Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy Review For FPGEE PDF
Anatomy Review For FPGEE PDF
Uploaded by
Go Go ArtOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy Review For FPGEE PDF
Anatomy Review For FPGEE PDF
Uploaded by
Go Go ArtCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY
Bones
Vertebral column:
- Vertebral column:
o 7 cervical vertebrae
o 12 thoracic
o 5 lumbar
o Sacral bone
o 4 coccygeal bone (coccyx)
- Atlas: 1st cervical vertebra, has no body
- Vertebral canal: for spinal cord passage
Thoracic cage (rib cage):
- 7 true ribs (1-7)
- 5 false ribs (8-12)
- No. 11 & 12 = floating ribs
- Costal cartilage
- Sternum
- Xyphoid process
- Intercostal space: between each rib & the next one
- Infrasternal angle: b/w rt & lt costal arch
Skull:
- Cranial bone (top of skull)
- Occipital bone (back of skull:4,5), foramen
magnum: for medulla oblongata, mastoid Frontal Parietal
margin
- Sphenoid bone (b/w frontal, occipital, &
temporal bones:6,8,9)
- Temporal bone (b/w occipital, sphenoid, & Orbital Temporal
Sphenoid Occipital
parietal bones:8,10,13): squamous, petrous, Zygomatic archMastoid
tympanic
- Frontal bone Maxilla
- Maxilla & Mandible
- Zygomatic arch & mastoid portion Mandible
- Bregma (Point of intersection of the sagittal and coronal sutures)
Shoulder:
- Shoulder (pectoral) girdle: scapula (shoulder blade)
- Clavicle
- Coracoid process: attach with biceps muscle
- Acromion: projecting over head of humerus
- Glenoid cavity: articlar cavity of the shoulder
1 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Upper limb:
- Humerus
- TOP: Head of humerus: greater tubercle & lesser tubercle
- BOTTOM: Condyle of humerus:
o Medial epicondyle: attach to flexor ms
o Lateral epicondyle: attach to extensor ms
o Capitulum: to radius bone
o Trochlea: to ulna bone
- Radius (lateral; out):
o TOP: Head of radius: attach to capitulum, articular circumference (w/
ulna)
o Bottom: Ulnar notch, articular carpal surface, styloid process
- Ulna (medial; in):
o TOP: Trochlear notch: attach to trochlea, Radial notch
o Bottom: Head of ulna, styloid process, articular circumference (w/ radius)
- Hand:
o 8 Carpal bones (Scaphoid, Lunate, Pisiform, Triquetrum, Trapezium,
Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate) SLPTTTCH
o Metacarpal bones
o Phalanges (proximal, middle, distal phalanx)
Hip:
- Pelvic girdle Ilium
- Hip bone (ilium, ischium, pubis)
- Obturator foramen
Ischium
Lower limb:
- Femur: Obturator
o TOP: Head of femur: greater Pubis foramen
trochanter & lesser trochanter
o Shaft
o Bottom: Medial & lateral epicondyle: attach to knee
- Patella (knee cap)
- Tibia (in):
o Bottom: Medial malleolus
- Fibula (out):
o TOP: Head of fibula
o Bottom: Lateral malleolus
- Foot:
o 7 Tarsal bones of the ankle (Talus, Calcaneus, Cuboideum, 3 Cuneiform
bones)
o Navicular, Cuboid, Medial cuneiform, Intermediate cuneiform, & Lateral
cuneiform
o Metatarsal bones
o Phalanges (proximal, middle, distal phalanx)-base, head, shaft of phalanx
2 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Muscles
Back:
- Trapezius (2)
- Latissimus dorsi (4)
- Rhomboideus major (5) & minor (6)
- Serratus posterior superior (9) & inferior (8)
Neck:
- Rectus capitis posterior major (25) & minor
(26)
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle (from neck to
thorax, p. 80 &81)
Face:
- Frontal belly (8) & occipital belly (9)
- Orbital (19) & lacrimal (inside)
- Labial (28 & around the mouth)
- Articularis anterior (23)
- Articularis superior (24) 10
- Articularis posterior (25)
- Temporalis
- Zygomaticus major (bottom) & minor (top)
below 19
- Buccinator (10)
Chest (Thorax):
- Pectoralis major & minor
- Subclavius
- Serratus anterior
- External, internal, & innermost intercostals muscles
Abdomen:
- Rectus abdominus & rectus sheath
- Internal & external abdominal oblique muscle
- Transversus abdominus
- Linea alba (tendon)
3 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Upper limb:
- Deltoid
- Biceps brachii with long head & short head
- Triceps brachii with long head, medial head, & lateral head
