Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cooling System Specifications: General Coolant Information
Cooling System Specifications: General Coolant Information
Uploaded by
Kamal PakdamanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cooling System Specifications: General Coolant Information
Cooling System Specifications: General Coolant Information
Uploaded by
Kamal PakdamanCopyright:
Available Formats
SEBU6400-05 35
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
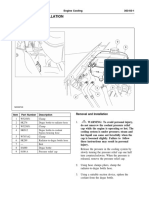
Cooling System Many engine failures are related to the above
conditions: cracking of the cylinder head and/or of
Specifications the engine block, piston seizure, leakage of the water
pump, failure of the water pump, and pitting of the
cylinder liners and cylinder block.
i03614065
These problems can be avoided through proper
General Coolant Information maintenance of the cooling system. Periodically
evaluate the maintenance practices in order to make
SMCS Code: 1350; 1395 sure that the cooling system is properly maintained.
NOTICE
Refer to the engine Operation and Maintenance
Properties of Coolant/Antifreeze
Manual for any coolant information that may be
Coolant/antifreeze is normally composed of three
specific to that application.
elements: water, glycol, and additives. Each element
must meet specific guidelines.
Functions of Cooling System
Water
The cooling systems of modern gas engines are
precisely balanced. The performance of the cooling Water is used in the cooling system in order to
system affects many of the engine components. transfer heat.
Optimum performance can only be obtained by
proper installation and maintenance of the cooling NOTICE
system. Never use water alone without Supplemental Coolant
Additives (SCA) or without inhibited coolant. Water
The engine cooling system is designed to meet alone is corrosive at engine operating temperatures.
specific guidelines. The proper coolant/antifreeze will Water alone does not provide adequate protection
provide the following functions: against boiling or freezing.
• Adequate heat transfer Deionized water or distilled water is
recommended for use in engine cooling systems.
• Compatibility with the cooling system components
such as hoses, seals, and piping
If distilled water or deionized water is not available,
use water with the properties that are listed in Table 8.
• Protection from water pump cavitation
Table 8
• Protection from other cavitation erosion
Caterpillar Minimum Acceptable Water Requirements
• Protection from freezing and from boiling Property Maximum Limit ASTM Test
• Protection from the buildup of corrosion, of sludge, 40 mg/L “D512”,
Chloride (Cl)
and of scale (2.4 grains per US gal) “D4327”
100 mg/L
If a cooling system fails to perform any of the above Sulfate (SO4) “D516”
(5.9 grains per US gal)
functions, the following conditions can occur:
170 mg/L
Total Hardness “D1126”
(10 grains per US gal)
• Overheating
340 mg/L
Total Solids “D1888”
• Overcooling (20 grains per US gal)
Acidity pH of 5.5 to 9.0 “D1293”
• Leaks from hoses, from seals, and from piping
• Cavitation erosion
• Damage from freezing or from boiling
• Plugging of passages for the coolant/antifreeze in
components such as radiators, aftercoolers, oil
coolers, and other heat exchangers
You might also like
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cooling System Recom Gas EngineDocument13 pagesCooling System Recom Gas Enginebambang eengNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water System Guide - 4-2429GDocument11 pagesCooling Water System Guide - 4-2429GA2 BhaskarNo ratings yet
- This Document Has Been Printed From SPI2. NOT FOR RESALE: AdditivesDocument1 pageThis Document Has Been Printed From SPI2. NOT FOR RESALE: AdditivesAHMADNo ratings yet
- Application Engineering Bulletin: Automotive Industrial Marine G-Drive Genset Powergen Antifreeze in Warm ClimatesDocument3 pagesApplication Engineering Bulletin: Automotive Industrial Marine G-Drive Genset Powergen Antifreeze in Warm ClimatesCesar G.No ratings yet
