Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KNGF-Guideline: For Physical Therapy in Patients With Stress Urinary Incontinence
KNGF-Guideline: For Physical Therapy in Patients With Stress Urinary Incontinence
Uploaded by
silkofosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KNGF-Guideline: For Physical Therapy in Patients With Stress Urinary Incontinence
KNGF-Guideline: For Physical Therapy in Patients With Stress Urinary Incontinence
Uploaded by
silkofosCopyright:
Available Formats
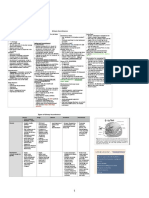
KNGF-Guideline
for Physical Therapy in patients Royal Dutch Society for Physical Therapy
with Stress urinary incontinence identifying problem categories I, II and III
treatment plan for men with stress urinary incontinence
disorder I II III
SUI with pelvic floor dysfunction SUI without SUI + general factors
men with prostate problems at - history-taking
men with urinary incontinence pelvic floor impeding recovery or
risk for urinary incontinence - physical examination no voluntary control no involuntary voluntary control + unfavorable
- other examinations dysfunction adjustment processes
control present influence on
- e.g. urinalysis
- micturition diary pelvic floor muscle
- PVR (estimating flow rate, function due
uroflowmetry)
to respiratory
- digital rectal palpation continence
dysfunction,
nurse
dysfunction
(pelvic)
of parts of
family physician family physician advice physical therapist musculoskeletal
(primary care) (primary care) (direct access) system
components,
voiding posture,
no red flags? toileting regime
and behavior
problem problem simple no goal recovering voluntary control compensation or – recovering PF – recovering PF – compensation - recovering PF function
identification: identification problem
adjustment function function – optimizing PF - optimizing PF
prostate
carcinoma? – optimizing PF – optimizing PF - adaptation and
- pathology, type of UI unclear PVR < 100 mL
compensation of
- recurrent UI no evidence collect patient’s
of reduced medical data restrictions (as much as
- UI with pain, blood in urine
- recurrent UTI flow rate (with their possible)
- (severe?) micturition problems permission)
- urinary tract obstruction strategy achieving voluntary control compensation single to multiple single to multiple single to single to multiple to fully
- PF radiation treatment through voluntary to fully automatic to fully automatic multiple to fully automatic task
- radical PF surgery
control, and im- tasks tasks automatic tasks
stop, wait medical proving voluntary
until available data control
history-taking therapy - verbal instruction and/or – practicing the – PFMT if – exercises to – PFMT – addressing impeding
complex
physical examination yes
problem biofeedback ‘Knack’ while insufficient address un- factors if possible
other examinations:
- urine culture - digital palpation by patient coughing progress favorable factors Note: full
- uroflowmetry or PT recovery not – informing patient
- cystoscopy (P)PT
+/- – PFMT during – PFPT to speed up – PFMT possible about possibilities and
PVR 100 mL - (m)UDT
- PVR incontinence products only PPT (invasive procedures): trunk progress impossibilities
reduced
flow rate - electrostimulation (with stabilization if insufficient
Identifying impairments, limitations PFMT) progress: PFPT to – education
and participation restrictions:
- nature of incontinence, differentiate diagnostic process - electrostimulation (only) speed up progress
from UTI for
- PFPT in case of doubt about – exercise therapy
- nature of disorder physical therapy
patient’s ability to contract
referral to specialist referral to specialist - severity of disorder
(secondary care) (secondary care) PF muscles – PFMT
by:
- history-taking: nature, severity (VAS,
techniques: – +/- PFPT, depending
PRAFAB, PSC), questions on risk factors,
PFPT prior ideas, views (‘illness beliefs’) – tugging PF on speed of recovery
yes
to surgery - physical examination: inspection at – tapping
rest, during movement, general, local
– digital vibration
- anal palpation (only by PPT), testing
