Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fig. 6. Example of Device For Radioscopic Testing of Welded Joints
Fig. 6. Example of Device For Radioscopic Testing of Welded Joints
Uploaded by
qc_5310406550 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThis document provides guidance on radiographic testing techniques and standards. It discusses two image quality classes (R1 and R2) that have different film and radiation sensitivity requirements. For both classes, the front intensifying screen thickness must be between 0.02mm and 0.25mm. The distance between the radiation source and sample should be selected using formulas to ensure the density of radiographic images meets minimum standards. Image quality is assessed using indicators that are placed on or next to welds being tested.
Original Description:
Original Title
welded_pipes_made_of_thermomechanically_rolled_materials_10.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidance on radiographic testing techniques and standards. It discusses two image quality classes (R1 and R2) that have different film and radiation sensitivity requirements. For both classes, the front intensifying screen thickness must be between 0.02mm and 0.25mm. The distance between the radiation source and sample should be selected using formulas to ensure the density of radiographic images meets minimum standards. Image quality is assessed using indicators that are placed on or next to welds being tested.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageFig. 6. Example of Device For Radioscopic Testing of Welded Joints
Fig. 6. Example of Device For Radioscopic Testing of Welded Joints
Uploaded by
qc_531040655This document provides guidance on radiographic testing techniques and standards. It discusses two image quality classes (R1 and R2) that have different film and radiation sensitivity requirements. For both classes, the front intensifying screen thickness must be between 0.02mm and 0.25mm. The distance between the radiation source and sample should be selected using formulas to ensure the density of radiographic images meets minimum standards. Image quality is assessed using indicators that are placed on or next to welds being tested.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
x-rays. The use of radioscopic methods is al- mal manner.
The density of the symbol image
lowed (Fig. 6), yet only in cases when the in the radiogram lower than the background
manufacturer can demonstrate their appro- density indicates that the protection against
priate sensitivity. backscattered radiation is insufficient and that
additional precautions should be used. A radi-
ation beam should be directed onto the centre
of a weld section being tested and should be
perpendicular to the pipe surface at this point.
A length subjected to an assessment should be
so that the thickness X-rayed at the ends of the
usable length of a radiogram does not exceed
the thickness X-rayed in the radiogram cen-
tre by more than 10% for image quality class
R1 and by more than 20% for image quality
class R2. It is necessary to use a technique of
X-raying through one wall. If, due to the size
of the object, such a technique cannot be used,
it is allowed to use a technique of X-raying
Fig. 6. Example of device for radioscopic testing
through two walls (by prior agreement). The
of welded joints
distance between the film and the weld sur-
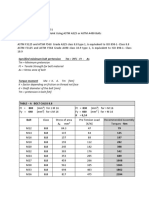
There are two image quality classes, i.e. face should be as small as possible.
R1 and R2: The minimum distance between the source
• class R1 (class B): radiographic testing and the sample ,f, should be selected using
technique by means of X-radiation of appropriate formulas or diagrams. The con-
heightened sensitivity; ditions of exposition should be so that the
• class R2 (class A): radiographic testing density of a radiogram in the tested area of
technique by means of X-radiation of nor- weld material free from imperfections is not
mal sensitivity. lower than 2.0 for image quality class R1 (2.3
For image quality class R1 it is necessary for image quality class B) and not lower than
to use at least fine-grained films (at least C4 1.7 for image quality class R2 (2.0 for image
class), whereas for image quality class R2 quality class B).
one should use at least medium-grained films The quality of an image should be deter-
(at least C5 class). For both image quality mined using an image quality indicator (IQI)
classes (R1 and R2), the thickness of front made of mild steel, grade specified in stand-
intensifying screens should be between 0.02 ards PN-EN 462-1 (PN-ISO 19232-1) and PN-
mm and 0.25 mm. Rear intensifying screens EN 462-2 (PN-ISO 19232-2). An IQI should
can have other thicknesses. Fluorescent in- be placed on the surface from the radiation
tensifying screens should not be used. source side or next to the weld or, in the case
The amount of backscattered and internal of a wire-type IQI – across the weld. Image
X-radiation should be limited to a minimum. quality indicators should be placed from the
When in doubt as to the efficiency of protec- film side only if the surface from the source
tion against backscattered radiation, it is ad- side is inaccessible. In such cases it is neces-
visable to fix a characteristic sign (usually a sary to place a letter “F” next to an IQI and
1.5mm-thick letter B) behind the film holder make a note of this change of the procedure in
or film frame and make a radiogram in a nor- the test report [4, 10].