- Tab 5 Coolant System TroubleshootingDocument18 pagesTab 5 Coolant System TroubleshootingagvassNo ratings yet
- Fluid Recommendations ###Document5 pagesFluid Recommendations ###benjir shuvoNo ratings yet
- Winter Lay-Up Task Sheet - Indirect Cooled Where Danger of FreezingDocument7 pagesWinter Lay-Up Task Sheet - Indirect Cooled Where Danger of FreezingRicky WrightNo ratings yet
- 04-2429H - Coolant System GuidelinesDocument12 pages04-2429H - Coolant System GuidelinesAdeel RazaNo ratings yet
- Cooling System Maintenance For Heavy Duty Engines: Technical Service Bulletin 88-1Document3 pagesCooling System Maintenance For Heavy Duty Engines: Technical Service Bulletin 88-1Agus Setiawan Feat AvrNo ratings yet
- 04 2429GDocument11 pages04 2429Gzanella159051No ratings yet
- Service Bulletin: WarningDocument11 pagesService Bulletin: Warningninzau100% (1)
- Water Treatment For Engine Cooling SystemsDocument8 pagesWater Treatment For Engine Cooling SystemsJavier F Pacheco PuentesNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Treatment and Analysing: Lmbo QFKD Fkpqor'qflkDocument7 pagesCooling Water Treatment and Analysing: Lmbo QFKD Fkpqor'qflkRonald Bienemi Paez100% (1)
- An Introduction To CoolantsDocument247 pagesAn Introduction To CoolantstollywhistleNo ratings yet
- Keeper: Coolants and Cooling System MaintenanceDocument3 pagesKeeper: Coolants and Cooling System MaintenanceAung Myo ThantNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Coolants PDFDocument57 pagesAn Introduction To Coolants PDFPETER ADAMNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Treatment and Analysing: Operating InstructionDocument7 pagesCooling Water Treatment and Analysing: Operating Instructionamin32No ratings yet
- Cooling SystemDocument20 pagesCooling System0128 Nguyễn Thanh BìnhNo ratings yet
- HYDRONIC 4 Dodge Ram 24-Valve (Feb00)Document20 pagesHYDRONIC 4 Dodge Ram 24-Valve (Feb00)zjbli534No ratings yet
- Water Temperature Regulators (Thermostats) : ReplaceDocument5 pagesWater Temperature Regulators (Thermostats) : ReplacePedro SchembriNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Treatment - Bulletins - WartsilaDocument9 pagesCooling Water Treatment - Bulletins - WartsilaAfsanul TanveerNo ratings yet
- Tech Doc Coolant AnalysisDocument2 pagesTech Doc Coolant AnalysisJakub BohdálekNo ratings yet
- Water Requirements, Volvo CoolantsDocument1 pageWater Requirements, Volvo CoolantsCesar BlancoNo ratings yet
- Guía de Interpretación de Análisis de RefrigeranteDocument2 pagesGuía de Interpretación de Análisis de RefrigeranteTeófilo LimasNo ratings yet
- Wartsila OEM Engine Manufacturer ApprovalsDocument8 pagesWartsila OEM Engine Manufacturer ApprovalsSivakumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Fluid RecommendationsDocument6 pagesFluid RecommendationsAlfredoNo ratings yet
- Fully Formulated Coolant/Antifreeze: Water Quality Calcium Magnesium (Hardness) Maximum 170 PPM As (Caco + Mgco)Document5 pagesFully Formulated Coolant/Antifreeze: Water Quality Calcium Magnesium (Hardness) Maximum 170 PPM As (Caco + Mgco)Antonio Tavara HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Low-Down On Low Delta-T Syndrome: Get It Right The First TimeDocument3 pagesThe Low-Down On Low Delta-T Syndrome: Get It Right The First TimePradeep SukumaranNo ratings yet
- CoolantDocument6 pagesCoolantNay Win HtetNo ratings yet
- Gei 41004Document10 pagesGei 41004Ivan Poma MontesNo ratings yet
- Mi 1748 TDocument6 pagesMi 1748 Tamir barekatiNo ratings yet
- Coolant OAT Bulletin LT32533Document2 pagesCoolant OAT Bulletin LT32533Castro RicardoNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop SystemDocument3 pagesClosed Loop SystemSubbarayan SaravanakumarNo ratings yet
- Pressed 0Document12 pagesPressed 0Rath AsypadenNo ratings yet
- White Paper Koelstystemen ENDocument5 pagesWhite Paper Koelstystemen ENMuhammad SyaqirinNo ratings yet
