Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCM 106 Pharmacology Study Guide
NCM 106 Pharmacology Study Guide
Uploaded by
Angel HannahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dental Hygiene Board Exam Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesDental Hygiene Board Exam Sample Questionsgeislernet100% (5)
- 7 AIIMS May 11 PDFDocument38 pages7 AIIMS May 11 PDFSayeed KhanNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria Schematic Diagram (Pathophysiology0Document3 pagesDiphtheria Schematic Diagram (Pathophysiology0Kathlene Boleche100% (1)
- EASA Part-66 Exam Questions of Module 01 - Part IIDocument24 pagesEASA Part-66 Exam Questions of Module 01 - Part IISteven J. Selcuk100% (2)
- Cancer BulletsDocument3 pagesCancer Bulletsraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Internship QuestionDocument8 pagesPre-Internship QuestionPeprah OndibaNo ratings yet
- Online CAT Question PaperDocument2 pagesOnline CAT Question PaperSudeep Yadav100% (1)
- 3y1s Surgpath Lec 8. Liver&gb (Agb) SamplexDocument1 page3y1s Surgpath Lec 8. Liver&gb (Agb) SamplexCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- Microbio Exam 3Document13 pagesMicrobio Exam 3Cathy LyNo ratings yet
- Most ImportantDocument3 pagesMost ImportantBanu KubendiranNo ratings yet
- GENPATHODocument4 pagesGENPATHOMitch C.No ratings yet
- Glomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MHPEDocument10 pagesGlomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MHPEJulie Gemarino LumasagNo ratings yet
- Dr. Frank Pagdunzulan: Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument41 pagesDr. Frank Pagdunzulan: Diseases of The Immune SystemFu Xiao ShanNo ratings yet
- 021 Test Ex3 (Sp10) KeyDocument5 pages021 Test Ex3 (Sp10) KeymiamikikoNo ratings yet
- I Semester Examination (ICM)Document4 pagesI Semester Examination (ICM)Sudeep YadavNo ratings yet
- Toxi RevDocument18 pagesToxi RevDomingo Primo Vivas IIINo ratings yet
- Patho QuestDocument4 pagesPatho QuestRosel Ann BontiaNo ratings yet
- Nephro Canvas Samplex (21-22)Document28 pagesNephro Canvas Samplex (21-22)EllaineNo ratings yet
- 問答題庫Document7 pages問答題庫celine7119No ratings yet
- Is RecallsDocument15 pagesIs RecallskthmntsNo ratings yet
- HS202 Pathology ExamDocument6 pagesHS202 Pathology ExamJulio dR AltavasNo ratings yet
- Pharma Testbank RnpediaDocument28 pagesPharma Testbank RnpediaDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- 3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDocument25 pages3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDENTAL REVIEWER ONLYNo ratings yet
- IMSEDocument5 pagesIMSEharith r donovanNo ratings yet
- Review Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesReview Test QuestionsMarichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- MCN Exam 4 Study Guide - Pt. 5 Neuromusclar Disorders in ChildrenDocument6 pagesMCN Exam 4 Study Guide - Pt. 5 Neuromusclar Disorders in ChildrenColin MacKenzieNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument6 pagesNeonatal JaundiceDoc Prince CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: Disorders of The Immune Response 1: Eina Jane & Co. 2009Document16 pagesChapter 19: Disorders of The Immune Response 1: Eina Jane & Co. 2009greenflames09100% (1)
- INICET JULY 2021 Solved Paper PDF PathologyDocument36 pagesINICET JULY 2021 Solved Paper PDF Pathologysusan291No ratings yet
- General Biology Part 2-2Document3 pagesGeneral Biology Part 2-2Markee Nepomuceno AngelesNo ratings yet
- Mean MPL For This Exam: 76.89Document3 pagesMean MPL For This Exam: 76.89rosamundraeNo ratings yet