46 BIULETYN INSTYTUTU SPAWALNICTWA No. 3/2013
You might also like
- Profile RadiographyDocument7 pagesProfile Radiographydebduttamallik100% (1)
- Level II QuestionsDocument8 pagesLevel II Questionsabdallah250057% (7)
- Sam Prince Franklin - 20MIS1115 - Physics Lab 9Document7 pagesSam Prince Franklin - 20MIS1115 - Physics Lab 9Sam100% (1)
- Rad Interpretation NotesDocument85 pagesRad Interpretation NotesJames Keller100% (12)
- 8.4.4 - Radiographic Training ProgramDocument31 pages8.4.4 - Radiographic Training ProgramMaduabuchi Serge Enemuo100% (1)
- Ideal Radiograph & Radiographic ErrorsDocument99 pagesIdeal Radiograph & Radiographic Errorsvanshika0% (1)
- Measurement Made Simple With Ar - Manoj R. Thakur PDFDocument194 pagesMeasurement Made Simple With Ar - Manoj R. Thakur PDFrarbka rarbkaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circuit BuilderDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuit BuilderRico Gurley100% (1)
- RT&Radiographic Interpretation NotesDocument85 pagesRT&Radiographic Interpretation Notesapply19842371100% (1)
- Inspection Group: Radiographic Inspection (Source & Film Positions)Document14 pagesInspection Group: Radiographic Inspection (Source & Film Positions)EswaranNo ratings yet
- Radiography Examination ProcedureDocument8 pagesRadiography Examination ProcedureSivaraman SelvarajNo ratings yet
- RT Quiz1Document4 pagesRT Quiz1AhmedA.Hassan50% (2)
- TCVN 4395-1986Document11 pagesTCVN 4395-1986huytai8613No ratings yet
- Interpretation of Weld RadiographsDocument10 pagesInterpretation of Weld RadiographsarianaseriNo ratings yet
- A Primer On Radiographic TestingDocument9 pagesA Primer On Radiographic TestingMohamed abdelrazzaqNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Inspection of Solid Propellant Using Computer Radiography (CR) System With 450 KV X-Ray SourceDocument5 pagesRadiographic Inspection of Solid Propellant Using Computer Radiography (CR) System With 450 KV X-Ray SourceMalolan VasudevanNo ratings yet
- 3 Intro To Radiography 03092013 OKDocument39 pages3 Intro To Radiography 03092013 OKsalehNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing ProcedureDocument12 pagesRadiographic Testing ProcedureJake SparrowNo ratings yet
- RT IDocument22 pagesRT Ijohn shepard100% (1)
- Welding of Pipelines and Related Facilities: Api Standard 1104 Nineteenth Edition, September 1999Document62 pagesWelding of Pipelines and Related Facilities: Api Standard 1104 Nineteenth Edition, September 1999Riki AkbarNo ratings yet
- Sop RTDocument9 pagesSop RTEddy Dwi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- API English (39-57)Document19 pagesAPI English (39-57)Alex Mamani calizayaNo ratings yet
- (Polish Journal of Medical Physics and Engineering) Estimation of The Effective Focal Spot Sizes in Medical Diagnostic X-Ray Tube AssembliesDocument9 pages(Polish Journal of Medical Physics and Engineering) Estimation of The Effective Focal Spot Sizes in Medical Diagnostic X-Ray Tube AssembliesAimanNo ratings yet
- Trigger 21 Faci Guide PoiDocument4 pagesTrigger 21 Faci Guide Poi2083120No ratings yet
- ASTM E384 (2022) - Part5Document1 pageASTM E384 (2022) - Part5david4231993No ratings yet
- Procedure For Radiography TestingDocument9 pagesProcedure For Radiography TestingKarrar TalibNo ratings yet
- Basic NDT - RT QB - 1Document17 pagesBasic NDT - RT QB - 1prabhakaran.S100% (1)
- As RI GEN 002 With AnswersDocument6 pagesAs RI GEN 002 With AnswersKarthikeyan GanesanNo ratings yet
- RT3 PDFDocument80 pagesRT3 PDFJustin Diraviraj100% (1)
- GridsDocument85 pagesGridsDileep JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Radiographic Image QualityDocument7 pagesConcepts of Radiographic Image QualityKyla J.No ratings yet
- Radiography of Welds Using Selenium 75, Ir 192 and X-Rays: TH TH THDocument5 pagesRadiography of Welds Using Selenium 75, Ir 192 and X-Rays: TH TH THSundar KumarNo ratings yet
- Examination Radiographic TechniqueDocument2 pagesExamination Radiographic TechniqueMICHAELNo ratings yet
- RT ProcedureDocument18 pagesRT Procedure1339979No ratings yet
- Effect of Exposure Time Reduction Towards Sensitivity and SNR For CR Application in NDTDocument6 pagesEffect of Exposure Time Reduction Towards Sensitivity and SNR For CR Application in NDTअनन्त मित्र पटेलNo ratings yet
- Computed Radiography Testing (CRT) : A Solution For Corrosion Under InsulationDocument2 pagesComputed Radiography Testing (CRT) : A Solution For Corrosion Under InsulationGistek MarcoNo ratings yet
- SensitometryDocument31 pagesSensitometryLuis RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 010Document2 pagesChapter 010Lip N' Lab CosmeticsNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Weld RadiographsDocument14 pagesInterpretation of Weld RadiographsJuliogNo ratings yet
