Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C7 Lecture Notes
C7 Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
Jonathan Navallo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesOriginal Title
C7 Lecture Notes.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesC7 Lecture Notes
C7 Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
Jonathan NavalloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
CHAPTER 7: INVESTMENT OF EXCESS CASH
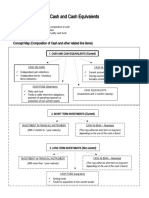
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS Investments in time deposit, money market
instruments, and treasury bills should be
Money – standard medium of exchange;
classified as follows:
currency and coins in circulation and legal
tender. Three months or less – cash and cash
equivalents
Cash – money and other negotiable
instruments payable in money and acceptable More than three months but within one
by the bank for deposit; checks, bank drafts, year – short-term financial assets/temporary
and money orders. investments and classified as current assets
Postdated checks – received but not More than one year – non-current or long-
considered as cash yet because they are term investments.
unacceptable by the bank.
“Cash” must be an item unrestricted in use.
CASH FUND FOR A CERTAIN
PURPOSE
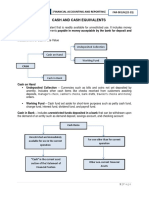
CASH ITEMS INCLUDED IN CASH
Current asset (cash and cash equivalents)
1. Cash on hand – undeposited cash – for use in current operations/ payment of
collections and other cash items awaiting current obligation
deposit
Long-term investment – for noncurrent
2. Cash in bank – demand deposit or checking purpose/payment of non-current obligation
account and saving deposit which are
unrestricted as to withdrawal. “The classification of cash fund as current or
non-current should parallel the classification of
3. Cash fund – set aside for current purposes the related liability”
such as petty cash fund, payroll fund and
dividend fund.
BANK OVERDRAFT – Credit balance of
cash in bank account; current liability and can
CASH EQUIVALENTS be offset against other bank accounts with
debit balances.
Short-term and highly liquid investments
readily convertible into cash; insignificant risk
of changes in value because of changes in
interest rates COMPENSATING BALANCE
“Only highly liquid investments that are Minimum checking or demand deposit account
acquired three months before maturity balance that must be maintained in a borrowing
can qualify as cash equivalents” arrangement.
Classification of compensating balance:
MEASUREMENT OF CASH a) Part of cash if deposit is not legally
restricted because of an informal
a) Cash is measured at face value. compensating balance agreement
b) Cash in foreign currency at current b) Classified separately as “cash held as
exchange rate. compensating balance” if deposit is
c) A bank/financial institution in bankruptcy legally restricted because of formal
or financial difficulty, should write down compensating balance agreement;
cash to estimated realizable value current assets if the related loan is short
term.
UNDELIVERED/UNRELEASED PETTY CASH FUND
CHECK Money set aside for small expenses
Drawn and recorded but not given to the payee a) Imprest fund system – system control
before the end of reporting period. of cash which wherein all cash receipts
should be deposited intact and all cash
disbursements should be made by
means of check
POSTDATED CHECK DELIVERED b) Fluctuating fund system – the checks
drawn to replenish the fund do not
Drawn, recorded and already given to payee
necessarily equal the petty cash
but bears a date subsequent to the end of
disbursements.
reporting period.
STALE CHECK/CHECK LONG
OUSTANDING Not encashed by payee
within a relatively long period of time;
presentment must be made within a
“reasonable time” after its issue to remain
outstanding.
WINDOW DRESSING
Deliberate misstatement of assets,
liabilities, equity, income and expenses.
Opening the book of accounts beyond the close
of reporting period for the purpose of showing a
better financial position and performance.
LAPPING
Conceal cash shortage; series of
postponements of entries for the collection
made from another customer.