diagnosis of diagnosis pelvic floor function
surgery no voluntary no voluntary
prostate of USUI - voiding posture and toileting behavior
carcinoma control control
Further examinations
measurement instruments: PFMT refer to
PFPT after surgery yes - micturition diary
surgery:
family
yes - pad test
radical doctor or
analysis,
prostatectomy medical
no evaluation
specialist/
USUI? referring
doctor
identifying problem categories I, II and III
analysis, identifying modifiable prognostic factors, trial therapy (6 sessions)
no stop degree of modifiability
evaluation
favorable result no result
v v
PF = pelvic floor; PFPT = pelvic floor physical therapy; (P)PT= (pelvic) physical therapist; UI = urinary incontinence; USUI = urodynamic stress urinary incontinence; continue contact referring doctor
UTI = urinary tract infection; PVR = post-voidal residue; (m)UDT = (mobile) urodynamic testing; VAS = visual analog scale; GPE = global perceived effect;
PSC = patient-specific complaints evaluation evaluate result: PRAFAB, GPE, PSC, VAS (pad test, micturition diary)
monitoring check-up + reminder (if necessary) t therapy (if required) u
V-02/2011 The complete guideline is available from www.kngfrichtlijnen.nl © KNGF
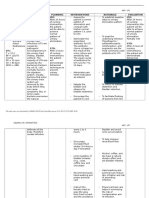
KNGF-Guideline
for Physical Therapy in patients Royal Dutch Society for Physical Therapy
with Stress urinary incontinence
- history-taking women with urinary incontinence identifying problem categories I, II and III
- physical
examination treatment plan for women with stress urinary incontinence
- other examinations
- e.g. urinalysis
- micturition diary
disorder I II III
SUI with pelvic floor dysfunction SUI without SUI + general factors
continence nurse pelvic floor impeding recovery or
no voluntary control no involuntary voluntary control + unfavorable dysfunction adjustment processes
control present influence on
(pelvic) physical therapist pelvic floor muscle
family physician (direct access)
advice function due
(primary care)
to respiratory
dysfunction,
dysfunction
red flags? of parts of
no
problem simple problem musculoskeletal
identification system
no
components,
voiding posture,
- pathology, type of UI unclear collect patient’s toileting regime
- recurrent UI medical data
- UI with pain, blood in urine and behavior
(with their
- recurrent UTI permission)
- (severe?) micturition problems goal recovering voluntary control compensation or – recovering PF – recovering PF – compensation – recovering PF function
- urinary tract obstruction adjustment function function – optimizing PF – optimizing PF
- PF radiation treatment
- radical PF surgery medical data – optimizing PF – optimizing PF
stop, wait available
until available strategy achieving voluntary control compensation single to multiple single to multiple single to single to multiple to fully
complex through voluntary to fully automatic to fully automatic multiple to fully automatic tasks
yes
problem control, and tasks tasks automatic tasks
improving
(P)PT +/- voluntary control
history-taking incontinence
physical examination products
other examinations: therapy verbal instruction and/or – practicing the – PFMT if insuf- – exercises to – PFMT – addressing impeding
- urine culture biofeedback ‘Knack’ while ficient progress address un- factors if possible
- uroflowmetry
- cystoscopy Identifying impairments, limitations and coughing favorable factors Note: full
participation restrictions: diagnostic process
- (m)UDT for physical only PPT (invasive procedures): – PFPT to speed up – PFMT recovery not – informing patient
- PVR - nature of incontinence, differentiate
from UTI therapy - electrostimulation (with – PFMT during progress possible about possibilities and
- nature of disorder PFMT) trunk if insufficient impossibilities
- severity of disorder - electrostimulation (only) stabilization progress: PFPT to
referral to specialist
(secondary care) - PFPT in case of doubt about speed up progress – education
by: patient’s ability to contract
- history-taking: nature, severity (VAS, PF muscles – exercise therapy
PRAFAB, PSC), questions on risk factors,
