Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsCPM Steps PDF
CPM Steps PDF
Uploaded by
Patrick TaclibonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 22004pujadasNo ratings yet
- 5 CPM - 5 Steps To RememberDocument1 page5 CPM - 5 Steps To RememberChelsea D PyperNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Postfix in CDocument7 pagesEvaluating Postfix in CJunald BayogNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument18 pagesExampleSaif AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- Max Arithmetic Operators: List of Max/Msp Objects Used in This ChapterDocument1 pageMax Arithmetic Operators: List of Max/Msp Objects Used in This Chapterjackim123No ratings yet
- Stacks TSDocument34 pagesStacks TSGamer MusicNo ratings yet
- The List, Stack, and Queue Adts Abstract Data Type (Adt)Document17 pagesThe List, Stack, and Queue Adts Abstract Data Type (Adt)Jennelyn SusonNo ratings yet
- 2-D SIMD Algorithms in The Perfect Shue Networks: N P N P L N P P L I PEDocument16 pages2-D SIMD Algorithms in The Perfect Shue Networks: N P N P L N P P L I PEAnonymous RrGVQjNo ratings yet
- Short Paths, Big Improvements (Edmonds Karp Algorithm)Document9 pagesShort Paths, Big Improvements (Edmonds Karp Algorithm)Maverik_89No ratings yet
- Unit 1: Asymptotic NotationsDocument24 pagesUnit 1: Asymptotic NotationsPraveenNo ratings yet
- Ece 590 - Digital System Design Using Hardware Description Languages Spring 2006Document17 pagesEce 590 - Digital System Design Using Hardware Description Languages Spring 2006Omar Valenzuela LopezNo ratings yet
- Name: Ghulam Ali Roll Number: BSEM-F18-130: Applications in RoutingDocument3 pagesName: Ghulam Ali Roll Number: BSEM-F18-130: Applications in RoutingTHE Out.siderNo ratings yet
- Stack Applications June 2012Document11 pagesStack Applications June 2012Marl MwegiNo ratings yet
- CCT203 Study Guide - Chapter4Document18 pagesCCT203 Study Guide - Chapter4jollycharmNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design QuestionsDocument6 pagesCompiler Design QuestionsNaman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Critical PathDocument10 pagesHow To Calculate Critical PathSriNo ratings yet
- Level 1 IplanningandschedulingDocument26 pagesLevel 1 IplanningandschedulingvarunsingriNo ratings yet
- Bellman FordDocument8 pagesBellman FordBebeNo ratings yet
- Exhaustive Search and Backtracking: Example 1: Binary StringsDocument16 pagesExhaustive Search and Backtracking: Example 1: Binary Stringslaurentiu.melinteNo ratings yet
- Calculate Critical Path Float ES EF LS LFDocument9 pagesCalculate Critical Path Float ES EF LS LFnazishtila100% (1)
- Assembly Language Lecture6Document10 pagesAssembly Language Lecture6bmas19692No ratings yet
- Introduction To Data StructuresDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Data StructureskiranNo ratings yet
- Programming in Lua - Control Flow: Fabio MascarenhasDocument11 pagesProgramming in Lua - Control Flow: Fabio MascarenhasPamela GarciaNo ratings yet
- PetljeDocument4 pagesPetljeRade PralicaNo ratings yet
- Ansys Commands and AcronymsDocument3 pagesAnsys Commands and AcronymsRupali PatilNo ratings yet
- Weatherwax Pacheco ProblemsDocument12 pagesWeatherwax Pacheco ProblemsnarendraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - DS - ClassDocument77 pagesUnit 2 - DS - ClassRaghav ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pspice TransientDocument7 pagesPspice TransientSatya YadavNo ratings yet
- Stack Applications: CS501 Irena PevacDocument23 pagesStack Applications: CS501 Irena PevachhqhamzaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Laboratory: Subject: Digital System ProcessingDocument18 pagesMatrix Laboratory: Subject: Digital System ProcessingLove DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document18 pagesSession 3unniNo ratings yet
- 1.about The Ford Fulkerson MethodDocument6 pages1.about The Ford Fulkerson MethodBao MaiNo ratings yet
- DS UnitIIDocument57 pagesDS UnitIIRexline S JNo ratings yet
- Edmonds-Karp Algorithm Analysis: January 20, 2017Document2 pagesEdmonds-Karp Algorithm Analysis: January 20, 2017Victor PuriceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document5 pagesLecture 05Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- HSPICE Quick ManualDocument4 pagesHSPICE Quick ManualSurila GuglaniNo ratings yet
- Wa0009.Document27 pagesWa0009.Seetha LaxmiNo ratings yet
- Ict351 3 Reasoning About ProgramsDocument27 pagesIct351 3 Reasoning About ProgramstheoskatokaNo ratings yet
