Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marik Covid Protocol Summary
Marik Covid Protocol Summary
Uploaded by
Camille05Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marik Covid Protocol Summary
Marik Covid Protocol Summary
Uploaded by
Camille05Copyright:
Available Formats
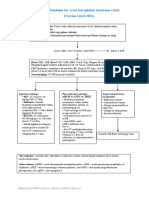
Critical Care COVID-19 Management Protocol General schema for respiratory support in patients with COVID-19
(updated 5-11-2020) TRY TO AVOID INTUBATION IF POSSIBLE
Low-Flow Nasal Cannula
Prophylaxis
■ Typically set at 1-6 Liters/Min
While there is very limited data (and none specific for COVID-19), the following “cocktail” may
have a role in the prevention/mitigation of COVID-19 disease.
■ Vitamin C 500 mg BID and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID High Flow Nasal Cannula
■ Accept permissive hypoxemia (O2 Saturation > 86%)
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day
■ Titrate FiO2 based on patient’s saturation
■ Melatonin (slow release): Begin with 0.3mg and increase as tolerated to 2 mg ■ Accept flow rates of 60 to 80 L/min
at night
■ Trial of inhaled Flolan (epoprostenol)
■ Vitamin D3 1000-4000 u/day Attempt proning (cooperative proning)
Deterioration
■
Mildly Symptomatic patients (at home):
Recovery
■ Vitamin C 500mg BID and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID Invasive Mechanical Ventilation
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day ■ Target tidal volumes of ~6 cc/kg
■ Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown) ■ Lowest driving pressure and PEEP
■ Vitamin D3 2000-4000 u/day ■ Sedation to avoid self-extubation
Trial of inhaled Flolan
Optional: Hydroxychloroquine 400mg BID day 1 followed by 200mg BID for
■
■
4 days
Prone Positioning
■ Optional: Ivermectin 150-200ug/kg (single dose)
■ Exact indication for prone ventilation is unclear
■ Optional: ASA 81/325mg/day ■ Consider in patients with PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 150
In symptomatic patients, monitoring with home pulse oximetry is recommended.
Ambulatory desaturation below 94% should prompt hospital admission
Mildly Symptomatic patients (on floor): VV-ECMO
■ Indications remain unclear
■ Vitamin C 500 mg PO q 6 hourly and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID (if available)
■ Early discussion with ECMO center or team may be advisable
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day
■ Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown)
■ Vitamin D3 2000-4000 u/day ■ Optional: Ivermectin 150-200 ug/kg (single dose)
■ Enoxaparin 60 mg daily ■ N/C 2L /min if required (max 4 L/min; consider early t/f to ICU for escalation
■ Famotidine 40mg daily (20mg in renal impairment) of care).
■ Methylprednisolone 40 mg q 12 hourly; increase to 80 mg q 12 if poor response ■ T/f EARLY to the ICU for increasing respiratory signs/symptoms and arterial
■ Optional: Hydroxychloroquine 400 mg BID day 1 followed by 200 mg BID for desaturations.
4 days continued on next page
■ Optional: Remdesivir (if available)
Find the latest version at evms.edu/covidcare
Critical Care COVID-19 Management Protocol
(updated 5-11-2020)
Respiratory symptoms (SOB; hypoxia- requiring N/C ≥ 4 L min: 11. Maintain EUVOLEMIA
admit to ICU): 12. Early norepinephrine for hypotension.
Essential Treatment (dampening the STORM)
13. Escalation of respiratory support; See General Schema for Respiratory
1. Methylprednisolone 80 mg loading dose then 40 mg q 12 hourly for at Support in Patients with COVID-19.
least 7 days and until transferred out of ICU. In patients with poor response,
increase to 80 mg q 12 hourly. 14. Treatment of Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS)
2. Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 3g IV q 6 hourly for at least 7 days and/or until ■ A sub-group of patients will develop MAS. A ferritin > 4400 ng/ml
transferred out of ICU. Note caution with POC glucose testing. is considered diagnostic of MAS. Other diagnostic features include
increasing AST/ALT and increasing CRP.
