Professional Documents
Culture Documents
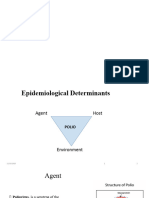
20 - Polio
20 - Polio
Uploaded by
Julia SalvioCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CMS Neuro 1 Answers PDFDocument13 pagesCMS Neuro 1 Answers PDFRehan Ali86% (7)
- CMS Neuro 1 AnswersDocument13 pagesCMS Neuro 1 AnswersKomal Menon100% (14)
- IV Fluids ChartDocument1 pageIV Fluids Chartzahidtaniv71% (7)
- Cerebral Palsy Revalida FormatDocument10 pagesCerebral Palsy Revalida FormatChelsea CalanoNo ratings yet
- Bobath Approach: Concepts and PrinciplesDocument30 pagesBobath Approach: Concepts and PrinciplesJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Kenneth Anthony Tiu Regida100% (8)
- PoliomyelitisDocument74 pagesPoliomyelitisSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument3 pagesPoliomyelitisrandymarkpaduaNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument3 pagesPoliomyelitisDiana Fadhilah SariNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument22 pagesMeningitisdieanisNo ratings yet
- POLIODocument13 pagesPOLIOTaimur KhalilNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Poliomyelitis Written ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 6 Poliomyelitis Written ReportFranceska AntonioNo ratings yet
- Poliomyelitis: Key FactsDocument3 pagesPoliomyelitis: Key FactsJhania Maine LinxNo ratings yet
- Floppy BabyDocument11 pagesFloppy Babysmitha lakkavallyNo ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NotesDocument13 pagesPediatrics NotesYsa BonifacioNo ratings yet
- R A B I E S: Dave Jay S. Manriquez RNDocument15 pagesR A B I E S: Dave Jay S. Manriquez RNOdylon CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Poliomyeli TIS: Name:Nurzawani Binti Shamsudin Matric No: 0918424Document19 pagesPoliomyeli TIS: Name:Nurzawani Binti Shamsudin Matric No: 0918424Jerryuk20100% (1)
- Polio 150416150654 Conversion Gate01Document35 pagesPolio 150416150654 Conversion Gate01Bheru Lal0% (1)
- PT Ortho Assignment Poliomyelitis: Target Organ: Spinal Cord (Ant - Horn Motor Cells) & Brainstem (BulbarDocument3 pagesPT Ortho Assignment Poliomyelitis: Target Organ: Spinal Cord (Ant - Horn Motor Cells) & Brainstem (BulbarLakshita PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)Document16 pagesCerebral Palsy (CP)Divija ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument4 pagesPoliomyelitisGerard Adad Misa100% (1)
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument47 pagesAcute Flaccid ParalysisVandanaNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument30 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysismed.student657No ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument30 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysismed.student657No ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis Beyond Polio - A Case Based ApproachDocument10 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis Beyond Polio - A Case Based ApproachP T ArchanaNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument14 pagesPoliomyelitisadericky84100% (1)
- Polio Final YrDocument54 pagesPolio Final YrMobin Ur Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- OrthosDocument6 pagesOrthosBatch V Med 2 SY 21-22No ratings yet
- POLIOMYELITISDocument26 pagesPOLIOMYELITISIzhra Margate100% (1)
- Poliomyelitis: Dr. Ken Wirastuti, M Kes, SP.S, KIC Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fk. UnissulaDocument14 pagesPoliomyelitis: Dr. Ken Wirastuti, M Kes, SP.S, KIC Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fk. UnissulakhairunnisanurainiNo ratings yet
- Seizures:epilepsyDocument8 pagesSeizures:epilepsysmitha lakkavallyNo ratings yet
- PolioDocument8 pagesPolioKailash Nagar100% (2)
- Presented By: Gayramara Arben John ZDocument36 pagesPresented By: Gayramara Arben John ZgoykicoshenNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument2 pagesPoliomyelitisAlyssa Marie GatbuntonNo ratings yet
- Back Pain Guidelines-1 - 0Document5 pagesBack Pain Guidelines-1 - 0ANTONIO Toledo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis: Moderator: Dr. Bhavana Koppad Asso. Professor Dept of Pediatrics, JNMCDocument32 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis: Moderator: Dr. Bhavana Koppad Asso. Professor Dept of Pediatrics, JNMCmed.student657No ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure & Cerebral PalsyDocument6 pagesFebrile Seizure & Cerebral PalsyKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitesDocument35 pagesPoliomyelitesped medNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy SyndromesDocument6 pagesEpilepsy SyndromesHanin AlSiniNo ratings yet