PFPT prior ideas, views (‘illness beliefs’)
to surgery yes - physical examination: inspection at rest, techniques: – PFMT
during movement, general, local
- tugging PF
- vaginal/anal palpation (only by PPT),
testing pelvic floor function - tapping – +/- PFPT, depending
- voiding posture and toileting behavior - digital vibration on speed of recovery
diagnosis of USUI surgery no
voluntary no voluntary
Further examinations
measurement instruments: control control
PFPT after yes
surgery - micturition diary
- pad test PFMT refer to
family
no analysis, doctor or
evaluation medical
specialist/
referring
stop
doctor
identifying problem categories I, II and III trial therapy (6 sessions)
identifying modifiable prognostic factors,
degree of modifiability
favorable result no result
v v
continue contact referring doctor
PF = pelvic floor; PFPT = pelvic floor physical therapy; (P)PT= (pelvic) physical therapist; UI = urinary incontinence; USUI = urodynamic stress urinary incontinence;
UTI = urinary tract infection; PVR = post-voidal residue; (m)UDT = (mobile) urodynamic testing; VAS = visual analog scale; GPE = global perceived effect; evaluation evaluatie resultaat: vragenlijsten PRAFAB, GEE, PSK, VAS (padtest, mictielijsten)
PSC = patient-specific complaints
monitoring check-up + reminder (if necessary) t therapy (if required) u
V-02/2011 The complete guideline is available from www.kngfrichtlijnen.nl © KNGF
You might also like
- Exercise After Breast Augmentation A Randomized.13Document7 pagesExercise After Breast Augmentation A Randomized.13CPR tyoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Balance Monitoring PosterDocument1 pageFluid Balance Monitoring PosterSania oktaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Leg Edema Exercises Brochure - EN (LR) PDFDocument2 pagesChronic Leg Edema Exercises Brochure - EN (LR) PDFsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Sacred Healing Plants, Foods As MedicineDocument31 pagesSacred Healing Plants, Foods As MedicineShineiNo ratings yet
- The Fall of The House of UsherDocument24 pagesThe Fall of The House of UsherpoenariusenidaNo ratings yet
- Stress Urinary Incontinence - FlowchartDocument2 pagesStress Urinary Incontinence - FlowcharteliansubiratsNo ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument1 pageAPPENDICITISAmber BlodduweddNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Biofeedback Therapy For Pelvic Floor Disorders Narayanan2019Document8 pagesA Practical Guide To Biofeedback Therapy For Pelvic Floor Disorders Narayanan2019Yvonne MedinaNo ratings yet
- Presentation ERAS Digestive TutorialDocument32 pagesPresentation ERAS Digestive TutorialFebriadi R100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Urinary EliminationTrixy Marie EcotNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning (Desired or Expected Outcomes) Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning (Desired or Expected Outcomes) Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAsniah Hadjiadatu Abdullah100% (1)
- Demystifying Medical DocumentationDocument37 pagesDemystifying Medical Documentationadultmedicalconsultants100% (14)
- Oab GuidelinesDocument2 pagesOab GuidelinesamirzoevaNo ratings yet
- Urinery IncontinsetenceDocument1 pageUrinery IncontinsetenceLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- CuesDocument2 pagesCuesFrance SuarezNo ratings yet
- Exercise Prescription Softwares PDFDocument5 pagesExercise Prescription Softwares PDFNujella BalajiNo ratings yet
- Rcog2018 1e20645 NORMALDocument1 pageRcog2018 1e20645 NORMALberlianromaNo ratings yet
- Aquino NCP UtiDocument3 pagesAquino NCP UtiGianne ObaldoNo ratings yet
- 1 12 PDFDocument12 pages1 12 PDFAndalani Diri AstamiNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Functional Urinary IncontinenceDocument4 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Functional Urinary IncontinenceJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Subjective Objective Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesSubjective Objective Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlethen Janine SagunNo ratings yet
