Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre Seen - 20 Marker
Pre Seen - 20 Marker
Uploaded by
MUKESH KUMAROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre Seen - 20 Marker
Pre Seen - 20 Marker
Uploaded by
MUKESH KUMARCopyright:
Available Formats
Macroeconomics, as a branch of economics, studies the behavior, patterns and
performance of an economy as a whole. It also deals with the structure and decision –
making of an economy. Macroeconomic objectives are goals and policies which the
government wishes to implement to ensure a smooth and successful functioning of the
economy.
Macroeconomic policies aim to increase the level of national income to the maximum
extent possible. They also aim to provide economic growth to raise the standard of
living and utility of participants who constitute the economy. Macroeconomic objectives
include less unemployment, lower levels of inflation and deflation, economic growth and
a steady balance of payments. Economic growth refers to an increase in the production
of economic products and services, compared over specific periods of time.
Traditionally, it is measured as the Gross National Product or Gross Domestic Product.
The government and its economy are deeply influenced by such macroeconomic
objectives. The two macroeconomic objectives that are extremely essential for the
government to achieve are high employment rates and lesser levels of inflation.
Employment refers to a relationship between two parties or entities, usually based on a
contract wherein one party, any corporation, not – for – profit organization, for profit or
co – operative is the employer and the other is the employee. A higher rate of
employment contributes greatly towards the working of an economy. It not just helps to
maximize the potential output in an economy but also to achieve productive efficiency. A
high employment rate helps to reduce the economic inequalities that persist in society
by preventing relative poverty. It helps reduce the rate of crimes and other such ethical
activities. It enables the firms to acquire a larger workforce and tap into a greater pool of
talent. A firm gets the opportunity to work with a diversified workforce from all works of
life which in turn becomes a competitive advantage. A high rate of employment in other
spheres eases the burden on the governments in terms of providing subsidies and
unemployment benefits. It also enables more income taxes thereby improving the
budget position.
Inflation quantitatively measures the rate at which the average price level of selected
goods and services in an economy increases over a period of time. Expressed in terms
of a percentage, inflation decreases the purchasing power of a nation’s currency. In
simpler terms, inflation refers to the general level of price of goods and services
increasing. Less or the absence of inflation increases affordability for the entire
population. It increases the purchasing power of the consumers and helps businesses
maintain long – term spending plans. It encourages businesses invest in order to
increase productivity and efficiency. Lesser inflation contributes to a stable level of
Gross Domestic Product. Lesser inflation also contributes to lesser levels of
unemployment, considerably lower levels of income inequality and lesser economic
uncertainty.
Considering the multitude of benefits that achieving these macroeconomic objectives
have for an economy, it becomes imperative for governments to take steps in that
direction. However, governments also face some hurdles in their path to achieve these
objectives.
Tackling unemployment is one of the biggest challenges especially in countries with
considerably larger populations. In order to increase the level of employment, it is
essential to have people who have the required skills for certain job positions. While
some sections of the population may be deprived of basic resources such as education,
others might simply be unwilling to apply for jobs. A large part of the population may
also not be of the required working age and hence may also not have certain skills such
as technological capabilities etc. Some firms and corporations also let go of their staff to
cut down on their costs, thereby increasing the work pressure on a certain group of
people. This leads to a dearth of viable job opportunities for a larger section of the
population.
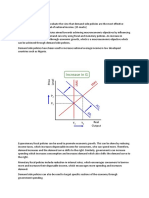
Obtaining a level of controlled or less inflation is also a somewhat difficult objective to
achieve. Aggregate demand refers to the measurement of the total demand of finished
goods and services in an economy. It is expressed as the total amount of money
exchanged for those particular goods and services at a set price level. It is often difficult
to curb the levels of inflation as the prices of goods are not always controllable and the
aggregate demand of these goods and services is often too high. High government
expenditure and high uncontrollable consumer spending also leads to inflation to a large
extent.