- Brachioradialus
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- Extensor carpi radialis longus
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor digitorum (fingers & profundus deep) & Extensor digitorum
Lower limb:
- Gluteus maximus, medius, & minimus
- Anterior of femur:
o Adductor longus, brevis, & magnus
- Posterior of femur:
o Biceps femoris with long head & short head
o Semitendinosus
o Quadriceps
- Anterior of lower leg:
o Tibialis anterior
o Extensor digitorum longus (from leg to fingers)
- Posterior of lower leg:
o Plantaris (behind the knee)
o Gastrocnemius ( )
- Foot: Flexor digitorum brevis
4 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Heart
- Base & apex
- Pericardium:
o Fibrous pericardium
o Serous pericardium
o Pericardial cavity (contains serous fluid)
- Right & Left atria
- Right & Left ventricles
- Interarterial septum
- Interventricular septum
- Atrioventricular septum
- Myocardium
- Conducting system:
o Sinoatrial (SA) node
o Atrioventricular (AV) node
o Trunk (Bundle of HIS, Purkinje fibers)
- Endocardium
Right atrium:
- Opening of (superior & inferior) vena cava
- Valve of inferior vena cava
Right ventricle:
- Tricuspid valve (right atrioventricuar valve)
- Pulmonary valve
- Anterior, posterior, & septal papillary muscles
Left atrium:
- Opening of pulmonary veins
Left ventricle:
- Mitral valve (left atrioventricuar valve)
- Aortic valve
- Anterior & posterior papillary muscles
5 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Arteries
Pulmonary arteries:
- Pulmonary trunk: rt (behind ascending aorta) & lt pulmonary arteries
- Bifurcation of pulmonary trunk
Ductus arteriosus:
Short arterial duct in the fetus between the division of the pulmonary trunk and the
arch of the aorta. It is patent until birth
Aorta:
Ascending aorta: rt & lt coronary arteries
- Arch of aorta
- Brachiocephalic trunk
- Common carotid artery:
o Carotid body
o Carotid sinus (contains baroreceptors)
o Carotid bifurcation
Common Crotid Artery
External Carotid Artery Internal Carotid Artery
-Superior thyroid artery
-Cervical part
-Ascending pharyngeal artery
-Petrous part
-Lingual artery
-Cavernous part
-Facial artery
-Cerebral part
-Occipital artery
-Temporal artery
-Maxillary artery
Cerebral arteries:
- Anterior, middle, & posterior cerebral arteries
- Cerebral arterial circle (circle of Willis)
Subclavian artery:
- Vertebral artery
- Basilar artery terminate as posterior cerebral artery
Internal thoracic (mammary) artery
6 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Upper limb arteries:
- Axillary artery
- Brachial artery
- Radial artery
- Ulnar artery
- Palmar & carpal arteries
Descending aorta:
- Thoracic aorta
- Abdominal aorta
o Inferior phrenic artery
o Lumbar & sacral arteries
o Celiac trunk
- Common hepatic artery
- Splenic artery
- Superior & inferior mesenteric arteries
- Suprarenal artery
- Renal artery
- Testicular or ovarian artery
- Bifurcation of aorta
- Common iliac artery:
o Internal iliac artery
Lower limb arteries:
- External iliac artery
- Femoral artery
- Popliteal artery:
o Anterior & posterior tibial arteries
o Peroneal (fibular) artery
o Dorsalis pedis artery
7 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Veins
Pulmonary veins:
- Right superior & inferior pulmonary veins
- Left superior & inferior pulmonary veins
Coronary veins
Superior vena cava:
- Right & left brachiocephalic veins
- Internal jugular vein Facial vein
- External jugular vein
Cerebral veins:
- Superficial & deep cerebral veins
- Veins of brainstem & cerebellum
Upper limb veins:
- Subclavian vein
- Axillary vein
- Brachial veins
- Radial veins
- Ulnar veins
Azygos vein:
Lumbar vein arises from ascending lumbar vein and opens into superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava:
- Inferior phrenic veins
- Hepatic veins
- Suprarenal veins
- Renal veins
- Testicular or ovarian veins
Portal vein of the liver: Right & left branches
- Superior & inferior mesenteric veins splenic vein & superior rectal vein
Common iliac vein:
- Internal (hypogastric) iliac vein: Rectal venous (hemorrhoidal) plexus: middle &
