
• Are realistic about the probable success of your projects
• Understand that others can contribute even if they lack your drive to win
• Don’t turn every project into a competition for your subordinates; encourage them to cooperate
• Express appreciation to your staff for their contributions to projects
HEDONISM
• Make sure that others perceive you as businesslike and professional
• Be careful of spontaneous decisions—collect data to justify your choices
• Remember that when others do not want to socialize, it doesn’t reflect on you or their job commitment
• Tell your subordinates what change is needed but let them set the pace for change
ALTRUISTIC
• Recognize that people may try to exploit your good nature to avoid their responsibilities
• Remember that business requirements are usually more important than staff problems
• Respect the fact that other people may not share your interest in helping the less fortunate
• Remember that hard and important decisions rarely make everyone happy
AFFILIATION
• Don’t let social networking distract you from your leadership responsibilities
• Identify appropriate roles for subordinates as individuals and members of the team
• Show respect for corporate expectations, time limits, and deadlines
• Be sure that your staff perceives you as decisive, assertive, and in charge
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 16
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
Development Opportunities
TRADITION
• Remember that some people like and need rules
• Show respect for company expectations by staying on schedule for your performance goals
• Remember that not all of your subordinates will be self-motivated; give them clear direction and guidance
• Give your staff specific feedback regarding success and areas for improvement
SECURITY
• Try to understand the reasons behind current practices before changing them
• Recognize that your ideas may threaten some people
• Be sure that your staff supports your new ideas
• Be careful not to make decisions that are inconsistent with the organization’s goals
COMMERCE
• Avoid sacrificing long-term productivity for short-term payoffs
• Ask your staff for suggestions to enhance the quality of the workplace
• Remember that if your staff is happy, they will be more productive
• Listen to staff for ways to improve their connection to work
AESTHETICS
• Think carefully about potential gaps in the marketing effort
• Invite your staff to offer ideas about how to improve morale
• Think about the public image of you and your company
• Discuss with your colleagues possible future strategies for your team and the organization
SCIENCE
• Pay attention to the practical realities of business while you try to understand them more fully
• Remember that data and technology are tools, not ends in themselves
• Learn to speed up your decision making so that you can move on to new problems
• Ensure that your solutions to problems are realistic given the resources available
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 17
Leadership Forecast™ Values Report
Scales %
RECOGNITION 25
POWER 86
HEDONISM 98
ALTRUISTIC 95
AFFILIATION 94
TRADITION 41
SECURITY 35
COMMERCE 79
AESTHETICS 39
SCIENCE 80
LOW AVERAGE HIGH
Subscale Scores
Recognition Power Hedonism
Lifestyle Lifestyle Lifestyle
Beliefs Beliefs Beliefs
Occupational Preferences Occupational Preferences Occupational Preferences
Aversions Aversions Aversions
Preferred Associates Preferred Associates Preferred Associates
Altruistic Affiliation Tradition
Lifestyle Lifestyle Lifestyle
Beliefs Beliefs Beliefs
Occupational Preferences Occupational Preferences Occupational Preferences
Aversions Aversions Aversions
Preferred Associates Preferred Associates Preferred Associates
Security Commerce Aesthetics
Lifestyle Lifestyle Lifestyle
Beliefs Beliefs Beliefs
Occupational Preferences Occupational Preferences Occupational Preferences
Aversions Aversions Aversions
Preferred Associates Preferred Associates Preferred Associates
Science
Lifestyle
Beliefs
Occupational Preferences
Aversions
Preferred Associates
Sam Poole| UH634244 | 10.28.2019 18
You might also like
- William K. Wimsatt, JR., Cleanth Brooks - Literary Criticism - A Short History, 4-Volume Set-Routledge (2022)Document855 pagesWilliam K. Wimsatt, JR., Cleanth Brooks - Literary Criticism - A Short History, 4-Volume Set-Routledge (2022)Ángel Molina CFCNo ratings yet
- SITXHRM003 - LEAD AND MANAGE PEOPLE v1.1Document65 pagesSITXHRM003 - LEAD AND MANAGE PEOPLE v1.1pablo zarate50% (4)
- HiPo Sample Report Eng USDocument24 pagesHiPo Sample Report Eng USGabriela Calle GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Benjamin-Gehant Leaderfocus GlobalDocument10 pagesBenjamin-Gehant Leaderfocus Globalapi-637418753No ratings yet
- Challenge: Leadership ForecastDocument19 pagesChallenge: Leadership ForecastMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Leader BehaviorsDocument27 pagesLeader Behaviorsmar40134910No ratings yet
