Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometry (Topics 3 & 4) Revision
Geometry (Topics 3 & 4) Revision
Uploaded by
MaddyAndersonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometry (Topics 3 & 4) Revision
Geometry (Topics 3 & 4) Revision
Uploaded by
MaddyAndersonCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics Higher Level for the IB Diploma
Revision: Geometry (Topics 3 & 4)
Coursebook chapters: 9–14
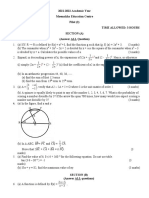
1. Find the area of the shaded region.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 3 or 4) [4 marks]
2. Do not use a calculator to answer this question.
Find the exact solutions of the equation sin 2θ = 3 cos 2θ for 0 ≤ θ ≤ 180°.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 3 or 4) [5 marks]
3. In triangle ABC, AB = 6.5 cm, BC = 12 cm and Ĉ = 29°.
Find the two possible values of  .
(accessible to students on the path to grade 3 or 4) [5 marks]
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2013. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 5
Mathematics Higher Level for the IB Diploma
4. Find the angles of the triangle with vertices A(4, 6, 2), B(1, 1, 2) and C(0, −1, 3). Give your
answers correct to the nearest degree.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 3 or 4) [9 marks]
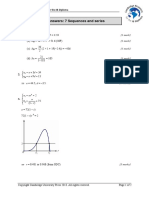
5. Do not use a calculator to answer this question.
The graph of the function f(x) = A sin(kx) + B is shown below.
Find the values of k, A and B.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 3 or 4) [5 marks]
6. Do not use a calculator to answer this question.
1
Solve the equation cos(2x + 30°) = for 0° ≤ x ≤ 360°.
2
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6) [5 marks]
x 3 y 1
7. Find the coordinates of the point where the line with Cartesian equation =z–4
5 3
intersects the plane with equation 4x – y + 2z = 7.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6) [5 marks]
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2013. All rights reserved. Page 2 of 5
Mathematics Higher Level for the IB Diploma
8 Do not use a calculator to answer this question.
2
Solve the equation tan x – sec x – 1 = 0 for x ∈ [0, 2π].
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6) [7 marks]
9. Triangle ABC has  = 2θ, B̂ = θ and BC : AC = 5 : 4.
(a) Find the exact value of cos .
(b) Hence find the angles of the triangle.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6) [6 marks]
10. Do not use a calculator to answer this question.
(a) Express 3 cos x – sin x in the form R cos(x + θ) where R > 0 and θ ∈ 0, .
2
3
(b) State the maximum value of .
5 3 cos x sin x
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6) [6 marks]
11. Three planes have equations 4x – y + z = 8, x + y – 2z = 3 and 6x + y – 3z = a.
(a) Find the value of a for which the intersection of the three planes is a straight line.
(b) Find the equation of this line.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6) [8 marks]
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2013. All rights reserved. Page 3 of 5
Mathematics Higher Level for the IB Diploma
12. Line l1 has equation r = (6i − 7j − 7k) + s(2i + 5j + 3k). Line l2 passes through the origin and the
point B(4, −1, −2). The two lines intersect at point A.
(a) Write down a vector equation of l2.
(b) Find the coordinates of A.
(c) Find the angle between l1 and l2.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 3 or 4)
(d) Find the distance AB, and hence find the perpendicular distance from B to l1.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6)
[12 marks]
1
13. Given that A = arcsin find the exact value of cos A.
3
(accessible to students on the path to grade 7) [3 marks]
14. Do not use a calculator to answer this question.
cos cos
Given that θ ∈ 0, and that vectors sin and sin are perpendicular,
2 sin cos
(a) Show that tan 2θ = 2.
(b) Hence find the exact value of tan θ.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 7) [9 marks]
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2013. All rights reserved. Page 4 of 5
Mathematics Higher Level for the IB Diploma
15. (a) Use the formulae for sin(A + B) and sin (A – B) to show that:
sin(A + B) + sin (A – B) = 2 sin A cos B.
2
(b) Hence show that sin θ + sin 3θ = 4 sin θ cos θ.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 7) [5 marks]
1 3 k 1
16. (a) Find the angle between the lines r = 2 t 1 and r = 2 s 1 .
2 1 3 2
(accessible to students on the path to grade 3 or 4)
(b) Find the value of k for which the lines l1 and l2 intersect.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 5 or 6)
3 1
(c) (i) Calculate 1 1 .
1 2
(ii) For the value of k found in part (b), find the Cartesian equation of the plane Π
containing lines l1 and l2.