inferior recta veins
- External iliac vein
Lower limb veins:
- Femoral vein
- Great sephanous vein
- Popliteal vein:
o Anterior & posterior tibial veins
o Small sephanous vein
8 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Digestive System
Oral cavity:
- Lips
- Hard palate & soft palate with palatine raphe (line) in b/w
- Uvula
- Frenulum of upper & lower lips
- Gums (gingiva)
- 3 major salivary glands: sublingual, submandibular, & parotid
- 5 small salivary glands: labial, buccal, molar, palatine, & lingual
- Teeth: incisor, canine, premolar, molar, & wisdom
- Tooth:
o Crown of tooth
o Neck of tooth
o Root of tooth
- Frenulum of tongue (attach the tongue to lower gum)
- Tongue histology: filiform, conical, fungiform, vallate, lenticular, foliate papillae
Pharynx:
- Oropharynx
- Nasopharynx
- Laryngopharynx
- Palatine tonsil
- Nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoids)
Esophagus:
- Cervical, thoracic, & abdominal parts
- Histology (from top to bottom):
o Tunica mucosa (stratified, nonkeratinized squamous epithelium)
o Esophageal glands
o Tunica muscularis
o Tunica adventitia
Stomach:
- Pyloric sphincter
- Anterior & posterior surface
- Great & lesser curvature
- Cardia, fundus, corpus, & pylorus
- Histology (from top to bottom):
o Villous folds
o Tunica mucosa (simple columnar epithelium)
o Tela submucosa
o Tunica muscularis
o Tela subserosa
o Serous membrane
9 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Small intestine:
- Duodenum, jejunum, ileum
- Histology (from top to bottom):
o Intestinal villi & glands
o Tunica mucosa (simple columnar epithelium)
o Tela submucosa
o Tunica muscularis
o Tela subserosa
o Tunica serosa
Large intestine (colon):
- Cecum
- Vermiform appendix
- Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon
- Rt & Lt colic flexures
- Rectum & anus
- Histology (same as small intestine): Tunica mucosa (simple, goblet-cell rich
columnar epithelium)
Pancreas:
- Head, body, & tail
- Pancreatic lobule & duct
Liver:
- Lobes: right, caudate, quadrate, left
- Cardiac, esophageal, gastric, duodenal, colic, renal, & suprarenal impressions
- Groove for vena cava
- Hilum (for portal vein)
- Gallblader:
o Fundus, body, & neck
o Cystic duct
o Bile duct
o Biliary glands
Spleen
- Splenic pulp:
o White pulp (lymphoreticular tissue in form of arterial sheaths)
o Red pulp (venous sinuses with erythrocytes, reticular tissue)
- Lymphatic nodules (follicles)
- Hilum
10 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Respiratory System
Nose:
- Nasal septum
- Superior, middle, & inferior nasal concha
- Nasal (olfactory) glands
- Paranasal sinuses (name according to location):
o Maxillary sinus
o Sphenoidal sinus
o Frontal sinus
o Ethmoidal sinus
Larynx:
- Thyroid cartilage
- Thyroid membrane
- Superior & inferior horns (cornu)
- Cricoid cartilage
- Arytenoid, corniculate, & cuneiform cartilages
- Epiglottis
- Glottis
- Lymph nodes of larynx
Trachea:
- Cervical & thoracic parts
- Tracheal cartilages & muscle
- Bifurcation of trachea (where it divides into rt & lt bronchi)
- Histology: Tunica mucosa (pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with
goblet cells)
Bronchi:
- Lobar & segmental bronchi
- Right (superior, middle & inferior) lobar bronchus
- 2 Left inferior lobar bronchi
- Respiratory bronchioles
Lungs:
- Base & apex
- Right lung:
o Upper, Middle, & Lower lobes
o Oblique & horizontal fissures
- Left lung:
o Upper & Lower lobes
o Oblique fissure
- Pleura: visceral & parietal pleura
- Pleural cavity
- Mediastinum
- Alveoli: alveolar duct & sac
11 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Urogenital System
Kidneys:
- Renal cortex
- Renal medulla
- Renal pelvis: renal calices (single calyx)
- Renal pyramids
- Nephron:
o Renal corpuscle: Glomerulus & glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule
o Proximal convoluted tubules
o Loop of Henle (descending & ascending)
o Distal convoluted tubules
o Collecting tubule
- Renal arteries & veins:
o Interlobar arteries & veins
o Arcuate arteries & viens