3. Full anticoagulation: Unless contraindicated we suggest FULL
Methylprednisolone 120 mg q 6-8 hourly for at least 3 days, then wean
anticoagulation (on admission to the ICU) with enoxaparin, i.e 1 mg kg s/c
■
according to Ferritin, CRP, AST/ALT. Ferritin should decrease by at least
q 12 hourly (dose adjust with Cr Cl < 30mls/min). Heparin is suggested with
15% before weaning corticosteroids.
CrCl < 15 ml/min.
15. Monitoring: Daily: PCT, CRP, IL-6, BNP, Troponins, Ferritin, Neutrophil-
Note: Early termination of ascorbic acid and corticosteroids will likely result in a
rebound effect. Lymphocyte ratio, D-dimer and Mg. CRP, IL-6 and Ferritin track disease
severity closely. Thromboelastogram (TEG) on admission and repeated as
Additional Treatment Components (the Full Monty) indicated.
4. Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown).
16. Post ICU management
5. Famotidine 40mg daily (20mg in renal impairment)
a. Enoxaparin 40-60 mg s/c daily
6. Vitamin D 2000-4000 u/day b. Methylprednisone 40 mg day, the wean slowly
7. Magnesium: 2 g stat IV. Keep Mg between 2.0 and 2.4 mmol/l. Prevent c. Vitamin C 500 mg PO BID
hypomagnesemia (which increases the cytokine storm and prolongs Qtc). d. Melatonin 3-6 mg at night
8. Optional: Azithromycin 500 mg day 1 then 250 mg for 4 days
9. Optional: Atorvastatin 40-80 mg/day.
10. Broad-spectrum antibiotics if superadded bacterial pneumonia is suspected
based on procalcitonin levels and resp. culture (no bronchoscopy).
Developed and updated by Paul Marik, MD, Chief of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine,
Find the latest version at evms.edu/covidcare Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, VA
You might also like
- ACLS 2020 Algorithms: American Heart Association 2020 GuidelinesDocument8 pagesACLS 2020 Algorithms: American Heart Association 2020 GuidelinesNofi Nurina100% (4)
- Contrast Reaction Card PediatricDocument2 pagesContrast Reaction Card PediatricJenniffer FlorenciaNo ratings yet
- RFH COVID-19 ICU Resource Pack FULL PDFDocument15 pagesRFH COVID-19 ICU Resource Pack FULL PDFQuique GarciaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument7 pagesOsteoarthritisRgm UyNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol Summaryshubham rathodNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDFDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol Summary PDFJody VivasNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryInternos YopalNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCaterina PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDFDocument1 pageMarik Covid Protocol Summary PDFCiuvat Dumitru ValentinNo ratings yet
- CCF IpDocument1 pageCCF IpBryan FjbNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument2 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHBhanu Kumar100% (1)
- COVID MX BsmmuDocument2 pagesCOVID MX BsmmuNuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- CVD Protocol ENGLISHDocument2 pagesCVD Protocol ENGLISHCornel ComanNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document4 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Adrian BoboceaNo ratings yet
- CNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Document1 pageCNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Fitri RachmadaniNo ratings yet
- MX Protocol Book FinalDocument42 pagesMX Protocol Book FinalPawan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CMSCN R IgevDocument2 pagesCMSCN R Igevdiana8827534No ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHJhonn BlackNo ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document2 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Nandor KissNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHfernandohNo ratings yet
- WB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)Document49 pagesWB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)El MirageNo ratings yet
- AIIMS COVID Algorithm 1.5-1 PDFDocument1 pageAIIMS COVID Algorithm 1.5-1 PDFAnutosh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases Pharmacology PDFDocument7 pagesClinical Cases Pharmacology PDFAnkur HazraNo ratings yet