(d) Find the exact distance of the point (5, 1, 2) from Π.
(accessible to students on the path to grade 7)[15 marks]
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2013. All rights reserved. Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry Supplementary ProblemsDocument4 pagesAnalytic Geometry Supplementary ProblemsJohn Elver VeriNo ratings yet
- DHS 9758 2023 Prelim P1Document7 pagesDHS 9758 2023 Prelim P1cyclonususNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 04 For Standard Board Exam 2020 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 04 For Standard Board Exam 2020 1 PDFSathya ArevalaganNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 0912024Document24 pagesAdobe Scan 0912024subhajitmitra999No ratings yet
- HL Vectors Old QBDocument19 pagesHL Vectors Old QBmavelNo ratings yet
- Maths Year 10B Paper 2Document16 pagesMaths Year 10B Paper 2Krishan BalajiNo ratings yet
- P1Document5 pagesP1MohPlaysNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedDocument2 pagesVibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedShadhasanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class-10 Paper - 1ST Term Exam NewDocument9 pagesMaths Class-10 Paper - 1ST Term Exam NewRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument16 pagesClass Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 Answersshubham Awasthi100% (1)
- Kami Export - Vincent Lu - International Advanced Level Mathematics - Internal Examination 2 Combined - QPDocument21 pagesKami Export - Vincent Lu - International Advanced Level Mathematics - Internal Examination 2 Combined - QPVincey LuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Pilot 2Document3 pagesMathematics Pilot 2Kaung Wai HtetNo ratings yet
- IX Maths QPDocument6 pagesIX Maths QPlavdu496No ratings yet
- IB Math Higher Level PDFDocument2 pagesIB Math Higher Level PDFNicolas SachioNo ratings yet
- Section A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxDocument8 pagesSection A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y Axvoon sjNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Csee 1998Document2 pagesMathematics Csee 1998Estar KaitelNo ratings yet
- Ak - 0606 Mock Exam 1 Paper1 - FinalDocument9 pagesAk - 0606 Mock Exam 1 Paper1 - Finalejljn1No ratings yet
- Practice Paper - 2019 X (Mathematics)Document8 pagesPractice Paper - 2019 X (Mathematics)Shoaib AnsariNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument11 pagesCoordinate GeometryHedy LimNo ratings yet
- May 2015Document8 pagesMay 2015anowNo ratings yet
- Euclid Combined ContestDocument125 pagesEuclid Combined ContestManikantan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Jee 2010Document77 pagesJee 2010nav.aulakh933No ratings yet
- Math Preboards BangaloreDocument6 pagesMath Preboards Bangalorekarun.senthil.kumar.25No ratings yet
- MAT2021Document32 pagesMAT2021Thin Zar Sun LwinNo ratings yet
- Uace Maths 1 2024Document3 pagesUace Maths 1 2024arthur brightonNo ratings yet
- 12 SQP CH 4Document3 pages12 SQP CH 4vivinsam786No ratings yet
- May 2013Document7 pagesMay 2013anowNo ratings yet
- 2013 ACSBR MYE Sec 3 AMDocument4 pages2013 ACSBR MYE Sec 3 AMtoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 10 Math22 23 sp01Document22 pages10 Math22 23 sp01Sangket MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- A Math Common Test Practise 3Document8 pagesA Math Common Test Practise 3Fangru CaoNo ratings yet
- University of Malta: Junior College JUNE 2013Document4 pagesUniversity of Malta: Junior College JUNE 2013Reign MatshabelaNo ratings yet
- Vectors - 1Document3 pagesVectors - 1Hugo Zuidweg RedondoNo ratings yet
- Section A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxDocument8 pagesSection A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxlllNo ratings yet
- Class IX-Mathematics-Sample Paper-1Document7 pagesClass IX-Mathematics-Sample Paper-1Shiv GorantiwarNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xi Sample Paper Test 03 For Annual Exam 2022 23Document5 pagesMaths Class Xi Sample Paper Test 03 For Annual Exam 2022 23RudraNo ratings yet
- Pure 1 Chapters 3 and 4 WsDocument47 pagesPure 1 Chapters 3 and 4 WsAfnan JaradatNo ratings yet
- QP - 0606 Mock Exam 1 Paper1 - FinalDocument10 pagesQP - 0606 Mock Exam 1 Paper1 - Finalejljn1No ratings yet
- Preboard Sample Paper 2019-20 Subject: Mathematics Grade: X Name: DateDocument4 pagesPreboard Sample Paper 2019-20 Subject: Mathematics Grade: X Name: DateGolden hazmatNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise 10 To 12Document8 pagesRevision Exercise 10 To 12Joseph AngNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2023 1Document7 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2023 1Megha SainiNo ratings yet