- Karl Avillo - MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesKarl Avillo - MicrobiologySanielle Karla Garcia LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Genpath - Glomerular Diseases (Primary Glomerulopathies (Nephritic) )Document5 pagesGenpath - Glomerular Diseases (Primary Glomerulopathies (Nephritic) )Julie Gemarino LumasagNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory and Immune ResponseDocument13 pagesInflammatory and Immune Responsemimie23100% (1)
- Rickettsia, Mycoplasma. Fungi, ProtozoaDocument4 pagesRickettsia, Mycoplasma. Fungi, ProtozoaVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mock Board Exam in Microbiology/ Virology/Mycology/ParasitologyDocument12 pagesMock Board Exam in Microbiology/ Virology/Mycology/ParasitologyShera Heart Go100% (1)
- Longo 2015Document10 pagesLongo 2015Juan Jose SantivañezNo ratings yet
- longo2015Document10 pageslongo2015guillito85No ratings yet
- IS AnsDocument6 pagesIS AnsAnne MorenoNo ratings yet
- Nonmalignant WBC DisordersDocument7 pagesNonmalignant WBC DisordersHarvey Mher Rarang100% (3)
- اخر اختبار 24.3.2022 طب عام1Document8 pagesاخر اختبار 24.3.2022 طب عام1Sharafaddin Ahmed Abbas SharafaddinNo ratings yet
- Eval Exam-Ans Key-Ref-Onco - 2010Document3 pagesEval Exam-Ans Key-Ref-Onco - 2010marlon armamento100% (1)
- QuizDocument2 pagesQuizAdam Troy TaglucopNo ratings yet
- GIT NursingDocument8 pagesGIT NursingBasa, Rica Mae P.No ratings yet
- Banco Ciencias Básicas 2019 - UnlockedDocument40 pagesBanco Ciencias Básicas 2019 - UnlockedAlvaroNo ratings yet
- Molecular Oncology in Gynecologic CancerDocument7 pagesMolecular Oncology in Gynecologic CancerChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- FINALS OphthaDocument7 pagesFINALS OphthaGio GelilangNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument56 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Infinithink Natural ScienceDocument6 pagesInfinithink Natural ScienceCamille ManaloNo ratings yet
- ?2023-05-23 @ped BM2Document4 pages?2023-05-23 @ped BM2VineeNo ratings yet
- Question - Bank - Pharmacology - SGS - 242.pdf - Filename - UTF-8''Question Bank Pharmacology SGS 242Document20 pagesQuestion - Bank - Pharmacology - SGS - 242.pdf - Filename - UTF-8''Question Bank Pharmacology SGS 242Mustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- JIMENEZKaycelyn-Drus StudyDocument11 pagesJIMENEZKaycelyn-Drus Studykaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- (Sgy Samplex Prelim 2) Surgery-Remedial-ReviewerDocument21 pages(Sgy Samplex Prelim 2) Surgery-Remedial-ReviewerDeepbluexNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacilliDocument5 pagesGram Positive Non Spore Forming BacilliSophia LiteratoNo ratings yet
- Notes: Tuesday, 27 January 2015 4:11 PMDocument11 pagesNotes: Tuesday, 27 January 2015 4:11 PMhectorNo ratings yet
- Stevens - Immulogy and Serology Study Questions (3rd Edition)Document35 pagesStevens - Immulogy and Serology Study Questions (3rd Edition)John Dale DuranoNo ratings yet
- Animal Proposal (Yojana)Document24 pagesAnimal Proposal (Yojana)Sreekanth reddyNo ratings yet
- 3rd PT Biotech2011Document5 pages3rd PT Biotech2011Krisburt Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Long TestDocument2 pagesLymphatic System Long TestSucceed ReviewNo ratings yet
- ABC Transporters and Multidrug ResistanceFrom EverandABC Transporters and Multidrug ResistanceAhcène BoumendjelNo ratings yet
- TCW Midterms Notes and LEDocument17 pagesTCW Midterms Notes and LEAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Document34 pagesCase Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Angel Hannah100% (1)
