Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6: Reproduction of Flowering Plants Activity 1 and 2: Pollination and Fertilization Notes
Chapter 6: Reproduction of Flowering Plants Activity 1 and 2: Pollination and Fertilization Notes
Uploaded by
Sumaya HammoudCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Luz ClaritaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction of PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction of PlantsJohn Nowell DiestroNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument53 pagesPlant and Animal ReproductionSheryl Osorio100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDrDibendu Kumar BejNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2Maro Ridhwan RidhiwaniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument21 pagesReproduction in Plantsrani bloriaNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Reproduction in Plants 3Document30 pagesCH 12 Reproduction in Plants 3Shvet MahajanNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceDocument41 pagesGrade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceJulie Mae Sajulga JacobeNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesNotes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsAdnan SathikNo ratings yet
- How Do Plants Reproduce? Lesson 1: I. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesHow Do Plants Reproduce? Lesson 1: I. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsJulliena BakersNo ratings yet
- How Do Org ReproduceDocument32 pagesHow Do Org ReproducePankaj Kumar100% (1)
- Fertilisation in Plants: Objective: To Know How Gametes Fuse Together in PlantsDocument8 pagesFertilisation in Plants: Objective: To Know How Gametes Fuse Together in PlantsMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- Pollination in PlantsDocument214 pagesPollination in PlantsAbraham SekyiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Jann LarNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductionChal WijeNo ratings yet
- 2 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument35 pages2 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceCool VighneshNo ratings yet
- Cbse X Sexual Reproduction in Plants: ScienceDocument12 pagesCbse X Sexual Reproduction in Plants: ScienceDaniel SunnyNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument23 pagesSexual ReproductionMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeDocument23 pagesLECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeJemuel LuminariasNo ratings yet
- Pollination, Fertilisation and GerminationDocument25 pagesPollination, Fertilisation and GerminationAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document101 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Gabrielle MorganNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 2022Document97 pagesReproduction in Plants 2022Newera WizzzNo ratings yet
- Q.11 (A) Name The Important Parts of A FlowerDocument6 pagesQ.11 (A) Name The Important Parts of A FlowerFari NaheedNo ratings yet
- 2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument59 pages2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceCool VighneshNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- Plant Sexual ReproductionDocument22 pagesPlant Sexual ReproductionmarijaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Marie Lm DamascoNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument15 pagesAsexual Reproductioneugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Module 5: Heredity: OutcomesDocument22 pagesModule 5: Heredity: OutcomesNavtej DeyalNo ratings yet
- Plant Animal ReproductionDocument7 pagesPlant Animal ReproductionKyla Renz de LeonNo ratings yet
- Pollination NotesDocument6 pagesPollination Notesketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Part Two of Your JourneyDocument3 pagesWelcome To The Part Two of Your JourneyRaphael Louis DacanayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesChapter - 12 Reproduction in Plantsanju singhNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzDocument14 pagesACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzjundon.ivo.deborjaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Document6 pagesBiology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)47. Anas SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument17 pagesFlowering Plantsjoshua.brussell100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science SHS 17.2 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument29 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 17.2 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsWinsear VardeNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W5 Science 5Document48 pagesQ2 - W5 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesPlant Reproduction and Developmentits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants Powerpoint Class 3 and 4Document9 pagesFlowering Plants Powerpoint Class 3 and 4api-308489491No ratings yet
