Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Musc Sys
Musc Sys
Uploaded by
api-5108725570 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
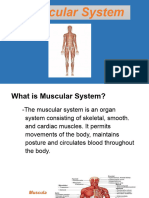
185 views15 pagesThere are three main types of muscles in the body - skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are voluntary and enable movement, smooth muscles are involuntary and work internal organs, and cardiac muscle is only found in the heart. Exercise causes muscles to contract in different ways - concentrically which shortens muscles, eccentrically which lengthens muscles under tension, and isometrically which keeps muscles the same length. The effects of exercise include increased blood flow to muscles, faster contraction, higher muscle temperature, and buildup of waste products which can cause fatigue.
Original Description:
Original Title
musc sys
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are three main types of muscles in the body - skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are voluntary and enable movement, smooth muscles are involuntary and work internal organs, and cardiac muscle is only found in the heart. Exercise causes muscles to contract in different ways - concentrically which shortens muscles, eccentrically which lengthens muscles under tension, and isometrically which keeps muscles the same length. The effects of exercise include increased blood flow to muscles, faster contraction, higher muscle temperature, and buildup of waste products which can cause fatigue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 views15 pagesMusc Sys
Musc Sys
Uploaded by
api-510872557There are three main types of muscles in the body - skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are voluntary and enable movement, smooth muscles are involuntary and work internal organs, and cardiac muscle is only found in the heart. Exercise causes muscles to contract in different ways - concentrically which shortens muscles, eccentrically which lengthens muscles under tension, and isometrically which keeps muscles the same length. The effects of exercise include increased blood flow to muscles, faster contraction, higher muscle temperature, and buildup of waste products which can cause fatigue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 15
HOW EXERCISE AFFECTS OUR MUSCLES
All our movements happen as a result of the
shortening (contracting) and lengthening
(extending) of muscles.
Our muscles:
Enable us to move our body parts
Give us our own individual shape
Protect and keep in place our abdominal
organs
Enable us to maintain a good posture
Help in the circulation of our blood
Generate body heat when they contract
There are over 600 skeletal muscles in the
body – 150 in the head and neck.
1. Skeletal Muscles
These are voluntary muscles and are under
our control
They work as we instruct them too
We use them in everyday sporting activities
e.g. Walking, running and jumping
2. Smooth Muscles
These are involuntary muscles which work
automatically
These are not under our conscious control
They work our internal organs such as the
stomach, gut and bladder
3. Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac or heart muscle is a special type of
involuntary muscle
It is found only in the heart
It contracts regularly, continuously,
automatically and without tiring
There are three main types of muscular
contraction:
Isotonic and concentric
Isotonic and eccentric
isometric
Isotonic contraction with muscles working
concentrically
Our muscles shorten as they contract
The ends of the move closer together
Our biceps work in this way when we do a
pull-up
Isotonic contraction with muscles working
eccentrically
Our muscles lengthen as they contract under
tension
The ends of the muscle move further apart
Our biceps work in this way when we lower
our body from a pull-up position
Isometric contraction
Our muscles stay the same length as they
contract
There is no movement, so the ends of the
muscles stay the same distance apart
Our shoulder muscles work in this way when
we pull in a tug-of-war
There is an increased flow of blood to the
working muscles
Muscles take up more of the oxygen from the
blood
The muscles contract more often and more
quickly
More of the muscle fibres contract
There is a rise in temperature in the muscles
Our stores adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and
creatine phosphate (CP) in the muscles are
used up
Waste products such as carbon dioxide and
lactic acid build up in the muscles
These waste products may lead to tiredness
and cramp (muscle fatigue)
Our store of muscle glucose are used up
Our ability to carry on will be affected
Overuse of muscles can lead to soreness and
strains
When we play sport we move our limbs in
many different directions.