o Afferent arterioles (entering glomerulus)
o Efferent arterioles (exiting glomerulus)
Ureters:
- Abdominal & pelvic parts
- Histology (from top to bottom):
o Tunica mucosa (transitional epithelium)
o Tunica muscularis
o Tunica adventitia
Urinary bladder:
- Apex, body, fundus, & cervix
- Histology (from top to bottom):
o Tunica mucosa (transitional epithelium)
o Tela submucosa
o Tunica muscularis
o Tela subserosa
o Tunica serosa
- Trigone
- Uvula
Male genitalia:
- Scrotum
- Testis:
o Lobules
o Convoluted seminiferous tubules
- Epididymis
- Paradidymis
- Ductus deferens
- Ejaculatory duct
- Seminal vesicle with excretory duct
- Spermatic cord
12 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
- Prostate: base (top) & apex (bottom): rt, lt, & middle lobes
- Bulbouretheral (Cowper’s) gland
- Penis:
o Root
o Body (shaft)
o Glans
o Prepuce (foreskin)
- Urethera:
o Prostatic part
o Membranous part
o Spongy part
Female genitalia:
- Ovary:
o Primary ovarian follicles
o Vesicular ovarian (Graafian) follicles
o Ovum (oocyte)
o Corpus luteum (Endocrine gland arising from ruptured follicle)
- Uterine (Fallopian) tube, oviduct:
o Fimbriae
o Ampulla
o Isthmus
o Histology: Tunica mucosa (ciliated columnar epithelium with glandular
cells)
- Uterus:
o Body & fundus
o Cervix w/ cervical canal
o Histology (from out to in):
Tunica serosa “perimetrium”
Tela subserosa
Tunica muscularis “myometrium”
Tunica mucosa “endometrium” (simple columnar epithelium &
glands)
- Vagina:
o Hymen
o Hisology:
Tunica muscularis
Tunica mucosa (glycogen-rich, stratified, nonkeratinized squamous
epithelium)
- Clitoris
- Vestibular (Bartholin’s) glands
- Urethra
Embryonic terms:
- Umbilical cord
- Placenta (attached to endometrium)
- Amnionic fluid
13 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
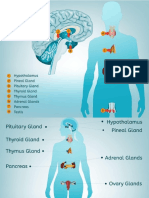
Endocrine Glands
Pituitary gland (Hypohysis):
- Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe)
- Neurohypophysis (posterior lobe)
- Infundibilum
Pineal body (gland):
In the CNS
Thyroid gland:
- Right & Left lobes
- Isthmus of thyroid gland
- Pyramidal lobe
- Lobules
- Accessory thyroid glands
- Histology:
o Stroma
o Parenchyma: essential for thyroid function
Superior & inferior parathyroid glands
Adrenal (suprarenal) glands:
- Anterior & posterior surfaces
- Renal surface
- Hilum
- Adrenal cortex
- Adrenal medulla
- Accessory suprarenal glands
Thymus gland:
- Right & left lobes
- Thymic lobules
- Cortex & medulla
14 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic vessels:
Afferent & efferent lymphatic vessels
Regional lymph nodes:
- Head & neck (10):
o Occipital o Submental
o Mastoid o Submandibular
o Parotid (superficial & deep) o Anterior cervical (jugular)
o Facial o Thyroid
o Lingual o Lateral cervical
- Upper limb (5):
o Axillary lymphatic plexus & nodes
o Brachial
o Pectoral
o Cubital
o Supratrochlear
- Thorax (6):
o Paramammary
o Parasternal
o Intercostal
o Paravertebral
o Prepericardial
o Superior phrenic
- Abdomen (3):
o Right, intermediate, & left lumbar
o Inferior phrenic
o Inferior epigasric
- Visceral (10):
o Celiac o Splenic
o Gastric o Hepatic
o Pyloric o Cystic
o Pancreatic o Mesentric
o Pancreatoduodenal o Common iliac
- Pelvis (3):
o Parauterine
o Paravaginal
o Pararectal
- Lower limb (4):
o Inguinal
o Popliteal
o Anterior & posterior tibial
o Fibular
15 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
NEROUS SYSTEM
Meninges
(From top to bottom)
Cranial dura mater
Subdural space
Cranial arachnoid
Subarachnoid space
Subarachnoid cisterns
Cranial pia mater
Spinal dura mater
Epidural space
Spinal arachnoid
Subarachnoid space
Spinal pia mater
16 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Central Nervous System
Spinal Cord:
- Cervical & lumbosacral enlargements
- Segments of spinal cord (same names of vertebral column segments)
- Central canal
- Gray matter (H-shaped):
o Anterior, posterior, & lateral columns & horns
o Anterior & posterior gray commissures
- White matter (myelinated nerves):
o Anterior & posterior white commissures
o Anterior, posterior, & lateral funiculus