- MTP LeadershipDocument22 pagesMTP Leadershipapi-3712367No ratings yet
- Optimising StrengthsDocument3 pagesOptimising StrengthsJames BrookNo ratings yet
- Bato Brittaney DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesBato Brittaney DISC and MotivatorsBrittaney BatoNo ratings yet
- Maria Chabelie Violago AmaganDocument11 pagesMaria Chabelie Violago AmaganKENEDY FLORESNo ratings yet
- Paula Carmela DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesPaula Carmela DISC and MotivatorsPaula J.No ratings yet
- High Potential Talent: Core Competencies For Emerging LeadershipDocument36 pagesHigh Potential Talent: Core Competencies For Emerging LeadershipMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Barrientos Jessica DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesBarrientos Jessica DISC and MotivatorsJessNo ratings yet
- Patawaran Jhemmy DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesPatawaran Jhemmy DISC and MotivatorsEmma PataNo ratings yet
- DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesDISC and MotivatorsShahir S.No ratings yet
- Leadership Assessment Scorecard2.0Document18 pagesLeadership Assessment Scorecard2.0baishakhi.connorNo ratings yet
- Value SystemDocument26 pagesValue SystemARPIT TIRKEYNo ratings yet
- Hernanda Adhira DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesHernanda Adhira DISC and MotivatorsAdhira Hernanda Nurul UrfahNo ratings yet
- 4-Transformative Leadership 101Document40 pages4-Transformative Leadership 101irene apiladaNo ratings yet
- MENDOZA ANA LEE DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesMENDOZA ANA LEE DISC and MotivatorsANA LEE MENDOZANo ratings yet
- DISC Resut - Mona RabagoDocument11 pagesDISC Resut - Mona RabagomonaaurellerabagoworkNo ratings yet
- Legal Political Cultural EnvironmentDocument26 pagesLegal Political Cultural EnvironmentRaam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Disc & Motivators Report For: Princess Angel MonjasDocument11 pagesDisc & Motivators Report For: Princess Angel MonjasAngel MonjasNo ratings yet
- BaXal Mark Ronnie DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesBaXal Mark Ronnie DISC and MotivatorsMark Ronnie BañalNo ratings yet
- Go Josanne DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesGo Josanne DISC and MotivatorsgojosanneNo ratings yet
- NenejwhuwDocument11 pagesNenejwhuwnnek7089No ratings yet
- Global Environment Political, Legal and Cultural DifferencesDocument29 pagesGlobal Environment Political, Legal and Cultural DifferencesPulokesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Chavira Alan DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesChavira Alan DISC and MotivatorsAlan ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Leader BASIS - English USDocument16 pagesLeader BASIS - English USMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Disc & Motivators Report For: Jorgie MacaseroDocument11 pagesDisc & Motivators Report For: Jorgie Macaserojorgie macaseroNo ratings yet
- Workplace Insights - Bryan Mark A Sangma-Workplace-InsightsDocument5 pagesWorkplace Insights - Bryan Mark A Sangma-Workplace-InsightsAttong Bryan AmpangNo ratings yet
- Not Intuitively Obvious: Transition to the Professional Work EnvironmentFrom EverandNot Intuitively Obvious: Transition to the Professional Work EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Sanchez Rick Jerold DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesSanchez Rick Jerold DISC and MotivatorsRic SánchezNo ratings yet
- 4-Transformative Leadership 101Document40 pages4-Transformative Leadership 101gizex2013100% (2)
- Sarcia Toby Bruce DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesSarcia Toby Bruce DISC and MotivatorsTOBY BRUCE SARCIANo ratings yet
- Group No. b18 DobDocument13 pagesGroup No. b18 DobFahad DhanseNo ratings yet
- Disc & Motivators Report For: Maria RosalesDocument11 pagesDisc & Motivators Report For: Maria RosalesVictor Raul Solis GaravitoNo ratings yet
- Densing Wauie DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesDensing Wauie DISC and Motivatorswauie densingNo ratings yet
- Disc & Motivators Report For: Yo JoinDocument10 pagesDisc & Motivators Report For: Yo JoinlolsnchNo ratings yet
- Lpi Sample ReportDocument11 pagesLpi Sample ReportSimranKhuranaAroraNo ratings yet
- Life Coaching Report KHoustonDocument11 pagesLife Coaching Report KHoustonKyle HoustonNo ratings yet
- HBO-Contemporary Issues in LeadershipDocument19 pagesHBO-Contemporary Issues in LeadershipTin AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Job Aid Effective Delegation WorksheetDocument19 pagesJob Aid Effective Delegation WorksheetCosmin Corlatescu100% (2)
- Leadership Presentation 2Document17 pagesLeadership Presentation 2api-325817256100% (1)