- Flour OsDocument3 pagesFlour OsMuhammad Abu DzarNo ratings yet
- 2020 21 Matrix Covid19 st6 7 Who Switched To 2019 CoreDocument4 pages2020 21 Matrix Covid19 st6 7 Who Switched To 2019 CoreOzhenNo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAPHDocument2 pagesPARTOGRAPHZairah Mae BangguiyaoNo ratings yet
- Effects of A Short Term Resistance Program Using.9Document8 pagesEffects of A Short Term Resistance Program Using.9Michelle ThomasNo ratings yet
- ESA Prospect Thoracotomy Poster v10Document1 pageESA Prospect Thoracotomy Poster v10Andreea ShalidaNo ratings yet
- MOD 2016-11-14 General Surgery Curriculum Subject Outlines - Operative Management-2Document36 pagesMOD 2016-11-14 General Surgery Curriculum Subject Outlines - Operative Management-2KW WongNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Open and Closed Chain Exercise and Knee Joint Position On Patellar Tracking in Lateral Patellar Compression SyndromeDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Open and Closed Chain Exercise and Knee Joint Position On Patellar Tracking in Lateral Patellar Compression SyndromeSalem DaldoulNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationSiafei RabeNo ratings yet
- Effects of Taping On Pain and Function in Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome - A Randomized Controlled TrialDocument11 pagesEffects of Taping On Pain and Function in Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome - A Randomized Controlled Trialsaeed seedNo ratings yet
- PhysicalActivityBrochure Finalv2 FIXEDDocument3 pagesPhysicalActivityBrochure Finalv2 FIXEDagNo ratings yet
- CHP Poster Final - April 2023Document1 pageCHP Poster Final - April 2023api-620860184No ratings yet
- Urinary Retention NCP GARCIA J.Document2 pagesUrinary Retention NCP GARCIA J.Jimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map: Urinary EliminationDocument1 pageConcept Map: Urinary EliminationKring kringNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesMEDSURG Urinary SystemQV MangubatNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Lower Urinary TractDocument5 pagesDisorders of Lower Urinary TractMuhammadR1No ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain in Physical Therapy Practice PDFDocument12 pagesAbdominal Pain in Physical Therapy Practice PDFdanielNo ratings yet
- Evidenciasenla Rehabilitacindel Hombro Doloroso 2018Document109 pagesEvidenciasenla Rehabilitacindel Hombro Doloroso 2018Alan Calderón BerrioNo ratings yet
- Exercise Vs Exercise Plus ManualDocument14 pagesExercise Vs Exercise Plus Manual양종혁No ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Activation in Conventional Therapeutic Exercises and Heavy Resistance Exercises - Implications For RehabilitationDocument15 pagesNeuromuscular Activation in Conventional Therapeutic Exercises and Heavy Resistance Exercises - Implications For RehabilitationАлексNo ratings yet
- Assis G - Proposta de Protocolo de Avaliação e Treinamento Da MAP para Atendimento À Mulher Com IUDocument9 pagesAssis G - Proposta de Protocolo de Avaliação e Treinamento Da MAP para Atendimento À Mulher Com IUAnderson Araujo CorreaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CONSULTATION RHU MergedDocument2 pagesGENERAL CONSULTATION RHU Mergedmondirah pandaNo ratings yet
- 15 UrinalysisDocument9 pages15 UrinalysisJaney Ceniza تNo ratings yet
- Role of Lasuna Taila Vasti in Artava Vyapada - Menstrual IrregularitiesDocument3 pagesRole of Lasuna Taila Vasti in Artava Vyapada - Menstrual IrregularitiesMSKCNo ratings yet
- I DDuQgUQe NQ7kIFAHv A Word Parts Lecture Supplement SuffixesDocument1 pageI DDuQgUQe NQ7kIFAHv A Word Parts Lecture Supplement Suffixes22alhumidi2020No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledCherry CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Syndromic Management of STIsDocument1 pageSyndromic Management of STIsJoyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Unit 4Document1 pageTutorial Unit 4Norzalikah TarapiduNo ratings yet