- InfixDocument17 pagesInfixAARAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Simple FFTDocument19 pagesSimple FFTSudeshna KunduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document48 pagesLecture 6Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- Domanais Arkin Zyke ArrayDocument17 pagesDomanais Arkin Zyke ArrayYkee PogieNo ratings yet
- Wall SolutionDocument2 pagesWall SolutionhNo ratings yet
- Atari Basic Reference Guide (c061948 Rev.b) 1983Document12 pagesAtari Basic Reference Guide (c061948 Rev.b) 1983her234tzu100% (1)
- CN Unit-Iii Part 2Document25 pagesCN Unit-Iii Part 2chinnupyariNo ratings yet
- e-PG Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Applications of Stacks - I Module No: CS/DS/9 Quadrant 1-E-TextDocument11 pagese-PG Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Applications of Stacks - I Module No: CS/DS/9 Quadrant 1-E-TextUtkarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Binary AdderDocument3 pagesBinary AdderDhaivat PandyaNo ratings yet
- AI TheoryDocument4 pagesAI TheorySumedh SumedhNo ratings yet
- Transfer FunctionsDocument18 pagesTransfer FunctionsSolayao, Jan Marvin J.No ratings yet
- Expression EvaluationDocument5 pagesExpression Evaluationtank prakashNo ratings yet
- Moving LoadDocument6 pagesMoving LoadSyarief AbdurrachmanNo ratings yet
- DS Mod 2Document107 pagesDS Mod 2PushpeshNo ratings yet
- Applications of Bfs Algorithm: Backward Skip 10splay Videoforward Skip 10SDocument4 pagesApplications of Bfs Algorithm: Backward Skip 10splay Videoforward Skip 10SNitin KashyapNo ratings yet
- Fletcher Reeves HandoutDocument6 pagesFletcher Reeves Handoutloweschevy12No ratings yet
- L13 Parallel AddersDocument11 pagesL13 Parallel AddersVishnu MaskarNo ratings yet
- Pert CPMDocument7 pagesPert CPMChandrikaSelvamaniNo ratings yet
- Graph 2Document4 pagesGraph 2Haroon AshrafNo ratings yet
- MEDC DB3 Data SheetDocument2 pagesMEDC DB3 Data SheetHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From 21. LED Bulkhead Light - AdditionalDocument2 pagesExtracted Pages From 21. LED Bulkhead Light - AdditionalHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal Dr. GhodbaneDocument6 pagesProject Proposal Dr. GhodbaneHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- 2-Garnada Mall Shops MEP Work.Document1 page2-Garnada Mall Shops MEP Work.Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From 16. LED Mirror LightDocument2 pagesExtracted Pages From 16. LED Mirror LightHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- 31 SDMS 07rev01Document25 pages31 SDMS 07rev01Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Unique Outputs of Each Process Are Show in A Different ColourDocument20 pagesUnique Outputs of Each Process Are Show in A Different ColourHazaratali Dakhani100% (3)
- Ai 22 PK 355Document17 pagesAi 22 PK 355Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- PlanningWeddingonaBudget bklt0419Document8 pagesPlanningWeddingonaBudget bklt0419Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Jifa30 183Document5 pagesJifa30 183Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Pmbok Guide 6: Ed. Process Flow ChartDocument1 pagePmbok Guide 6: Ed. Process Flow ChartHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Commercial Fish Production: Model Project Report ForDocument6 pagesCommercial Fish Production: Model Project Report ForHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
CPM Steps PDF
CPM Steps PDF
Uploaded by
Patrick Taclibon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageOriginal Title
CPM steps.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCPM Steps PDF
CPM Steps PDF
Uploaded by
Patrick TaclibonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
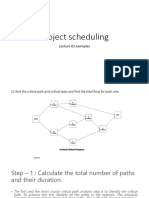
CRITICAL PATH METHOD STEP BY STEP
Determine path lengths:
-------------------------------
Identify all paths in the network.
Find length of all paths (total of all durations on that path) - there are 4 paths.
Longest path is CP (critical path).
Note: durations are stated on the top edge of each activity node.
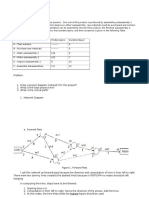
Determine floats:
----------------------
Float of all activities on CP = 0
Enter 0 on the bottom edge of each activity on the CP.
Go to next lower length path, float of activities on this non-CP = CP length - nonCP length
Continue this process until all paths are done, entering float values.
Do not overwrite any values when the same activity appears again in another path
calculation.
