Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 030
05 030
Uploaded by
Harish0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageOriginal Title
05_030
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page05 030
05 030
Uploaded by
HarishCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 1
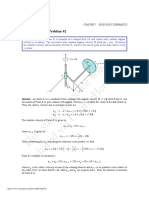
5.30
Water enters the horizontal, circular cross-sectional,
sudden contraction nozzle sketched in Fig. P5.30 at section (1)
with a uniformly distributed velocity of 25 fi/s and a pressure
of 75 psi. The water exits from the nozzle into the atmosphere
at section (2) where the uniformly distributed velocity is 100
ft/s. Determine the axial component of the anchoring force re-
{quired to hold the contraction in place.
For this prblem we tnclude tr the conol volume
the nozzle as well as the water at an instant behween sections
(i)and(2\as sidicated ta the sketch above. The horizontal
forces acting on the contents of the control Volunse are shown
in the sketch. Note that the. atmospheric forces cancel out
and ave not shown. Application of the horizontal or x-
divection component of the Jineay momentum, equation (&. 5.22)
to the flow through this contol volume yields
“4 puA, + Wy puA= FA-B- pA, @
From tha conservation of mass egnatio ( &y.5.127 we obtain
m7 UA, = 04, As
Tous 4.0) may be exptosed as
rn (ua 4) * BA, - -PAa
” TD, -p Da Dias
B= PABA FM lneu) = RTP - BPP pu, TP (Hy-t4)
or
a < ib 3 in y fu ae ft asf
Gal (jp) Tee - 04 (mE 2) ates He
cae
= 352 lb
f
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 22: Current and Resistance: SolutionsDocument5 pagesChapter 22: Current and Resistance: SolutionsHarishNo ratings yet
- HW9 9Document9 pagesHW9 9HarishNo ratings yet
- Solution To Exercise 7.5Document3 pagesSolution To Exercise 7.5HarishNo ratings yet
- 16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B TDocument3 pages16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B THarishNo ratings yet
- 6 1 .0 and C 6 1.0? Explain in TermsDocument2 pages6 1 .0 and C 6 1.0? Explain in TermsHarishNo ratings yet
- 07 Elec A7 PDFDocument3 pages07 Elec A7 PDFHarishNo ratings yet
- Budynas SM ch02 PDFDocument8 pagesBudynas SM ch02 PDFHarishNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: 7.42 Chapter 7, Problem 42Document2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: 7.42 Chapter 7, Problem 42HarishNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Textbook John H Lienhard Solution Manual PDFDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Textbook John H Lienhard Solution Manual PDFHarishNo ratings yet
- A Heat Transfer Textbook Fourth Edition Solution ManualDocument3 pagesA Heat Transfer Textbook Fourth Edition Solution ManualHarish0% (1)
- Chapter13 ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapter13 ProblemsHarishNo ratings yet
- Home Work No 3Document2 pagesHome Work No 3HarishNo ratings yet
- NominilDocument5 pagesNominilHarishNo ratings yet
- Cengel 7th - P4-37Document1 pageCengel 7th - P4-37HarishNo ratings yet
- Career ObjectiveDocument2 pagesCareer ObjectiveHarishNo ratings yet