- The Global Divide Dependency TheoryDocument2 pagesThe Global Divide Dependency TheoryAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- NCM 119 Day 1Document4 pagesNCM 119 Day 1Angel HannahNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument17 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- 23 Antiseizure AgentsDocument3 pages23 Antiseizure AgentsAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- 24 Anti ParkinsonismDocument5 pages24 Anti ParkinsonismAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- 22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument5 pages22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Make Table For Morphology!: 1.) Identification: Staphylococcus AureusDocument16 pagesMake Table For Morphology!: 1.) Identification: Staphylococcus AureusAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- TablesDocument2 pagesTablesAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Microorganisms Encountered in The Respiratory TractDocument4 pagesChapter 20: Microorganisms Encountered in The Respiratory TractAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- STS EssayDocument1 pageSTS EssayAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Asma G.SDocument5 pagesAsma G.SAfia FaheemNo ratings yet
- Everlast INTERVAL TRAINING ROUND TIMER PDFDocument1 pageEverlast INTERVAL TRAINING ROUND TIMER PDFanniaanniaNo ratings yet
- Operation Reasrech On IglooDocument18 pagesOperation Reasrech On IglooMd Yeasin ArafatNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2014 PDFDocument153 pagesAnnual Report 2014 PDFகோகுல் இராNo ratings yet
- Open-Circuit Time Constant Analysis: Asas As Hs K Bsbs BsDocument24 pagesOpen-Circuit Time Constant Analysis: Asas As Hs K Bsbs BsSHAIK MUSTHAFANo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Electricity Bill in PakistanDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Your Electricity Bill in PakistanGhayas Ud-din DarNo ratings yet
- Likedislikedon't LikeDocument3 pagesLikedislikedon't LikeBriza PaolaNo ratings yet
- Bael-Tree Details and Medicinal UsesDocument4 pagesBael-Tree Details and Medicinal UsesSanjay PatilNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENDocument1 pageData Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENJanne LaineNo ratings yet
- Module 1 What Is Geography and TourismDocument22 pagesModule 1 What Is Geography and TourismLeanne Abegail EstabilloNo ratings yet
- RPT CasesDocument13 pagesRPT CasesSNLTNo ratings yet
- Electronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptDocument22 pagesElectronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptneilNo ratings yet
- New WITTMANN Robots For Large and Small Injection Molding MachinesDocument4 pagesNew WITTMANN Robots For Large and Small Injection Molding MachinesMonark HunyNo ratings yet
- Absolute Priority Based Cell ReselectionDocument11 pagesAbsolute Priority Based Cell ReselectionNeoRa Ndivo RamsNo ratings yet
- Owner: PT. Baker Hughes User: Cok Gede Reza Description: Modified Safety Pin, Add. Handrail & Add. Anti Slip Step Stair at Pressure Test BayDocument3 pagesOwner: PT. Baker Hughes User: Cok Gede Reza Description: Modified Safety Pin, Add. Handrail & Add. Anti Slip Step Stair at Pressure Test BayMuhammad AlpianNo ratings yet
- Valve Body 55Document3 pagesValve Body 55Davidoff RedNo ratings yet
- 8210.40 Single Band RET For Multiband Antennas (Controlling White Antenna Array)Document1 page8210.40 Single Band RET For Multiband Antennas (Controlling White Antenna Array)Mohammad AlloushNo ratings yet
- Low Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoDocument4 pagesLow Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoPranjal Jalan100% (1)