- Mac-036he, 048he, 060he - IomDocument26 pagesMac-036he, 048he, 060he - IomOscar A. Jiménez ColónNo ratings yet
- MAC-120HE Air-Cooled Chiller - IOMDocument28 pagesMAC-120HE Air-Cooled Chiller - IOMOscar A. Jiménez ColónNo ratings yet
- Astm D6210 08Document2 pagesAstm D6210 08Gabriel ChelloNo ratings yet
- Submarine Main Propulsion Diesels - Chapter 8Document15 pagesSubmarine Main Propulsion Diesels - Chapter 8Michael ChungNo ratings yet
- Laying-Up And: Launching GuideDocument28 pagesLaying-Up And: Launching GuideAlexeyNo ratings yet
- MI - 1748 Rev FDocument21 pagesMI - 1748 Rev FSudarshan Dhumal100% (2)
- Operation & Maintinance of Diesel Generator - 101527Document15 pagesOperation & Maintinance of Diesel Generator - 101527Wasim IqbalNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Treatment and Periodical Test of The Cooling WaterDocument4 pagesCooling Water Treatment and Periodical Test of The Cooling WaterGaurav MaithilNo ratings yet
- Cat Cooling SystemDocument107 pagesCat Cooling SystemDaniel AmanorNo ratings yet
- Es Fleetguard Coolnat LT15070 SpesifcationDocument2 pagesEs Fleetguard Coolnat LT15070 SpesifcationahmedalgaloNo ratings yet
- Total Anti FreezeDocument2 pagesTotal Anti FreezeMd ShNo ratings yet
- CERC - Bilateral Schedule ProcedureDocument11 pagesCERC - Bilateral Schedule Procedurebalwant_negi7520No ratings yet
- Torre de EnfriamientoDocument28 pagesTorre de Enfriamientojovanny5k5666100% (1)
- Knowing Your Cooling SystemDocument119 pagesKnowing Your Cooling SystemDaniel Amanor100% (1)
- Technical Service Bulletin Re-Print From Baldwin Filter CompanyDocument2 pagesTechnical Service Bulletin Re-Print From Baldwin Filter Companyvoyager1No ratings yet
- Emergency Diesel Generator Engine Cooling SystemsDocument11 pagesEmergency Diesel Generator Engine Cooling SystemsEng1 ApollohxNo ratings yet
- Búsqueda Del Medio - SEBD0518 - Know Your Cooling System (0708, 1Document105 pagesBúsqueda Del Medio - SEBD0518 - Know Your Cooling System (0708, 1Wilder UrtadoNo ratings yet
- CFS B0807 PDFDocument12 pagesCFS B0807 PDFRath AsypadenNo ratings yet
- Water Requirements, Volvo CoolantsDocument1 pageWater Requirements, Volvo CoolantsmostafaNo ratings yet
- 13.8.4.1 Guidelines For Water Pump Replacement: Series 60 Service ManualDocument2 pages13.8.4.1 Guidelines For Water Pump Replacement: Series 60 Service ManualvictoverNo ratings yet
- Refits, More Ways to Make Your Boat Better.: Cruising Boats, How to Select, Equip and Maintain, #5From EverandRefits, More Ways to Make Your Boat Better.: Cruising Boats, How to Select, Equip and Maintain, #5Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Marine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedFrom EverandMarine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedNo ratings yet
- 4-Method Statement UPV ASTM C597 - VER - 001Document4 pages4-Method Statement UPV ASTM C597 - VER - 001Kamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Khelifi Decision Support Tool For Used Oil Regeneration Technologies 2006-1 PDFDocument6 pagesKhelifi Decision Support Tool For Used Oil Regeneration Technologies 2006-1 PDFKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Sizing Combustion Air DuctsDocument2 pagesSizing Combustion Air DuctsKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Air Duct SizingDocument1 pageVentilation Air Duct SizingKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Harrison THE ENGINEERING ASPECTS OF A USED OIL 1994 PDFDocument5 pagesHarrison THE ENGINEERING ASPECTS OF A USED OIL 1994 PDFKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- CarburetorDocument7 pagesCarburetorKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Combustion Air FormulasDocument2 pagesCombustion Air FormulasKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Sr4b Generator Component DescriptionDocument14 pagesSr4b Generator Component DescriptionKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Engine Block Cleaning ProcedureDocument7 pagesEngine Block Cleaning ProcedureKamal PakdamanNo ratings yet