Do the forward pass:
---------------------------
Go to critical path.
Enter 1 into the top left corner of the starting activity, do the same for any other parallel
starting activities. This is ES (early start).
Go in forward direction.
Enter ES+duration-1 into the top right corner. This is EF (early finish).
Add 1 to this EF value and enter it into the ES of the successor activity.
Do this for each activity in the path, in forward direction from start to finish.
Do this until all paths are done, in decreasing order of path lengths.
Do not overwrite any values once written.
Do the backward pass:
------------------------------
For each activity in CP, starting with the last activity in sequence, copy EF to LF (bottom right
corner) and ES to EF (bottom left corner). Do this for each activity in the path, in backward
direction from finish to start.
Copy the EF of the last CP activity into the EF of last activities of all non-CPs.
Pick the next lower length path, go to last activity, enter LS (=LF-duration+1 OR ES+float).
Traverse backwards until values are entered for all LF & LS for all activities on this path. Note
that LF of predecessor = LS of successor -1.
Do this until all paths are done, in decreasing order of path lengths.
Do not overwrite any values once written.
You might also like
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 22004pujadasNo ratings yet
- 5 CPM - 5 Steps To RememberDocument1 page5 CPM - 5 Steps To RememberChelsea D PyperNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Postfix in CDocument7 pagesEvaluating Postfix in CJunald BayogNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument18 pagesExampleSaif AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- Max Arithmetic Operators: List of Max/Msp Objects Used in This ChapterDocument1 pageMax Arithmetic Operators: List of Max/Msp Objects Used in This Chapterjackim123No ratings yet
- Stacks TSDocument34 pagesStacks TSGamer MusicNo ratings yet
- The List, Stack, and Queue Adts Abstract Data Type (Adt)Document17 pagesThe List, Stack, and Queue Adts Abstract Data Type (Adt)Jennelyn SusonNo ratings yet
- 2-D SIMD Algorithms in The Perfect Shue Networks: N P N P L N P P L I PEDocument16 pages2-D SIMD Algorithms in The Perfect Shue Networks: N P N P L N P P L I PEAnonymous RrGVQjNo ratings yet
- Short Paths, Big Improvements (Edmonds Karp Algorithm)Document9 pagesShort Paths, Big Improvements (Edmonds Karp Algorithm)Maverik_89No ratings yet
- Unit 1: Asymptotic NotationsDocument24 pagesUnit 1: Asymptotic NotationsPraveenNo ratings yet
- Ece 590 - Digital System Design Using Hardware Description Languages Spring 2006Document17 pagesEce 590 - Digital System Design Using Hardware Description Languages Spring 2006Omar Valenzuela LopezNo ratings yet
- Name: Ghulam Ali Roll Number: BSEM-F18-130: Applications in RoutingDocument3 pagesName: Ghulam Ali Roll Number: BSEM-F18-130: Applications in RoutingTHE Out.siderNo ratings yet
- Stack Applications June 2012Document11 pagesStack Applications June 2012Marl MwegiNo ratings yet
- CCT203 Study Guide - Chapter4Document18 pagesCCT203 Study Guide - Chapter4jollycharmNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design QuestionsDocument6 pagesCompiler Design QuestionsNaman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Critical PathDocument10 pagesHow To Calculate Critical PathSriNo ratings yet
- Level 1 IplanningandschedulingDocument26 pagesLevel 1 IplanningandschedulingvarunsingriNo ratings yet
- Bellman FordDocument8 pagesBellman FordBebeNo ratings yet
- Exhaustive Search and Backtracking: Example 1: Binary StringsDocument16 pagesExhaustive Search and Backtracking: Example 1: Binary Stringslaurentiu.melinteNo ratings yet
- Calculate Critical Path Float ES EF LS LFDocument9 pagesCalculate Critical Path Float ES EF LS LFnazishtila100% (1)
- Assembly Language Lecture6Document10 pagesAssembly Language Lecture6bmas19692No ratings yet
- Introduction To Data StructuresDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Data StructureskiranNo ratings yet
- Programming in Lua - Control Flow: Fabio MascarenhasDocument11 pagesProgramming in Lua - Control Flow: Fabio MascarenhasPamela GarciaNo ratings yet
- PetljeDocument4 pagesPetljeRade PralicaNo ratings yet
- Ansys Commands and AcronymsDocument3 pagesAnsys Commands and AcronymsRupali PatilNo ratings yet
- Weatherwax Pacheco ProblemsDocument12 pagesWeatherwax Pacheco ProblemsnarendraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - DS - ClassDocument77 pagesUnit 2 - DS - ClassRaghav ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pspice TransientDocument7 pagesPspice TransientSatya YadavNo ratings yet