- 07 Science Key Notes ch12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument1 page07 Science Key Notes ch12 Reproduction in Plantsnufail aliNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Document8 pagesEarth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument2 pagesParts of A FlowerIrish cambriNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of Life (Plant Reproduction)Document15 pagesPerpetuation of Life (Plant Reproduction)Grace Gaje DizonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringblistedxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument80 pagesChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingDocument34 pagesReproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsJada MillerNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFDocument18 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFCatherine Mistiola100% (1)
- BIO 101 Lecture 12Document23 pagesBIO 101 Lecture 12bamimoreridwan06No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction StudentDocument64 pagesPlant Reproduction StudentmrkoutsantanouNo ratings yet
- Grade-7-Q2-Module-4-Sexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdDocument20 pagesGrade-7-Q2-Module-4-Sexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdroseNo ratings yet
- DC5 - Biology - 22ND June 2023Document30 pagesDC5 - Biology - 22ND June 2023siddiquinabil92No ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesSexual Reproductionshashwatdwivedi9000No ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument50 pagesPlant Reproductiongoldennyeche080No ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument15 pagesPerpetuation of LifeMomo Capoquian100% (1)
- 7.e.c Evaporation Part 2Document14 pages7.e.c Evaporation Part 2Sumaya HammoudNo ratings yet
- I. Answer by True or False and Correct The False Statement.: Solutions Revision SheetDocument2 pagesI. Answer by True or False and Correct The False Statement.: Solutions Revision SheetSumaya HammoudNo ratings yet
- Date: Chemical Reactions Sheet Name: Grade: Seven Subject: Chemistry Teacher: Sumayya HammoudDocument1 pageDate: Chemical Reactions Sheet Name: Grade: Seven Subject: Chemistry Teacher: Sumayya HammoudSumaya HammoudNo ratings yet
- Allergies Grade 8Document1 pageAllergies Grade 8Sumaya HammoudNo ratings yet
Chapter 6: Reproduction of Flowering Plants Activity 1 and 2: Pollination and Fertilization Notes
Chapter 6: Reproduction of Flowering Plants Activity 1 and 2: Pollination and Fertilization Notes
Uploaded by
Sumaya HammoudOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6: Reproduction of Flowering Plants Activity 1 and 2: Pollination and Fertilization Notes
Chapter 6: Reproduction of Flowering Plants Activity 1 and 2: Pollination and Fertilization Notes
Uploaded by
Sumaya HammoudCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6: Reproduction of Flowering Plants
Activity 1 and 2: Pollination and Fertilization
Notes:
Plants have roots, stem, leaves and a flower. Each one of these parts has its job. Roots will absorb from
the soil, leaves will make the food of the plant, stem will transport liquids to all of the plant and the
flower will do reproduction.
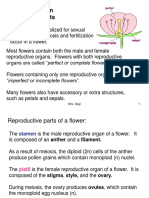
The flower is made of the sepals, petals, stamens and a pistil.
The male and female reproductive parts of flowering plants are the stamen and pistil.
- Stamen is the male reproductive part of the flower.
It consists of the anther and the filament.
The anther produces pollen grains.
- Pistil is the female reproductive part of the flower.
Top part of the pistil is called the stigma.
Stigma is supported by the style.
Base part of the pistil is the ovary.
Ovary contains one or more ovules.
❖ Flowers that contain both male and female reproductive parts are called bisexual flowers (perfect
flower).
❖ Flowers that contain either male or female reproductive parts are called unisexual flowers (imperfect
flower).
How pollination happens:
• For fertilization to take place, pollen grains need to be transferred from the stamen to the
stigma.
• If the transfer of pollen grain takes place in the same flower, then it is called direct pollination.
• If the transfer of pollen grain takes place from one flower to another, then it is called indirect
pollination.
• This transfer of pollen grains is done by wind, water, insects or animals.
How fertilization happens:
• After the pollen grain lands on the sticky stigma, the tube cell produces a pollen tube inside the
pistil into the ovule.
• The male gametes (sperm) travel through the pollen tube to reach the ovule.
• After they reach the ovule, one of the male gametes fuses with the female gamete leading to
fertilization.
• Fertilization leads to the formation of zygote.
• The zygote divides multiple times to form an embryo within the ovule.
• At the end, the ovule develops and turns into a seed and the ovary becomes a fruit.