- BairdDocument6 pagesBairdMuhammad salahuddinNo ratings yet
- Special 13 BTS SIGN AsthmaDocument1 pageSpecial 13 BTS SIGN AsthmacositaamorNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument10 pagesAmiodaronesarahhhNo ratings yet
- Management of Convulsions After The Neonatal Period: DR NgugiDocument22 pagesManagement of Convulsions After The Neonatal Period: DR NgugitheintrovNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Emergency Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPediatric Emergency Pocket GuideHongMingNo ratings yet
- ConnectorDocument4 pagesConnectoryetaung8No ratings yet
- VTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHDocument13 pagesVTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHreham ONo ratings yet
- SHYA Episode 16 ShownotesDocument7 pagesSHYA Episode 16 ShownotesKarthikNo ratings yet
- Suspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsDocument6 pagesSuspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsMuhamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Charts and Hearts PDFDocument51 pagesCharts and Hearts PDFBen ScottNo ratings yet
- Seven Ps For RSI BOARDDocument2 pagesSeven Ps For RSI BOARDJames BrownNo ratings yet
- Contrast Reaction Card AdultDocument2 pagesContrast Reaction Card AdultJenniffer FlorenciaNo ratings yet
- UVA Phenobarb Protocol Sdutta 8-4-21Document3 pagesUVA Phenobarb Protocol Sdutta 8-4-21Shourik DuttaNo ratings yet
- Opioids MedicalDocument11 pagesOpioids MedicalduckyouisaacNo ratings yet
- NSAIDSDocument18 pagesNSAIDSduckyouisaacNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010anon_336736395No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityChris LeeNo ratings yet
- AtropinDocument9 pagesAtropinarfitaaaaNo ratings yet
- PRN Medications: Indications & UseDocument23 pagesPRN Medications: Indications & Usedis_is_me100% (1)
- Agitated PatientDocument2 pagesAgitated PatientCassandra GeldenhuysNo ratings yet
- Convulsive Status Epilepticus 1003Document9 pagesConvulsive Status Epilepticus 1003aamir6312No ratings yet
- MS2 EndocrineDocument9 pagesMS2 EndocrineDaphney Ruth LeocadioNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Call For Help 2222 Commence/continue CPR (5 Initial Breaths Then CV Ratio 15:2)Document1 pagePaediatric Advanced Life Support: Call For Help 2222 Commence/continue CPR (5 Initial Breaths Then CV Ratio 15:2)Vijay RNo ratings yet
- Farma StrokeDocument37 pagesFarma StrokeDAHLIANo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012kivuNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia-Icu Management ProtocolDocument3 pagesEclampsia-Icu Management ProtocolmatentenNo ratings yet
- Medical TherapyDocument6 pagesMedical Therapyvinay reddyNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1Document1 pageCOVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1shivani shindeNo ratings yet
- Routine Anesthesia Set UpDocument4 pagesRoutine Anesthesia Set UpSteve Johnstone100% (2)
- Treatment Protocol Covid-19Document4 pagesTreatment Protocol Covid-19Shiv singhNo ratings yet
- Hypertermia CrisisDocument1 pageHypertermia CrisislisaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Social Antecedents To Dev of InteroceptionDocument13 pagesSocial Antecedents To Dev of InteroceptionCamille05No ratings yet
- GUI-23-8394 Advanced Prostate Cancer AlgorithmDocument2 pagesGUI-23-8394 Advanced Prostate Cancer AlgorithmCamille05No ratings yet
- Delayed or Missed Diagnosis of Cervical Instability After Traumatic Injury - Usefulness of Dynamic Flexion and Extension RadiographsDocument4 pagesDelayed or Missed Diagnosis of Cervical Instability After Traumatic Injury - Usefulness of Dynamic Flexion and Extension RadiographsCamille05No ratings yet
- Tips For Triage NursesDocument4 pagesTips For Triage NursesCamille05No ratings yet
- Medicinal MushroomsDocument4 pagesMedicinal MushroomsCamille05No ratings yet
- Zinc and RhinovirusDocument9 pagesZinc and RhinovirusCamille05No ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument2 pagesBibliographyCamille05No ratings yet