- S01 Iso 17636 2Document5 pagesS01 Iso 17636 2Debendra Dev KhanalNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Focal Spots of Industrial X-Ray Tubes by Pinhole ImagingDocument7 pagesMeasurement of Focal Spots of Industrial X-Ray Tubes by Pinhole ImagingERNESTO ENRIQUE FERNANDEZ BAPTISTANo ratings yet
- Radiographic Interpretation: Coursework 2Document5 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: Coursework 2Mangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- Validation and Application of Computed Radiography (CR) Tangential Technique For Wall Thickness Measurement of 10 Inch Carbon Steel PipeDocument8 pagesValidation and Application of Computed Radiography (CR) Tangential Technique For Wall Thickness Measurement of 10 Inch Carbon Steel PipebineshNo ratings yet
- GridsDocument38 pagesGridsx6tmnbjp8kNo ratings yet
- NDT - RADIOGRAPHDocument12 pagesNDT - RADIOGRAPHDedy TriandaNo ratings yet
- RI CW BDocument5 pagesRI CW Bmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Scatter Radiation-Its Origin Is The Compton Scatter, The Incoming (High Energy Photon Uses A Part of ItsDocument6 pagesScatter Radiation-Its Origin Is The Compton Scatter, The Incoming (High Energy Photon Uses A Part of ItsmarrapescaNo ratings yet
- Optically Pumped DFB Lasers Based On GaN Using 10th-Order Laterally Coupled Surface GratingsDocument4 pagesOptically Pumped DFB Lasers Based On GaN Using 10th-Order Laterally Coupled Surface GratingsPaola GongoraNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Test Procedure Asf-RtDocument12 pagesRadiographic Test Procedure Asf-RtgiovaniNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Examination Exercise 4Document2 pagesRadiographic Examination Exercise 4mohammed jawadNo ratings yet
- UT Plate AngleDocument3 pagesUT Plate Anglefikril shaharudinNo ratings yet
- Control of Sactter Radiation Week 9Document62 pagesControl of Sactter Radiation Week 9Rupali SinghNo ratings yet
- Radiography Test Procedure Part - 1Document21 pagesRadiography Test Procedure Part - 1Ahmed Lepda100% (1)
- Fundamental Principles of ExposureDocument35 pagesFundamental Principles of ExposureNorjanna TahilNo ratings yet
- Asnt 3Document6 pagesAsnt 3amin.adineh97No ratings yet
- RT Pipe NDT ProcedureDocument30 pagesRT Pipe NDT ProcedureReadersmo100% (1)
- 460 Ewert PDFDocument40 pages460 Ewert PDFdaddadNo ratings yet
- RT 244 10 GRIDSDocument47 pagesRT 244 10 GRIDSYuda Fhunkshyang100% (1)
- RT Specific ExamDocument3 pagesRT Specific ExamGoutam Kumar Deb100% (2)
- Industrial X-Ray Computed TomographyFrom EverandIndustrial X-Ray Computed TomographySimone CarmignatoNo ratings yet
- Topics On Optical and Digital Image Processing Using Holography and Speckle TechniquesFrom EverandTopics On Optical and Digital Image Processing Using Holography and Speckle TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Techniques PresentationDocument17 pagesRoot Cause Techniques Presentationqc_531040655No ratings yet
- ASTM D1621 Compression Testing of Expanded Plastics and FoamsDocument2 pagesASTM D1621 Compression Testing of Expanded Plastics and Foamsqc_531040655No ratings yet
- Bolt Torque - Astm & IsoDocument2 pagesBolt Torque - Astm & Isoqc_53104065550% (4)
- Intercure 99 Application Guidelines UkDocument14 pagesIntercure 99 Application Guidelines Ukqc_531040655No ratings yet
- Flowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018Document16 pagesFlowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018qc_531040655No ratings yet
- Flowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018Document16 pagesFlowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018qc_531040655No ratings yet
- Bolt Torque - Astm & IsoDocument2 pagesBolt Torque - Astm & Isoqc_531040655100% (1)
- Pre Qulified JointsDocument6 pagesPre Qulified Jointsqc_531040655No ratings yet
- Revision Test-Consent FormDocument1 pageRevision Test-Consent Formqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 39untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page39untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 37untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page37untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 40untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page40untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- Project: EXPO 2020 - OV016 - USA PAVILION Inspection and Test Plan (Itp)Document5 pagesProject: EXPO 2020 - OV016 - USA PAVILION Inspection and Test Plan (Itp)qc_531040655No ratings yet