You might also like
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Luz ClaritaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction of PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction of PlantsJohn Nowell DiestroNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument53 pagesPlant and Animal ReproductionSheryl Osorio100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDrDibendu Kumar BejNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2Maro Ridhwan RidhiwaniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument21 pagesReproduction in Plantsrani bloriaNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Reproduction in Plants 3Document30 pagesCH 12 Reproduction in Plants 3Shvet MahajanNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceDocument41 pagesGrade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceJulie Mae Sajulga JacobeNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesNotes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsAdnan SathikNo ratings yet
- How Do Plants Reproduce? Lesson 1: I. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesHow Do Plants Reproduce? Lesson 1: I. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsJulliena BakersNo ratings yet
- How Do Org ReproduceDocument32 pagesHow Do Org ReproducePankaj Kumar100% (1)
- Fertilisation in Plants: Objective: To Know How Gametes Fuse Together in PlantsDocument8 pagesFertilisation in Plants: Objective: To Know How Gametes Fuse Together in PlantsMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- Pollination in PlantsDocument214 pagesPollination in PlantsAbraham SekyiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Jann LarNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductionChal WijeNo ratings yet
- 2 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument35 pages2 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceCool VighneshNo ratings yet
- Cbse X Sexual Reproduction in Plants: ScienceDocument12 pagesCbse X Sexual Reproduction in Plants: ScienceDaniel SunnyNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument23 pagesSexual ReproductionMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeDocument23 pagesLECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeJemuel LuminariasNo ratings yet
- Pollination, Fertilisation and GerminationDocument25 pagesPollination, Fertilisation and GerminationAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document101 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Gabrielle MorganNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 2022Document97 pagesReproduction in Plants 2022Newera WizzzNo ratings yet
- Q.11 (A) Name The Important Parts of A FlowerDocument6 pagesQ.11 (A) Name The Important Parts of A FlowerFari NaheedNo ratings yet
- 2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument59 pages2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceCool VighneshNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- Plant Sexual ReproductionDocument22 pagesPlant Sexual ReproductionmarijaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Marie Lm DamascoNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument15 pagesAsexual Reproductioneugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Module 5: Heredity: OutcomesDocument22 pagesModule 5: Heredity: OutcomesNavtej DeyalNo ratings yet
- Plant Animal ReproductionDocument7 pagesPlant Animal ReproductionKyla Renz de LeonNo ratings yet
- Pollination NotesDocument6 pagesPollination Notesketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Part Two of Your JourneyDocument3 pagesWelcome To The Part Two of Your JourneyRaphael Louis DacanayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesChapter - 12 Reproduction in Plantsanju singhNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzDocument14 pagesACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzjundon.ivo.deborjaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Document6 pagesBiology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)47. Anas SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument17 pagesFlowering Plantsjoshua.brussell100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science SHS 17.2 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument29 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 17.2 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsWinsear VardeNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W5 Science 5Document48 pagesQ2 - W5 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesPlant Reproduction and Developmentits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants Powerpoint Class 3 and 4Document9 pagesFlowering Plants Powerpoint Class 3 and 4api-308489491No ratings yet
- 07 Science Key Notes ch12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument1 page07 Science Key Notes ch12 Reproduction in Plantsnufail aliNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Document8 pagesEarth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument2 pagesParts of A FlowerIrish cambriNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of Life (Plant Reproduction)Document15 pagesPerpetuation of Life (Plant Reproduction)Grace Gaje DizonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringblistedxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument80 pagesChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingDocument34 pagesReproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsJada MillerNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFDocument18 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFCatherine Mistiola100% (1)
- BIO 101 Lecture 12Document23 pagesBIO 101 Lecture 12bamimoreridwan06No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction StudentDocument64 pagesPlant Reproduction StudentmrkoutsantanouNo ratings yet
- Grade-7-Q2-Module-4-Sexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdDocument20 pagesGrade-7-Q2-Module-4-Sexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdroseNo ratings yet
- DC5 - Biology - 22ND June 2023Document30 pagesDC5 - Biology - 22ND June 2023siddiquinabil92No ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesSexual Reproductionshashwatdwivedi9000No ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument50 pagesPlant Reproductiongoldennyeche080No ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument15 pagesPerpetuation of LifeMomo Capoquian100% (1)
- 7.e.c Evaporation Part 2Document14 pages7.e.c Evaporation Part 2Sumaya HammoudNo ratings yet
- I. Answer by True or False and Correct The False Statement.: Solutions Revision SheetDocument2 pagesI. Answer by True or False and Correct The False Statement.: Solutions Revision SheetSumaya HammoudNo ratings yet
- Date: Chemical Reactions Sheet Name: Grade: Seven Subject: Chemistry Teacher: Sumayya HammoudDocument1 pageDate: Chemical Reactions Sheet Name: Grade: Seven Subject: Chemistry Teacher: Sumayya HammoudSumaya HammoudNo ratings yet
- Allergies Grade 8Document1 pageAllergies Grade 8Sumaya HammoudNo ratings yet