Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Data
Basic Data
Uploaded by
Dilnesa EjiguOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Data
Basic Data
Uploaded by
Dilnesa EjiguCopyright:
Available Formats
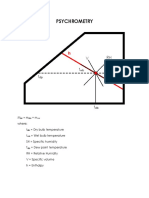
3 PSYCHROMETRY
rs 11 Basic Data
Title Symbol Unit Equation Example
2
Partial pressure of water P kg/cm p=p'- A×P×(t-t')
vapor at dry bulb temp. mmhg A=0.00066×(1+0.00115×t')
o
when p,P are in mmhg and temp. in C
saturation pr. of vapor
at wet bulb temp, p' mmhg/
2
kg/cm
total barometric pr. P mmhg/
2
kg/cm
o
dry bulb temp. t C
o
wet bulb temp. t' C
at saturation point, dry and wet bulb temperatures are same
saturation pr. of vapor px mmhg/
2
at dry bulb temp. kg/cm
wet bulb depression is the difference between dry and wet bulb temps (t – t')
relative humidity = 100 × p/px
dew point
when partial pressure vapor reaches its saturation pr. at a given temp.,air is said to be
saturated at that temp. and has reached its dew point.
Saturation humidity
o
or dew point hs C hs = h + q × (t × ts) / 539
absolute
humidity h q =0.24 + 0.45 × h
heat capacity q
o
dry bulb temp. t C
saturation
o
temp. ts C
absolute humidity is the actual weight of water vapour in a unit weight of dry air. It is expressed in
kg/kg
reltive humidity of air water vapour mixture is defined as ratio of pressure existing to that at saturation
for the same dry bulb temperature
Source : Cement Manufacturers Hand book
rs 11 Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- CementProject PlanDocument54 pagesCementProject PlanDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- GB 50205-2001 - EnglishDocument143 pagesGB 50205-2001 - EnglishDilnesa Ejigu100% (1)
- GB 50204-2002 Code For Acceptance of Construction Quality of Concrete Structures. Part 1Document70 pagesGB 50204-2002 Code For Acceptance of Construction Quality of Concrete Structures. Part 1Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- FF-113 - Fire Protection Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageFF-113 - Fire Protection Schematic DiagramNIDHILNo ratings yet
- 2 Psychormetrics AnalysisDocument108 pages2 Psychormetrics Analysishasan bishNo ratings yet
- Formulas in Cooling TowerDocument6 pagesFormulas in Cooling TowerGringoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9v18sol PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial 9v18sol PDFSohayb GattousNo ratings yet
- Evt474 Chapter 2Document50 pagesEvt474 Chapter 2Fakhrul AimanNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument14 pagesHeat ExchangersAdrian StoicescuNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant Standard Operating ProceduresDocument4 pagesSteam Power Plant Standard Operating Proceduresarvidkumar8706050% (4)
- Thermodynamics 3BDocument16 pagesThermodynamics 3BChang MarthaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesThermodynamicsQUANG HUY DANGNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Lab Report Group 1 CC03Document18 pagesThermodynamic Lab Report Group 1 CC03Chang MarthaNo ratings yet
- PsychrometricesDocument9 pagesPsychrometriceskawsar_002No ratings yet
- AT12 MabaoDocument17 pagesAT12 MabaoMichael Alex MabaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 BSE2201 PsychrometryDocument63 pagesLecture 3 BSE2201 PsychrometryBrian LiNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics 2Document26 pagesApplied Thermodynamics 2Ankit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic1 PsychrometryDocument14 pagesTopic1 Psychrometrypy.arqr23No ratings yet
- 2022 EnergyBal L8-F HumidityDocument12 pages2022 EnergyBal L8-F HumidityJude BlanksonNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Air ConditioningDocument46 pagesFundamental of Air ConditioningOlay KwongNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document17 pagesLec 7Sadaf MustafaNo ratings yet
- Thermo 1 Review and Rankine CycleDocument32 pagesThermo 1 Review and Rankine CycleKenneth DilancoNo ratings yet
- Thermal ReliefDocument1 pageThermal ReliefMohd ShoebNo ratings yet
- PsychrometryDocument48 pagesPsychrometryashwinharry69No ratings yet
- Psychrometric Data EngDocument1 pagePsychrometric Data EngMc Jason LaureteNo ratings yet
- E4 M#2 PTD Asd2021Document54 pagesE4 M#2 PTD Asd2021Muhammad SupriyadiNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance On Nonreactive System: CHE531 Chemical Process Principles IiDocument26 pagesEnergy Balance On Nonreactive System: CHE531 Chemical Process Principles IiAYALEYDENNo ratings yet
- On Separating and Throttling Calorimeter Converted 1Document19 pagesOn Separating and Throttling Calorimeter Converted 1Gee DevilleNo ratings yet
- 9 PsychrometryDocument71 pages9 PsychrometryPratyush NagareNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 13: Dr. Muzaffar AliDocument41 pagesLecture # 13: Dr. Muzaffar Alikamran bhatNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Notes (Psychrometric)Document3 pagesAir Conditioning Notes (Psychrometric)Yohan ManaligodNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart (Or Humidity Chart)Document38 pagesPsychrometric Chart (Or Humidity Chart)muhammad izzulNo ratings yet
