Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Recognizing Expenses When Incurred Rather Than When Paid
Recognizing Expenses When Incurred Rather Than When Paid
Uploaded by
Nath BongalonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Recognizing Expenses When Incurred Rather Than When Paid
Recognizing Expenses When Incurred Rather Than When Paid
Uploaded by
Nath BongalonCopyright:
Available Formats
Time Period Assumption - Requires that companies recognize revenue in the accounting period in
which the performance obligation is satisfied.
- Accountants divide the economic life of a business into artificial time
period Expense Recognition Principle
Interim Periods - Dictates that efforts (expenses) should be matched with results
(revenues)
- Monthly and Quarterly time periods
Fiscal Year e v
R
i tin
reg
n
u
aco
rf o
ep
th
c o
E icltT feo
uP
zv
m
n
ero
p
g
siartcm
R co
u
en
u
b
rc d
ceistf o
an
rm
e aco
R
in nv
rd
ac ep
r n
P
cetl h
h
w
in
escabd
it
atned
eu
lig
b
n
g
g ew
R
acrin o
td
m
u
A
r ed
ltip
gd
ith
n
p
x
E
ivp
n
to
s.
o n
tigles(G
n
u AP
s eR
en
p
x
E
atch sin
m
u
n
rev
eralys
).
n to
h
rtsw
efo
n ito
g
co
pv
racm
w
x
ep
en
g
th
rc erio
P
u eth
ak
m
n
thl
sy
o
d
- Time period that is 1 YEAR in length ( first day of the month until 12
months later which is last day of the month)
Calendar Year
- January 1 to December 31
ACCRUAL – VERSUS CASH – BASIS ACCOUNTING
Accrual-Basis Accounting
- Companies record transactions that change a company’s financial
statements in the periods in which the events occur.
- Companies recognize revenues when they perform services rather than
when they receive cash payment
- Recognizing expenses when incurred rather than when paid
Cash-Basis Accounting
- Companies record revenue when they receive cash
- Record expense when they pay out cash
REVENUE AND EXPENSE RECOGNITION PRINCIPLE
Revenue Recognition Principle
ADJUSTING ENTRIES
Adjusting Entries are classified either as deferrals or accruals.
ADJUSTING
ENTRIES
Deferrals Accruals
Accrued
Prepaid Revenue Accrued
Unearned Expenses
Expense revenues for
Revenue expenses
expenses paid services
cash received incurred but
in cash before performed but
before services not yet paid
they are used or not yet received
are performed in cash or
consumed in cash or
recorded recorded
You might also like
- Renault Wiring DiagramDocument4 pagesRenault Wiring Diagramkamaleon dorado100% (1)
- Social Realism and Representation of The Working Class in Contemporary British CinemaDocument85 pagesSocial Realism and Representation of The Working Class in Contemporary British Cinemastevea18922100% (2)
- Law On Sales ReviewerDocument1 pageLaw On Sales ReviewerNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument47 pagesInventoriesMarjorie NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Poster Summer Program 2022Document1 pagePoster Summer Program 2022kenedysilvabjNo ratings yet
- Railway CatalogDocument20 pagesRailway CatalogCounter RoverNo ratings yet
- SAS TechnicalDocument19 pagesSAS TechnicalAnfal BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- Det-Tronics Flame DetectionDocument2 pagesDet-Tronics Flame DetectionGabriel MendezNo ratings yet
- Space ProgrammingDocument1 pageSpace ProgrammingCherilyn SalvañaNo ratings yet
- Materi Uas - Final - Suham C Aks18Document45 pagesMateri Uas - Final - Suham C Aks18suhamcahyonoNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual Transporter 2016 10-29Document109 pagesWorkshop Manual Transporter 2016 10-29samueleNo ratings yet
- Student FlyerDocument1 pageStudent FlyerKrishna HaraleNo ratings yet
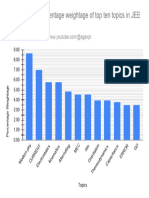
- Comparison of Percentage Weightage of Top Ten Topics in JEE MainDocument1 pageComparison of Percentage Weightage of Top Ten Topics in JEE Mainrineeth22745No ratings yet
- Gspaper 2 Book 5Document412 pagesGspaper 2 Book 5minatoackerman69No ratings yet
- New Karting Generation: A Z (E) : S P A C (K V), G C (T K V) N D V (Z P)Document1 pageNew Karting Generation: A Z (E) : S P A C (K V), G C (T K V) N D V (Z P)api-25888683No ratings yet