- Quatre Agro Enterprise Private LimitedDocument25 pagesQuatre Agro Enterprise Private Limitedp23pallavNo ratings yet
- HDR10+ System Whitepaper: September 4, 2019 HDR10+ Technologies, LLCDocument14 pagesHDR10+ System Whitepaper: September 4, 2019 HDR10+ Technologies, LLCDragomir ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Tac85 11Document32 pagesTac85 11TateNo ratings yet
- Describe Physical and Chemical Change OperationallyDocument2 pagesDescribe Physical and Chemical Change OperationallyMaria Anna GraciaNo ratings yet
- Costing By-Product and Joint ProductsDocument36 pagesCosting By-Product and Joint ProductseltantiNo ratings yet
- Speech Patterns: Christine Martin - Steph Estavillo - Melanie PadillaDocument24 pagesSpeech Patterns: Christine Martin - Steph Estavillo - Melanie PadillaChristineMartinNo ratings yet
- Price List 2018Document20 pagesPrice List 2018Imml TasbiNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp ExperimentDocument34 pagesOp-Amp ExperimentArooj Mukarram100% (1)
- Tutorial-2 - Heterocycles Nomenclature-Part-IIDocument18 pagesTutorial-2 - Heterocycles Nomenclature-Part-IIamirNo ratings yet
- English3 Q2 Mod2 TensesOfTheVerb V3Document33 pagesEnglish3 Q2 Mod2 TensesOfTheVerb V3Johanna Zandra MariaNo ratings yet
- Rakit Lampu LedDocument11 pagesRakit Lampu LedIbnusyam UtihNo ratings yet
NCM 106 Pharmacology Study Guide
NCM 106 Pharmacology Study Guide
Uploaded by
Angel HannahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCM 106 Pharmacology Study Guide
NCM 106 Pharmacology Study Guide
Uploaded by
Angel HannahCopyright:
Available Formats
NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY
STUDY GUIDE
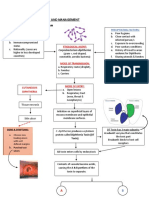
1. ANTINEOPLASTIC ANTIBIOTICS iii. Pulmonary toxicity + inhibit cell growth and
a) ACTION: break up DNA links and interstitial pneumonitis division.
prevent DNA synthesis by inserting iv. Hepatic/Renal toxicity ii. Epidermal Growth Factor
themselves between base pairs, g) SAMPLE MEDS: v. Alopecia Inhibitor via Erlotinib for fast
causing a mutation that leads to cell i. Busulfan vi. Necrosis and cellulitis growing cells.
death ii. Carboplatin e) NOTES: iii. Proteasome inhibitor
b) INDICATION: neoplasms i. kill cells during the M phase b) INDICATION: chronic myelocytic
c) C/I: 3. ANTI-METABOLITES ii. Extravasation could be a huge leukemia and multiple myeloma
i. pregnancy + lactation a) ACTION: inhibit DNA production in problem c) C/I:
ii. allergy cells that depend on certain natural f) SAMPLE MEDS: end in -axel or -oside i. pregnancy + lactation
iii. bone marrow suppression metabolites to produce their DNA i. Docetaxel ii. allergy
iv. renal/hepatic dysfunction b) INDICATIONS:Leukemias, GI and ii. Etoposide iii. pts with arrhythmia
v. Bleomycin + mitomycin → basal cell cancers d) ADVERSE EFFECTS:
pulmonary problems c) C/I: 5. HORMONE SITE SPECIFIC i. Imatinib → GI upset
vi. idarubicin → cardiac problems i. pregnancy + lactation a) ACTION: block the release of ii. the side effects that occur in
d) ADVERSE EFFECTS: ii. allergy gonadotropin hormones in the others do not appear here
i. hematological effects iii. bone marrow suppression breast/prostate cancer if the tumors e) ADVERSE REACTIONS:
ii. CNS effects iv. renal/hepatic dysfunction are responsive to those hormones. i. Hepatotoxicity
iii. Pulmonary toxicity + v. GI ulceration may also block.interfere with ii. CNS: confusion, abnormal
interstitial pneumonitis d) ADVERSE REACTIONS: receptor site. thinking, uncontrolled
iv. Hepatic/renal toxicity i. Leucovorin b) INDICATION: breast cancer and emotions
v. Alopecia ii. Hematological effects prostatic cancer iii. Telithromycin (Ketek) causes
e) NOTES: iii. CNS effects c) C/I: px to have difficulty focusing