- Gas Regulator OperationDocument2 pagesGas Regulator OperationKamal Pakdaman100% (1)
- 1 Determination of The Empirical Formula of Silver Oxide (Flinn AP Lab 1) - Short VersionDocument5 pages1 Determination of The Empirical Formula of Silver Oxide (Flinn AP Lab 1) - Short Versionsohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Electric-Resistance-Welded Low-Carbon Steel Pipe For The Chemical IndustryDocument5 pagesElectric-Resistance-Welded Low-Carbon Steel Pipe For The Chemical IndustryRoland CepedaNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Ceramic Composite Armour SystemDocument5 pagesLightweight Ceramic Composite Armour SystemaamirmubNo ratings yet
- The Diamond Thief EspDocument2 pagesThe Diamond Thief EspIsaí Alberto Bolaños PérezNo ratings yet
- (Mod. IFCC Method) For The Determination of SGOT (AST) Activity in Serum. (For in Vitro Diagnostic Use Only)Document1 page(Mod. IFCC Method) For The Determination of SGOT (AST) Activity in Serum. (For in Vitro Diagnostic Use Only)Dinesh Sreedharan100% (1)
- Materials 3 2 1 PDFDocument8 pagesMaterials 3 2 1 PDFAmaliNo ratings yet
- Informasi Nilai Gizi Satuan: Bifidobacterium Lactis NCC 2818 1 × 10 CFU/100gDocument1 pageInformasi Nilai Gizi Satuan: Bifidobacterium Lactis NCC 2818 1 × 10 CFU/100gTheresia Stephani SihiteNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0956713513003289 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0956713513003289 Mainahmad ilham ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Jotter Exp 6Document2 pagesJotter Exp 6Atiq AqilahNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition - 90 QPDocument16 pagesHuman Nutrition - 90 QPStephen AreriNo ratings yet
- Dyeing Technologies and Their ApplicationsDocument2 pagesDyeing Technologies and Their ApplicationsJuanNo ratings yet
- Hysol EA 9396Document4 pagesHysol EA 9396Nasos MasourasNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument11 pagesMark SchemeAmani MuneneNo ratings yet
- Vic Stucco Report - Part 2Document95 pagesVic Stucco Report - Part 2Fare NienteNo ratings yet
- Clinker Manufacture PDFDocument54 pagesClinker Manufacture PDFKEERTHI INDUSTRIES80% (5)
- Export RoHS 20220131 15413641Document2 pagesExport RoHS 20220131 15413641soporte tecnico memNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces (Multiple Choice) QP PDFDocument14 pagesIntermolecular Forces (Multiple Choice) QP PDFMohamed TarekNo ratings yet
- Production of Lithium and Sodium Lubricating Greases: October 2015Document11 pagesProduction of Lithium and Sodium Lubricating Greases: October 2015sujit kcNo ratings yet
- Transport in Cells WorksheetDocument7 pagesTransport in Cells WorksheetCamille ComasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet4Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet4Lê Anh QuangNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Mofs - X C PolymerDocument1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Mofs - X C PolymerPranav DubeyNo ratings yet
- Metal Clusters:: Structure and Bonding in Higher BoranesDocument23 pagesMetal Clusters:: Structure and Bonding in Higher BoranesSumedha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Dura Slag MSDS November 2011Document6 pagesDura Slag MSDS November 2011tarcizocruzNo ratings yet
- Ayden Seetal Intermolecular Forces Student Exploration MODIFIED PDFDocument6 pagesAyden Seetal Intermolecular Forces Student Exploration MODIFIED PDFLama AshiNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document12 pagesNull 1Bijoy BiswasNo ratings yet
- Reconditioning Lead Acid Batteries With Epsom SaltDocument1 pageReconditioning Lead Acid Batteries With Epsom SaltpablorodrigodasilvaNo ratings yet
- Oxidationpond - 14 04 2020Document15 pagesOxidationpond - 14 04 2020AatifNo ratings yet
- Sandy Beach GranigliaDocument2 pagesSandy Beach GranigliaCamilo Ponce de LeonNo ratings yet
- Eriksson 1990Document23 pagesEriksson 1990Rara IqromNo ratings yet
- CHE011Document2 pagesCHE011bookfishNo ratings yet