- National Standards For Music Education LKDocument1 pageNational Standards For Music Education LKMary Maxwell100% (1)
- STRAP Software - Client Projects - Emirates Stadium - Atir EngineeringDocument6 pagesSTRAP Software - Client Projects - Emirates Stadium - Atir EngineeringAreaya mahetemNo ratings yet
- TPM & MaintenanceDocument17 pagesTPM & MaintenanceGopalakrishnan100% (5)
- Program Bus PitDocument1 pageProgram Bus PitTudor AlinNo ratings yet
- Bunn VPR Parts ManualDocument26 pagesBunn VPR Parts Manualsatx840No ratings yet
- Range Flyer Hiperbaric 2Document6 pagesRange Flyer Hiperbaric 2ab.belfakirNo ratings yet
- Poultry Production Pig Production Climate Control AirMaster Co. Big Dutchman enDocument12 pagesPoultry Production Pig Production Climate Control AirMaster Co. Big Dutchman encrudu gabrielNo ratings yet
- P-Release and PPAP To Be Secured According IB Deadlines For A Predictable LaunchDocument5 pagesP-Release and PPAP To Be Secured According IB Deadlines For A Predictable LaunchPANDIAN PERIASAMYNo ratings yet
- Propert y Rel Ease: Property I Nformati OnDocument1 pagePropert y Rel Ease: Property I Nformati OnLuckyE.SantosoNo ratings yet
- SW USB Pro Series - Setup Guide: Extron Cable Cubby 100Document4 pagesSW USB Pro Series - Setup Guide: Extron Cable Cubby 100Iqbal TelkomNo ratings yet
- Nature of Carbon FootprintDocument1 pageNature of Carbon FootprintnyqinokyNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual Transporter 2016 22-29Document91 pagesWorkshop Manual Transporter 2016 22-29samueleNo ratings yet
- 00028112020-Nr 300 6-Speed Automatic Transmission 09D PDFDocument56 pages00028112020-Nr 300 6-Speed Automatic Transmission 09D PDFOleksiy OsiychukNo ratings yet
- C1 0,02uf 2000V C2 0,02uf 2000V: Spark GapDocument2 pagesC1 0,02uf 2000V C2 0,02uf 2000V: Spark GapamanNo ratings yet
- Upsc - Ias (Eng) : EssayDocument53 pagesUpsc - Ias (Eng) : EssayCHAITANYA THUMMALANo ratings yet
- Secondary Annual Result 2024Document2 pagesSecondary Annual Result 2024loop000001No ratings yet
- Fuel Supply SystemDocument97 pagesFuel Supply Systemomid khalvandeNo ratings yet
- VW 3 Cylinder ManualDocument116 pagesVW 3 Cylinder ManualvictorjoseteixeiraNo ratings yet
- Csatbook 3Document289 pagesCsatbook 3Ravi PidatalaNo ratings yet
- D3E800051E4 MaintenanceDocument105 pagesD3E800051E4 MaintenanceOndřej PolákNo ratings yet
- Case Study EdFinancial Services Achieves NIST Compliance For Service AccountsDocument2 pagesCase Study EdFinancial Services Achieves NIST Compliance For Service AccountsRadu CostinNo ratings yet
- East Harlem School: Glück+ (2008) 150 Students (Elementary) New York, NYDocument3 pagesEast Harlem School: Glück+ (2008) 150 Students (Elementary) New York, NYJinyong ParkNo ratings yet
- Palmer House Function Space BrochureDocument13 pagesPalmer House Function Space BrochurewrwyhiehheiqbnittpNo ratings yet
- Csatbook 2Document147 pagesCsatbook 2Ummati KhatoonNo ratings yet
- Study Stone Durability 2019Document4 pagesStudy Stone Durability 2019mz zhenNo ratings yet
- Route 292 6 22 03 MAPDocument1 pageRoute 292 6 22 03 MAPJason BentleyNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument3 pagesMatrixfarhanyazdaniNo ratings yet
- Matlab Sample CodesDocument9 pagesMatlab Sample Codes202118bt961No ratings yet
- History of PLCDocument1 pageHistory of PLCErick Daniel Figueroa CamachoNo ratings yet
- Semana 8 - Lectura - Caso Qué Necesito para CambiarDocument3 pagesSemana 8 - Lectura - Caso Qué Necesito para CambiarLEO chavez MONSALVENo ratings yet
- Mixing in An Internal Mixer Calculations-001Document1 pageMixing in An Internal Mixer Calculations-001Baba JuniorNo ratings yet
- National Core Arts Standards LKDocument4 pagesNational Core Arts Standards LKMary MaxwellNo ratings yet
- UnnamedDocument1 pageUnnamederic1388No ratings yet
- Plate CalcsDocument1 pagePlate CalcsKrish AãrkãyNo ratings yet
- Class 6 (A)Document2 pagesClass 6 (A)DB BhandariNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ADocument2 pagesClass 6 ADB BhandariNo ratings yet
