Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ending Inventory C Ost of Goods Sold/365
Ending Inventory C Ost of Goods Sold/365
Uploaded by
Erika Mae Legaspi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageThe document discusses various financial ratios used to analyze a company's liquidity, borrowing capacity, profitability, and cash flow. It defines ratios like days' sales in inventory and accounts receivable turnover, which measure how quickly a company collects payments and turns over inventory. The document also covers common analysis methods like vertical analysis and trend analysis used to compare companies and identify changes over time.
Original Description:
Original Title
FINANCIAL RATIOS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various financial ratios used to analyze a company's liquidity, borrowing capacity, profitability, and cash flow. It defines ratios like days' sales in inventory and accounts receivable turnover, which measure how quickly a company collects payments and turns over inventory. The document also covers common analysis methods like vertical analysis and trend analysis used to compare companies and identify changes over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageEnding Inventory C Ost of Goods Sold/365
Ending Inventory C Ost of Goods Sold/365
Uploaded by
Erika Mae LegaspiThe document discusses various financial ratios used to analyze a company's liquidity, borrowing capacity, profitability, and cash flow. It defines ratios like days' sales in inventory and accounts receivable turnover, which measure how quickly a company collects payments and turns over inventory. The document also covers common analysis methods like vertical analysis and trend analysis used to compare companies and identify changes over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
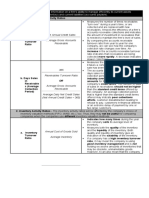
FINANCIAL RATIOS - The lower the number of days’ sales in
A. Liquidity ratios inventory, the better the inventory control
B. Borrowing capacity (leverage) ratios
C. Profitability ratios Ending Inventory
D. Special ratios C ost of Goods Sold /365
E. Cash Flow ratios
Accounts Receivable Turnover
ANALYSES - Indicates the liquidity of the receivables
Common-Size Analysis
- Expresses comparison in percentages Net Sales
- Makes comparisons of firms of different Average Gross Receivables
sizes
Accounts Receivable Turnover in Days
1. Vertical Analysis (use of same accounting Average Gross Receivables
period; base amount is selected)
Net Sales/365
2. Horizontal Analysis (use of same account;
base year is selected)
Inventory Turnover
Cost of Goods Sold
Cross-sectional Analysis
Average Inventory
Trend Analysis
- Studies the financial history of a firm for
comparison
- Helps detect problems or observe good
management
SOLVENCY
Quick ratio =
Current Assets
Current ratio =
Current Liabilities
PROFITABILITY
Return on Sales
Return on Assets
Return on Net Working Capital
Days’ Sales in Receivables
- A/R should include trade notes receivable
- Other receivables not related to sales on
account should NOT be included
Gross Receivables
Net Sales/ 365
Days’ Sales in Inventory
- All of the inventory accounts should be
included
- Estimates the number of days that it will
take to sell the current inventory
You might also like
- B. Donation To Private Educational Institutions Are Deductible in Full AmountDocument19 pagesB. Donation To Private Educational Institutions Are Deductible in Full AmountErika Mae Legaspi100% (5)
- LEGASPI - Pestel AnalysisDocument3 pagesLEGASPI - Pestel AnalysisErika Mae Legaspi100% (2)
- Mas Handout 1Document13 pagesMas Handout 1Rue Scarlet100% (2)
- Pa-Note Nalang Pag May Babaguhin Kayong SagotDocument26 pagesPa-Note Nalang Pag May Babaguhin Kayong SagotErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Share Capital: Memorandum Method VS Journal Entry MethodDocument12 pagesAccounting For Share Capital: Memorandum Method VS Journal Entry MethodErika Mae Legaspi100% (2)
- MAS-42O: Financial Statement Analysis: - T R S ADocument11 pagesMAS-42O: Financial Statement Analysis: - T R S AStefanie FerminNo ratings yet
- Mas 15Document11 pagesMas 15Christine Jane AbangNo ratings yet
- Manacc PresentationDocument65 pagesManacc Presentationnemelyn laguitanNo ratings yet
- Cia1002 Fsa Lecture DZDocument53 pagesCia1002 Fsa Lecture DZathirah jamaludinNo ratings yet
- Resa Material Financial Statement AnalysisDocument12 pagesResa Material Financial Statement Analysispatrickjames.ravelaNo ratings yet
- Financial AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinancial AnalysisLeilanie M. GabrielNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management 2 Financial Analysis: Percentage Composition StatementsDocument13 pagesStrategic Cost Management 2 Financial Analysis: Percentage Composition StatementsAlexandra Nicole IsaacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Financial Statements Analysis Using RatiosDocument23 pagesLesson 5 - Financial Statements Analysis Using Ratiosmcervitillo106No ratings yet