KITTING
Conceal cash shortage; possible when the
entity maintains current accounts in different
banks; no entry is made for drawing and
deposit of check
Cash short or over account – a temporary or
suspense account; offsetting account in cash
shortage or cash overage
You might also like
- Dentist Chart of AccountDocument4 pagesDentist Chart of AccountrajawhbNo ratings yet
- Examination of Conscience For Seminarians 27th Nov 2005Document2 pagesExamination of Conscience For Seminarians 27th Nov 2005FrDylan James100% (5)
- Portfolio Part 2: Practical Case Study InstructionsDocument4 pagesPortfolio Part 2: Practical Case Study InstructionsNour KhairallahNo ratings yet
- LOK SABHA MUN GuideDocument19 pagesLOK SABHA MUN GuideAkshat TotlaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Rhetorical Analysis FinalDocument7 pagesComparative Rhetorical Analysis Finalapi-296678382No ratings yet
- 10 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pages10 Cash and Cash EquivalentsuncianojhezrhyllemhaeNo ratings yet
- NOTESmidtermDocument6 pagesNOTESmidtermAlexis Jhan MagoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMary Jullianne Caile SalcedoNo ratings yet
- C and CE NotesDocument4 pagesC and CE NotesFrancine PimentelNo ratings yet
- Audit Problems FinalDocument48 pagesAudit Problems FinalShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS ReviewerDocument2 pagesCASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS ReviewerhelloangelodavidNo ratings yet
- INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 (Module)Document2 pagesINTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 (Module)April GumiranNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJUST KINGNo ratings yet
- Sta Clara - Summary Part 1Document49 pagesSta Clara - Summary Part 1Carms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- Notes (Audit Prob)Document6 pagesNotes (Audit Prob)kodzuken.teyNo ratings yet
- 02 - Cash & Cash EquivalentDocument5 pages02 - Cash & Cash EquivalentEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesSummary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsMhico Mateo100% (1)
- Audit ProblemsDocument47 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument32 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTSssDocument9 pagesCASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTSssChristian NavalesNo ratings yet
- #10 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pages#10 Cash and Cash Equivalentsmilan100% (3)
- CFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Substantive Test of CashDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Substantive Test of CashJesievelle Villafuerte NapaoNo ratings yet
- Iv.-Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesIv.-Cash and Cash Equivalentsby ScribdNo ratings yet
- Ia1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesIa1 ReviewerVeronica SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheDocument4 pagesCash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheannyeongNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument32 pagesModule 3 Cash and Cash Equivalentschuchu tv100% (1)
- INTACC - Chapter 1Document4 pagesINTACC - Chapter 1MeriiiNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument34 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents Lecture Notesyna kyleneNo ratings yet
- Mastery of Practical Accounting 1:: Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesMastery of Practical Accounting 1:: Cash & Cash EquivalentsMaria IbonNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsCamille Joyce Corpuz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lessons - Far 1Document23 pagesCompiled Lessons - Far 1Gwyn OliverNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting, Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument3 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting, Cash and Cash Equivalentgodardo suraltaNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument20 pagesIntacc ReviewerAvos NnNo ratings yet
- 02 Cash Cash EquivalentDocument5 pages02 Cash Cash EquivalentalteregoNo ratings yet
- and Highly Liquid Investment Readily Convertible Into CashDocument3 pagesand Highly Liquid Investment Readily Convertible Into CashGirl Lang AkoNo ratings yet
- Accouting For Cash and Cash Equivalents CASH IncludesDocument4 pagesAccouting For Cash and Cash Equivalents CASH IncludesSecurity Bank Personal LoansNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Document7 pagesAcccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Rey HandumonNo ratings yet
- Ia1 Mod 1Document9 pagesIa1 Mod 1omssheshNo ratings yet
- Cash Part1Document7 pagesCash Part1cuaresmamonicaNo ratings yet
- FAR LectureDocument6 pagesFAR Lecturewingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsAngel RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsCLEAR MELODY VILLARANNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash Equivalents NotesDocument2 pagesCash Cash Equivalents NotesRoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cash and Cash Equivalent - REVIEWERDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Cash and Cash Equivalent - REVIEWERAiyana AlaniNo ratings yet
- Ia1 QualiDocument44 pagesIa1 QualiAiyana AlaniNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument67 pagesReviewerKyungsoo DohNo ratings yet
- Audit of CashDocument6 pagesAudit of Cashannebernadette watanNo ratings yet
- NU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesNU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDawn QuimatNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerMaliha KansiNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerWinnie ToribioNo ratings yet
- Int. Acc 1 Chap 1Document6 pagesInt. Acc 1 Chap 1Nicole Anne Santiago SibuloNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentsazieruga32No ratings yet
- Pre 2 Auditing Concepts and Applications Module 1 and 2Document3 pagesPre 2 Auditing Concepts and Applications Module 1 and 2Anjilla Amor RubiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pages1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsHamida Ismael MacabantogNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentsyes it's kaiNo ratings yet
- Assets - Syn 101Document35 pagesAssets - Syn 101Marianne SironNo ratings yet