- Scope Sequence of Architectural ServicesDocument1 pageScope Sequence of Architectural Servicesezhil2arasanNo ratings yet
- Cat Dcs SisDocument2 pagesCat Dcs SisAbule MogesNo ratings yet
- SSP VW 3 2 and 3 6 Liter FSI Engine 823603Document75 pagesSSP VW 3 2 and 3 6 Liter FSI Engine 823603Вадим ПушкарскийNo ratings yet
- DATECORRIGENDUM4Document1 pageDATECORRIGENDUM4gaurangpatelNo ratings yet
- T NV Iro NM en Ed Uc Ati On: Shree Amar Kalyan Secondary School, Maijogmai, IlamDocument4 pagesT NV Iro NM en Ed Uc Ati On: Shree Amar Kalyan Secondary School, Maijogmai, IlamDB BhandariNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument1 pageIntroSaniya SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Systair Cirec: Notice TechniqueDocument25 pagesSystair Cirec: Notice TechniqueNabil HOUHOUNo ratings yet
- 071 CLU3 Rev-5.0Document17 pages071 CLU3 Rev-5.0Piotr StankiewiczNo ratings yet
- Ewd 16Document20 pagesEwd 16Antonio GomezNo ratings yet
- RCoA - NAP7 - BookDocument567 pagesRCoA - NAP7 - Bookeric22hkNo ratings yet
- Relevant Costing For Non Routine Decision Making - Managment ScienceDocument1 pageRelevant Costing For Non Routine Decision Making - Managment ScienceNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On The Effects of Bullying To Teenagers With Broken FamilyDocument5 pagesA Case Study On The Effects of Bullying To Teenagers With Broken FamilyNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- TiuaonsgtdnDocument2 pagesTiuaonsgtdnNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Intangible AssetDocument2 pagesIntangible AssetNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- The LithosphereDocument8 pagesThe LithosphereNath Bongalon100% (1)
- Sample ProblemDocument5 pagesSample ProblemNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesDalton's Atomic TheoryNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- (Ex. Liquors) (Ex. Grape Wine) (Ex. Beer) (Ex. Chewing Tobacco)Document1 page(Ex. Liquors) (Ex. Grape Wine) (Ex. Beer) (Ex. Chewing Tobacco)Nath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bank ReconciliationDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Bank ReconciliationNath Bongalon100% (1)
- 1st PPT GEO3Document17 pages1st PPT GEO3Nath BongalonNo ratings yet
- 15 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable Financing 2Document10 pages15 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable Financing 2Nath BongalonNo ratings yet
- George Polya: December 1887 - September 1985Document1 pageGeorge Polya: December 1887 - September 1985Nath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Classification of TrianglesDocument4 pagesClassification of TrianglesNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- 08 Acctg Ed 1 - Bank Reconciliation PDFDocument3 pages08 Acctg Ed 1 - Bank Reconciliation PDFNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Triangle Classification: Sides AnglesDocument2 pagesTriangle Classification: Sides AnglesNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Learning or Not: Active and Passive ClassesDocument6 pagesLearning or Not: Active and Passive ClassesNath Bongalon60% (5)
- 12 Acctg Ed 1 - Notes Receivable PDFDocument17 pages12 Acctg Ed 1 - Notes Receivable PDFNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- 13 Acctg Ed 1 - Loan ReceivableDocument17 pages13 Acctg Ed 1 - Loan ReceivableNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- 03 Acctg Ed 1 - Conceptual Framework 2 PDFDocument5 pages03 Acctg Ed 1 - Conceptual Framework 2 PDFNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- 14 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable FinancingDocument19 pages14 Acctg Ed 1 - Receivable FinancingNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- 11 Acctg Ed 1 - Estimation of Doubtful Accounts PDFDocument12 pages11 Acctg Ed 1 - Estimation of Doubtful Accounts PDFNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Charles DarwinDocument4 pagesCharles DarwinNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory - Day 04Document2 pagesAuditing Theory - Day 04Nath BongalonNo ratings yet