Brain (3rd, 4th, & lateral ventricles):
Brainstem:
Hindbrain:
- Medulla oblongata
Metencephalon:
- Pons
- Cerebellum:
o Anterior & posterior lobes
o Rt & lt hemispheres
o Cerebellar peduncles (fibers provide connections to & from cerebellum)
Midbrain:
o Cerebral peduncle
o Substantia nigra
Forebrain (Diencephalon):
o Epithalamus
o Pineal gland (body)
o Dorsal thalamus
o Metathalamus
o Ventral thalamus (subthalamus)
o Hypothalamus (anterior & posterior regions)
o Pituitary gland
Endbrain:
- Cerebrum (two hemispheres)
o Cerebral cortex
o Cerebral gyri (s: gyrus): Convolutions of the cerebral hemispheres
o Cerebral sulci (s: sulcus): Fissures between gyri
o Cerebral lobes (4): frontal, parietal, temporal & occipital
o Longitudinal & transverse fissures
o Olfactory brain
- Corpus callosum: Massive transverse fibers connecting right & left hemispheres
- Basal nuclei (corpus striatum)
17 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Peripheral Nervous System
Cranial nerves (12 pairs of nerves):
All of them emerge from the base of the brain and exit through the base of the skull,
except of the trochlear (IV)
- Olfactory nerve (I)
- Optic nerve (II)
- Oculomotor nerve (III)
- Trochlear nerve(IV)
- Trigeminal nerve (V)
- Abducent nerve (VI)
- Facial nerve (VII)
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
- Vagus nerve (X)
- Accessory nerve (XI)
- Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
- Maxillary & mandibular nerves
Spinal nerves (Anterior “ventral” & posterior “dorsal” roots & branches):
Cervix:
- Cervical nerves & plexus (the only posterior nerve)
- Phrenic nerve
- Brachial plexus
- Supraclavicular part:
o Dorsal scapular nerve
o Long thoracic nerve
o Suprascapular nerve
- Infraclavicular part:
o Medial & lateral pectoral nerves
o Musculocutaneous nerve (for biceps muscle)
Upper limb:
- Ulnar nerve
- Radial nerve
- Palmar nerves (of the hand)
Thorax:
- Subscapular nerve
- Thoracodorsal nerve
- Axillary nerve
- Thoracic nerves:
o Anterior branches (intercostal nerves)
o Posterior branches
18 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Lumbar:
- Lumbar nerves & plexus:
o Anterior & posterior branches
o Iliohypogastric nerve
o Ilioinguinal nerve
o Genitofemoral nerve
o Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
o Obturator nerve
- Sacral nerves & Coccygeal nerve:
o Anterior & posterior branches
Lower limb:
- Femoral nerve
- Superior & inferior gluteal nerves
- Sciatic nerve (thickest nerve of the body)
- Tibial nerve
- Fibular nerves (superficial & deep)
- Plantar nerves (of the foot)
Genital area:
- Pudendal nerve
- Coccygeal nerve & plexus
19 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic (visceral) plexus: Ganglia of autonomic plexus
Thoracic aortic plexus:
- Cardiac plexus & ganglia
- Esophageal plexus
- Pulmonary plexus
Abdominal aortic plexus:
- Celiac plexus & ganglia
- Aorticorenal ganglia
- Superior & inferior mesenteric ganglia & plexus
- Phrenic ganglia
- Gastric plexus
- Enteric plexus
- Superior rectal plexus
- Hepatic plexus
- Splenic plexus
- Pancreatic plexus
- Suprarenal plexus
- Renal plexus
- Ureteric plexus
- Testicular/ovarian plexus
- Iliac plexus
- Femoral plexus
Superior hypogasric plexus:
- Rt & left hypogastric nerves
- Middle & inferior rectal plexus
- Prostatic plexus
- Uterovaginal plexus
SYMPATHETIC PART (SYSTEM): Sympathetic trunk (ganglia of symp trunk):
- Superior & middle cervical ganglia
- Cervicothoracic ganglion
- Thoracic ganglia
- Lumbar ganglia
- Sacral ganglia
PARASYMPATHETIC PART (SYSTEM):
Cranial part (III, VII, IX, X):
- Terminal ganglion
- Ciliary ganglion
- Otic ganglion
- Submandibular ganglion
- Sublingual ganglion
Pelvic part: Pelvic ganglia
20 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Sense Organs
Eye (Organ of Vision)
- Optic nerve
- Eyeball:
o Anterior & posterior poles
o Equator
o Internal & external axis
Fibrous tunic of eyeball (external wall):
- Sclera
- Canal of Schlemm (involved in the discharge of aqueous humor from the anterior
chamber)
- Cornea
Vascular tunic of eyeball (middle layer):
