Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 viewsMist Eliminator Design - Scribd
Mist Eliminator Design - Scribd
Uploaded by
ratninp9368This document provides guidance on sizing vane mist eliminators based on factors like gas and liquid density. It outlines a procedure for calculating the maximum velocity and required face area using proprietary K-factors. It also estimates pressure drop through different vane styles, noting pocketed designs have higher drop but the overall range is typically 0.2 to 0.8 kPa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- PPE AssignmentDocument16 pagesPPE AssignmentlibbissujessyNo ratings yet
- 06 DPI Jun 17 ScribdDocument68 pages06 DPI Jun 17 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- Mist Eliminator DesignDocument2 pagesMist Eliminator DesignEng Alf75% (4)
- Vane Mist Eliminator DesignDocument2 pagesVane Mist Eliminator DesignEng Alf100% (1)
- Ductulator May 2010Document8 pagesDuctulator May 2010haroub_nasNo ratings yet
- Frank Loeffler - Pipe Tube Conveyor PDFDocument12 pagesFrank Loeffler - Pipe Tube Conveyor PDFIgor San Martín Peñaloza0% (1)
- Albers TUDelft Introduction, Heave CompensationDocument17 pagesAlbers TUDelft Introduction, Heave Compensationnvkurup100% (1)
- Uuuu PDFDocument15 pagesUuuu PDFMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Separator Design MethodologyDocument19 pagesSeparator Design Methodologyromdhan88100% (1)
- External Metal LouvresDocument28 pagesExternal Metal LouvresQuitzs QuitzsNo ratings yet
- General Design Procedures: Size Selection ProblemsDocument7 pagesGeneral Design Procedures: Size Selection ProblemsShamsi MursalliNo ratings yet
- S04 - Basic Parameters and Design of Cast in Situ Box GirderDocument71 pagesS04 - Basic Parameters and Design of Cast in Situ Box GirderSMR STPNo ratings yet
- CTBEST PVM 300 Process Design of Separation VesselsDocument22 pagesCTBEST PVM 300 Process Design of Separation Vesselsrzepedac100% (2)
- Wind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194Document13 pagesWind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194nakkipatty100% (2)
- CarlVanGeem Curviameter PaperDocument10 pagesCarlVanGeem Curviameter PaperVictor MedranoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Model Test With Ship Sea Trial PDFDocument8 pagesComparison of Model Test With Ship Sea Trial PDFSunil Kumar P GNo ratings yet
- ZFG AT Image Flyer Eng WebDocument6 pagesZFG AT Image Flyer Eng Webingenieria.apvialesNo ratings yet
- Reynolds AirfoilDocument24 pagesReynolds Airfoilcv cvNo ratings yet
- Wind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194Document13 pagesWind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194Joshua BerryNo ratings yet
- Final Acoustic Enclosure PresentationDocument48 pagesFinal Acoustic Enclosure PresentationsartajyadNo ratings yet
- Caster Crown PPT Ver 1.01Document32 pagesCaster Crown PPT Ver 1.01bill_porter_1953No ratings yet
- Limestone - Slurry OptimizationDocument5 pagesLimestone - Slurry OptimizationSharif M Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- BridgeGirdersRegionalSpecsAB MB SK TG 2013 04 EDocument23 pagesBridgeGirdersRegionalSpecsAB MB SK TG 2013 04 Esilvereyes18No ratings yet
- Estimation of Turbomachinery Losses Through Cascade TestingDocument54 pagesEstimation of Turbomachinery Losses Through Cascade Testingchandrasingh4564No ratings yet
- Duct & Vent EngineeringDocument70 pagesDuct & Vent Engineeringtop20202080% (5)
- AC Duct Design PDFDocument6 pagesAC Duct Design PDFkumar123rajuNo ratings yet
- Ductulator May 2010Document10 pagesDuctulator May 2010Arshavin Watashi Wa100% (1)