- Well and Goes To Party. Develops Coughing Fit and Goes Blue and Then Everything Is Okay. 36Document8 pagesWell and Goes To Party. Develops Coughing Fit and Goes Blue and Then Everything Is Okay. 36Dean HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Benign Epilepsies - Part 1Document35 pagesBenign Epilepsies - Part 1Azeem Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument81 pagesPoliomyelitisKaycee Glene CalubNo ratings yet
- PolioDocument21 pagesPoliothunder beardedNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Motor Unit PresentationDocument18 pagesDisorders of The Motor Unit Presentationccash2No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 High Risk NewbornDocument38 pagesChapter 5 High Risk NewbornJobelle Acena100% (1)
- The Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesThe Nervous SystemKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- POLIOMYELITISDocument15 pagesPOLIOMYELITISEndahD'LamdaNo ratings yet
- Johannes H. SaingDocument67 pagesJohannes H. SaingRomMy WiEn MicKhoNo ratings yet
- Congential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersDocument7 pagesCongential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersNichole CollinsNo ratings yet
- PolioDocument2 pagesPolioEdfeb9No ratings yet
- EncephalitisDocument33 pagesEncephalitisJona de VeraNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Septic PolyarthritisDocument3 pagesNeonatal Septic PolyarthritismedinamargaretkellyNo ratings yet
- Seizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaDocument4 pagesSeizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument9 pagesCerebral PalsyAngy100% (2)
- Lec 5 CNSDocument9 pagesLec 5 CNShusainozelNo ratings yet
- SarafDocument17 pagesSarafInggrid GraciaNo ratings yet
- Seizure Disorder Types: Partial - Local Onset May or May Not Impair Consciousness SimpleDocument4 pagesSeizure Disorder Types: Partial - Local Onset May or May Not Impair Consciousness Simpleampogison08No ratings yet
- Meeting Special Needs: A practical guide to support children with EpilepsyFrom EverandMeeting Special Needs: A practical guide to support children with EpilepsyNo ratings yet
- Vertigo, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVertigo, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaFrom EverandThe Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Radiation (Uvr) : ApplicationDocument28 pagesUltraviolet Radiation (Uvr) : ApplicationJulia Salvio100% (1)
- UltrasoundDocument24 pagesUltrasoundJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Radiation (Uvr)Document34 pagesUltraviolet Radiation (Uvr)Julia SalvioNo ratings yet
- UE ProsthesisDocument23 pagesUE ProsthesisJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- IFCDocument22 pagesIFCJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Functional Electrical Nerve StimulatorDocument15 pagesFunctional Electrical Nerve StimulatorJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Rehabilitation of FracturesDocument30 pagesTreatment and Rehabilitation of FracturesJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain ExcercisesDocument55 pagesLow Back Pain ExcercisesJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Congenital Deformities: Gay G. Crisostomo-San Antonio, PTRP, MDDocument46 pagesCongenital Deformities: Gay G. Crisostomo-San Antonio, PTRP, MDJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Gait Deviations in Orthotics & ProstheticsDocument10 pagesGait Deviations in Orthotics & ProstheticsJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- GSC - DDH LCPD SCFE and OthersDocument3 pagesGSC - DDH LCPD SCFE and OthersJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument117 pagesCardiac RehabilitationJulia Salvio100% (1)
- CVA Ken Presentation FINALDocument110 pagesCVA Ken Presentation FINALJulia Salvio100% (1)
- Culture Is The Widening of The Mind and of The Spirit - Jawaharlal NehruDocument17 pagesCulture Is The Widening of The Mind and of The Spirit - Jawaharlal NehruJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Donatelli Chapter 2 Shoulder 2018Document16 pagesDonatelli Chapter 2 Shoulder 2018Julia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Electro NotesDocument9 pagesElectro NotesJulia Salvio100% (1)