- Aritya Putri Fena Rizki Disc and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesAritya Putri Fena Rizki Disc and MotivatorsFena ArityaNo ratings yet
- Disc & Motivators Report For: Ardy BellosilloDocument11 pagesDisc & Motivators Report For: Ardy BellosilloArdy BellosilloNo ratings yet
- Andiza Lucky DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesAndiza Lucky DISC and MotivatorsLucky AndizaNo ratings yet
- Erina Ira DISC and MotivatorsDocument11 pagesErina Ira DISC and MotivatorsiraalerinaNo ratings yet
- Tony RobinsDocument11 pagesTony Robinsjlatienza436No ratings yet
- Week 3 & 4Document23 pagesWeek 3 & 4Nur Aina Batrisyia Bt Abdul AzidNo ratings yet
- PCM 135 Leadership & Human Relations Management: Assignment Cum Test 2Document6 pagesPCM 135 Leadership & Human Relations Management: Assignment Cum Test 2Affan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Parco Mariah Moira DISC and Motivators 2Document11 pagesParco Mariah Moira DISC and Motivators 2Taylors VersionNo ratings yet
- Disc & Motivators Report For: Warnie CosioDocument11 pagesDisc & Motivators Report For: Warnie CosioKrisp KrispNo ratings yet
- Hogan Leadership Forecast Series With SummaryDocument63 pagesHogan Leadership Forecast Series With Summarysushil.tripathiNo ratings yet
- NB - Authentic Leadership - Article - Fin - May11thDocument5 pagesNB - Authentic Leadership - Article - Fin - May11thawokunle victorNo ratings yet
- TQM Leadership Module PDFDocument44 pagesTQM Leadership Module PDFOmer Sharif MadniNo ratings yet
- The Leader - Mahathir MohammadDocument4 pagesThe Leader - Mahathir Mohammadelusive15100% (4)
- Abdullah Roll No.23Document1 pageAbdullah Roll No.23amkhan8466No ratings yet
- Free Personality Test 16personalities 8Document1 pageFree Personality Test 16personalities 8Firdaus MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Every Leader Is An ArtistDocument4 pagesEvery Leader Is An ArtistBenjamin Codilla Gerez, Jr.No ratings yet
- Simple Satya Narayana HomaDocument4 pagesSimple Satya Narayana HomaMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Shiva Parvati S SansDocument4 pagesShiva Parvati S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Saptarshi S SansDocument4 pagesSaptarshi S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Santana Gopala S SansDocument4 pagesSantana Gopala S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Sani S SansDocument4 pagesSani S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Saraswati S SansDocument4 pagesSaraswati S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Pitri S SansDocument4 pagesPitri S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Ganapati S SansDocument4 pagesGanapati S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Simple Sri Rama HomaDocument4 pagesSimple Sri Rama HomaMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Narasimha S SansDocument4 pagesNarasimha S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Navagraha S SansDocument4 pagesNavagraha S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Durga S SansDocument4 pagesDurga S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Leader BASIS - English USDocument16 pagesLeader BASIS - English USMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Dattatreya S SansDocument4 pagesDattatreya S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Brihaspati S SansDocument4 pagesBrihaspati S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Insight: Hogan Personality Inventory (HPI)Document18 pagesInsight: Hogan Personality Inventory (HPI)Markus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Coaching: Development Plan For Strategic Self-AwarenessDocument18 pagesCoaching: Development Plan For Strategic Self-AwarenessMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- HC560419 EcHPISafetyMLV2D GeneralDocument5 pagesHC560419 EcHPISafetyMLV2D GeneralMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Chandi S SansDocument4 pagesChandi S SansMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Insight: Motives, Values, Preferences Inventory (MVPI)Document14 pagesInsight: Motives, Values, Preferences Inventory (MVPI)Markus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- HDS Insight SampleDocument15 pagesHDS Insight SampleMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- HC560419 EcMVPICCML Global - enDocument7 pagesHC560419 EcMVPICCML Global - enMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- HC560419 EcHPIHDSMVPIPESML General - enDocument7 pagesHC560419 EcHPIHDSMVPIPESML General - enMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Judgment: Decoding Your Thinking and Decision-Making StylesDocument9 pagesJudgment: Decoding Your Thinking and Decision-Making StylesMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Emotional: IntelligenceDocument9 pagesEmotional: IntelligenceMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Challenge: Leadership ForecastDocument19 pagesChallenge: Leadership ForecastMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- High Potential Talent: Core Competencies For Emerging LeadershipDocument36 pagesHigh Potential Talent: Core Competencies For Emerging LeadershipMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Basis USEnglish-1Document16 pagesBasis USEnglish-1Markus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Flash Report: Hogan Personality InventoryDocument2 pagesFlash Report: Hogan Personality InventoryMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- HC560419 EcHPICBML Global - enDocument6 pagesHC560419 EcHPICBML Global - enMarkus LandingtonNo ratings yet