i. Toxic to rapidly dividing cells iv. Pulmonary toxicity + i. pregnancy + lactation and accommodating to light
ii. Affect S phase interstitial pneumonitis ii. allergy f) NOTE:
f) SAMPLE MEDS: ending in -mycin or v. Renal/Hepatic toxicity iii. bone marrow suppression i. attack cancer cells not healthy
-rubucin vi. Alopecia iv. renal/hepatic dysfunction cells
i. Bleomycin e) NOTES: v. GI ulcerations ii. results in fewer toxic effects
ii. Doxorubicin i. inhibit dna production by vi. Toremifene → hypercalcemia g) SAMPLE MEDS:
inhibiting metabolites needed d) ADVERSE REACTIONS: i. Bortezomib
2. ALKYLATING AGENTS for dna synthesis of dna in i. Menopause associated effects ii. Imatinib
a) ACTION: inhibit susceptible cells ii. Increase in risk for
b) ACTION: disrupts cellular ii. S-phase specific cardiovascular disease 7. MISC. ANTINEOPLASTICS
mechanisms that affect DNA, RNA f) SAMPLE MEDS: some end in -bine iii. Abiraterone → increase risk of a) ACTIONS: cause cell death
and other cellular proteins that lead i. Cladribine adrenocortical insuff b) INDICATION: neoplasms
to cell death ii. Cytarabine iv. Increased/Decreased effects c) C/I:
c) INDICATION: lymphomas, leukemia, of the hormones on the body i. pregnancy + lactation
myelomas, ovarian, breast and 4. MITOTIC INHIBITOR → Virilization ii. allergy
testicular cancer, and pancreatic a) ACTION: interfere with the ability of e) NOTES: d) ADVERSE REACTIONS:
cancer the cell to divide i. Hormones and hormonal i. Hematological effects
d) C/I: b) INDICATIONS: tumors, and agents are used to treat ii. CNS effects
i. pregnancy + lactation leukemias specific cancers that respond iii. Hepatic/Renal toxicity
ii. allergy c) C/I: to hormone stimulation, like iv. Alopecia
iii. bone marrow suppression i. pregnancy + lactation breast and prostate cancer v. Necrosis + cellulitis
iv. renal/hepatic dysfunction ii. allergy f) SAMPLE MEDS:
e) ADVERSE EFFECTS: iii. bone marrow suppression i. Anastrozole e) SAMPLE MEDS:
i. Hematological effects iv. renal/hepatic dysfunction ii. Flutamide i. Belinostat
ii. GI effects v. GI ulcerations ii. Talc powder
iii. Hepatic/Renal toxicity vi. Eribulin → arrhythmia due to 6. CANCER CELL SPECIFIC
iv. Alopecia prolonging QT a) ACTION:
f) NOTES: d) ADVERSE REACTIONS: i. act on specific enzymes
i. Cell-cycle non specific i. Hematological effects needed for protein building by
ii. Most effective against slow- ii. CNS effects specific tumor cells, which
growing tumors
You might also like
- Dental Hygiene Board Exam Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesDental Hygiene Board Exam Sample Questionsgeislernet100% (5)
- 7 AIIMS May 11 PDFDocument38 pages7 AIIMS May 11 PDFSayeed KhanNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria Schematic Diagram (Pathophysiology0Document3 pagesDiphtheria Schematic Diagram (Pathophysiology0Kathlene Boleche100% (1)
- EASA Part-66 Exam Questions of Module 01 - Part IIDocument24 pagesEASA Part-66 Exam Questions of Module 01 - Part IISteven J. Selcuk100% (2)
- Cancer BulletsDocument3 pagesCancer Bulletsraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Internship QuestionDocument8 pagesPre-Internship QuestionPeprah OndibaNo ratings yet
- Online CAT Question PaperDocument2 pagesOnline CAT Question PaperSudeep Yadav100% (1)
- 3y1s Surgpath Lec 8. Liver&gb (Agb) SamplexDocument1 page3y1s Surgpath Lec 8. Liver&gb (Agb) SamplexCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- Microbio Exam 3Document13 pagesMicrobio Exam 3Cathy LyNo ratings yet
- Most ImportantDocument3 pagesMost ImportantBanu KubendiranNo ratings yet
- GENPATHODocument4 pagesGENPATHOMitch C.No ratings yet
- Glomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MHPEDocument10 pagesGlomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases Glomerular Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MHPEJulie Gemarino LumasagNo ratings yet
- Dr. Frank Pagdunzulan: Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument41 pagesDr. Frank Pagdunzulan: Diseases of The Immune SystemFu Xiao ShanNo ratings yet
- 021 Test Ex3 (Sp10) KeyDocument5 pages021 Test Ex3 (Sp10) KeymiamikikoNo ratings yet
- I Semester Examination (ICM)Document4 pagesI Semester Examination (ICM)Sudeep YadavNo ratings yet
- Toxi RevDocument18 pagesToxi RevDomingo Primo Vivas IIINo ratings yet
- Patho QuestDocument4 pagesPatho QuestRosel Ann BontiaNo ratings yet
- Nephro Canvas Samplex (21-22)Document28 pagesNephro Canvas Samplex (21-22)EllaineNo ratings yet
- 問答題庫Document7 pages問答題庫celine7119No ratings yet
- Is RecallsDocument15 pagesIs RecallskthmntsNo ratings yet
- HS202 Pathology ExamDocument6 pagesHS202 Pathology ExamJulio dR AltavasNo ratings yet
- Pharma Testbank RnpediaDocument28 pagesPharma Testbank RnpediaDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- 3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDocument25 pages3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDENTAL REVIEWER ONLYNo ratings yet
- IMSEDocument5 pagesIMSEharith r donovanNo ratings yet
- Review Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesReview Test QuestionsMarichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- MCN Exam 4 Study Guide - Pt. 5 Neuromusclar Disorders in ChildrenDocument6 pagesMCN Exam 4 Study Guide - Pt. 5 Neuromusclar Disorders in ChildrenColin MacKenzieNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument6 pagesNeonatal JaundiceDoc Prince CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: Disorders of The Immune Response 1: Eina Jane & Co. 2009Document16 pagesChapter 19: Disorders of The Immune Response 1: Eina Jane & Co. 2009greenflames09100% (1)
- INICET JULY 2021 Solved Paper PDF PathologyDocument36 pagesINICET JULY 2021 Solved Paper PDF Pathologysusan291No ratings yet
- General Biology Part 2-2Document3 pagesGeneral Biology Part 2-2Markee Nepomuceno AngelesNo ratings yet
- Mean MPL For This Exam: 76.89Document3 pagesMean MPL For This Exam: 76.89rosamundraeNo ratings yet
- Karl Avillo - MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesKarl Avillo - MicrobiologySanielle Karla Garcia LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Genpath - Glomerular Diseases (Primary Glomerulopathies (Nephritic) )Document5 pagesGenpath - Glomerular Diseases (Primary Glomerulopathies (Nephritic) )Julie Gemarino LumasagNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory and Immune ResponseDocument13 pagesInflammatory and Immune Responsemimie23100% (1)
- Rickettsia, Mycoplasma. Fungi, ProtozoaDocument4 pagesRickettsia, Mycoplasma. Fungi, ProtozoaVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mock Board Exam in Microbiology/ Virology/Mycology/ParasitologyDocument12 pagesMock Board Exam in Microbiology/ Virology/Mycology/ParasitologyShera Heart Go100% (1)
- Longo 2015Document10 pagesLongo 2015Juan Jose SantivañezNo ratings yet
- longo2015Document10 pageslongo2015guillito85No ratings yet
- IS AnsDocument6 pagesIS AnsAnne MorenoNo ratings yet
- Nonmalignant WBC DisordersDocument7 pagesNonmalignant WBC DisordersHarvey Mher Rarang100% (3)
- اخر اختبار 24.3.2022 طب عام1Document8 pagesاخر اختبار 24.3.2022 طب عام1Sharafaddin Ahmed Abbas SharafaddinNo ratings yet
- Eval Exam-Ans Key-Ref-Onco - 2010Document3 pagesEval Exam-Ans Key-Ref-Onco - 2010marlon armamento100% (1)
- QuizDocument2 pagesQuizAdam Troy TaglucopNo ratings yet