- FME17 Lecture Guide 1 PsychrometryDocument9 pagesFME17 Lecture Guide 1 PsychrometryAllaine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- L11 (Psychrometry)Document25 pagesL11 (Psychrometry)Kavin KabilanNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Psychrometry With Sample ProblemsDocument21 pages2.0 Psychrometry With Sample ProblemsRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry: V RH T T SHDocument13 pagesPsychrometry: V RH T T SHKAL ELNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note Drying May19Document50 pagesLecture Note Drying May19ara_1909No ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 - BSE2201 - Air Conditioning Processes & CyclesDocument74 pagesLecture - 4 - BSE2201 - Air Conditioning Processes & CyclesBrian LiNo ratings yet
- Storage Tank Heat Loss Calcs - 28.09.2009Document10 pagesStorage Tank Heat Loss Calcs - 28.09.2009Ali MoazamiNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower. Application - TreybalDocument89 pagesCooling Tower. Application - TreybalProcess TiglobalNo ratings yet
- ACT Lecture 2 Handout PsychrometryDocument36 pagesACT Lecture 2 Handout PsychrometryumerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 DryingDocument34 pagesChapter 6 DryingPMNo ratings yet
- Week 2.apsychrometry-Air ConditioningdocxDocument20 pagesWeek 2.apsychrometry-Air ConditioningdocxMariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S153751101100119X MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S153751101100119X MainugurnazgumusssNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Psychrometry)Document11 pagesModule 4 (Psychrometry)Shirley Pelagio100% (1)
- Week 4Document26 pagesWeek 4abdullahghaya124No ratings yet
- Methodology: Totalproduction (Areaofplantation) (0.70) Totalareaplanted (3)Document9 pagesMethodology: Totalproduction (Areaofplantation) (0.70) Totalareaplanted (3)rey mondNo ratings yet
- Edr 3 Prob 4Document7 pagesEdr 3 Prob 4Arfel Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Psychro PDFDocument29 pagesPsychro PDFKhoyrul HudaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower. Application - TreybalDocument89 pagesCooling Tower. Application - TreybalPinak ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Qpedia Nov08 Estimating The Effect of Moist Air On Natural Convection Heat TransferDocument7 pagesQpedia Nov08 Estimating The Effect of Moist Air On Natural Convection Heat TransferGe YemoNo ratings yet
- Of Some Industrial or Scientific Process.: Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesOf Some Industrial or Scientific Process.: Air ConditioningRenz MagatNo ratings yet
- Humid Air Diagram PDFDocument2 pagesHumid Air Diagram PDFFarid SedekyNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Plant DesignDocument13 pagesWastewater Treatment Plant DesignAlyannaKatePalasNo ratings yet
- HVAC Training-Intro Youtube RevisionDocument167 pagesHVAC Training-Intro Youtube RevisionHaji Muhammad Abushasa100% (1)
- Antoine'sDocument3 pagesAntoine'sGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry & Air ConditioningDocument39 pagesPsychrometry & Air ConditioningAMIE Study Circle, RoorkeeNo ratings yet
- PsychrometricsDocument9 pagesPsychrometricsSeptimiuNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry and Air ConditioningDocument40 pagesPsychrometry and Air Conditioninghabtish2000No ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart NotesDocument50 pagesPsychrometric Chart NotesMohammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Coldstorage Principle of PsychrometricsDocument90 pages9.0 Coldstorage Principle of PsychrometricsSweekar KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Ginger Initial MoistureDocument18 pagesGinger Initial MoistureEdbert ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Storage Tank Heat Loss Calcs - 28.09.2009Document10 pagesStorage Tank Heat Loss Calcs - 28.09.2009siva kumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-1 Air ConditioningDocument2 pagesTutorial-1 Air ConditioningammarNo ratings yet
- Gas Vapor MixturesDocument47 pagesGas Vapor MixturesMo SalihNo ratings yet
- (Class 1-5) Lectures-1Document38 pages(Class 1-5) Lectures-1Aniruddha BagchiNo ratings yet
- GB50205 2001钢结构工程施工质量验收规范英文版内部资料Document131 pagesGB50205 2001钢结构工程施工质量验收规范英文版内部资料Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Safety PauseDocument4 pagesSafety PauseSafrin SangiaNo ratings yet
- Cement EnvironmentDocument212 pagesCement EnvironmentDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- W-20 MemorandumDocument2 pagesW-20 MemorandumDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Es 1176-4 - 2005Document30 pagesEs 1176-4 - 2005Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Lime Plant EIADocument144 pagesLime Plant EIADilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Standard ES 4050 ES 1176-2:2005: First Edition 2005-03-12Document67 pagesEthiopian Standard ES 4050 ES 1176-2:2005: First Edition 2005-03-12Dilnesa Ejigu100% (1)