Flexion – our limbs bend at a joint
Extension – our limbs straighten at a joint
Abduction – our limbs are moved away from a
line down the middle of the body
Adduction – our limbs are moved towards a
line down the middle of the body
Rotation – this is a circular movement (part of
the body turns whilst the rest remains still)
Circumduction – the end of a bone moves in a
circle, for example swinging your arm in a
circle at the shoulder
You might also like
- 6 Week Program 6 Week ProgramDocument15 pages6 Week Program 6 Week ProgramRelja NovakovicNo ratings yet
- 6 Weeks of THE WORK Workout CalendarDocument1 page6 Weeks of THE WORK Workout CalendarnatalipaskalNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- The Muscular System: AIM: To Understand The Structure and Function of MusclesDocument28 pagesThe Muscular System: AIM: To Understand The Structure and Function of MusclesdayafloNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: AIM: To Understand The Structure and Function of MusclesDocument28 pagesThe Muscular System: AIM: To Understand The Structure and Function of MusclespuhiNo ratings yet
- Task 2 PublishedDocument13 pagesTask 2 Publishednickoh28No ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument12 pagesThe Muscular SystemMarielle Grace PadilloNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument32 pagesUnit IvCanhgNo ratings yet
- 9-1 PE Revision GuideDocument27 pages9-1 PE Revision GuideChrisNo ratings yet
- PE20#1 The Muscular SystemDocument146 pagesPE20#1 The Muscular SystemJasmine GañganNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesThe Muscular Systemrp buitNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument49 pagesThe Muscular SystemTessa Lonka TenidoNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument49 pagesMuscular SystemHindrix Mitch100% (1)
- Muscular System2Document43 pagesMuscular System2LeocadiaNo ratings yet
- Muscul Ar: Syste MDocument37 pagesMuscul Ar: Syste MMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument89 pagesMusclesSelena ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesThe Muscular SystemMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM (Voice Record)Document26 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM (Voice Record)Roger TerminatorNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument27 pagesMuscular Systemapi-531520430No ratings yet
- MUSCLESDocument6 pagesMUSCLESTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Muscle TermsDocument26 pagesMuscle Termscandace728No ratings yet
- q1 Lesson 2 The Body TissuesDocument22 pagesq1 Lesson 2 The Body TissuesLeocadiaNo ratings yet
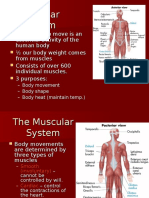
- The Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesDocument25 pagesThe Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesJoanna Poshnja100% (1)
- Week 6 Muscular System StudentsDocument27 pagesWeek 6 Muscular System StudentsanaflaviaaguiarNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Biology 2 - Group 1Document86 pagesMuscular System: Biology 2 - Group 1haylo100% (1)
- Anatomical, Mechanical and Physiological Bases of Movement (Skeletal System, Muscular System, Components of Fitness) Lecture 2Document9 pagesAnatomical, Mechanical and Physiological Bases of Movement (Skeletal System, Muscular System, Components of Fitness) Lecture 2gierica sisonNo ratings yet
- Refined Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesRefined Muscular SystemogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Locomotor SystemDocument2 pagesLocomotor Systemlaura camilaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument1 pageThe Muscular SystemDiana Madalina MitrutNo ratings yet
- Pdhpe HSC Core 2Document10 pagesPdhpe HSC Core 2Toby FergusonNo ratings yet
- Multimedia PresentationDocument12 pagesMultimedia PresentationAngelyn De ArceNo ratings yet
- Isotonic ExerciseDocument2 pagesIsotonic ExerciseInspera WooNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Lesson 3Document25 pagesPhysical Fitness Lesson 3Carla Malloy JeffersonNo ratings yet
- BTEC Sport: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument15 pagesBTEC Sport: Anatomy and PhysiologyamyhowarthNo ratings yet
- Pathfit ReviewerDocument7 pagesPathfit ReviewerbantayalagaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Pe Revision BookletDocument39 pagesIGCSE Pe Revision BookletRainbootNo ratings yet
- Sport Presentation: by Scott CadmoreDocument55 pagesSport Presentation: by Scott CadmorescadmoreNo ratings yet
- T1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoDocument6 pagesT1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoMartín Benítez del HoyoNo ratings yet
- Written Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBDocument23 pagesWritten Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBNoronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- The Human MusclesDocument7 pagesThe Human Musclesogboifavour41No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument28 pagesMuscular SystemPridas GidNo ratings yet
- Muscular System - Bio 2 ADocument44 pagesMuscular System - Bio 2 A20181539No ratings yet
- BiomechDocument2 pagesBiomechKisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Activity and ExerciseDocument45 pagesActivity and ExerciseAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Muscular FitnessDocument44 pagesMuscular FitnessJack Messaros100% (1)
- Sexies GroupDocument92 pagesSexies GroupJamie BagundolNo ratings yet