- JR - Inter - Maths 1a - Pre Final 03 - Paper - 08 03 2023Document2 pagesJR - Inter - Maths 1a - Pre Final 03 - Paper - 08 03 2023likkishinzzNo ratings yet
- 10 Math22 23 sp10Document21 pages10 Math22 23 sp10MHV AUTOTEKNo ratings yet
- Sri Sri Academy: Iit Ramaiah Model Question Paper - 2009Document9 pagesSri Sri Academy: Iit Ramaiah Model Question Paper - 2009palab2008100% (2)
- Solomon J QP - C1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon J QP - C1 EdexcelMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Engineering First Year Part 1A Paper 4: Mathematics Examples Paper 1Document3 pagesEngineering First Year Part 1A Paper 4: Mathematics Examples Paper 1junk filesNo ratings yet
- Oswaal CBSE Class 12th Toppers Answers Year-2020 MathematicsDocument17 pagesOswaal CBSE Class 12th Toppers Answers Year-2020 Mathematicskharbandatanish51No ratings yet
- Class X Maths Set 1Document6 pagesClass X Maths Set 1Nipun50% (2)
- P1题库分类Document257 pagesP1题库分类hqy1993goodNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C1 Hardest QuestionsDocument83 pagesEdexcel C1 Hardest QuestionsAhmed sengabNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C1 Hardest QuestionsDocument83 pagesEdexcel C1 Hardest QuestionsabidhassanNo ratings yet
- Hardest Past Paper Questions Between 2009-2015 2. Hardest Mixed Exercise Questions From The Text Book 3. Hardest Solomon Paper QuestionsDocument83 pagesHardest Past Paper Questions Between 2009-2015 2. Hardest Mixed Exercise Questions From The Text Book 3. Hardest Solomon Paper QuestionsAli EhabNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Sample PapersDocument207 pagesClass Xii Sample PapersBigsmokeNo ratings yet
- AS Practice Paper M8Document6 pagesAS Practice Paper M8saNo ratings yet
- Maths - PB A 2 - CLASS - XII 22-23 FinalDocument5 pagesMaths - PB A 2 - CLASS - XII 22-23 FinalsidharthNo ratings yet
- DHS P2Document7 pagesDHS P2Bryan TangNo ratings yet
- 160.102 Linear Mathematics - Massey - Exam - SEMESTER ONE 2018 - Remove MetaDocument10 pages160.102 Linear Mathematics - Massey - Exam - SEMESTER ONE 2018 - Remove MetaDonNo ratings yet
- MA Sample Paper 17 UnsolvedDocument7 pagesMA Sample Paper 17 Unsolvedbjpparty144No ratings yet
- 2019 Sample Question Matriculation Examination Department of Myanmar Examination Mathematics Time Allowed: (3) Hours Write Your Answers in The Answer BookletDocument2 pages2019 Sample Question Matriculation Examination Department of Myanmar Examination Mathematics Time Allowed: (3) Hours Write Your Answers in The Answer BookletSMhNo ratings yet
- 11 Mathematics sp01Document37 pages11 Mathematics sp01Bhati JiNo ratings yet
- May 2017Document8 pagesMay 2017anowNo ratings yet
- The State of Gmos On Social MediaDocument16 pagesThe State of Gmos On Social MediaMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian-Israeli Community: Jonah B CohenDocument4 pagesEthiopian-Israeli Community: Jonah B CohenMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability (Topic 5) Revision AnswersDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability (Topic 5) Revision AnswersMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes: 25 Mathematical InductionDocument2 pagesChapter Notes: 25 Mathematical InductionMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- 2018 20721 Moesm1 EsmDocument6 pages2018 20721 Moesm1 EsmMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- 20 Further Applications of Calculus Self-Assessment AnswersDocument2 pages20 Further Applications of Calculus Self-Assessment AnswersMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Her Land, Her Story: A Community-Run Digital Storytelling Project Exploring Climate-Gender-Health Relationships in Southern Senegal (1944 Words)Document6 pagesHer Land, Her Story: A Community-Run Digital Storytelling Project Exploring Climate-Gender-Health Relationships in Southern Senegal (1944 Words)MaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- 19 Further Integration Methods Self-AssessmentDocument1 page19 Further Integration Methods Self-AssessmentMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability (Topic 5) Revision AnswersDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability (Topic 5) Revision AnswersMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- 20 Further Applications of Calculus Self-AssessmentDocument1 page20 Further Applications of Calculus Self-AssessmentMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment: 5 The Theory of