- GIT NursingDocument8 pagesGIT NursingBasa, Rica Mae P.No ratings yet
- Banco Ciencias Básicas 2019 - UnlockedDocument40 pagesBanco Ciencias Básicas 2019 - UnlockedAlvaroNo ratings yet
- Molecular Oncology in Gynecologic CancerDocument7 pagesMolecular Oncology in Gynecologic CancerChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- FINALS OphthaDocument7 pagesFINALS OphthaGio GelilangNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument56 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Infinithink Natural ScienceDocument6 pagesInfinithink Natural ScienceCamille ManaloNo ratings yet
- ?2023-05-23 @ped BM2Document4 pages?2023-05-23 @ped BM2VineeNo ratings yet
- Question - Bank - Pharmacology - SGS - 242.pdf - Filename - UTF-8''Question Bank Pharmacology SGS 242Document20 pagesQuestion - Bank - Pharmacology - SGS - 242.pdf - Filename - UTF-8''Question Bank Pharmacology SGS 242Mustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- JIMENEZKaycelyn-Drus StudyDocument11 pagesJIMENEZKaycelyn-Drus Studykaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- (Sgy Samplex Prelim 2) Surgery-Remedial-ReviewerDocument21 pages(Sgy Samplex Prelim 2) Surgery-Remedial-ReviewerDeepbluexNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacilliDocument5 pagesGram Positive Non Spore Forming BacilliSophia LiteratoNo ratings yet
- Notes: Tuesday, 27 January 2015 4:11 PMDocument11 pagesNotes: Tuesday, 27 January 2015 4:11 PMhectorNo ratings yet
- Stevens - Immulogy and Serology Study Questions (3rd Edition)Document35 pagesStevens - Immulogy and Serology Study Questions (3rd Edition)John Dale DuranoNo ratings yet
- Animal Proposal (Yojana)Document24 pagesAnimal Proposal (Yojana)Sreekanth reddyNo ratings yet
- 3rd PT Biotech2011Document5 pages3rd PT Biotech2011Krisburt Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Long TestDocument2 pagesLymphatic System Long TestSucceed ReviewNo ratings yet
- ABC Transporters and Multidrug ResistanceFrom EverandABC Transporters and Multidrug ResistanceAhcène BoumendjelNo ratings yet
- TCW Midterms Notes and LEDocument17 pagesTCW Midterms Notes and LEAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Document34 pagesCase Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Angel Hannah100% (1)
- The Global Divide Dependency TheoryDocument2 pagesThe Global Divide Dependency TheoryAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- NCM 119 Day 1Document4 pagesNCM 119 Day 1Angel HannahNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument17 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- 23 Antiseizure AgentsDocument3 pages23 Antiseizure AgentsAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- 24 Anti ParkinsonismDocument5 pages24 Anti ParkinsonismAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- 22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument5 pages22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Make Table For Morphology!: 1.) Identification: Staphylococcus AureusDocument16 pagesMake Table For Morphology!: 1.) Identification: Staphylococcus AureusAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- TablesDocument2 pagesTablesAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Microorganisms Encountered in The Respiratory TractDocument4 pagesChapter 20: Microorganisms Encountered in The Respiratory TractAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- STS EssayDocument1 pageSTS EssayAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Asma G.SDocument5 pagesAsma G.SAfia FaheemNo ratings yet
- Everlast INTERVAL TRAINING ROUND TIMER PDFDocument1 pageEverlast INTERVAL TRAINING ROUND TIMER PDFanniaanniaNo ratings yet