- RECEIVABLESDocument12 pagesRECEIVABLESNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Taxation New Topics Cpa Borad Exam As of October 2017Document2 pagesTaxation New Topics Cpa Borad Exam As of October 2017Nath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Whodoyousayiam? Who Said It?: Chapter/Ve RseDocument3 pagesWhodoyousayiam? Who Said It?: Chapter/Ve RseNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Accounting FOR Partnership SDocument3 pagesAccounting FOR Partnership SNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- CostAccountingModule MidtermPeriod2022Document29 pagesCostAccountingModule MidtermPeriod2022Shawn PeridoNo ratings yet
- Example of JD & JSDocument3 pagesExample of JD & JSOmar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Essay On Globalization OnDocument2 pagesEssay On Globalization OnIcsofit OutfitNo ratings yet
- MDCI Calc Practical E-Notes-2Document18 pagesMDCI Calc Practical E-Notes-2AnuragNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Business Foundations A Changing World 11th Edition Ferrell Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Business Foundations A Changing World 11th Edition Ferrell Test Bank PDFloganwatersabdqsfgekj100% (19)
- GROUP II PPT (2 5pm) Chapter 7, Food IndustryDocument29 pagesGROUP II PPT (2 5pm) Chapter 7, Food IndustryMaryjo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Farhan Autocad Civil EngineerDocument9 pagesFarhan Autocad Civil EngineerKhan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- McDonald's SWOT Analysis (2024 Updated)Document19 pagesMcDonald's SWOT Analysis (2024 Updated)Testing KDNo ratings yet
- Mai Shemeis CV 2023Document4 pagesMai Shemeis CV 2023khalid EletrebyNo ratings yet
- Fas 161 PDFDocument2 pagesFas 161 PDFTonyNo ratings yet
- SLT Ar 2012Document204 pagesSLT Ar 2012sriramrangaNo ratings yet
- NOC From Builder - Fresh Flat Purchase 18-12-2018Document3 pagesNOC From Builder - Fresh Flat Purchase 18-12-2018yogeshpatil.sunriseNo ratings yet
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument65 pagesRoot Cause Analysissyed ali mesum rizviNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module - Lesson 5Document5 pagesNSTP Module - Lesson 5Maira Garcia C.No ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi MaraDocument5 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mararaihana abdulkarimNo ratings yet
- 03 Quiz 1 AubDocument3 pages03 Quiz 1 Aubken dahunanNo ratings yet
- PGPF 04 019 Kancharapu Akhil Kumar CF AssignmnetDocument59 pagesPGPF 04 019 Kancharapu Akhil Kumar CF Assignmnetak kancharapuNo ratings yet
- Marao Inopacan Leyte CY 2020-2022Document56 pagesMarao Inopacan Leyte CY 2020-2022Ken BocsNo ratings yet
- 2021W ADMS 4537 Course OutlineDocument4 pages2021W ADMS 4537 Course OutlineAtputhanNo ratings yet
- Suraj Project DraftDocument56 pagesSuraj Project DraftA. DivyaNo ratings yet
- Distributor AgreementDocument11 pagesDistributor AgreementDonishaNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 1 - Special Journals & Subsidiary Ledgers, Problem #5Document9 pagesLearning Task 1 - Special Journals & Subsidiary Ledgers, Problem #5Feiya LiuNo ratings yet
- Noter Onayli Belgeler 12-09-2022Document6 pagesNoter Onayli Belgeler 12-09-2022MetinNo ratings yet
- Monthly Order Mei 2021Document20 pagesMonthly Order Mei 2021Otong KruwelNo ratings yet
- Cities: Activity BookDocument18 pagesCities: Activity BookAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Andargachew BeyeneDocument87 pagesAndargachew Beyenekibrom kidaneNo ratings yet
- Zanini, Curtis & Company - August 2022Document27 pagesZanini, Curtis & Company - August 2022fredNo ratings yet
- Commissioner of Internal Revenue v. Unioil Corp., G.R. No. 204405, (August 4, 2021)Document23 pagesCommissioner of Internal Revenue v. Unioil Corp., G.R. No. 204405, (August 4, 2021)Kriszan ManiponNo ratings yet