- Ethiopian ES 4050 ES 1176-3:2005: First Edition 2005-03-12Document12 pagesEthiopian ES 4050 ES 1176-3:2005: First Edition 2005-03-12Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- GB 50040-96 Code For Design of Dynamic MachineDocument104 pagesGB 50040-96 Code For Design of Dynamic MachineDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- GB 50204-2002 Code For Acceptance of Construction Quality of Concrete Structuress. Part 2Document46 pagesGB 50204-2002 Code For Acceptance of Construction Quality of Concrete Structuress. Part 2Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Rs 21Document1 pageRs 21Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- 30 Pneumatic Conveyors: Rs 108 Sizing Air LiftsDocument2 pages30 Pneumatic Conveyors: Rs 108 Sizing Air LiftsDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- 2 Basic Laws of Physics: rs8 Losses in Fluid FlowDocument2 pages2 Basic Laws of Physics: rs8 Losses in Fluid FlowDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- 2 Basic Laws of Physics: rs9 Equations of Heat TransferDocument3 pages2 Basic Laws of Physics: rs9 Equations of Heat TransferDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Rs 33Document2 pagesRs 33Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- 30 Pneumatic Conveyors: Rs 110 Pneumatic Screw Pumps (FK Pumps)Document3 pages30 Pneumatic Conveyors: Rs 110 Pneumatic Screw Pumps (FK Pumps)Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- FLS-pneumatic Transfer From Storage (Tse)Document22 pagesFLS-pneumatic Transfer From Storage (Tse)Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevators, Bucket Conveyors and MoreDocument22 pagesBucket Elevators, Bucket Conveyors and MoreDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2Document28 pagesSeminar 2Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- V4s44 Concrete DurabilityDocument8 pagesV4s44 Concrete DurabilityDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Rs 20Document1 pageRs 20Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- 3 Psychrometry: Rs 10 Latent Heat of Evaporation, EnthalpyDocument2 pages3 Psychrometry: Rs 10 Latent Heat of Evaporation, EnthalpyDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- 03 Power EngineeringDocument46 pages03 Power EngineeringRahul JotwaniNo ratings yet
- Risk of Gas Freeing Operation & Precautions For Oil TankersDocument3 pagesRisk of Gas Freeing Operation & Precautions For Oil TankersIonescu Eda100% (1)
- Effect of Cavitation On Hydraulic Turbines-A ReviewDocument6 pagesEffect of Cavitation On Hydraulic Turbines-A ReviewRanjeetTwaynaNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Tingkatan 5 JawapanDocument25 pagesModul Fizik Tingkatan 5 JawapanNureen ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - QuestionsDocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - QuestionsXeno XeurekaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Reynold NumberDocument7 pagesLab 5 Reynold NumberFgj JhgNo ratings yet
- Adjunct To D1250-08 Temperature and Pressure Volume Correction Factors For Generalized Crude Oils, Refined Products, and Lubricating OilsDocument1 pageAdjunct To D1250-08 Temperature and Pressure Volume Correction Factors For Generalized Crude Oils, Refined Products, and Lubricating OilsGilasAmarthaAbieyogaNo ratings yet
- Fluid FlowDocument11 pagesFluid FlowFabian NdegeNo ratings yet
- Air Dispersion Modeling Conversions and FormulasDocument16 pagesAir Dispersion Modeling Conversions and Formulasvelmurugan00000No ratings yet
- Pages From Leak Test Level 2Document63 pagesPages From Leak Test Level 2ManivannanMudhaliarNo ratings yet
- Steam Tracing SpecificationDocument14 pagesSteam Tracing SpecificationPankaj SahuNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers Course - Baher - Part 01Document24 pagesHeat Exchangers Course - Baher - Part 01Baher ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Meteorology An Invitation To The Atmosphere 6th Edition AhrensDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Meteorology An Invitation To The Atmosphere 6th Edition Ahrenscerasin.cocoon5pd1100% (54)
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument1 pageHazardous Area ClassificationyuthonlineNo ratings yet
- (Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic CoursesDocument47 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic Courseseng_ebrahim_2000100% (1)
- Topics-III RefhvacDocument21 pagesTopics-III Refhvacwarren carozcaNo ratings yet
- Calculation For Pressure Drop in Various Water Pipelines: Formulae UsedDocument10 pagesCalculation For Pressure Drop in Various Water Pipelines: Formulae UsedSUKANTA DALAI100% (1)
- Drs 2170Document4 pagesDrs 2170Ronaldo JuniorNo ratings yet
- Hello!: I Am Sir DeanDocument30 pagesHello!: I Am Sir DeanDean MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Shengji Group Product Catalog2018Document24 pagesShengji Group Product Catalog2018SIMON S. FLORES G.No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Process Calculations - K. v. Narayanan and B. LakshmikuttyDocument167 pagesStoichiometry and Process Calculations - K. v. Narayanan and B. LakshmikuttyAshish Kumar50% (16)
- 2.9 Flue Gas SystemDocument12 pages2.9 Flue Gas SystemDangolNo ratings yet
- Charles - LawDocument19 pagesCharles - Lawshort bondpaperNo ratings yet
- Jnjk'aja J ADocument2 pagesJnjk'aja J AJV CustodioNo ratings yet
- Bulk Separator - V-1201 Method StatementDocument2 pagesBulk Separator - V-1201 Method StatementRoshin99No ratings yet