- Financial Statement ANALYSISDocument65 pagesFinancial Statement ANALYSISnemelyn laguitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document24 pagesChapter 6Hakim JanNo ratings yet
- Liquidity and Short Term ObligationsDocument15 pagesLiquidity and Short Term ObligationsgazmeerNo ratings yet
- FM301-WEEK3 and 4Document7 pagesFM301-WEEK3 and 4Eddie CalzadoraNo ratings yet
- ACAD - EDGE Edition 1 (Ratio Analysis)Document13 pagesACAD - EDGE Edition 1 (Ratio Analysis)Sarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Activity Ratios - They Provide Information On A Firm's Ability To Manage Efficiently Its Current AssetsDocument2 pagesActivity Ratios - They Provide Information On A Firm's Ability To Manage Efficiently Its Current AssetsQueen ValleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Merchandising Business: Far-ReviewerDocument6 pagesChapter 10 Merchandising Business: Far-ReviewerMethusela BantilloNo ratings yet
- 02 Analysis of Financial Statements HandoutsDocument13 pages02 Analysis of Financial Statements HandoutsCheska EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument15 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisJaztine Danikka GimpayaNo ratings yet
- FBF 10103 - LECT2 Financial AnalysisDocument20 pagesFBF 10103 - LECT2 Financial AnalysisNurul AsikinNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesFinancial Statements Analysis PDFEstrada, Jemuel A.No ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument3 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisSHENo ratings yet
- Analysis of FSDocument10 pagesAnalysis of FSJhondel RabinoNo ratings yet
- LotusDocument18 pagesLotusfathima rusdhaNo ratings yet
- Turnover Average Average Rate: Efficiency Ratios)Document2 pagesTurnover Average Average Rate: Efficiency Ratios)Yuri MinNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios - Sheet1Document4 pagesFinancial Ratios - Sheet1Melanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management.Document3 pagesWorking Capital Management.Christine MalayoNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios 4Document4 pagesFinancial Ratios 4Natasha Claire MangulabnanNo ratings yet
- (Bridging Blaze) Fmdfina Finals ReviewerDocument22 pages(Bridging Blaze) Fmdfina Finals ReviewerTrixie GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document6 pagesChapter 13Hareem Zoya WarsiNo ratings yet
- 06 MAS - FS AnalysisDocument8 pages06 MAS - FS AnalysisRimuru TempestNo ratings yet
- Finance Chap3Document8 pagesFinance Chap3bf8yv7y74dNo ratings yet
- Activity Ratios: Accounts Receivable Turnover, Inventory Turnover, Total Asset TurnoverDocument4 pagesActivity Ratios: Accounts Receivable Turnover, Inventory Turnover, Total Asset TurnoverQaiSer JafferyNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Ratios I. Liquidity: Current Ratio Current Assets Current LiabilitiesDocument7 pagesCommonly Used Ratios I. Liquidity: Current Ratio Current Assets Current LiabilitiesDaddii Dopez DineroNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysiis TenchniquesDocument24 pagesFinancial Analysiis TenchniquesShreya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis Using RatiosDocument26 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Using RatiosSophia NicoleNo ratings yet
- FM CHAPTER 3 Definition of Terms and SummaryDocument4 pagesFM CHAPTER 3 Definition of Terms and SummaryJoyceNo ratings yet
- Turnover Ratios (Teoría)Document14 pagesTurnover Ratios (Teoría)leonardo ramirezNo ratings yet
- MAS 08 - FS Analysis PDFDocument20 pagesMAS 08 - FS Analysis PDFAaron tamboongNo ratings yet
- STRACOSMAN - Chapter 6Document6 pagesSTRACOSMAN - Chapter 6Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument10 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisLeora CameroNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis 2Document4 pagesFinancial Analysis 2Meynard AguilarNo ratings yet
- Perpetual Inventory MethodDocument2 pagesPerpetual Inventory MethodGabriela Joseline Santivañez IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Part III - Developing The Entrepreneurial PlanDocument24 pagesPart III - Developing The Entrepreneurial Plannivedita choudhuryNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis Antonio Jaramillo DayagDocument11 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Antonio Jaramillo DayagAldrin RomeroNo ratings yet
- FS Analysis PDFDocument20 pagesFS Analysis PDF수지No ratings yet
- Financial Analysis and Reporting 1Document4 pagesFinancial Analysis and Reporting 1Anonymous ryxSr2No ratings yet
- Substantive Procedures - Class of Transactions: Sales and Sales ReturnDocument16 pagesSubstantive Procedures - Class of Transactions: Sales and Sales ReturnCyrra BalignasayNo ratings yet
- Ratios Used To Evaluate Short Term Financial Position (Short Term Solvency and Liquidity)Document3 pagesRatios Used To Evaluate Short Term Financial Position (Short Term Solvency and Liquidity)MJNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument34 pagesWorking Capital ManagementNirmal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business and Accountancy, Business and Management 2Document5 pagesFundamentals of Business and Accountancy, Business and Management 2joyce dionglayNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis GRC NotesDocument10 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis GRC NotesShahanna Faith JaymeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 - SlidesDocument20 pagesLecture 2.1 - Slidessfalcao91No ratings yet