- GCSE Revision Guide 2 2Document48 pagesGCSE Revision Guide 2 2Ravi BhollahNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy, Physiology in Sports-1Document15 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy, Physiology in Sports-1avik mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 FIT MEDocument7 pagesTopic 2 FIT MESleepy HeadNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesMuscular Systemchristianoliver.aceroNo ratings yet
- ATS-11 - Muscular System - JMDocument22 pagesATS-11 - Muscular System - JMJouel SalloumNo ratings yet
- 14 140408043036 Phpapp02Document28 pages14 140408043036 Phpapp0249742806No ratings yet
- Personal Trainer-E-BookDocument4 pagesPersonal Trainer-E-BooksampradanaNo ratings yet
- Specialized Tissue That Enable The Body and Its Parts To MoveDocument23 pagesSpecialized Tissue That Enable The Body and Its Parts To MoveJJ Almagro100% (1)
- The Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8Document44 pagesThe Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8ninya puella100% (1)
- Local Media7531542316752723014Document6 pagesLocal Media7531542316752723014gminoetvsgalupoNo ratings yet
- Physiological Principles of SotaiDocument13 pagesPhysiological Principles of SotaiBuyu IkkanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsDocument4 pagesThe Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsNeil AdelanNo ratings yet
- Ankles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingDocument18 pagesAnkles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingJess Zausa MasulaNo ratings yet
- Do Bodybuilders Have More Muscles? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandDo Bodybuilders Have More Muscles? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Ancient Olympics True or FalseDocument1 pageAncient Olympics True or Falseapi-510872557No ratings yet
- Ancient OlympicsDocument1 pageAncient Olympicsapi-510872557No ratings yet
- Joint Worksheet - Form 1Document2 pagesJoint Worksheet - Form 1api-510872557No ratings yet
- Revision Form 1Document3 pagesRevision Form 1api-510872557No ratings yet
- Our Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesOur Skeletal Systemapi-510872557No ratings yet
- Form 1 Lesson 2 Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesForm 1 Lesson 2 Reading Comprehensionapi-510872557No ratings yet
- Art 1Document5 pagesArt 1api-510872557No ratings yet
- Soc Stud 1Document2 pagesSoc Stud 1api-510872557No ratings yet
- Kami Export - 1.4.3 Practice - Setting and Reaching Goals (Practice)Document3 pagesKami Export - 1.4.3 Practice - Setting and Reaching Goals (Practice)Brianna StangeNo ratings yet
- Apakah Vo2 MaxDocument2 pagesApakah Vo2 MaxzaharibbNo ratings yet
- One Rep Max Calculator - Strength LevelDocument1 pageOne Rep Max Calculator - Strength LevelJesse SkeltonNo ratings yet
- Five Steps in TrainingDocument14 pagesFive Steps in TrainingIvan Kulev100% (1)
- 30 Day Fitness ChallengeDocument1 page30 Day Fitness ChallengeGleason Ray GeronaNo ratings yet
- Pe Exercise TableDocument1 pagePe Exercise TablenAndrei Paul MabatanNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Calendar: 10 Rounds WK2 Boxing 2 10 Rounds WK2 Boxing 3Document1 pageHybrid Calendar: 10 Rounds WK2 Boxing 2 10 Rounds WK2 Boxing 3lamagumaNo ratings yet
- Lactate ThresholdDocument22 pagesLactate Thresholdmarin0410No ratings yet
- Clusters NSCADocument21 pagesClusters NSCAUlfNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Activity 7Document8 pagesPhysioEx Activity 7i1011221013No ratings yet
- Buckley Et Al (2015) - Multimodal High-Intensity Interval Training IncreasesDocument6 pagesBuckley Et Al (2015) - Multimodal High-Intensity Interval Training IncreasesRodrigo MelloNo ratings yet
- Increase Your VO2maxDocument8 pagesIncrease Your VO2maxAnonymous u0Hw9gGMoaNo ratings yet
- Accredited: Sports ScientistDocument4 pagesAccredited: Sports ScientistChi Chung CHANNo ratings yet
- The Best 12 CrossFit Workouts To Build Muscle, Increase Strength and Burn FatDocument1 pageThe Best 12 CrossFit Workouts To Build Muscle, Increase Strength and Burn FatWes WorldNo ratings yet
- Excercise 2 Activity 7 DoniDocument6 pagesExcercise 2 Activity 7 DoniDoni SaragihNo ratings yet
- FitnessLog Denuyo XFDocument4 pagesFitnessLog Denuyo XFZoe Peter Yloi DenuyoNo ratings yet
- PT-4 Week 2 ExercisesDocument3 pagesPT-4 Week 2 ExercisesElijah Judson AlanzalonNo ratings yet
- Article+0202 168 174Document7 pagesArticle+0202 168 174SintaabasNo ratings yet
- A. Sequential Steps For Designing A Resistance Training ProgramDocument62 pagesA. Sequential Steps For Designing A Resistance Training ProgramNicole Ba�ares100% (1)
- VO2 MaxDocument9 pagesVO2 MaxMuhammad Aji WiyudaNo ratings yet
- Tabla 2023-1Document31 pagesTabla 2023-1Pedro NavajaNo ratings yet
- Productlist 20221121Document3 pagesProductlist 20221121idboggNo ratings yet
- No Whining No Complaining No ExcusesDocument48 pagesNo Whining No Complaining No ExcusesCheehiong LimNo ratings yet
- Training For Strength and HypertrophyDocument13 pagesTraining For Strength and Hypertrophykhubaib10100% (1)
- Chapter 22Document33 pagesChapter 22Sahithya M100% (1)
- HIIT Exercises ListDocument8 pagesHIIT Exercises ListJeanNo ratings yet
- My Three Week "Cardio" Activity Log: Goal ActualDocument1 pageMy Three Week "Cardio" Activity Log: Goal ActualJaine CasangcapanNo ratings yet
- FDF P3W1Document12 pagesFDF P3W1鲁纯玮No ratings yet