- Choroid (vascular coat lying between the retina and sclera)
- Ciliary body (contains ciliary muscles & processes)
- Iris
- Pupil
Internal (sensory) tunic of eyeball:
- Retina:
o Pigmented part
o Nervous part
o Neuroepithelial (photosensitive) layer: contains rods & cones
o Optic disc ( )
- Retinal blood vessels
Chambers of the eye:
- Anterior chamber:
o Aqueous humor (98% water, 1.4% NaCl, & traces of protein & sugar)
- Posterior chamber:
o Aqueous humor (secreted from ciliary processes)
- Viterous chamber:
o Viterous body (98% water, hyaloyronic acid (make it gelatinous) & traces
of protein, NaCl, & fibrils)
o Viterous humor (fluid part of the vitreous body)
Lens
Muscles of the eye:
Orbital muscle, superior, medial, lateral, & inferior rectus, superior & inferior oblique
Lacrimal apparatus:
- Lacrimal gland & sac & Nasolacrimal duct
Ear (Vistibulocochlear Organ)
21 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Internal ear:
- Membraneous labyrinth:
o Edolymph: fluid within memb labyrinth
o Perilymph: fluid surrounding memb labyrinth
- Vestibular labyrinth:
o Endolymphatic duct & sac
o Utriculosaccular duct
o Utircle
o Semicircular ducts (anterior, posterior, & lateral)
o Saccule
- Cochlear labyrinth:
o Cochlear aqueduct (connecting perilymphatic space w/ subarachnoid
space)
o Spiral organ of Corti (transforms sound waves into nerve impulses)
- Osseous labyrinth:
o Vestibule (encloses utricle & saccule)
- Osseous semicircular canals
- Cochlea
- Internal acoustic (auditory) meatus (canal)
Middle ear:
- Tympanic cavity
- Tympanic membrane (eardrum)
- Auditory ossicles:
o Stapes (2)
o Incus (7)
o Malleus (12)
Auditory (pharyngotympanic, Eustachian) tube:
- Osseous part
- Cartilaginous part
External ear:
- External acoustic (auditory) meatus (canal)
- Auricle (Pinna):
o Concha (cavity) of auricle
Olfactory Organ
- Nasal mucosa
- Olfactory gland (of Bowman)
Gustatory Organ
- Taste bud
- Taste pore
Integumentary System
22 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
Anatomy Review for FPGEE
Cutis (epidermis + dermis)
Epidermis (Stratified, keratinized squamous epithelium):
- Stratum corneum (undergoes continual desquamation)
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum spinosum (polygonal cells with spinus processes)
- Stratum basale
Dermis “corium” (collagenous and elastic fibers rich in nerves and blood vessels
and devoid of fat):
- Papillary layer
- Reticular layer
- Subcutaneous tissue
Cutaneous glands:
- Sweat glands & ducts
- Ceruminous glands
- Sebaceous glands
Hair (Pili) follicle:
- Bulb of hair:
o Hair papilla
- Hair root
- Hair shaft
Nails:
- Nail matrix (bed)
- Wall of nail
- Body of nail
- Root of nail
- Lamula
Breast:
- Nipple
- Mammary gland (with lobes & lobules)
- Lactiferous ducts
- Accessory mammary glands
23 Done by: Abrar Thabit, PharmD
You might also like
- Compendium of Pharmaceuticals and Specialties PDFDocument2 pagesCompendium of Pharmaceuticals and Specialties PDFJainner Contreras100% (1)
- Fpgee ProcessDocument3 pagesFpgee ProcessNicole ChanNo ratings yet
- Pebc Evaluating Exam Sample QuestionDocument50 pagesPebc Evaluating Exam Sample QuestionZain zanzoonNo ratings yet
- Studying RoutineDocument12 pagesStudying RoutineKelvin Lim Wei Liang100% (1)
- Refer Books Sort ListDocument12 pagesRefer Books Sort ListDr-Ram ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide For Foreign Pharmacy Licensing ExamDocument6 pagesReference Guide For Foreign Pharmacy Licensing Examcarp liciniaNo ratings yet
- FpgeeqaDocument60 pagesFpgeeqaDr-Usman KhanNo ratings yet
- Lang 10 EditionDocument235 pagesLang 10 Editionraju niraulaNo ratings yet
- Pebc StatisticsDocument1 pagePebc Statisticscesar138No ratings yet
- Concept of Atomic Number Leads To The Synthesis of New Element To The LaboratyDocument6 pagesConcept of Atomic Number Leads To The Synthesis of New Element To The LaboratyDIANA DORADO100% (5)
- Manshrof Theory Part 1Document51 pagesManshrof Theory Part 1iNo ratings yet
- Manan 1000 Q - ADocument294 pagesManan 1000 Q - ADrSamia El Wakil0% (1)