- Effect of Surgery For Stress Incontinence On Female Sexual FunctionDocument9 pagesEffect of Surgery For Stress Incontinence On Female Sexual FunctionMariana HernandezNo ratings yet
- Clinical DocumentationDocument18 pagesClinical DocumentationKHAIRUL REDZUANNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sensorimotor Insoles On Lower Limbs Muscles Activity in People With Flexible FlatfootDocument13 pagesEffect of Sensorimotor Insoles On Lower Limbs Muscles Activity in People With Flexible FlatfootOndřej LaštovičkaNo ratings yet
- Electromyographic Analysis of Traditional and Nontraditional Abd 2006Document16 pagesElectromyographic Analysis of Traditional and Nontraditional Abd 2006Yan MatosNo ratings yet
- CPG - Women's Health and Orthopaedic Section's ICF-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines On Pelvic Girdle Pain in The Antepartum PopulationDocument24 pagesCPG - Women's Health and Orthopaedic Section's ICF-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines On Pelvic Girdle Pain in The Antepartum Populationmfrengifo.casasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Petty Musculoskeletal Examination and AssessmentDocument2 pagesChapter 13 Petty Musculoskeletal Examination and AssessmentRohmat ChrNo ratings yet
- July 2012 Pnle Pearls of Success Part 6: Medical and Surgical Health NursingDocument7 pagesJuly 2012 Pnle Pearls of Success Part 6: Medical and Surgical Health NursingNicole OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Stress Urinary Incontinence: Dr. Murad H. AssalyaDocument27 pagesStress Urinary Incontinence: Dr. Murad H. Assalyamorad.hassan4767No ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPbulok netflakesNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Well-Being Diagnostic Tests Sheet1Document2 pagesAssessment of Fetal Well-Being Diagnostic Tests Sheet1msbunnileeNo ratings yet
- Total Knee Replacement - EnglishDocument21 pagesTotal Knee Replacement - Englishjoey hoNo ratings yet
- Boston Care Ivf MethodolgyDocument58 pagesBoston Care Ivf Methodolgylijo workNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimNo ratings yet
- Weight Lifting and Lymphedema: Clearing Up MisconceptionsDocument4 pagesWeight Lifting and Lymphedema: Clearing Up MisconceptionssilkofosNo ratings yet
- NL Handout 2013-03-05 PDFDocument21 pagesNL Handout 2013-03-05 PDFsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Input4 Insufficiency 2012-03-05 PDFDocument14 pagesInput4 Insufficiency 2012-03-05 PDFsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Mode of Action of Cupping Local Metabolism and Pain Thresholds in Neck Pain Patients and Healthy Subjects 2014Document11 pagesMode of Action of Cupping Local Metabolism and Pain Thresholds in Neck Pain Patients and Healthy Subjects 2014silkofosNo ratings yet
- Gonstead Extremity AdjustingDocument63 pagesGonstead Extremity AdjustingsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Acupoint Stimulation For Fibromyalgia 2013Document15 pagesAcupoint Stimulation For Fibromyalgia 2013silkofosNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain Practice Guidelines 2013Document12 pagesLow Back Pain Practice Guidelines 2013silkofosNo ratings yet
- Evidence Statement Anal Incontinence Flowchart PDFDocument2 pagesEvidence Statement Anal Incontinence Flowchart PDFsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines For Physical Therapy in Patients With Intermittent ClaudicationDocument51 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines For Physical Therapy in Patients With Intermittent ClaudicationsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Intermittant Claudication FlowchartDocument2 pagesIntermittant Claudication FlowchartsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Discectomy Rehab CohraneDocument105 pagesDiscectomy Rehab CohranesilkofosNo ratings yet
- KNGF Evidence Statement: Anal IncontinenceDocument2 pagesKNGF Evidence Statement: Anal IncontinencesilkofosNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation After Lumbar Discectomy, Microdiscectomy and Decompressive LaminectomyDocument8 pagesRehabilitation After Lumbar Discectomy, Microdiscectomy and Decompressive LaminectomysilkofosNo ratings yet