- Operation Reasrech On IglooDocument18 pagesOperation Reasrech On IglooMd Yeasin ArafatNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2014 PDFDocument153 pagesAnnual Report 2014 PDFகோகுல் இராNo ratings yet
- Open-Circuit Time Constant Analysis: Asas As Hs K Bsbs BsDocument24 pagesOpen-Circuit Time Constant Analysis: Asas As Hs K Bsbs BsSHAIK MUSTHAFANo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Electricity Bill in PakistanDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Your Electricity Bill in PakistanGhayas Ud-din DarNo ratings yet
- Likedislikedon't LikeDocument3 pagesLikedislikedon't LikeBriza PaolaNo ratings yet
- Bael-Tree Details and Medicinal UsesDocument4 pagesBael-Tree Details and Medicinal UsesSanjay PatilNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENDocument1 pageData Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENJanne LaineNo ratings yet
- Module 1 What Is Geography and TourismDocument22 pagesModule 1 What Is Geography and TourismLeanne Abegail EstabilloNo ratings yet
- RPT CasesDocument13 pagesRPT CasesSNLTNo ratings yet
- Electronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptDocument22 pagesElectronics Cooling: Mechanical Power Engineering DeptneilNo ratings yet
- New WITTMANN Robots For Large and Small Injection Molding MachinesDocument4 pagesNew WITTMANN Robots For Large and Small Injection Molding MachinesMonark HunyNo ratings yet
- Absolute Priority Based Cell ReselectionDocument11 pagesAbsolute Priority Based Cell ReselectionNeoRa Ndivo RamsNo ratings yet
- Owner: PT. Baker Hughes User: Cok Gede Reza Description: Modified Safety Pin, Add. Handrail & Add. Anti Slip Step Stair at Pressure Test BayDocument3 pagesOwner: PT. Baker Hughes User: Cok Gede Reza Description: Modified Safety Pin, Add. Handrail & Add. Anti Slip Step Stair at Pressure Test BayMuhammad AlpianNo ratings yet
- Valve Body 55Document3 pagesValve Body 55Davidoff RedNo ratings yet
- 8210.40 Single Band RET For Multiband Antennas (Controlling White Antenna Array)Document1 page8210.40 Single Band RET For Multiband Antennas (Controlling White Antenna Array)Mohammad AlloushNo ratings yet
- Low Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoDocument4 pagesLow Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoPranjal Jalan100% (1)
- Quatre Agro Enterprise Private LimitedDocument25 pagesQuatre Agro Enterprise Private Limitedp23pallavNo ratings yet
- HDR10+ System Whitepaper: September 4, 2019 HDR10+ Technologies, LLCDocument14 pagesHDR10+ System Whitepaper: September 4, 2019 HDR10+ Technologies, LLCDragomir ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Tac85 11Document32 pagesTac85 11TateNo ratings yet
- Describe Physical and Chemical Change OperationallyDocument2 pagesDescribe Physical and Chemical Change OperationallyMaria Anna GraciaNo ratings yet
- Costing By-Product and Joint ProductsDocument36 pagesCosting By-Product and Joint ProductseltantiNo ratings yet
- Speech Patterns: Christine Martin - Steph Estavillo - Melanie PadillaDocument24 pagesSpeech Patterns: Christine Martin - Steph Estavillo - Melanie PadillaChristineMartinNo ratings yet
- Price List 2018Document20 pagesPrice List 2018Imml TasbiNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp ExperimentDocument34 pagesOp-Amp ExperimentArooj Mukarram100% (1)
- Tutorial-2 - Heterocycles Nomenclature-Part-IIDocument18 pagesTutorial-2 - Heterocycles Nomenclature-Part-IIamirNo ratings yet
- English3 Q2 Mod2 TensesOfTheVerb V3Document33 pagesEnglish3 Q2 Mod2 TensesOfTheVerb V3Johanna Zandra MariaNo ratings yet
- Rakit Lampu LedDocument11 pagesRakit Lampu LedIbnusyam UtihNo ratings yet