- Immunology Review For FPGEEDocument8 pagesImmunology Review For FPGEEMina MinawyNo ratings yet
- How I Prepared NABP FPGEE Exam in One Week? (June 2021)Document4 pagesHow I Prepared NABP FPGEE Exam in One Week? (June 2021)scotmartinNo ratings yet
- Management TheoryDocument63 pagesManagement TheoryFaisal Ibrahim100% (2)
- Complete Fpgee Application SummaryDocument6 pagesComplete Fpgee Application SummaryStephanie Camille Samonte100% (1)
- Coursera - Pharmacist Licensure ProcsDocument13 pagesCoursera - Pharmacist Licensure Procsaudio habibiNo ratings yet
- DR G DuttaDocument758 pagesDR G DuttaFrançoise B100% (1)
- Fpgee PlanDocument9 pagesFpgee PlanDoha AnberNo ratings yet
- First Section of Manan's TheoryDocument34 pagesFirst Section of Manan's TheoryM Imran SajidNo ratings yet
- The Comprehensive FPGEE Review IncludingDocument3 pagesThe Comprehensive FPGEE Review IncludingFestus MgbemeNo ratings yet
- Fpgec ApplicationDocument3 pagesFpgec ApplicationGeorgeNo ratings yet
- My Recalls July 21Document3 pagesMy Recalls July 21Docter NezNo ratings yet
- 2005 Evaluation QuestionsDocument51 pages2005 Evaluation QuestionsAnn100% (1)
- Fpgee SummaryDocument23 pagesFpgee Summaryzxcasdqwe123No ratings yet
- 8 B. Social, Behavioral, Economic, and Administrative SciencesDocument140 pages8 B. Social, Behavioral, Economic, and Administrative SciencesSamson SeiduNo ratings yet
- FpgeeqDocument60 pagesFpgeeqMuhammad Abdullah100% (1)
- Pebc Qualifying MCQ Study ScheduleDocument2 pagesPebc Qualifying MCQ Study SchedulegegeNo ratings yet
- Careers in PharmacyDocument6 pagesCareers in PharmacyChaitanya GaddeNo ratings yet
- FPGEEDocument1 pageFPGEERushank ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Naplex Mpje BulletinDocument49 pagesNaplex Mpje BulletinAssignment Abroad0% (1)
- FPGEC ApplicationBulletin 2019Document44 pagesFPGEC ApplicationBulletin 2019espharma educationNo ratings yet
- PEBC EE BlueprintDocument2 pagesPEBC EE BlueprintcoolchapNo ratings yet
- FPGEE QuestionDocument5 pagesFPGEE QuestionSammy Saloom0% (1)
- Fpgee Blue PrintDocument5 pagesFpgee Blue PrintPradeep BuddharajuNo ratings yet
- AL GRAWANY Medical Notes - EndocrinologyDocument51 pagesAL GRAWANY Medical Notes - EndocrinologyDJ AKRODOKNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Historypharmacopoeia 180817063405 PDFDocument111 pagesPharmacy Historypharmacopoeia 180817063405 PDFchandra sekhar gowra0% (1)
- Canada ExamDocument6 pagesCanada ExamKrizza MacayaNo ratings yet
- CLEAR 2005 - Scores and Reports3 - CObyrneLilaDocument21 pagesCLEAR 2005 - Scores and Reports3 - CObyrneLilaMithNo ratings yet
- Nap Lex Theory 2Document30 pagesNap Lex Theory 2Dyehen Slevin KelevraNo ratings yet
- Part A: Job Analysis Information Sheet of Hospital PharmacistDocument3 pagesPart A: Job Analysis Information Sheet of Hospital PharmacistTan Su SuanNo ratings yet
- Pebc CVS QuestionnaireDocument53 pagesPebc CVS QuestionnaireNOORNo ratings yet
- 4 Competency 4 Mock Test May 2013Document38 pages4 Competency 4 Mock Test May 2013Andrew MeNo ratings yet
- Pebc Evaluating Exam Sample Question PDFDocument39 pagesPebc Evaluating Exam Sample Question PDFRicky100% (1)
- PEBCHandbookDocument15 pagesPEBCHandbookversion1403No ratings yet
- Total Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEDocument1,601 pagesTotal Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEClaire Cura100% (2)
- Naplex Mpje: 2017 Candidate Registration BulletinDocument51 pagesNaplex Mpje: 2017 Candidate Registration BulletinLam LamNo ratings yet
- Ont Drug Benefit ActDocument11 pagesOnt Drug Benefit Actbijalshah7985No ratings yet
- Pebc CompilationDocument14 pagesPebc CompilationAarti AroraNo ratings yet
- DSFDSFDocument11 pagesDSFDSFShohrat RizviNo ratings yet
- PEBC EnglishDocument4 pagesPEBC EnglishSaiKai54No ratings yet
- Foreign Grads Info LetterDocument3 pagesForeign Grads Info LetterRoman WinerNo ratings yet
- CPR SummaryDocument2 pagesCPR SummaryaqsamerajNo ratings yet
- Drug Info+Document56 pagesDrug Info+zaidhusam100% (1)
- Gpat MaterialDocument22 pagesGpat Materialsangram_pharma914567% (3)