- Hartrevalidatie PRL Eng KNGFDocument52 pagesHartrevalidatie PRL Eng KNGFsilkofosNo ratings yet
- KNGF Evidence Statement: Anal IncontinenceDocument22 pagesKNGF Evidence Statement: Anal IncontinencesilkofosNo ratings yet
- CrossFit Coach GeneralDocument1 pageCrossFit Coach Generalglobowens0% (1)
- Nutrition: Naveed Ahmed KhanDocument21 pagesNutrition: Naveed Ahmed KhanAnum ManzoorNo ratings yet
- (New Horizons in Public Policy Series) Howard J. Elcock - Political Leadership (2001, Edward Elgar Pub) PDFDocument226 pages(New Horizons in Public Policy Series) Howard J. Elcock - Political Leadership (2001, Edward Elgar Pub) PDFgulistan.alpaslan8134No ratings yet
- Model Question Paper SampleDocument8 pagesModel Question Paper SampleMilanSinghBaisNo ratings yet
- Acute Stridor in Children CA1080 v.8Document13 pagesAcute Stridor in Children CA1080 v.8jahangirealamNo ratings yet
- Motivation in OrganizationsDocument25 pagesMotivation in OrganizationsMaka T ForomaNo ratings yet
- Issues in Therapy With Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender ClientsDocument33 pagesIssues in Therapy With Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender ClientsOlena Baeva0% (1)
- Care & Maintenance of Contact LenseDocument26 pagesCare & Maintenance of Contact LenseGurria NaheedNo ratings yet
- Tender For EndoscopeDocument131 pagesTender For EndoscopeJasjit Singh100% (1)
- Ch05 Presentation CPRDocument28 pagesCh05 Presentation CPRDawn KleinNo ratings yet
- Arya 2014Document15 pagesArya 2014pratyusha vallamNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Terminologies in Fish Disease: Jitendra Lama Roll No: 16Document4 pagesCommonly Used Terminologies in Fish Disease: Jitendra Lama Roll No: 16Santosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Moda Dil DenemeDocument262 pagesModa Dil Denemenewbiology90100% (1)
- Schilder's Disease: EpidemiologyDocument4 pagesSchilder's Disease: EpidemiologyUky SuGoyNo ratings yet
- Rochester Treatment of Asthma 3 1906Document4 pagesRochester Treatment of Asthma 3 1906IGNo ratings yet
- Limbic SystemDocument4 pagesLimbic SystemAyu NurdiyanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1-ResearchDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 1-ResearchLyn Valles100% (3)
- Active COVID-19 Workplace Outbreaks in Oregon (Published 10/7)Document5 pagesActive COVID-19 Workplace Outbreaks in Oregon (Published 10/7)KGW News100% (2)
- 2856 - Jemds Title PageDocument2 pages2856 - Jemds Title PageKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Knjiga Rezimea EIP 2012Document197 pagesKnjiga Rezimea EIP 2012MilicaMilijicNo ratings yet
- Amputation Rehabilitation and Prosthetic Restoration. From Surgery To Community ReintegrationDocument7 pagesAmputation Rehabilitation and Prosthetic Restoration. From Surgery To Community ReintegrationGabriela Istrati-StanciugelNo ratings yet
- Walter Whitehead A Brief History of The Man and His Varnish Frafjord British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2007 45-8-622 622Document1 pageWalter Whitehead A Brief History of The Man and His Varnish Frafjord British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2007 45-8-622 622mandible removerNo ratings yet
- Simulated Practice Test-3 General Education PDFDocument15 pagesSimulated Practice Test-3 General Education PDFdiraNo ratings yet
- Dose-Response Study of N, N-Dimethyltryptamine in HumansDocument11 pagesDose-Response Study of N, N-Dimethyltryptamine in HumansAnonymous zxTFUoqzklNo ratings yet
- Dissertations AbstractsDocument76 pagesDissertations AbstractsdrjunejanitinNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Ilmiah Simantek ISSN: 2550-0414 Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2018Document11 pagesJurnal Ilmiah Simantek ISSN: 2550-0414 Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2018SandiNo ratings yet
- Fire Door Assembly Classifications: DecodedDocument3 pagesFire Door Assembly Classifications: DecodedTty SmithNo ratings yet
- MoHFW Directory - 7Document22 pagesMoHFW Directory - 7nagarjunaNo ratings yet