- 21untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page21untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- Symbol Section: Merican Nstitute of Teel OnstructionDocument1 pageSymbol Section: Merican Nstitute of Teel Onstructionqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 31untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page31untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 33untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page33untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 26untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page26untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 38untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page38untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 28untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page28untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 22untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page22untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 24untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page24untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 23extract PagesDocument1 page23extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 30untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page30untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 27untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page27untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 16untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page16untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 19untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page19untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- 15untitled Extract PagesDocument1 page15untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655No ratings yet
- Mri AssignmentDocument3 pagesMri AssignmentaparjotNo ratings yet
- (L8) Magnetic Field 19th JulyDocument37 pages(L8) Magnetic Field 19th JulyRishabh TaNo ratings yet
- USM ReportDocument21 pagesUSM ReportChandrakant SaurabhNo ratings yet
- Biasing in Magnetic Tape RecordingDocument4 pagesBiasing in Magnetic Tape RecordingkirillNo ratings yet
- 3RT60231AN20 Datasheet enDocument8 pages3RT60231AN20 Datasheet enKhanh Huy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Forced Vibration CUDocument5 pagesForced Vibration CUKomborerai MuvhiringiNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Van de Graaff GeneratorDocument3 pagesDesign and Implementation of Van de Graaff GeneratorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Problem So LN Balan Is 6Document2 pagesProblem So LN Balan Is 6Eddy Ahmed100% (2)
- X Ray TubeDocument70 pagesX Ray Tubesgoeldoc_550661200100% (1)
- DC MachineDocument94 pagesDC MachineyazdanieNo ratings yet
- Tentative: IPS Alpha Technology, LTDDocument19 pagesTentative: IPS Alpha Technology, LTDSetiawan Abdul RochimNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion3Document8 pagesDynamics of Uniform Circular Motion3Bry RamosNo ratings yet
- IAT-II Question Paper With Solution of 18ELE13 Basic Electrical Engineering March-2021-Lokasree B SDocument1 pageIAT-II Question Paper With Solution of 18ELE13 Basic Electrical Engineering March-2021-Lokasree B SJohanNo ratings yet
- Bitsat DPP-1 DT 06-04-2015Document7 pagesBitsat DPP-1 DT 06-04-2015Phani KumarNo ratings yet
- Schneider HVX 12KV-24KV Catalog (English)Document41 pagesSchneider HVX 12KV-24KV Catalog (English)Kalidass Back100% (1)
- IB Physics - Rigid Body Mechanics - Grade GorillaDocument3 pagesIB Physics - Rigid Body Mechanics - Grade Gorillamona safwatNo ratings yet
- Microwave Sensor Technology HFE0407 - PolivkaDocument8 pagesMicrowave Sensor Technology HFE0407 - Polivkatecnolectronica890No ratings yet
- Physics PDFDocument44 pagesPhysics PDFHarini Balakrishnan50% (2)
- CH 4 Structure of AtomsDocument12 pagesCH 4 Structure of AtomsNitish DhenwalNo ratings yet
- Components of ABS: Wheel Speed SensorDocument2 pagesComponents of ABS: Wheel Speed Sensorizhar aliNo ratings yet
- Old Mwe PappersDocument8 pagesOld Mwe Pappersaravind venkataNo ratings yet
- +Q Remains at Its Center, The Electric: © 2016 Pearson Education, IncDocument14 pages+Q Remains at Its Center, The Electric: © 2016 Pearson Education, IncOmar Al-SomaliNo ratings yet
- Boundless Lecture Slides: Available On The Boundless Teaching PlatformDocument47 pagesBoundless Lecture Slides: Available On The Boundless Teaching PlatformAvirup RayNo ratings yet
- SS 316 03Document12 pagesSS 316 03Muhammad Asif IqbalNo ratings yet
- 2-Pole 3phase Brochure PDFDocument1 page2-Pole 3phase Brochure PDFNeo RK PrimeNo ratings yet
- KCL and KVLDocument113 pagesKCL and KVLmanjuvenammaNo ratings yet