There are a few ways in which the government can solve the above mentioned
problems to achieve these macroeconomic benefits. These include both fiscal and
monetary policies. Fiscal policy refers to government spending and tax policies which
impact economic conditions, such as higher aggregate demand for goods and services,
employment and economic growth. Monetary policy is the demand side of economic
policy and refers to actions taken by the central bank of a nation to control money
supply with the aim to achieve macroeconomic benefits to ensure successful and
sustainable economic growth. Macroeconomic objectives can be achieved by revising
the terms and regulations of employment; controlling the price of essential goods and
services in the market; introducing strict monetary policies to reduce inflation; providing
viable job opportunities to unemployed people; increasing business investments so that
a larger number of people are able to avail job opportunities; increasing interest rates in
a controlled manner to control inflation and by reducing tax and increasing subsidies.
You might also like
- Pmap Do 174Document24 pagesPmap Do 174Tan-Uy Jefferson Jay100% (2)
- FRM Study PlanDocument4 pagesFRM Study PlanMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument85 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAnonymous 0wXXmp1No ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionChristianJerryNo ratings yet
- EconDocument19 pagesEconkajan thevNo ratings yet
- What Is Fiscal Policy?: Reem HeakalDocument4 pagesWhat Is Fiscal Policy?: Reem HeakalAngelaLouiseSimpsonNo ratings yet
- Government PolicyDocument11 pagesGovernment Policycarter sasaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document14 pagesUnit 2sonika7No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics and Micro EconomicsDocument8 pagesMacroeconomics and Micro EconomicsDeepanshi PNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument20 pagesFiscal PolicyPranav VaidNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy - 1Document6 pagesFiscal Policy - 1Prashant SinghNo ratings yet
- How Fiscal Policy WorksDocument3 pagesHow Fiscal Policy WorksMaviel Maratas SarsabaNo ratings yet
- Business Studies 4 (Unit 1)Document8 pagesBusiness Studies 4 (Unit 1)haidulamonicaNo ratings yet
- Public FinanceDocument20 pagesPublic FinanceMinaw BelayNo ratings yet
- Macro EconomicsDocument14 pagesMacro EconomicsMarwah YaseenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Allocation, Distribution and StabilisationDocument63 pagesUnit 2-Allocation, Distribution and Stabilisationironman73500No ratings yet
- EssayDocument5 pagesEssayJim_Tsao_4234No ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument6 pagesFiscal Policyapi-3695543100% (1)
- Role of Government in An Economy SystemDocument6 pagesRole of Government in An Economy SystemprosmaticNo ratings yet
- Assignment Q2Document3 pagesAssignment Q2DanielLim225No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledNaimee PareshaNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument3 pagesFiscal PolicyklainerflNo ratings yet
- Fiscal FunctionsDocument3 pagesFiscal FunctionsAshashwatmeNo ratings yet
- Expansionary and Fiscal Policy Tools To Stabilize The EconomyDocument22 pagesExpansionary and Fiscal Policy Tools To Stabilize The EconomyAndrea Marie O. JadraqueNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Govt. (Macro) Eco PoliciesDocument4 pagesGR 10 Govt. (Macro) Eco PoliciesAditi JaysonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Summary Fiscal PolicyDocument4 pagesLesson Summary Fiscal PolicyCam Tu LeNo ratings yet
- What Is Fiscal Policy?Document10 pagesWhat Is Fiscal Policy?Samad Raza KhanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Aims and ConflictsDocument18 pagesMacroeconomic Aims and ConflictsJenney TatNo ratings yet
- Demand Side PolicyDocument15 pagesDemand Side PolicyAnkit Shukla100% (1)
- Using RealDocument2 pagesUsing RealShreyas ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument3 pagesEffects of Fiscal and Monetary PolicyReene FranceNo ratings yet
- Fiscal and Monetary Policy PDFDocument2 pagesFiscal and Monetary Policy PDFAbbas KazmiNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy Refers To The Use of Government Spending and Tax Policies ToDocument5 pagesFiscal Policy Refers To The Use of Government Spending and Tax Policies ToSaclao John Mark GalangNo ratings yet