- Chest Physical TherapyDocument28 pagesChest Physical TherapyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Shortwave and Microwave DiathermyDocument31 pagesShortwave and Microwave DiathermyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument53 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentJulia Salvio50% (2)
- 19 - GBSDocument1 page19 - GBSJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesMyasthenia GravisJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Potts DiseaseDocument1 pagePotts DiseaseJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Etiology: Molecular Mimicry - Myelin-ReactiveDocument2 pagesEtiology: Molecular Mimicry - Myelin-ReactiveJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Amputation Lower ExtremityDocument5 pagesAmputation Lower ExtremityJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Injury: Relevant Anatomy: Peripheral Neuroanatomy andDocument7 pagesPeripheral Nerve Injury: Relevant Anatomy: Peripheral Neuroanatomy andJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Kernicterus (Infiltration of Bilirubin IntoDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsy: Kernicterus (Infiltration of Bilirubin IntoJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument2 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary System: Relevant Anatomy & Physiology: HeartDocument12 pagesCardiopulmonary System: Relevant Anatomy & Physiology: HeartJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- (NEW) Slide Deck Session 4 - Final. Participation in GovernanceDocument74 pages(NEW) Slide Deck Session 4 - Final. Participation in GovernanceRatsel IsmeNo ratings yet
- Safety Signs: Members: Mariana Dìaz Maritza Neicum Sabina VallejosDocument11 pagesSafety Signs: Members: Mariana Dìaz Maritza Neicum Sabina VallejosSabina Vallejos MirandaNo ratings yet
- Theatre Practice StandardsDocument54 pagesTheatre Practice StandardsNugroho WibisonoNo ratings yet
- AIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015Document24 pagesAIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015AdamAce VelasquezNo ratings yet
- People Should Avoid Junk FoodsDocument4 pagesPeople Should Avoid Junk FoodsShireen BatoolNo ratings yet
- English Practice 62: I. PronunciationDocument9 pagesEnglish Practice 62: I. PronunciationLe QuocNo ratings yet
- AHN MCqs Provided by MirhaDocument3 pagesAHN MCqs Provided by MirhaAkml KhanNo ratings yet
- HOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Document18 pagesHOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Donajei Rica100% (1)
- What Philippine Law Was Created To Include in It The Code of Ethics of Filipino Nurses?Document3 pagesWhat Philippine Law Was Created To Include in It The Code of Ethics of Filipino Nurses?Shirlene Benigra GorospeNo ratings yet
- Cognitive RestructuringDocument3 pagesCognitive Restructuringiulia9gavrisNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pharmacology Clear and Simple A Guide To Drug Classifications and Dosage Calculations 3rd Edition WatkinsDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Pharmacology Clear and Simple A Guide To Drug Classifications and Dosage Calculations 3rd Edition WatkinsJean Taylor100% (46)
- Part Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelDocument18 pagesPart Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelIAN LAPINGNo ratings yet
- Communiqué Émis Par La PSCDocument4 pagesCommuniqué Émis Par La PSCL'express MauriceNo ratings yet
- Ve GL HirarcDocument34 pagesVe GL HirarcEncik AhmadNo ratings yet
- SchistosomiasisDocument12 pagesSchistosomiasisHarold Jake ArguellesNo ratings yet
- CDS Quality+Measures Codes 20oct11 FINALDocument278 pagesCDS Quality+Measures Codes 20oct11 FINALbetzyvazquezNo ratings yet
- Research Agenda of The College of Business and Entrepreneurship - DDocument57 pagesResearch Agenda of The College of Business and Entrepreneurship - DSev BlancoNo ratings yet