- ASME PTC19.3 TW-2010 Thermowell Design Standard: © Abb Month DD, YYYY - Slide 1Document23 pagesASME PTC19.3 TW-2010 Thermowell Design Standard: © Abb Month DD, YYYY - Slide 1John PaulNo ratings yet
- GB 3.1 Flow Converter 713 Manual 0704Document20 pagesGB 3.1 Flow Converter 713 Manual 0704CharbsNo ratings yet
- ArchiveDocument8 pagesArchiveMahmoud MegahedNo ratings yet
- AMCA 210 07 WT Introduction OP App 20131024 PDFDocument190 pagesAMCA 210 07 WT Introduction OP App 20131024 PDFManoel Camargo SampaioNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Sizing of Restriction Orifice For Single-Phase Fluids With PDFDocument8 pagesGuidelines For Sizing of Restriction Orifice For Single-Phase Fluids With PDFEPTCO LHDNo ratings yet
- CAVTDocument4 pagesCAVTRaj EaswarmoorthiNo ratings yet
- Detailing MembersDocument43 pagesDetailing Memberschithirai10No ratings yet
- VSB-VMB DBL008en PDFDocument4 pagesVSB-VMB DBL008en PDFhossein.ahmadi.85No ratings yet
- 2 DKSinghalDocument48 pages2 DKSinghalMostafizur Rahman100% (2)
- Storm Water Drainage System Revision)Document8 pagesStorm Water Drainage System Revision)hera4u2No ratings yet
- Atv DVWK M 127 e pt2 Appx5 9Document27 pagesAtv DVWK M 127 e pt2 Appx5 9otezgidenNo ratings yet
- Open Drain Separator SizingDocument23 pagesOpen Drain Separator SizingSuchart TarasapNo ratings yet
- 23.bladder AccumlatorDocument12 pages23.bladder AccumlatorM S GokulNo ratings yet
- Deep BeamDocument8 pagesDeep BeamShashikant Gaur0% (1)
- A Fresh Approach To Gas Lift, Alan Brodie PTCDocument15 pagesA Fresh Approach To Gas Lift, Alan Brodie PTCrps1977No ratings yet
- Problem 04 - Tower Sizing & Tray DesignDocument40 pagesProblem 04 - Tower Sizing & Tray DesignJorge Enciso AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Cement Bond Logging: Principles of Oil-Well CementingDocument32 pagesCement Bond Logging: Principles of Oil-Well CementingAPE GAS SECTION. B 2019No ratings yet
- Catálogo Compresores Baja Presion-AersenDocument32 pagesCatálogo Compresores Baja Presion-AersenJuan Camilo RestrepoNo ratings yet
- GHHDocument3 pagesGHHeldiego1790No ratings yet
- Bejan Gabriel G.P.Document10 pagesBejan Gabriel G.P.Gabriel BejanNo ratings yet
- Planing Hull Model Tests For CFD ValidationDocument10 pagesPlaning Hull Model Tests For CFD Validationfez960No ratings yet
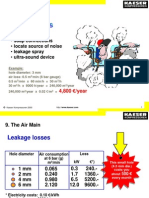
- Trace Leaks: 9. The Air MainDocument25 pagesTrace Leaks: 9. The Air Mainpaulo josé sá patachoNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionFrom EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesFrom EverandGas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesNo ratings yet
- How to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesFrom EverandHow to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsFrom EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechNo ratings yet
- Good, Bad and Ugly Process Burner FlamesDocument3 pagesGood, Bad and Ugly Process Burner Flamesratninp9368No ratings yet
- PDS - BearingCheck 894 and BearingCheck 824Document1 pagePDS - BearingCheck 894 and BearingCheck 824ratninp9368No ratings yet
- PTQ 2013 - Revamps - ScribdDocument68 pagesPTQ 2013 - Revamps - Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- Steel MinimillsDocument16 pagesSteel Minimillsratninp9368No ratings yet
- MNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFDocument51 pagesMNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFratninp9368No ratings yet
- Measurement Techniques Concerning Droplet Size Distribution of Electrosprayed WaterDocument3 pagesMeasurement Techniques Concerning Droplet Size Distribution of Electrosprayed Waterratninp9368No ratings yet
- The Weathering Magazine - Vietnam - ScribdDocument72 pagesThe Weathering Magazine - Vietnam - Scribdratninp9368100% (2)
- AERO QTR - 01-10 - ScribdDocument32 pagesAERO QTR - 01-10 - Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- MNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFDocument51 pagesMNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFratninp9368No ratings yet
- 05 DPI May 17 ScribdDocument47 pages05 DPI May 17 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- Effect of Fouling On Heat Exchanger - ScribdDocument40 pagesEffect of Fouling On Heat Exchanger - Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- 06 CT2 ScribdDocument80 pages06 CT2 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- 08 09 CT2 ScribdDocument116 pages08 09 CT2 Scribdratninp9368100% (1)
- 07 CT2 ScribdDocument76 pages07 CT2 Scribdratninp9368100% (1)
- 01 02 CT2 ScribdDocument68 pages01 02 CT2 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- 05 CT2 ScribdDocument68 pages05 CT2 Scribdratninp9368100% (1)
Mist Eliminator Design - Scribd
Mist Eliminator Design - Scribd
Uploaded by
ratninp93680 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views2 pagesThis document provides guidance on sizing vane mist eliminators based on factors like gas and liquid density. It outlines a procedure for calculating the maximum velocity and required face area using proprietary K-factors. It also estimates pressure drop through different vane styles, noting pocketed designs have higher drop but the overall range is typically 0.2 to 0.8 kPa.
Original Description:
na
Original Title
Mist Eliminator Design_Scribd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidance on sizing vane mist eliminators based on factors like gas and liquid density. It outlines a procedure for calculating the maximum velocity and required face area using proprietary K-factors. It also estimates pressure drop through different vane styles, noting pocketed designs have higher drop but the overall range is typically 0.2 to 0.8 kPa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views2 pagesMist Eliminator Design - Scribd
Mist Eliminator Design - Scribd
Uploaded by
ratninp9368This document provides guidance on sizing vane mist eliminators based on factors like gas and liquid density. It outlines a procedure for calculating the maximum velocity and required face area using proprietary K-factors. It also estimates pressure drop through different vane styles, noting pocketed designs have higher drop but the overall range is typically 0.2 to 0.8 kPa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Mist Eliminator Design
The design of vane mist eliminators depends on many factors, but a preliminary sizing
can be undertaken relatively easily using proprietary K-factors in the same way as for
wire mesh demisters.
Face Area
Although it should be treated withcaution and confirmed with supplierbefore actualuse,
the following procedure may be used:
Vvme= K·{ (L ± V ) / V}0,5
where:
Vvme = Max velocity in vanes, m/s
K = K-Factor, see below, m/s
L= Density of liquid, kg/m3
V= Density of vapour, kg/m3
and:
Avme (m2) = Q (m3/s) / Vvme (m/s)
Vane Style K-Factor
Vane mist eliminator (vertical gas flow) 0,175
Vane mist eliminator (horizontal gas flow) 0,200
Vane pack standard (horizontal gas flow) 0,225
Vane pack pocketed (horizontal
(horizontal gas flow) 0,250
Pressure Drop
The disadvantage of using the moreexpensive, pocketed designs is thatthepressure drop
is higher. Toestimate the pressure drop, the following method can be used:
P = C·(L ±V) . K2
where:
P = Pressure drop, Pa
C = Vane design factor:
Vane mist eliminator style, C = 10
Vane pack standard style, C = 15
Vane pack pocketed style, C = 20
Typically, the pressure drop will be in the range of 0,2 ± 0,8 kPa (approx. 20 to 80 mm
watergauge).
You might also like
- PPE AssignmentDocument16 pagesPPE AssignmentlibbissujessyNo ratings yet
- 06 DPI Jun 17 ScribdDocument68 pages06 DPI Jun 17 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- Mist Eliminator DesignDocument2 pagesMist Eliminator DesignEng Alf75% (4)
- Vane Mist Eliminator DesignDocument2 pagesVane Mist Eliminator DesignEng Alf100% (1)
- Ductulator May 2010Document8 pagesDuctulator May 2010haroub_nasNo ratings yet
- Frank Loeffler - Pipe Tube Conveyor PDFDocument12 pagesFrank Loeffler - Pipe Tube Conveyor PDFIgor San Martín Peñaloza0% (1)
- Albers TUDelft Introduction, Heave CompensationDocument17 pagesAlbers TUDelft Introduction, Heave Compensationnvkurup100% (1)
- Uuuu PDFDocument15 pagesUuuu PDFMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Separator Design MethodologyDocument19 pagesSeparator Design Methodologyromdhan88100% (1)
- External Metal LouvresDocument28 pagesExternal Metal LouvresQuitzs QuitzsNo ratings yet
- General Design Procedures: Size Selection ProblemsDocument7 pagesGeneral Design Procedures: Size Selection ProblemsShamsi MursalliNo ratings yet
- S04 - Basic Parameters and Design of Cast in Situ Box GirderDocument71 pagesS04 - Basic Parameters and Design of Cast in Situ Box GirderSMR STPNo ratings yet
- CTBEST PVM 300 Process Design of Separation VesselsDocument22 pagesCTBEST PVM 300 Process Design of Separation Vesselsrzepedac100% (2)
- Wind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194Document13 pagesWind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194nakkipatty100% (2)
- CarlVanGeem Curviameter PaperDocument10 pagesCarlVanGeem Curviameter PaperVictor MedranoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Model Test With Ship Sea Trial PDFDocument8 pagesComparison of Model Test With Ship Sea Trial PDFSunil Kumar P GNo ratings yet
- ZFG AT Image Flyer Eng WebDocument6 pagesZFG AT Image Flyer Eng Webingenieria.apvialesNo ratings yet
- Reynolds AirfoilDocument24 pagesReynolds Airfoilcv cvNo ratings yet
- Wind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194Document13 pagesWind Loading-Base Station Antennas White Paper TP - 103194Joshua BerryNo ratings yet
- Final Acoustic Enclosure PresentationDocument48 pagesFinal Acoustic Enclosure PresentationsartajyadNo ratings yet
- Caster Crown PPT Ver 1.01Document32 pagesCaster Crown PPT Ver 1.01bill_porter_1953No ratings yet
- Limestone - Slurry OptimizationDocument5 pagesLimestone - Slurry OptimizationSharif M Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- BridgeGirdersRegionalSpecsAB MB SK TG 2013 04 EDocument23 pagesBridgeGirdersRegionalSpecsAB MB SK TG 2013 04 Esilvereyes18No ratings yet
- Estimation of Turbomachinery Losses Through Cascade TestingDocument54 pagesEstimation of Turbomachinery Losses Through Cascade Testingchandrasingh4564No ratings yet
- Duct & Vent EngineeringDocument70 pagesDuct & Vent Engineeringtop20202080% (5)
- AC Duct Design PDFDocument6 pagesAC Duct Design PDFkumar123rajuNo ratings yet
- Ductulator May 2010Document10 pagesDuctulator May 2010Arshavin Watashi Wa100% (1)
- ASME PTC19.3 TW-2010 Thermowell Design Standard: © Abb Month DD, YYYY - Slide 1Document23 pagesASME PTC19.3 TW-2010 Thermowell Design Standard: © Abb Month DD, YYYY - Slide 1John PaulNo ratings yet
- GB 3.1 Flow Converter 713 Manual 0704Document20 pagesGB 3.1 Flow Converter 713 Manual 0704CharbsNo ratings yet
- ArchiveDocument8 pagesArchiveMahmoud MegahedNo ratings yet
- AMCA 210 07 WT Introduction OP App 20131024 PDFDocument190 pagesAMCA 210 07 WT Introduction OP App 20131024 PDFManoel Camargo SampaioNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Sizing of Restriction Orifice For Single-Phase Fluids With PDFDocument8 pagesGuidelines For Sizing of Restriction Orifice For Single-Phase Fluids With PDFEPTCO LHDNo ratings yet
- CAVTDocument4 pagesCAVTRaj EaswarmoorthiNo ratings yet
- Detailing MembersDocument43 pagesDetailing Memberschithirai10No ratings yet
- VSB-VMB DBL008en PDFDocument4 pagesVSB-VMB DBL008en PDFhossein.ahmadi.85No ratings yet
- 2 DKSinghalDocument48 pages2 DKSinghalMostafizur Rahman100% (2)
- Storm Water Drainage System Revision)Document8 pagesStorm Water Drainage System Revision)hera4u2No ratings yet
- Atv DVWK M 127 e pt2 Appx5 9Document27 pagesAtv DVWK M 127 e pt2 Appx5 9otezgidenNo ratings yet
- Open Drain Separator SizingDocument23 pagesOpen Drain Separator SizingSuchart TarasapNo ratings yet
- 23.bladder AccumlatorDocument12 pages23.bladder AccumlatorM S GokulNo ratings yet
- Deep BeamDocument8 pagesDeep BeamShashikant Gaur0% (1)
- A Fresh Approach To Gas Lift, Alan Brodie PTCDocument15 pagesA Fresh Approach To Gas Lift, Alan Brodie PTCrps1977No ratings yet
- Problem 04 - Tower Sizing & Tray DesignDocument40 pagesProblem 04 - Tower Sizing & Tray DesignJorge Enciso AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Cement Bond Logging: Principles of Oil-Well CementingDocument32 pagesCement Bond Logging: Principles of Oil-Well CementingAPE GAS SECTION. B 2019No ratings yet
- Catálogo Compresores Baja Presion-AersenDocument32 pagesCatálogo Compresores Baja Presion-AersenJuan Camilo RestrepoNo ratings yet
- GHHDocument3 pagesGHHeldiego1790No ratings yet
- Bejan Gabriel G.P.Document10 pagesBejan Gabriel G.P.Gabriel BejanNo ratings yet
- Planing Hull Model Tests For CFD ValidationDocument10 pagesPlaning Hull Model Tests For CFD Validationfez960No ratings yet
- Trace Leaks: 9. The Air MainDocument25 pagesTrace Leaks: 9. The Air Mainpaulo josé sá patachoNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionFrom EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesFrom EverandGas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesNo ratings yet
- How to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesFrom EverandHow to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsFrom EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechNo ratings yet
- Good, Bad and Ugly Process Burner FlamesDocument3 pagesGood, Bad and Ugly Process Burner Flamesratninp9368No ratings yet
- PDS - BearingCheck 894 and BearingCheck 824Document1 pagePDS - BearingCheck 894 and BearingCheck 824ratninp9368No ratings yet
- PTQ 2013 - Revamps - ScribdDocument68 pagesPTQ 2013 - Revamps - Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- Steel MinimillsDocument16 pagesSteel Minimillsratninp9368No ratings yet
- MNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFDocument51 pagesMNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFratninp9368No ratings yet
- Measurement Techniques Concerning Droplet Size Distribution of Electrosprayed WaterDocument3 pagesMeasurement Techniques Concerning Droplet Size Distribution of Electrosprayed Waterratninp9368No ratings yet
- The Weathering Magazine - Vietnam - ScribdDocument72 pagesThe Weathering Magazine - Vietnam - Scribdratninp9368100% (2)
- AERO QTR - 01-10 - ScribdDocument32 pagesAERO QTR - 01-10 - Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- MNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFDocument51 pagesMNL Iscan Software REV 6 - Scribd PDFratninp9368No ratings yet
- 05 DPI May 17 ScribdDocument47 pages05 DPI May 17 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- Effect of Fouling On Heat Exchanger - ScribdDocument40 pagesEffect of Fouling On Heat Exchanger - Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- 06 CT2 ScribdDocument80 pages06 CT2 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- 08 09 CT2 ScribdDocument116 pages08 09 CT2 Scribdratninp9368100% (1)
- 07 CT2 ScribdDocument76 pages07 CT2 Scribdratninp9368100% (1)
- 01 02 CT2 ScribdDocument68 pages01 02 CT2 Scribdratninp9368No ratings yet
- 05 CT2 ScribdDocument68 pages05 CT2 Scribdratninp9368100% (1)