FunctionsDocument3 pagesSelf-Assessment: 5 The Theory of FunctionsMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Answers: 7 Sequences and Series: (1 Mark) (1 Mark)Document2 pagesSelf-Assessment Answers: 7 Sequences and Series: (1 Mark) (1 Mark)MaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability (Topic 5) RevisionDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability (Topic 5) RevisionMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment: 6 Transformations of Graphs: 1. The Diagram Shows The Graph of y G (X)Document2 pagesSelf-Assessment: 6 Transformations of Graphs: 1. The Diagram Shows The Graph of y G (X)MaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Answers: 25 Mathematical Induction: NN N RRDocument3 pagesSelf-Assessment Answers: 25 Mathematical Induction: NN N RRMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability (Topic 5) Revision AnswersDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability (Topic 5) Revision AnswersMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- 20 Further Applications of Calculus Self-AssessmentDocument1 page20 Further Applications of Calculus Self-AssessmentMaddyAndersonNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Trigonometry Project1Document7 pagesThe Principles of Trigonometry Project1api-206111791No ratings yet
- CirclesDocument14 pagesCirclesMario RectoNo ratings yet
- Amc LrsweDocument29 pagesAmc LrsweSwagata BhaumikNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesDocument18 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesMaster ChooklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31Document68 pagesChapter 31Anugrah ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Week 1Document10 pages10 - Week 1Jo-Anna CruzNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityRavi ModiNo ratings yet
- Integration Practice KeyDocument30 pagesIntegration Practice KeyzeelNo ratings yet
- AufEx4 02 01Document27 pagesAufEx4 02 01BSED SCIENCE 1ANo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics I B by Rao W.ODocument75 pagesPure Mathematics I B by Rao W.OBetty Njeri MbuguaNo ratings yet
- Variational Based FEMDocument67 pagesVariational Based FEMfefahimNo ratings yet
- CBSE VIII Class Mathematics Pre Mid Term Question PapersDocument4 pagesCBSE VIII Class Mathematics Pre Mid Term Question PapersVIGNESH YNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Linear Discriminant AnalysisDocument10 pagesObjectives:: Linear Discriminant AnalysisAlvin JeremiaNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document16 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Martin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- SHS 11-Gen Math Q1-Module 2 - Evaluating FunctionsDocument8 pagesSHS 11-Gen Math Q1-Module 2 - Evaluating Functionszsarena bautistaNo ratings yet
- IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Fall 2012, Professor Whitt Solutions To Homework Assignment 1Document16 pagesIEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Fall 2012, Professor Whitt Solutions To Homework Assignment 1Songya PanNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions PDFDocument5 pagesAdding and Subtracting Rational Expressions PDFapple henNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math 11 Lesson 4Document24 pagesGen. Math 11 Lesson 4Maricon SorongonNo ratings yet
- Maths For ScienceDocument838 pagesMaths For ScienceinfoparaclaseNo ratings yet
- CPT Maths NotesDocument9 pagesCPT Maths Notesanchal0% (1)
- GRADE 7 1st Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesGRADE 7 1st Quarter ExamAnnie Dosmanos100% (1)
- Pre-Cal Module 5Document31 pagesPre-Cal Module 5Hannah Grace Labor100% (2)
- SD Witama Nasional Plus: Daily Test IDocument3 pagesSD Witama Nasional Plus: Daily Test IIntan Tirta SariNo ratings yet
- Lec - 01-BDA24303-Differential EquationsDocument57 pagesLec - 01-BDA24303-Differential Equationsjohan razakNo ratings yet
- Diophantine Equations: Number Theory Meets Algebra and GeometryDocument7 pagesDiophantine Equations: Number Theory Meets Algebra and GeometryHazel Clemente CarreonNo ratings yet
- Path Integrals LinetskyDocument35 pagesPath Integrals LinetskyStephen GoodmanNo ratings yet
- Grade7 218137 1182 9378Document11 pagesGrade7 218137 1182 9378Gbuarts Eleah PiamonteNo ratings yet
- Unit Nine Lesson Four Intersection of Three PlanesDocument5 pagesUnit Nine Lesson Four Intersection of Three PlanesHan LinNo ratings yet
- What Are Magic Squares and How Are They Constructed?: F E D C B ADocument6 pagesWhat Are Magic Squares and How Are They Constructed?: F E D C B AJohanna MaxyneNo ratings yet