- 2020 Guidelines WebDocument249 pages2020 Guidelines WebDaryl Barrios LamedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Detecting The Mood Disorder FinalDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Detecting The Mood Disorder FinalTrixie MizonaNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Physical DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFactors That Affect Physical DevelopmentmomuNo ratings yet
- Immune Disorders..Ppt FairDocument79 pagesImmune Disorders..Ppt FairSumi SebastianNo ratings yet
- MSDS AstDocument6 pagesMSDS AstKRRNo ratings yet
- SWP 01 - Delivery, Unloading, Storage and Transferring of MaterialsDocument3 pagesSWP 01 - Delivery, Unloading, Storage and Transferring of MaterialsGerald Wong Ntt100% (1)
- Genato BSP2G123 M5 Case StudiesDocument4 pagesGenato BSP2G123 M5 Case StudiesCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Worry Flow ChartsDocument10 pagesWorry Flow ChartsPaige Bayly100% (1)
- FORM 4.1 Self Assesment Check ListDocument3 pagesFORM 4.1 Self Assesment Check ListNica ManlugonNo ratings yet
- Annex C: Parental Consent and Waiver FormDocument2 pagesAnnex C: Parental Consent and Waiver FormKeennith NarcaNo ratings yet
- Mou of East West TpaDocument13 pagesMou of East West Tpamalayanur rama chandraNo ratings yet
20 - Polio
20 - Polio
Uploaded by
Julia SalvioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
20 - Polio
20 - Polio
Uploaded by
Julia SalvioCopyright:
Available Formats
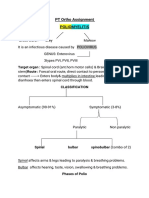
Affects upper part of cervical SC (C3-C5),
POLIOMYELITIS/POST-
o
diaphragm paralysis (phrenic nerve),
muscles needed for swallowing
POLIO SYNDROME Prevention
AKA polio/infantile paralysis Vaccination
o Salk Vaccine (formalin inactivated
Infectious dse caused by poliovirus
virulent strains)
Muscle weakness inability to move
o Sabin vaccine (attenuated live virus) –
Involves the legs, less commonly the head,
oral, 2 doses 8 wks apart, booster @ 1 yr
neck, and diaphragm
and before schooling
Up to 70% of infections have no symptoms
Treatment
Cause
No cure
Genus Enterovirus known as Poliovirus (PV)
Long-term rehab
o Colonize the oropharynx and intestines
Antibiotics to prevent infections, analgesics for
o Incubation: 3-35 days, commonly 6-20
pain
days
Prognosis
Transmission
Depends on number of surviving motor neurons
Highly contagious via fecal-oral and oral-oral
Recovery fastest in children
routes
Recovery usually 3-6 mos, may continue for
Most infectious between 7-10 days a and p
several yrs
appearance of symptoms
Post-polio Syndrome
Paralytic Polio
Between 25-50% can develop symptoms
High fever, headache, stiffness in the back and
decades p recovery
neck, asymmetrical weakness of various
o Muscle weakness and extreme fatigue
muscles, sensitivity to touch, difficulty
swallowing, muscle pain, loss of superficial and Slow, progressive disease
deep reflexes, paresthesia, irritability, Symptoms
constipation, difficulty urinating o Fatigue – m/c
Paralysis 1-10 days p early symptoms begin, o Muscle/jt pain
progress for 203 more days, usually complete o Weakness
when fever breaks o Difficulty walking/stair climbing
o Children < 5 y/o: Paralysis of one leg o Cold intolerance
o Adults: Quadriplegia o Atrophy
Spinal Polio – m/c form of paralytic polio o Dressing difficulties
o Viral invasion of motor neurons of ant
horn cell
o Max paralysis rapidly in 2-4 days, usually
involves fever and muscle pain
o DTR typically absent/diminished
Bulbar Polio – 2% of cases
o CN IX – swallowing, tongue movement,
taste
o CN X – heart, intestines, lungs
o CN XI – upper neck movement
Bulbospinal Polio
You might also like
- CMS Neuro 1 Answers PDFDocument13 pagesCMS Neuro 1 Answers PDFRehan Ali86% (7)
- CMS Neuro 1 AnswersDocument13 pagesCMS Neuro 1 AnswersKomal Menon100% (14)
- IV Fluids ChartDocument1 pageIV Fluids Chartzahidtaniv71% (7)
- Cerebral Palsy Revalida FormatDocument10 pagesCerebral Palsy Revalida FormatChelsea CalanoNo ratings yet
- Bobath Approach: Concepts and PrinciplesDocument30 pagesBobath Approach: Concepts and PrinciplesJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Kenneth Anthony Tiu Regida100% (8)
- PoliomyelitisDocument74 pagesPoliomyelitisSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument3 pagesPoliomyelitisrandymarkpaduaNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument3 pagesPoliomyelitisDiana Fadhilah SariNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument22 pagesMeningitisdieanisNo ratings yet