- Corrections - The APhA Complete Review For The FPGEEDocument2 pagesCorrections - The APhA Complete Review For The FPGEEBlsNo ratings yet
- HAAD Applicant KitDocument9 pagesHAAD Applicant KitMenGuitarNo ratings yet
- CoursesDocument2 pagesCoursesapi-586042393No ratings yet
- Lab 6: Laboratory Check List Thoracic Wall and Lungs Reading AssignmentDocument2 pagesLab 6: Laboratory Check List Thoracic Wall and Lungs Reading AssignmentSd Mun TzNo ratings yet
- EktremitasDocument40 pagesEktremitasBram wijayaNo ratings yet
- Objective C Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesObjective C Cheat SheetDiproNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation-Parapet Steel StructureDocument5 pagesDesign Calculation-Parapet Steel Structuremsiddiq1No ratings yet
- B 4 Qoq Pa PRDG 6 C XPDocument9 pagesB 4 Qoq Pa PRDG 6 C XPdhaval.desai98No ratings yet
- Yeastar S-Series Voip PBX: Performance and PowerDocument2 pagesYeastar S-Series Voip PBX: Performance and PowerJeronimo ReynosoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Disease Prediction Using Significant Attribute Selection and Classification ApproachDocument37 pagesDiabetes Disease Prediction Using Significant Attribute Selection and Classification Approachpriyanka dubeyNo ratings yet
- SURveying IIDocument159 pagesSURveying IIpieterNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Paper 4 MSDocument5 pagesPhysical Science Paper 4 MSsena06.mathenjwaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money-PowerpointDocument83 pagesTime Value of Money-Powerpointhaljordan313No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SlidesDocument66 pagesChapter 2 SlidesHeriansyah NajemiNo ratings yet
- Starrett Decimal Equivalent Card (Bulletin 1317)Document2 pagesStarrett Decimal Equivalent Card (Bulletin 1317)Franz CorasNo ratings yet
- LMA-Workshop-Sheet LABAN PDFDocument6 pagesLMA-Workshop-Sheet LABAN PDFsabinalazarNo ratings yet
- KPI Document - MN PerformanceDocument69 pagesKPI Document - MN Performancenazer elhamNo ratings yet
- PL/SQL User Defined Types Record and Table: Please Use Speaker Notes For Additional Information!Document15 pagesPL/SQL User Defined Types Record and Table: Please Use Speaker Notes For Additional Information!sekharmcpNo ratings yet
- Data Link Layer 1Document88 pagesData Link Layer 1PalashAhujaNo ratings yet
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-11-29 Ref:Dupont Suva Hp62Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-11-29 Ref:Dupont Suva Hp62Diego RamirezNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Belt Bucket ElevatorDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Belt Bucket ElevatorEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Capitulos GuiaDocument100 pagesCapitulos GuiaRicardo ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Arduino Caliper 2013-07-18Document2 pagesArduino Caliper 2013-07-18Barry SmalldonNo ratings yet
- CP JD 2003 CHT3500 Harverster Supplement World - CB21458306Document51 pagesCP JD 2003 CHT3500 Harverster Supplement World - CB21458306Jaime IglesiasNo ratings yet
- What Is An Electrostatic Force?Document3 pagesWhat Is An Electrostatic Force?Carlton GrantNo ratings yet
- FXZ1 (FRT, ZH) : Halogen FreeDocument4 pagesFXZ1 (FRT, ZH) : Halogen FreeMario LuvineriNo ratings yet
- FRWTMCver413eng PDFDocument168 pagesFRWTMCver413eng PDFdrakula85100% (1)
- NATO Vector GraphicsDocument16 pagesNATO Vector GraphicsMarius Lucian NeculaNo ratings yet
- Homework Gases Mel Arthor QueditDocument2 pagesHomework Gases Mel Arthor QueditMel Arthor QueditNo ratings yet
- Cache Memory SchemeDocument7 pagesCache Memory SchemejainvidishaNo ratings yet
- BGAS Question AnswerDocument14 pagesBGAS Question Answerراجہ شہزاد انور100% (1)
- FL Response Crpe PDFDocument10 pagesFL Response Crpe PDFNational Education Policy CenterNo ratings yet
- The Lava LampDocument5 pagesThe Lava LampMathew DegamoNo ratings yet
- Ih61h-Mhs & Ih61k-Mhs & Ih61m-Mhs - Bios - 110406Document32 pagesIh61h-Mhs & Ih61k-Mhs & Ih61m-Mhs - Bios - 110406WanAbboodNo ratings yet