- .1 - Government Economic Policy: The Macroeconomic AimsDocument3 pages.1 - Government Economic Policy: The Macroeconomic AimsMarisa VetterNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument9 pagesFiscal PolicyEnrique IglesiasNo ratings yet
- BE 3 Unit RecentDocument49 pagesBE 3 Unit RecentHasrat AliNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy: Jersey Ramos Billy Jean Pagdonsolan Mikee Merle Jeffrey VillabrilleDocument18 pagesFiscal Policy: Jersey Ramos Billy Jean Pagdonsolan Mikee Merle Jeffrey VillabrilleJersey RamosNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument2 pagesInflationhamza.shaheenNo ratings yet
- Wahid Rasool Imran Ali Jawad Ul Hassan Haseeb Azam: Ms. Maheen KhanDocument24 pagesWahid Rasool Imran Ali Jawad Ul Hassan Haseeb Azam: Ms. Maheen KhanWahid RasoolNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument21 pagesFiscal PolicyDilpreet Singh MendirattaNo ratings yet
- Economic DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEconomic DevelopmentJoanah TayamenNo ratings yet
- Consumption Saving and InvestmentDocument6 pagesConsumption Saving and InvestmentShyam PrajaptiNo ratings yet
- Economic Crises NoteDocument9 pagesEconomic Crises NoteAdetunbi TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Notes Assignment 2Document2 pagesNotes Assignment 2Glem T. CanilloNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy.Document19 pagesFiscal Policy and Monetary Policy.wayandragon247100% (1)
- My Assig. 1Document9 pagesMy Assig. 1Terna HonNo ratings yet
- Ans of Macro Q31-Q40Document5 pagesAns of Macro Q31-Q40Nishakumari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Macro - Consumption & InvestmentDocument77 pagesMacro - Consumption & InvestmentannsaralondeNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics CIA 3 2nd SemesterDocument33 pagesMacroeconomics CIA 3 2nd SemesterMeghansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy in IndiaDocument11 pagesFiscal Policy in IndiaMehak joshiNo ratings yet
- Merge Public PolicyDocument62 pagesMerge Public PolicyjoysellamohdalkaffNo ratings yet
- Economics 19e ch1 and CH 19 NotesDocument7 pagesEconomics 19e ch1 and CH 19 NotesUntzzerNo ratings yet
- 6 Economic GoalsDocument4 pages6 Economic Goalsrohanfyaz00100% (1)
- A Assignment ON "Trade Off Between Inflation & Unemployment"Document9 pagesA Assignment ON "Trade Off Between Inflation & Unemployment"parikharistNo ratings yet
- Conflicting Goals in Economic Growth PDFDocument2 pagesConflicting Goals in Economic Growth PDFMrunaal NaseryNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument6 pagesFiscal Policynoor fatimaNo ratings yet
- Inflation and UnemploymentDocument29 pagesInflation and UnemploymentJorge CárcamoNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policies LinksDocument3 pagesFiscal Policies LinksAmol MoryeNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy NewDocument12 pagesMonetary Policy NewAbdul Kader MandolNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy V UNIT-1Document10 pagesFiscal Policy V UNIT-1madhumithaNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument6 pagesFiscal Policynarayan100% (2)
- Business Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management Crew IV Aakash Tripathi G060 Arpit Chandak J012 Arpit Malhotra E041 Arunabha Banerjee F007 Devvrat Sharma E055Document18 pagesStrategic Financial Management Crew IV Aakash Tripathi G060 Arpit Chandak J012 Arpit Malhotra E041 Arunabha Banerjee F007 Devvrat Sharma E055MUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Report On Bajaj Finance: Group 1 Crew 2Document14 pagesReport On Bajaj Finance: Group 1 Crew 2MUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- GR-I-Crew-II-2018-Bajaj FinanceDocument51 pagesGR-I-Crew-II-2018-Bajaj FinanceMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- GR II Crew II 2018 Bajaj FinanceDocument15 pagesGR II Crew II 2018 Bajaj FinanceMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- GR I Crew XV 2018 TcsDocument18 pagesGR I Crew XV 2018 TcsMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- GR I Crew XV 2018 TcsDocument79 pagesGR I Crew XV 2018 TcsMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- 2 - International Parity ConditionsDocument116 pages2 - International Parity ConditionsMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- IAPM AssignmentsDocument29 pagesIAPM AssignmentsMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Videocon Industries Strategic Financial Management: Submitted To Prof. A B RastogiDocument15 