- POLIODocument13 pagesPOLIOTaimur KhalilNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Poliomyelitis Written ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 6 Poliomyelitis Written ReportFranceska AntonioNo ratings yet
- Poliomyelitis: Key FactsDocument3 pagesPoliomyelitis: Key FactsJhania Maine LinxNo ratings yet
- Floppy BabyDocument11 pagesFloppy Babysmitha lakkavallyNo ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NotesDocument13 pagesPediatrics NotesYsa BonifacioNo ratings yet
- R A B I E S: Dave Jay S. Manriquez RNDocument15 pagesR A B I E S: Dave Jay S. Manriquez RNOdylon CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Poliomyeli TIS: Name:Nurzawani Binti Shamsudin Matric No: 0918424Document19 pagesPoliomyeli TIS: Name:Nurzawani Binti Shamsudin Matric No: 0918424Jerryuk20100% (1)
- Polio 150416150654 Conversion Gate01Document35 pagesPolio 150416150654 Conversion Gate01Bheru Lal0% (1)
- PT Ortho Assignment Poliomyelitis: Target Organ: Spinal Cord (Ant - Horn Motor Cells) & Brainstem (BulbarDocument3 pagesPT Ortho Assignment Poliomyelitis: Target Organ: Spinal Cord (Ant - Horn Motor Cells) & Brainstem (BulbarLakshita PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)Document16 pagesCerebral Palsy (CP)Divija ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument4 pagesPoliomyelitisGerard Adad Misa100% (1)
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument47 pagesAcute Flaccid ParalysisVandanaNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument30 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysismed.student657No ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument30 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysismed.student657No ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis Beyond Polio - A Case Based ApproachDocument10 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis Beyond Polio - A Case Based ApproachP T ArchanaNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument14 pagesPoliomyelitisadericky84100% (1)
- Polio Final YrDocument54 pagesPolio Final YrMobin Ur Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- OrthosDocument6 pagesOrthosBatch V Med 2 SY 21-22No ratings yet
- POLIOMYELITISDocument26 pagesPOLIOMYELITISIzhra Margate100% (1)
- Poliomyelitis: Dr. Ken Wirastuti, M Kes, SP.S, KIC Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fk. UnissulaDocument14 pagesPoliomyelitis: Dr. Ken Wirastuti, M Kes, SP.S, KIC Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fk. UnissulakhairunnisanurainiNo ratings yet
- Seizures:epilepsyDocument8 pagesSeizures:epilepsysmitha lakkavallyNo ratings yet
- PolioDocument8 pagesPolioKailash Nagar100% (2)
- Presented By: Gayramara Arben John ZDocument36 pagesPresented By: Gayramara Arben John ZgoykicoshenNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument2 pagesPoliomyelitisAlyssa Marie GatbuntonNo ratings yet
- Back Pain Guidelines-1 - 0Document5 pagesBack Pain Guidelines-1 - 0ANTONIO Toledo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis: Moderator: Dr. Bhavana Koppad Asso. Professor Dept of Pediatrics, JNMCDocument32 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis: Moderator: Dr. Bhavana Koppad Asso. Professor Dept of Pediatrics, JNMCmed.student657No ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure & Cerebral PalsyDocument6 pagesFebrile Seizure & Cerebral PalsyKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitesDocument35 pagesPoliomyelitesped medNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy SyndromesDocument6 pagesEpilepsy SyndromesHanin AlSiniNo ratings yet
- Well and Goes To Party. Develops Coughing Fit and Goes Blue and Then Everything Is Okay. 36Document8 pagesWell and Goes To Party. Develops Coughing Fit and Goes Blue and Then Everything Is Okay. 36Dean HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Benign Epilepsies - Part 1Document35 pagesBenign Epilepsies - Part 1Azeem Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument81 pagesPoliomyelitisKaycee Glene CalubNo ratings yet
- PolioDocument21 pagesPoliothunder beardedNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Motor Unit PresentationDocument18 pagesDisorders of The Motor Unit Presentationccash2No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 High Risk NewbornDocument38 pagesChapter 5 High Risk NewbornJobelle Acena100% (1)