- Ia ReviewerDocument11 pagesIa Reviewermichelle donaireNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument10 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMs VampireNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentDarwyn HonaNo ratings yet
- Court of Tax Appeals: First DivisioDocument12 pagesCourt of Tax Appeals: First DivisioJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Court of Tax Appeals Quezon City First DivisionDocument54 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Court of Tax Appeals Quezon City First DivisionJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Cta 2D CV 06177 D 2008jun30 AssDocument72 pagesCta 2D CV 06177 D 2008jun30 AssJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- RMC 64-2015 Required Information On Receipts and InvoicesDocument1 pageRMC 64-2015 Required Information On Receipts and InvoicesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Notes Receivable: PresentationDocument2 pagesNotes Receivable: PresentationJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Classes of Inventories ConsignmentDocument3 pagesInventories: Classes of Inventories ConsignmentJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Loans Receivable: Effective RateDocument2 pagesLoans Receivable: Effective RateJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing: 1. Pledge of Accounts ReceivableDocument1 pageReceivable Financing: 1. Pledge of Accounts ReceivableJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing: 3. Factoring of Accounts Receivable 4. Discounting of Notes ReceivableDocument2 pagesReceivable Financing: 3. Factoring of Accounts Receivable 4. Discounting of Notes ReceivableJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- C6 Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesC6 Lecture NotesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- C6 Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesC6 Lecture NotesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- C10 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesC10 Lecture NotesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- C6 Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesC6 Lecture NotesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Two-Date Bank Reconciliation Proof of Cash: 1. Book BalanceDocument1 pageTwo-Date Bank Reconciliation Proof of Cash: 1. Book BalanceJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Elements of Financial StatementsDocument2 pagesElements of Financial StatementsJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- C6 Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesC6 Lecture NotesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Assumptions Scope of Conceptual Framework: 1. Going ConcernDocument2 pagesAssumptions Scope of Conceptual Framework: 1. Going ConcernJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Two-Date Bank Reconciliation Proof of Cash: 1. Book BalanceDocument1 pageTwo-Date Bank Reconciliation Proof of Cash: 1. Book BalanceJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- The Accountancy Profession: American Accounting AssociationDocument2 pagesThe Accountancy Profession: American Accounting AssociationJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Qualitative CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesFundamental Qualitative CharacteristicsJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Fraud Tree Focus InventorycompressedDocument64 pagesFraud Tree Focus InventorycompressedJonathan Navallo100% (1)
- North KoreaDocument37 pagesNorth KoreaKrishnamoorthyRajanbabu100% (1)
- App Iii Summer Midterm ExamDocument9 pagesApp Iii Summer Midterm ExamCharmaine PamintuanNo ratings yet
- INDIAN PENAL CODE-NotesDocument56 pagesINDIAN PENAL CODE-NotesCP Ispat Unit IINo ratings yet
- Essay Fintech Vs Traditional Tech - Angela Putri KeziaDocument4 pagesEssay Fintech Vs Traditional Tech - Angela Putri KeziaAngela KeziaNo ratings yet
- Ponce Enrile, Cayetano, Reyes & Manalastas Law Offices For PetitionerDocument5 pagesPonce Enrile, Cayetano, Reyes & Manalastas Law Offices For PetitionerJojo LaroaNo ratings yet
- Leakage of Electronic Medical Record - Threat To PrivacyDocument382 pagesLeakage of Electronic Medical Record - Threat To PrivacyNandhini RaviNo ratings yet
- Hanbali Sufi HistoryDocument10 pagesHanbali Sufi HistoryDawudIsrael1100% (1)
- The Anne Frank Diary FraudDocument8 pagesThe Anne Frank Diary FraudGordon Logan100% (1)
- Analysis of Bitcoin in Illicit FinanceDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Bitcoin in Illicit FinanceZennie AbrahamNo ratings yet
- 32 - Heirs of Reinoso Vs CADocument2 pages32 - Heirs of Reinoso Vs CAcncrned_ctzenNo ratings yet
- Intel MB Dh67Document9 pagesIntel MB Dh67PinkyNo ratings yet
- Baviera Sales OutlineDocument12 pagesBaviera Sales OutlineRom100% (1)
- Reference Check FormDocument2 pagesReference Check FormDavid ThomasNo ratings yet
- S4611 EN Col14 ILT FV CO A4Document23 pagesS4611 EN Col14 ILT FV CO A4Tabe TambeNo ratings yet
- Broadway and Production Contract Tours: Office Receipts (80% of Minimum)Document2 pagesBroadway and Production Contract Tours: Office Receipts (80% of Minimum)Lauren BNo ratings yet
- Real Estate MortgageDocument9 pagesReal Estate MortgageApril Roween AranzaNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument3 pagesLong QuizLeiza Lapuz Pelayo100% (1)
- Commanding Amazon's Army of Workers With Software: Christopher MimsDocument2 pagesCommanding Amazon's Army of Workers With Software: Christopher MimsJulinar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Memorandum: Department of The Interior and Local GovernmentDocument2 pagesMemorandum: Department of The Interior and Local GovernmentMdrrmo LucbanNo ratings yet
- Enrollment Form: Name of StudentDocument2 pagesEnrollment Form: Name of StudentThat's EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- 323-1851-160 (6500 5400 8700 Interworking Solution) Issue7Document168 pages323-1851-160 (6500 5400 8700 Interworking Solution) Issue7José Pedro Batista Leite100% (1)
- GSLC Shares, Treasury Shares, DividensDocument2 pagesGSLC Shares, Treasury Shares, DividensGeordy SusantoNo ratings yet
- Basic Features of BondsDocument1 pageBasic Features of Bondspmaina100% (1)
- Yu v. NLRCDocument3 pagesYu v. NLRCBettina Rayos del SolNo ratings yet
- Sunway Resort HotelDocument3 pagesSunway Resort HotelBrianLeNo ratings yet