- ACDIS White Paper - How To Review A Medical RecordDocument19 pagesACDIS White Paper - How To Review A Medical RecordCamille05100% (1)
- OCA Circular No. 51-2021Document2 pagesOCA Circular No. 51-2021MaricrisNo ratings yet
- EnemaDocument48 pagesEnemaPrajna TiwariNo ratings yet
- Case Report Glenohumeral Dysplasia, A Complication of Obstetrics Brachial Plexus PalsyDocument5 pagesCase Report Glenohumeral Dysplasia, A Complication of Obstetrics Brachial Plexus PalsyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Language of Teeth DCDocument6 pagesLanguage of Teeth DCapi-273181309No ratings yet
- Ram Kumar CBC-ReportDocument1 pageRam Kumar CBC-ReportRahul palNo ratings yet
- Burns DressingDocument4 pagesBurns DressingBalaMuruganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Neuroimmune Aspects of Sleep and Wakefulness: August 2016Document20 pagesChapter 3 Neuroimmune Aspects of Sleep and Wakefulness: August 2016Ganjar AdityoNo ratings yet
- Therapy of Bedridden PatientsDocument7 pagesTherapy of Bedridden PatientsKapil LakhwaraNo ratings yet
- Complications of Total Hip ReplacementDocument22 pagesComplications of Total Hip ReplacementNitya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDocument4 pagesDisorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDylan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Part 5: Neonatal ResuscitationDocument30 pagesPart 5: Neonatal ResuscitationMarcela ZerilloNo ratings yet
- How To Use Acupressure Therapy For Prevention and Treatment of DiabetesDocument7 pagesHow To Use Acupressure Therapy For Prevention and Treatment of Diabetesdprabhakar100% (1)
- Haematology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Document122 pagesHaematology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Mohammed RisqNo ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Bacterial Dna Synthesis: Dr. Ndayisaba CorneilleDocument32 pagesInhibitors of Bacterial Dna Synthesis: Dr. Ndayisaba CorneilleNdayisaba CorneilleNo ratings yet
- Patient Monitoring SystemDocument22 pagesPatient Monitoring SystemK.R.Raguram81% (26)
- Stages of Cancer, Differentiation and Staging of CancerDocument2 pagesStages of Cancer, Differentiation and Staging of CancerdyahNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids 6th EditionDocument57 pagesUrinalysis and Body Fluids 6th Editionsteve.moore218100% (44)
- Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022Document82 pagesGlobal Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022Leinad BarrackNo ratings yet
- Pendidikan: Ultan DR SDocument9 pagesPendidikan: Ultan DR SNur Athirah Aliah Ali OmarNo ratings yet
- 11 Physical Education Chapter 12Document9 pages11 Physical Education Chapter 12Pankaj BroNo ratings yet
- Conduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDocument2 pagesConduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- An Harmonic Smile Resulted From The Use of Ceramic Prosthesis With Zirconia Structure A Case ReportDocument3 pagesAn Harmonic Smile Resulted From The Use of Ceramic Prosthesis With Zirconia Structure A Case ReportAlexandru Codrin-IonutNo ratings yet
- Novel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudyDocument9 pagesNovel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudymarcelodentNo ratings yet
- Regulations - Addressing Complaints - Student1Document13 pagesRegulations - Addressing Complaints - Student1danushaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: 2. Literuture ReviewDocument14 pagesChapter Two: 2. Literuture ReviewAhmedNo ratings yet
- Deaf CommunityDocument11 pagesDeaf Communityapi-272869175No ratings yet
- Interpretacinclnicaypsicodinmicadelmmpi 2 140418094856 Phpapp01Document40 pagesInterpretacinclnicaypsicodinmicadelmmpi 2 140418094856 Phpapp01Consuelo Garcia0% (1)
- 2 UrinarySystemDocument83 pages2 UrinarySystemLemuel Lagasca Razalan IVNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance Situation in Dhaka BangladeshDocument8 pagesAntibiotic Resistance Situation in Dhaka BangladeshShaheen AkhterNo ratings yet