- The Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesThe Nervous SystemKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- POLIOMYELITISDocument15 pagesPOLIOMYELITISEndahD'LamdaNo ratings yet
- Johannes H. SaingDocument67 pagesJohannes H. SaingRomMy WiEn MicKhoNo ratings yet
- Congential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersDocument7 pagesCongential 3 Musculoskeletal 3 Neurological 3 Abusive DisordersNichole CollinsNo ratings yet
- PolioDocument2 pagesPolioEdfeb9No ratings yet
- EncephalitisDocument33 pagesEncephalitisJona de VeraNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Septic PolyarthritisDocument3 pagesNeonatal Septic PolyarthritismedinamargaretkellyNo ratings yet
- Seizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaDocument4 pagesSeizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument9 pagesCerebral PalsyAngy100% (2)
- Lec 5 CNSDocument9 pagesLec 5 CNShusainozelNo ratings yet
- SarafDocument17 pagesSarafInggrid GraciaNo ratings yet
- Seizure Disorder Types: Partial - Local Onset May or May Not Impair Consciousness SimpleDocument4 pagesSeizure Disorder Types: Partial - Local Onset May or May Not Impair Consciousness Simpleampogison08No ratings yet
- Meeting Special Needs: A practical guide to support children with EpilepsyFrom EverandMeeting Special Needs: A practical guide to support children with EpilepsyNo ratings yet
- Vertigo, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVertigo, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaFrom EverandThe Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Radiation (Uvr) : ApplicationDocument28 pagesUltraviolet Radiation (Uvr) : ApplicationJulia Salvio100% (1)
- UltrasoundDocument24 pagesUltrasoundJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Radiation (Uvr)Document34 pagesUltraviolet Radiation (Uvr)Julia SalvioNo ratings yet
- UE ProsthesisDocument23 pagesUE ProsthesisJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- IFCDocument22 pagesIFCJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Functional Electrical Nerve StimulatorDocument15 pagesFunctional Electrical Nerve StimulatorJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Rehabilitation of FracturesDocument30 pagesTreatment and Rehabilitation of FracturesJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain ExcercisesDocument55 pagesLow Back Pain ExcercisesJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Congenital Deformities: Gay G. Crisostomo-San Antonio, PTRP, MDDocument46 pagesCongenital Deformities: Gay G. Crisostomo-San Antonio, PTRP, MDJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Gait Deviations in Orthotics & ProstheticsDocument10 pagesGait Deviations in Orthotics & ProstheticsJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- GSC - DDH LCPD SCFE and OthersDocument3 pagesGSC - DDH LCPD SCFE and OthersJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument117 pagesCardiac RehabilitationJulia Salvio100% (1)
- CVA Ken Presentation FINALDocument110 pagesCVA Ken Presentation FINALJulia Salvio100% (1)
- Culture Is The Widening of The Mind and of The Spirit - Jawaharlal NehruDocument17 pagesCulture Is The Widening of The Mind and of The Spirit - Jawaharlal NehruJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Donatelli Chapter 2 Shoulder 2018Document16 pagesDonatelli Chapter 2 Shoulder 2018Julia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Electro NotesDocument9 pagesElectro NotesJulia Salvio100% (1)
- Chest Physical TherapyDocument28 pagesChest Physical TherapyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Shortwave and Microwave DiathermyDocument31 pagesShortwave and Microwave DiathermyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument53 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentJulia Salvio50% (2)