- Stack Applications: CS501 Irena PevacDocument23 pagesStack Applications: CS501 Irena PevachhqhamzaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Laboratory: Subject: Digital System ProcessingDocument18 pagesMatrix Laboratory: Subject: Digital System ProcessingLove DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document18 pagesSession 3unniNo ratings yet
- 1.about The Ford Fulkerson MethodDocument6 pages1.about The Ford Fulkerson MethodBao MaiNo ratings yet
- DS UnitIIDocument57 pagesDS UnitIIRexline S JNo ratings yet
- Edmonds-Karp Algorithm Analysis: January 20, 2017Document2 pagesEdmonds-Karp Algorithm Analysis: January 20, 2017Victor PuriceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document5 pagesLecture 05Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- HSPICE Quick ManualDocument4 pagesHSPICE Quick ManualSurila GuglaniNo ratings yet
- Wa0009.Document27 pagesWa0009.Seetha LaxmiNo ratings yet
- Ict351 3 Reasoning About ProgramsDocument27 pagesIct351 3 Reasoning About ProgramstheoskatokaNo ratings yet
- InfixDocument17 pagesInfixAARAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Simple FFTDocument19 pagesSimple FFTSudeshna KunduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document48 pagesLecture 6Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- Domanais Arkin Zyke ArrayDocument17 pagesDomanais Arkin Zyke ArrayYkee PogieNo ratings yet
- Wall SolutionDocument2 pagesWall SolutionhNo ratings yet
- Atari Basic Reference Guide (c061948 Rev.b) 1983Document12 pagesAtari Basic Reference Guide (c061948 Rev.b) 1983her234tzu100% (1)
- CN Unit-Iii Part 2Document25 pagesCN Unit-Iii Part 2chinnupyariNo ratings yet
- e-PG Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Applications of Stacks - I Module No: CS/DS/9 Quadrant 1-E-TextDocument11 pagese-PG Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Applications of Stacks - I Module No: CS/DS/9 Quadrant 1-E-TextUtkarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Binary AdderDocument3 pagesBinary AdderDhaivat PandyaNo ratings yet
- AI TheoryDocument4 pagesAI TheorySumedh SumedhNo ratings yet
- Transfer FunctionsDocument18 pagesTransfer FunctionsSolayao, Jan Marvin J.No ratings yet
- Expression EvaluationDocument5 pagesExpression Evaluationtank prakashNo ratings yet
- Moving LoadDocument6 pagesMoving LoadSyarief AbdurrachmanNo ratings yet
- DS Mod 2Document107 pagesDS Mod 2PushpeshNo ratings yet
- Applications of Bfs Algorithm: Backward Skip 10splay Videoforward Skip 10SDocument4 pagesApplications of Bfs Algorithm: Backward Skip 10splay Videoforward Skip 10SNitin KashyapNo ratings yet
- Fletcher Reeves HandoutDocument6 pagesFletcher Reeves Handoutloweschevy12No ratings yet
- L13 Parallel AddersDocument11 pagesL13 Parallel AddersVishnu MaskarNo ratings yet
- Pert CPMDocument7 pagesPert CPMChandrikaSelvamaniNo ratings yet
- Graph 2Document4 pagesGraph 2Haroon AshrafNo ratings yet
- MEDC DB3 Data SheetDocument2 pagesMEDC DB3 Data SheetHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From 21. LED Bulkhead Light - AdditionalDocument2 pagesExtracted Pages From 21. LED Bulkhead Light - AdditionalHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal Dr. GhodbaneDocument6 pagesProject Proposal Dr. GhodbaneHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- 2-Garnada Mall Shops MEP Work.Document1 page2-Garnada Mall Shops MEP Work.Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From 16. LED Mirror LightDocument2 pagesExtracted Pages From 16. LED Mirror LightHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- 31 SDMS 07rev01Document25 pages31 SDMS 07rev01Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Unique Outputs of Each Process Are Show in A Different ColourDocument20 pagesUnique Outputs of Each Process Are Show in A Different ColourHazaratali Dakhani100% (3)
- Ai 22 PK 355Document17 pagesAi 22 PK 355Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- PlanningWeddingonaBudget bklt0419Document8 pagesPlanningWeddingonaBudget bklt0419Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Jifa30 183Document5 pagesJifa30 183Hazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Pmbok Guide 6: Ed. Process Flow ChartDocument1 pagePmbok Guide 6: Ed. Process Flow ChartHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet
- Commercial Fish Production: Model Project Report ForDocument6 pagesCommercial Fish Production: Model Project Report ForHazaratali DakhaniNo ratings yet