pagesVideocon Industries Strategic Financial Management: Submitted To Prof. A B RastogiMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk ManagementDocument136 pagesCredit Risk ManagementMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Concepts: Dr. TinaikarDocument39 pagesExchange Rate Concepts: Dr. TinaikarMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Submission v2Document32 pagesSubmission v2MUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Market: Dr. TinaikarDocument198 pagesForeign Exchange Market: Dr. TinaikarMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Spirits in India PDFDocument3 pagesSpirits in India PDFMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- 3 - External DebtDocument30 pages3 - External DebtMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- 2, 3, 4, 10, 18 CompleteDocument12 pages2, 3, 4, 10, 18 CompleteMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Graphs For Mental HealthDocument17 pagesGraphs For Mental HealthMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- MainPresentationMoldova PDFDocument159 pagesMainPresentationMoldova PDFMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- RWE Investor Presentation PDFDocument35 pagesRWE Investor Presentation PDFMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument73 pagesChapter 13 PDFMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Interview Form PDFDocument2 pagesPreliminary Interview Form PDFMarcus AntoniusNo ratings yet
- SAP GL ConfigurationDocument164 pagesSAP GL ConfigurationTharaka Hettiarachchi100% (1)
- T&D Assignment On InfosysDocument9 pagesT&D Assignment On InfosysTasnim ZaraNo ratings yet
- SHRM Course OutlineDocument3 pagesSHRM Course OutlineMuhammad MoizNo ratings yet
- A Research Agenda For Social EntrepreneurshipDocument17 pagesA Research Agenda For Social EntrepreneurshipValéria GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Draft ManifestoDocument41 pagesDraft ManifestoThe Guardian91% (11)
- OrganisationalDocument16 pagesOrganisationalmahalvine669No ratings yet
- Ae1 RFP PDFDocument117 pagesAe1 RFP PDFAnonymous eKt1FCDNo ratings yet
- Amtranet Group - Garment ManufacturerDocument26 pagesAmtranet Group - Garment ManufacturerGarmentLearner100% (2)
- Pfeffer (2005) Producing Sustainable PDFDocument15 pagesPfeffer (2005) Producing Sustainable PDFdoncupidNo ratings yet
- Unified Forms - Property Financing-CIMB BANKDocument7 pagesUnified Forms - Property Financing-CIMB BANKNurul ShiedaNo ratings yet
- MBE Unit IDocument36 pagesMBE Unit Istandalonemba50% (2)
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Dr. Komal Randhawa Ravinder Singh Roll No: 9905Document26 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By: Dr. Komal Randhawa Ravinder Singh Roll No: 9905Gunveen AbrolNo ratings yet
- 01 - Rivera vs. EspirituDocument2 pages01 - Rivera vs. EspirituDustin GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Revised Guidelines PD 851Document4 pagesRevised Guidelines PD 851Abegail LeriosNo ratings yet
- Sales Management Case Study AnalysisDocument19 pagesSales Management Case Study AnalysisDevesh Rajak100% (1)
- Organizational StudyDocument61 pagesOrganizational StudyVishnu Nair0% (1)
- Technology and Wealth CreationDocument23 pagesTechnology and Wealth Creationnaveenyadav2011No ratings yet
- 020 SMC Vs TeodisioDocument2 pages020 SMC Vs TeodisioKelsey Olivar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Project Submitted ToDocument11 pagesHuman Resource Management: Project Submitted ToyuktimNo ratings yet
- The 5 Love Languages at WorkDocument3 pagesThe 5 Love Languages at WorkAmmalia RachmiNo ratings yet
- Small Scale Industries in IndiaDocument19 pagesSmall Scale Industries in Indiau409023No ratings yet
- Sheba University College GraduatesDocument4 pagesSheba University College GraduatesHilario Domingo Chicano100% (2)
- Final Memorandum of Appeal PauleDocument20 pagesFinal Memorandum of Appeal PauleIsaac Joshua AganonNo ratings yet
- Maintenance BusinessDocument13 pagesMaintenance BusinessArdyas Wisnu BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Cement Industry of PakistanDocument34 pagesCement Industry of PakistanMuhammad Haris HameedNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter Examples For TV BroadcastingDocument5 pagesCover Letter Examples For TV Broadcastingafjwoovfsmmgff100% (2)
- Legal Assistant Cover Letter - Corporate PurpleDocument2 pagesLegal Assistant Cover Letter - Corporate PurpleSaurabh Gangwar100% (1)