- 19 - GBSDocument1 page19 - GBSJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesMyasthenia GravisJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Potts DiseaseDocument1 pagePotts DiseaseJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Etiology: Molecular Mimicry - Myelin-ReactiveDocument2 pagesEtiology: Molecular Mimicry - Myelin-ReactiveJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Amputation Lower ExtremityDocument5 pagesAmputation Lower ExtremityJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Injury: Relevant Anatomy: Peripheral Neuroanatomy andDocument7 pagesPeripheral Nerve Injury: Relevant Anatomy: Peripheral Neuroanatomy andJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Kernicterus (Infiltration of Bilirubin IntoDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsy: Kernicterus (Infiltration of Bilirubin IntoJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument2 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary System: Relevant Anatomy & Physiology: HeartDocument12 pagesCardiopulmonary System: Relevant Anatomy & Physiology: HeartJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- (NEW) Slide Deck Session 4 - Final. Participation in GovernanceDocument74 pages(NEW) Slide Deck Session 4 - Final. Participation in GovernanceRatsel IsmeNo ratings yet
- Safety Signs: Members: Mariana Dìaz Maritza Neicum Sabina VallejosDocument11 pagesSafety Signs: Members: Mariana Dìaz Maritza Neicum Sabina VallejosSabina Vallejos MirandaNo ratings yet
- Theatre Practice StandardsDocument54 pagesTheatre Practice StandardsNugroho WibisonoNo ratings yet
- AIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015Document24 pagesAIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015AdamAce VelasquezNo ratings yet
- People Should Avoid Junk FoodsDocument4 pagesPeople Should Avoid Junk FoodsShireen BatoolNo ratings yet
- English Practice 62: I. PronunciationDocument9 pagesEnglish Practice 62: I. PronunciationLe QuocNo ratings yet
- AHN MCqs Provided by MirhaDocument3 pagesAHN MCqs Provided by MirhaAkml KhanNo ratings yet
- HOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Document18 pagesHOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Donajei Rica100% (1)
- What Philippine Law Was Created To Include in It The Code of Ethics of Filipino Nurses?Document3 pagesWhat Philippine Law Was Created To Include in It The Code of Ethics of Filipino Nurses?Shirlene Benigra GorospeNo ratings yet
- Cognitive RestructuringDocument3 pagesCognitive Restructuringiulia9gavrisNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pharmacology Clear and Simple A Guide To Drug Classifications and Dosage Calculations 3rd Edition WatkinsDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Pharmacology Clear and Simple A Guide To Drug Classifications and Dosage Calculations 3rd Edition WatkinsJean Taylor100% (46)
- Part Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelDocument18 pagesPart Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelIAN LAPINGNo ratings yet
- Communiqué Émis Par La PSCDocument4 pagesCommuniqué Émis Par La PSCL'express MauriceNo ratings yet
- Ve GL HirarcDocument34 pagesVe GL HirarcEncik AhmadNo ratings yet
- SchistosomiasisDocument12 pagesSchistosomiasisHarold Jake ArguellesNo ratings yet
- CDS Quality+Measures Codes 20oct11 FINALDocument278 pagesCDS Quality+Measures Codes 20oct11 FINALbetzyvazquezNo ratings yet
- Research Agenda of The College of Business and Entrepreneurship - DDocument57 pagesResearch Agenda of The College of Business and Entrepreneurship - DSev BlancoNo ratings yet
- 2020 Guidelines WebDocument249 pages2020 Guidelines WebDaryl Barrios LamedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Detecting The Mood Disorder FinalDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Detecting The Mood Disorder FinalTrixie MizonaNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Physical DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFactors That Affect Physical DevelopmentmomuNo ratings yet
- Immune Disorders..Ppt FairDocument79 pagesImmune Disorders..Ppt FairSumi SebastianNo ratings yet
- MSDS AstDocument6 pagesMSDS AstKRRNo ratings yet
- SWP 01 - Delivery, Unloading, Storage and Transferring of MaterialsDocument3 pagesSWP 01 - Delivery, Unloading, Storage and Transferring of MaterialsGerald Wong Ntt100% (1)
- Genato BSP2G123 M5 Case StudiesDocument4 pagesGenato BSP2G123 M5 Case StudiesCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Worry Flow ChartsDocument10 pagesWorry Flow ChartsPaige Bayly100% (1)
- FORM 4.1 Self Assesment Check ListDocument3 pagesFORM 4.1 Self Assesment Check ListNica ManlugonNo ratings yet
- Annex C: Parental Consent and Waiver FormDocument2 pagesAnnex C: Parental Consent and Waiver FormKeennith NarcaNo ratings yet
- Mou of East West TpaDocument13 pagesMou of East West Tpamalayanur rama chandraNo ratings yet