- Module 6 UnderstandingDocument2 pagesModule 6 UnderstandingLaarni ToleteNo ratings yet
- Test 10 - Use of EnglishDocument4 pagesTest 10 - Use of EnglishMadestrusNo ratings yet
- BMS Institute of Technology and Management: UHV PresentationDocument7 pagesBMS Institute of Technology and Management: UHV PresentationAnirudda SamadderNo ratings yet
- MM21 06 Iconology WarburgDocument21 pagesMM21 06 Iconology WarburgAnyád ApádNo ratings yet
- Disjunctive and ConjunctiveDocument11 pagesDisjunctive and Conjunctiveviper83% (6)
- Four Organizational Perspectives and Implementation of Planned Organizational ChangeDocument24 pagesFour Organizational Perspectives and Implementation of Planned Organizational Changeshamiri100% (4)
- Marg Institute of Design and Architecture Swarnabhoomi Ar 6911 Urban Design - AssignmentDocument2 pagesMarg Institute of Design and Architecture Swarnabhoomi Ar 6911 Urban Design - AssignmentPrarthana roy R100% (1)
- Composition Notes Essay C1 and C2Document7 pagesComposition Notes Essay C1 and C2Γιάννης ΜατσαμάκηςNo ratings yet
- 1 POSITION PAPER Abolition of Sangguniang Kabataan POSITION PAPERDocument4 pages1 POSITION PAPER Abolition of Sangguniang Kabataan POSITION PAPERApril CananeaNo ratings yet
- Johns Hopkins University Press Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To MLNDocument27 pagesJohns Hopkins University Press Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To MLNNegru CorneliuNo ratings yet
- Choric Speech PieceDocument3 pagesChoric Speech PieceJanella TinambacanNo ratings yet
- Vision of Public Leadership - NLDocument6 pagesVision of Public Leadership - NLAndriusNo ratings yet
- ECCE WritingDocument22 pagesECCE Writinggesu piero lopez mejiaNo ratings yet
- Brainteasers: 1) Assume That It Takes 6 Monkeys 6 Minutes To Eat 6 BananasDocument4 pagesBrainteasers: 1) Assume That It Takes 6 Monkeys 6 Minutes To Eat 6 BananasPratyush AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Rule of Law by A.V DiceyDocument2 pagesRule of Law by A.V Diceyrajbakhtiyar11No ratings yet
- Maria Full of GraceDocument1 pageMaria Full of GraceAaron DagalaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Operations Management First Canadian Edition Jay Heizer Barry Render Paul GriffinDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Operations Management First Canadian Edition Jay Heizer Barry Render Paul Griffinstudioustapa4839100% (41)
- Gayatri Mantra Super ScienceDocument18 pagesGayatri Mantra Super Sciencerathish00790% (10)
- Stoic ConditionalsDocument13 pagesStoic ConditionalsMilana KosticNo ratings yet
- A Developmental-Functionalist Approach To Child LanguageDocument236 pagesA Developmental-Functionalist Approach To Child LanguageValéria Garcez100% (1)
- Bomag Bw154 4 Bw174 4 AP Acp Am Wiring Diagram Function 207 2013 en deDocument22 pagesBomag Bw154 4 Bw174 4 AP Acp Am Wiring Diagram Function 207 2013 en destevenrobinson130398bdt100% (132)
- ENG 520: Contemporary Literary Theory: "Wilfred Owen's Strange Meeting (1918) : New Critical and Marxist Perspectives"Document18 pagesENG 520: Contemporary Literary Theory: "Wilfred Owen's Strange Meeting (1918) : New Critical and Marxist Perspectives"LAYLA •No ratings yet
- English: Grammar MentorDocument4 pagesEnglish: Grammar MentorAmit KasniaNo ratings yet
- View, Meditation and Action 1 - Dzongsar Jamyang Khyentse RinpocheDocument27 pagesView, Meditation and Action 1 - Dzongsar Jamyang Khyentse Rinpochealit arimbawaNo ratings yet
- Boyne, G. A. (2003) .Document29 pagesBoyne, G. A. (2003) .Fabrício Augusto da S. MartinsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mother Tongue Grade-2: Applicant DateDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mother Tongue Grade-2: Applicant DateJanice S. Villarmino100% (4)
- Nonnative and Second-Language Speech Perception: Commonalities and ComplementaritiesDocument35 pagesNonnative and Second-Language Speech Perception: Commonalities and ComplementaritiesDiego VerdugoNo ratings yet
- Influential Life Experiences Scramble 2019Document4 pagesInfluential Life Experiences Scramble 2019贺冬梅No ratings yet
- Philosophy, Vision, Mission, Goals & Core ValuesDocument2 pagesPhilosophy, Vision, Mission, Goals & Core ValuesDharlyn Mae ErojoNo ratings yet