- Working Capital Ratios and Other MetricsDocument20 pagesWorking Capital Ratios and Other MetricsnathanielNo ratings yet
- Week-5 (Financial Analysis Techniques)Document44 pagesWeek-5 (Financial Analysis Techniques)Ahmed IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document81 pagesChapter 6Kei Hanzu100% (1)
- Module 1 - Financial Statement Analysis - P1Document5 pagesModule 1 - Financial Statement Analysis - P1Jose Eduardo GumafelixNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument21 pagesRatio Analysissoumyasundar720No ratings yet
- Financial Performance Measurement: 0reviewing The ChapterDocument5 pagesFinancial Performance Measurement: 0reviewing The Chapterkent232323No ratings yet
- Business Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsFrom EverandBusiness Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesFrom EverandFinancial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Analysis of The Data Flow Diagram For Revenue CycleDocument34 pagesAnalysis of The Data Flow Diagram For Revenue CycleErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Acctng FinalsDocument27 pagesAcctng FinalsErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Strategy Formulation-ReviewerDocument2 pagesInnovation and Strategy Formulation-ReviewerErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- LEGASPI - Porter's AnalysisDocument1 pageLEGASPI - Porter's AnalysisErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Local Taxation and Real Property Taxation-SummaryDocument1 pageLocal Taxation and Real Property Taxation-SummaryErika Mae Legaspi100% (1)
- Reviewer - Module 1: 4. Implement StrategyDocument3 pagesReviewer - Module 1: 4. Implement StrategyErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- 12 - RecapitalizationDocument26 pages12 - RecapitalizationErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation: DeductionsDocument39 pagesIncome Taxation: DeductionsErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Diluted Earnings Per Share: Convertible BondsDocument40 pagesDiluted Earnings Per Share: Convertible BondsErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Eps Presentation On The Financial StatementsDocument9 pagesEps Presentation On The Financial StatementsErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Once CITIRA Becomes A LawDocument2 pagesOnce CITIRA Becomes A LawErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Basic Earnings Per ShareDocument47 pagesBasic Earnings Per ShareErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Diluted Eps: Options and WarrantsDocument32 pagesDiluted Eps: Options and WarrantsErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- 05 - Diluted EPS - Multiple Potential DilutersDocument22 pages05 - Diluted EPS - Multiple Potential DilutersErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Diluted Earning Per Share: Convertible Preference SharesDocument34 pagesDiluted Earning Per Share: Convertible Preference SharesErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant & EquipmentDocument19 pagesProperty, Plant & EquipmentErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Liabilities: B-ACTG214 SY2019-2020 de La Salle University - DasmariñasDocument158 pagesLiabilities: B-ACTG214 SY2019-2020 de La Salle University - DasmariñasErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
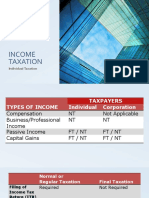
- TAX - Individual TaxationDocument40 pagesTAX - Individual TaxationErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- FAR1 - PPE - Subsequent MeasurementDocument11 pagesFAR1 - PPE - Subsequent MeasurementErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- 10 - Treasury SharesDocument44 pages10 - Treasury SharesErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Assessment On Accounting For Shareholders' Equity: Problem Solving RequirementsDocument4 pagesAssessment On Accounting For Shareholders' Equity: Problem Solving RequirementsErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- 05 - Legal CapitalDocument7 pages05 - Legal CapitalErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Assessment On Accounting For Shareholders' Equity Answer The Following QuestionsDocument1 pageAssessment On Accounting For Shareholders' Equity Answer The Following QuestionsErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- 08 - Preference SharesDocument38 pages08 - Preference SharesErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Shares Issued or Recorded at Less Than Par or at Less Than Value of Consideration ReceivedDocument38 pagesShares Issued or Recorded at Less Than Par or at Less Than Value of Consideration ReceivedErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- 07 - Delinquent SubscriptionDocument26 pages07 - Delinquent SubscriptionErika Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet