Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Topic 1
Tutorial Topic 1
Uploaded by
aidaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- B48BB Tutorial Questions v3Document16 pagesB48BB Tutorial Questions v3aidaNo ratings yet
- Idebe P-3-1Document156 pagesIdebe P-3-1Charles Ghati100% (3)
- Exercise WorkshopDocument5 pagesExercise WorkshopDanna SofíaNo ratings yet
- Insulated Pipe - Temperature Loss CalculationDocument5 pagesInsulated Pipe - Temperature Loss CalculationnopNo ratings yet
- EM Question BankDocument14 pagesEM Question BanksambannisNo ratings yet
- Scan Jul 03, 2023Document3 pagesScan Jul 03, 2023jackdish18No ratings yet
- Questions MechanicsDocument2 pagesQuestions Mechanicspravat DashNo ratings yet
- Term 3 - Practice ExamDocument2 pagesTerm 3 - Practice ExamCJNo ratings yet
- QB emDocument17 pagesQB emSenthil Kumar P100% (1)
- EM 3rd Sem AssignmentDocument1 pageEM 3rd Sem AssignmentN KumarNo ratings yet
- QB18 PDFDocument10 pagesQB18 PDFRaNo ratings yet
- Ge8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesGe8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFThamizh gomathiNo ratings yet
- Statics 1Document3 pagesStatics 1Lorenz Christopher Hermoso MendozaNo ratings yet
- Model QSTN Paper 1-Be100Document5 pagesModel QSTN Paper 1-Be100nanduNo ratings yet
- Ee Rev03 - Quiz 1Document5 pagesEe Rev03 - Quiz 1JAMEL C IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesDocument2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesJennifer Moore100% (1)
- Eng'G Mechanics & Strength of Matl'S: Chemical Engineering Reviewer Compiled By: Engr. Albert D.C. EvangelistaDocument15 pagesEng'G Mechanics & Strength of Matl'S: Chemical Engineering Reviewer Compiled By: Engr. Albert D.C. EvangelistaAlyssa ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power 1Document4 pagesWork Energy Power 1Gaming baseNo ratings yet
- MRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)Document35 pagesMRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)semofederationNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionsDocument38 pagesEngineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionskganesanNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSDocument3 pagesICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSArindam SardarNo ratings yet
- TorqueDocument2 pagesTorqueEndai DesuNo ratings yet
- EM QBDocument16 pagesEM QBJeganNo ratings yet
- SRB DRBDocument44 pagesSRB DRBAcads AccountNo ratings yet
- Exercise For in EquilibriumDocument7 pagesExercise For in EquilibriumPauling ChiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 2 2024 VectorsDocument5 pagesTutorial Sheet 2 2024 VectorsgideontakawilaNo ratings yet
- C Nsa192004 Pages:4Document4 pagesC Nsa192004 Pages:4TMX PoketooNo ratings yet
- Recit 11 SolDocument2 pagesRecit 11 SolLemuel YuNo ratings yet
- M1 Chap-3 Supporting MaterialDocument11 pagesM1 Chap-3 Supporting MaterialRocketNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Smacol S6 Mechanics Revision P425/2 Use .Document4 pagesSmacol S6 Mechanics Revision P425/2 Use .NANGOYE DEONo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions, Each Carries 5 Marks.: Pages: 2 Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer All Questions, Each Carries 5 Marks.: Pages: 2 Reg No.: - NameSibin SamNo ratings yet
- B. Inversely As The Square ofDocument6 pagesB. Inversely As The Square ofRogelio Jr. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument6 pagesDynamicskoeliaNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanics ActivitiesDocument71 pages1 Mechanics ActivitiesSimaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1b VectorsDocument6 pagesChapter 1b VectorsPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument5 pagesDynamicsИРадојичићNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 MechanicsDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 MechanicsEngg Pawan SainiNo ratings yet
- 2017 11 Lyp SP Sa1 Physics 04Document4 pages2017 11 Lyp SP Sa1 Physics 04Ritesh RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2ep23btech11028No ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences P1 (Physics) Half - Yearly Examinations JUNE 2020Document32 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences P1 (Physics) Half - Yearly Examinations JUNE 2020MfanafuthiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question Full 4Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question Full 4Samir BoseNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationDocument12 pagesSample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationSuhaim SahebNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Document14 pagesElectrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Sameera ShanakaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Exercise Workshop PDFDocument5 pagesExercise Workshop PDFVANESSA ESPEJO LEAÑONo ratings yet
- Sahodya 3Document2 pagesSahodya 3manvir270508No ratings yet
- Corona Leave Assignment - EmechDocument14 pagesCorona Leave Assignment - EmechraghulNo ratings yet
- MG Section 1 HWDocument8 pagesMG Section 1 HWAnonymous 9OUMMmSBHNo ratings yet
- Em QPDocument3 pagesEm QPkb210538No ratings yet
- Worksheet 01 MechanicsDocument10 pagesWorksheet 01 MechanicsImran Mirza0% (1)
- Coulomb's LawDocument6 pagesCoulomb's LawAarush MishraNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- Sheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesSheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionTony AtefNo ratings yet
- Topics 1,2,6 Summative SLDocument14 pagesTopics 1,2,6 Summative SLAhmad OmarNo ratings yet
- Infant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Document4 pagesInfant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Robinston Jeyasingh KNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument48 pagesJames Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & Solutionsfortnitegamerpro123451No ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- G19RA Chap5 - GasesDocument37 pagesG19RA Chap5 - GasesaidaNo ratings yet
- Thesis ReportDocument54 pagesThesis ReportaidaNo ratings yet
- IJE - Volume 29 - Issue 10 - Pages 1469-1477Document9 pagesIJE - Volume 29 - Issue 10 - Pages 1469-1477aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 2Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 2aidaNo ratings yet
- 18.06.2019-UBOC - Provision of Exploration - Appraisal and Development ServicesDocument7 pages18.06.2019-UBOC - Provision of Exploration - Appraisal and Development ServicesaidaNo ratings yet
- IDocument1 pageIaidaNo ratings yet
- Abstract F.veliyev, A.aslanovaDocument1 pageAbstract F.veliyev, A.aslanovaaidaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Petroleum-Chemistry Technologies: TOPIC 2.1 Introduction To Oil and Gas IndustryDocument49 pagesPetroleum and Petroleum-Chemistry Technologies: TOPIC 2.1 Introduction To Oil and Gas IndustryaidaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesDocument9 pagesPetroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesaidaNo ratings yet
- CompetitionDocument20 pagesCompetitionaidaNo ratings yet
- Dataset Lab 2Document1 pageDataset Lab 2aidaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Petroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesDocument1 pageQuiz 3 Petroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesaidaNo ratings yet
- H Static H Total H Static H Total: Bernoulli Principles DatasetDocument1 pageH Static H Total H Static H Total: Bernoulli Principles DatasetaidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 3Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 3aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 7: ©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016Document2 pagesTutorial Topic 7: ©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016aidaNo ratings yet
- Meseleler Menseyski (Dinamika)Document25 pagesMeseleler Menseyski (Dinamika)aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 1Document4 pagesTutorial Topic 1aidaNo ratings yet
- Petrel Ibooks Jan 2017 PDFDocument86 pagesPetrel Ibooks Jan 2017 PDFaidaNo ratings yet
- SCM Fault QC Petrel 2010Document12 pagesSCM Fault QC Petrel 2010aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 5Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 5aidaNo ratings yet
- Economy 3Document85 pagesEconomy 3aidaNo ratings yet
- SPE 134534 Practical Use of Well Test Deconvolution: Gringarten, A. C., SPE, Imperial College LondonDocument9 pagesSPE 134534 Practical Use of Well Test Deconvolution: Gringarten, A. C., SPE, Imperial College LondonaidaNo ratings yet
- RVFDocument31 pagesRVFephNo ratings yet
- S1: Shear Force in A BeamDocument3 pagesS1: Shear Force in A BeamBruhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document17 pagesLecture 1Okan BayarNo ratings yet
- Column Load Calculation Excel Sheet Examples.Document96 pagesColumn Load Calculation Excel Sheet Examples.Masaba SolomonNo ratings yet
- Class IX Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesClass IX Lesson Planmadhu sudhanNo ratings yet
- Viva-Voce 1 BDocument5 pagesViva-Voce 1 Bchanjaneyulu9100% (1)
- A Simple Model To Describe The Thixotropic Behavior OfpaintsDocument23 pagesA Simple Model To Describe The Thixotropic Behavior OfpaintsCereliaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class - 11 Physics Chapter 13 - Kinetic TheoryDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Class - 11 Physics Chapter 13 - Kinetic TheoryAngel KuttyNo ratings yet
- Machine Time Jarry enDocument19 pagesMachine Time Jarry enmariaNo ratings yet
- (F.N. Cogswell) Polymer Melt Rheology A Guide For PDFDocument197 pages(F.N. Cogswell) Polymer Melt Rheology A Guide For PDFSherafghan Iftikhar100% (1)
- Thermochemistry LectureDocument62 pagesThermochemistry LectureSiiveh DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Tablas - Parte 1Document117 pagesTablas - Parte 1Carlos Jesús Fabián ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Gravity & Friction Class Exercises PostDocument4 pagesGravity & Friction Class Exercises PostmanasNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering - Shashi K Gulhati & Manoj DattaDocument106 pagesGeotechnical Engineering - Shashi K Gulhati & Manoj Dattau3118675No ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument22 pagesThermal Physicsapi-3728553100% (1)
- LRFD Design Specifications For Shallow FoundationsDocument9 pagesLRFD Design Specifications For Shallow FoundationsTigerinzooNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.2 LDocument15 pagesLecture 4.2 Lعباس احمد المبدعNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document52 pagesLecture 3mani shankarNo ratings yet
- Physics2a 101118021050 Phpapp02Document315 pagesPhysics2a 101118021050 Phpapp02umesh52No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Prestressed Precast Hollow Core Slabs Using Strut and Tie Method PDFDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Design of Prestressed Precast Hollow Core Slabs Using Strut and Tie Method PDFZarko LazicNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square LawDocument6 pagesInverse Square LawMarc Peejay ViernesNo ratings yet
- Belt, Rope and Chain DrivesDocument60 pagesBelt, Rope and Chain DrivesJason Dequin VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 ADocument68 pagesLecture 02 AHữu Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Motion of A Freely Falling BodyDocument46 pagesMotion of A Freely Falling BodyAhmed MagedNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument32 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Newton's Laws of MotionLouie Jay Flores Candame50% (2)
- Nelson Thornes Answers To Assessment QuestionsDocument11 pagesNelson Thornes Answers To Assessment QuestionsMitul KaziNo ratings yet
- Rolling Resistance Measurement and Model DevelopmentDocument20 pagesRolling Resistance Measurement and Model DevelopmentRanjan SharmaNo ratings yet
- ISC Engineering Science PDFDocument2 pagesISC Engineering Science PDFUtkarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Room ShapeDocument8 pagesAcoustics Room ShapeJica Diaz100% (1)
Tutorial Topic 1
Tutorial Topic 1
Uploaded by
aidaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Topic 1
Tutorial Topic 1
Uploaded by
aidaCopyright:
Available Formats
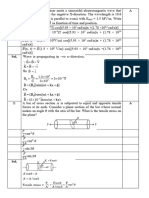
1
Tutorials Topic 1
1. One displacement vector sa has a magnitude 3.56 km and points due North. A
second displacement vector sb has a magnitude 5.67 km and points due North:
(a) Find the magnitude and direction of sa + sb.
(b) Find the magnitude and direction of sa - sb.
(c) Find the magnitude and direction of sb – sa.
2. At the moment of take-off, a Boeing 747 would typically have a velocity of 80 ms-1
with an angle of 10o to the horizontal runway:
(a) Calculate the vertical component of the aircraft’s velocity at the moment of take-
off.
(b) Calculate the horizontal component of the aircraft’s velocity at the moment of
take-off.
3. A van is being pulled by two forces that are applied by the two ropes shown in the
diagram. The dotted line bisects the angle between the forces. Each force has a
magnitude of 4000 N and each is directed at an angle of 30o to the horizontal. Use
the Parallelogram Law to calculate:
(a) The force required by a single rope that would produce the same overall effect as
the two forces below.
(b) The direction in which this single force should act.
Two ropes each
Van pulling with a
force of 4,000 N.
©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016
2
4. This is a pure Trigonometry question. The diagram shows sodium and chlorine
atoms in a cubic crystalline lattice. Each edge of the cube is 2.8 x 10-10 m in length.
(a) Determine the diagonal distance from one bottom corner of the cube to the far
top corner of the cube – see below.
(b) Determine the angle θ that this diagonal makes with the base of the cube.
5. Alex and Jane meet at a street corner and have a little chat. They then go their
separate ways. Alex walks due East along a level street, while Jane goes due North
up a steep hill.
When Alex has reached his next street corner, 200m from the first, Jane has also
reached her next street corner, which is up the hill (Jane’s corner is 150m as
measured along the street and 30 m vertically higher than the original street corner).
Given the above calculate the total displacement between Alex and Jane.
©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016
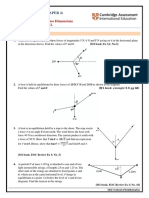
3
6. A semi-submersible rig is being manoeuvred by three tug boats and is moving at a
constant velocity. Tugs A and B exert a pull of 30 kN each as shown in the diagram.
Tug C is at the stern of the rig and acts in opposition to the pull from A and B.
Calculate the magnitude of the force exerted by C.
C Semi-sub
20o
B
7. Consider the following “three force problems”. Three forces act on a single point.
Determine whether the forces are in equilibrium or not:
3N
90o
4N
127o 143o
5N
8. A car weighs 13,500 N is moving up an incline at constant velocity. The incline
makes an angle of 25o with the horizontal. Determine the reaction force (frxn) acting
on the car.
©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016
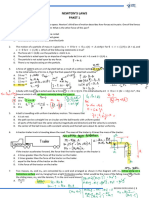
4
9. A wire is stretched between the tops of two identical buildings. When a tightrope
walker is at the centre of the wire, the tension in the wire is 2500 N. Each section of
the tight rope makes an angle of 6o with respect to the horizontal. Determine the
weight (in N) of the walker.
2o
“X” N
10. Two forces act on a body. They act at right angles to one another. One of the forces
has a magnitude of 200 N. The resultant force is of magnitude 300 N:
(a) Determine the magnitude of the other force.
(b) Calculate the angle between the resultant and the 200 N force.
11. An aircraft has a steady speed of 150 km hr-1 and is travelling due North. A strong
wind blows from the North-West with a speed of 60 km hr-1. What is the velocity
(magnitude and direction) of the aircraft with respect to the ground?
12. [This question will require more work and insight] Three ropes are tied together at a
single point. Their tensions are 50N, 100 N and 125 N. If the system does not move
calculate all the angles between the ropes.
©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016
You might also like
- B48BB Tutorial Questions v3Document16 pagesB48BB Tutorial Questions v3aidaNo ratings yet
- Idebe P-3-1Document156 pagesIdebe P-3-1Charles Ghati100% (3)
- Exercise WorkshopDocument5 pagesExercise WorkshopDanna SofíaNo ratings yet
- Insulated Pipe - Temperature Loss CalculationDocument5 pagesInsulated Pipe - Temperature Loss CalculationnopNo ratings yet
- EM Question BankDocument14 pagesEM Question BanksambannisNo ratings yet
- Scan Jul 03, 2023Document3 pagesScan Jul 03, 2023jackdish18No ratings yet
- Questions MechanicsDocument2 pagesQuestions Mechanicspravat DashNo ratings yet
- Term 3 - Practice ExamDocument2 pagesTerm 3 - Practice ExamCJNo ratings yet
- QB emDocument17 pagesQB emSenthil Kumar P100% (1)
- EM 3rd Sem AssignmentDocument1 pageEM 3rd Sem AssignmentN KumarNo ratings yet
- QB18 PDFDocument10 pagesQB18 PDFRaNo ratings yet
- Ge8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesGe8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFThamizh gomathiNo ratings yet
- Statics 1Document3 pagesStatics 1Lorenz Christopher Hermoso MendozaNo ratings yet
- Model QSTN Paper 1-Be100Document5 pagesModel QSTN Paper 1-Be100nanduNo ratings yet
- Ee Rev03 - Quiz 1Document5 pagesEe Rev03 - Quiz 1JAMEL C IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesDocument2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesJennifer Moore100% (1)
- Eng'G Mechanics & Strength of Matl'S: Chemical Engineering Reviewer Compiled By: Engr. Albert D.C. EvangelistaDocument15 pagesEng'G Mechanics & Strength of Matl'S: Chemical Engineering Reviewer Compiled By: Engr. Albert D.C. EvangelistaAlyssa ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power 1Document4 pagesWork Energy Power 1Gaming baseNo ratings yet
- MRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)Document35 pagesMRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)semofederationNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionsDocument38 pagesEngineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionskganesanNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSDocument3 pagesICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSArindam SardarNo ratings yet
- TorqueDocument2 pagesTorqueEndai DesuNo ratings yet
- EM QBDocument16 pagesEM QBJeganNo ratings yet
- SRB DRBDocument44 pagesSRB DRBAcads AccountNo ratings yet
- Exercise For in EquilibriumDocument7 pagesExercise For in EquilibriumPauling ChiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 2 2024 VectorsDocument5 pagesTutorial Sheet 2 2024 VectorsgideontakawilaNo ratings yet
- C Nsa192004 Pages:4Document4 pagesC Nsa192004 Pages:4TMX PoketooNo ratings yet
- Recit 11 SolDocument2 pagesRecit 11 SolLemuel YuNo ratings yet
- M1 Chap-3 Supporting MaterialDocument11 pagesM1 Chap-3 Supporting MaterialRocketNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Smacol S6 Mechanics Revision P425/2 Use .Document4 pagesSmacol S6 Mechanics Revision P425/2 Use .NANGOYE DEONo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions, Each Carries 5 Marks.: Pages: 2 Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer All Questions, Each Carries 5 Marks.: Pages: 2 Reg No.: - NameSibin SamNo ratings yet
- B. Inversely As The Square ofDocument6 pagesB. Inversely As The Square ofRogelio Jr. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument6 pagesDynamicskoeliaNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanics ActivitiesDocument71 pages1 Mechanics ActivitiesSimaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1b VectorsDocument6 pagesChapter 1b VectorsPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument5 pagesDynamicsИРадојичићNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 MechanicsDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 MechanicsEngg Pawan SainiNo ratings yet
- 2017 11 Lyp SP Sa1 Physics 04Document4 pages2017 11 Lyp SP Sa1 Physics 04Ritesh RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2ep23btech11028No ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences P1 (Physics) Half - Yearly Examinations JUNE 2020Document32 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences P1 (Physics) Half - Yearly Examinations JUNE 2020MfanafuthiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question Full 4Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question Full 4Samir BoseNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationDocument12 pagesSample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationSuhaim SahebNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Document14 pagesElectrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Sameera ShanakaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Exercise Workshop PDFDocument5 pagesExercise Workshop PDFVANESSA ESPEJO LEAÑONo ratings yet
- Sahodya 3Document2 pagesSahodya 3manvir270508No ratings yet
- Corona Leave Assignment - EmechDocument14 pagesCorona Leave Assignment - EmechraghulNo ratings yet
- MG Section 1 HWDocument8 pagesMG Section 1 HWAnonymous 9OUMMmSBHNo ratings yet
- Em QPDocument3 pagesEm QPkb210538No ratings yet
- Worksheet 01 MechanicsDocument10 pagesWorksheet 01 MechanicsImran Mirza0% (1)
- Coulomb's LawDocument6 pagesCoulomb's LawAarush MishraNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- Sheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesSheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionTony AtefNo ratings yet
- Topics 1,2,6 Summative SLDocument14 pagesTopics 1,2,6 Summative SLAhmad OmarNo ratings yet
- Infant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Document4 pagesInfant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Robinston Jeyasingh KNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument48 pagesJames Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & Solutionsfortnitegamerpro123451No ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- G19RA Chap5 - GasesDocument37 pagesG19RA Chap5 - GasesaidaNo ratings yet
- Thesis ReportDocument54 pagesThesis ReportaidaNo ratings yet
- IJE - Volume 29 - Issue 10 - Pages 1469-1477Document9 pagesIJE - Volume 29 - Issue 10 - Pages 1469-1477aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 2Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 2aidaNo ratings yet
- 18.06.2019-UBOC - Provision of Exploration - Appraisal and Development ServicesDocument7 pages18.06.2019-UBOC - Provision of Exploration - Appraisal and Development ServicesaidaNo ratings yet
- IDocument1 pageIaidaNo ratings yet
- Abstract F.veliyev, A.aslanovaDocument1 pageAbstract F.veliyev, A.aslanovaaidaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Petroleum-Chemistry Technologies: TOPIC 2.1 Introduction To Oil and Gas IndustryDocument49 pagesPetroleum and Petroleum-Chemistry Technologies: TOPIC 2.1 Introduction To Oil and Gas IndustryaidaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesDocument9 pagesPetroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesaidaNo ratings yet
- CompetitionDocument20 pagesCompetitionaidaNo ratings yet
- Dataset Lab 2Document1 pageDataset Lab 2aidaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Petroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesDocument1 pageQuiz 3 Petroleum and Petroleum Chemistry TechnologiesaidaNo ratings yet
- H Static H Total H Static H Total: Bernoulli Principles DatasetDocument1 pageH Static H Total H Static H Total: Bernoulli Principles DatasetaidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 3Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 3aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 7: ©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016Document2 pagesTutorial Topic 7: ©Heriot-Watt University B47AC V4 April 2016aidaNo ratings yet
- Meseleler Menseyski (Dinamika)Document25 pagesMeseleler Menseyski (Dinamika)aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 1Document4 pagesTutorial Topic 1aidaNo ratings yet
- Petrel Ibooks Jan 2017 PDFDocument86 pagesPetrel Ibooks Jan 2017 PDFaidaNo ratings yet
- SCM Fault QC Petrel 2010Document12 pagesSCM Fault QC Petrel 2010aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 5Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 5aidaNo ratings yet
- Economy 3Document85 pagesEconomy 3aidaNo ratings yet
- SPE 134534 Practical Use of Well Test Deconvolution: Gringarten, A. C., SPE, Imperial College LondonDocument9 pagesSPE 134534 Practical Use of Well Test Deconvolution: Gringarten, A. C., SPE, Imperial College LondonaidaNo ratings yet
- RVFDocument31 pagesRVFephNo ratings yet
- S1: Shear Force in A BeamDocument3 pagesS1: Shear Force in A BeamBruhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document17 pagesLecture 1Okan BayarNo ratings yet
- Column Load Calculation Excel Sheet Examples.Document96 pagesColumn Load Calculation Excel Sheet Examples.Masaba SolomonNo ratings yet
- Class IX Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesClass IX Lesson Planmadhu sudhanNo ratings yet
- Viva-Voce 1 BDocument5 pagesViva-Voce 1 Bchanjaneyulu9100% (1)
- A Simple Model To Describe The Thixotropic Behavior OfpaintsDocument23 pagesA Simple Model To Describe The Thixotropic Behavior OfpaintsCereliaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class - 11 Physics Chapter 13 - Kinetic TheoryDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Class - 11 Physics Chapter 13 - Kinetic TheoryAngel KuttyNo ratings yet
- Machine Time Jarry enDocument19 pagesMachine Time Jarry enmariaNo ratings yet
- (F.N. Cogswell) Polymer Melt Rheology A Guide For PDFDocument197 pages(F.N. Cogswell) Polymer Melt Rheology A Guide For PDFSherafghan Iftikhar100% (1)
- Thermochemistry LectureDocument62 pagesThermochemistry LectureSiiveh DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Tablas - Parte 1Document117 pagesTablas - Parte 1Carlos Jesús Fabián ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Gravity & Friction Class Exercises PostDocument4 pagesGravity & Friction Class Exercises PostmanasNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering - Shashi K Gulhati & Manoj DattaDocument106 pagesGeotechnical Engineering - Shashi K Gulhati & Manoj Dattau3118675No ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument22 pagesThermal Physicsapi-3728553100% (1)
- LRFD Design Specifications For Shallow FoundationsDocument9 pagesLRFD Design Specifications For Shallow FoundationsTigerinzooNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.2 LDocument15 pagesLecture 4.2 Lعباس احمد المبدعNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document52 pagesLecture 3mani shankarNo ratings yet
- Physics2a 101118021050 Phpapp02Document315 pagesPhysics2a 101118021050 Phpapp02umesh52No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Prestressed Precast Hollow Core Slabs Using Strut and Tie Method PDFDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Design of Prestressed Precast Hollow Core Slabs Using Strut and Tie Method PDFZarko LazicNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square LawDocument6 pagesInverse Square LawMarc Peejay ViernesNo ratings yet
- Belt, Rope and Chain DrivesDocument60 pagesBelt, Rope and Chain DrivesJason Dequin VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 ADocument68 pagesLecture 02 AHữu Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Motion of A Freely Falling BodyDocument46 pagesMotion of A Freely Falling BodyAhmed MagedNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument32 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Newton's Laws of MotionLouie Jay Flores Candame50% (2)
- Nelson Thornes Answers To Assessment QuestionsDocument11 pagesNelson Thornes Answers To Assessment QuestionsMitul KaziNo ratings yet
- Rolling Resistance Measurement and Model DevelopmentDocument20 pagesRolling Resistance Measurement and Model DevelopmentRanjan SharmaNo ratings yet
- ISC Engineering Science PDFDocument2 pagesISC Engineering Science PDFUtkarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Room ShapeDocument8 pagesAcoustics Room ShapeJica Diaz100% (1)