Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10ce201 Civil Engineering Materials and Geology Credits: 4:0:0 Objectives
10ce201 Civil Engineering Materials and Geology Credits: 4:0:0 Objectives
Uploaded by
Esrom AbebeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10ce201 Civil Engineering Materials and Geology Credits: 4:0:0 Objectives
10ce201 Civil Engineering Materials and Geology Credits: 4:0:0 Objectives
Uploaded by
Esrom AbebeCopyright:
Available Formats
10CE201 CIVIL ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND GEOLOGY
Credits: 4:0:0
Objectives:
• To understand the formation of rocks and properties of minerals
• To understand the properties of engineering materials
• To understand the tests to be done on materials
Outcomes:
• Students will be able to carry out engineering investigations
• Students will be able to identify important minerals
• Students will be able to select different building materials according to requirement
Unit I : General Geology and Mineralogy
Geology in Civil Engineering – branches of geology – Earth structure and composition –
elementary knowledge on continental drift and plate tectonics. Earth processes – weathering -
work of rivers, wind and sea and their Engineering importance – Elementary knowledge on
symmetry elements of important crystallographic systems – physical properties of minerals –
study of the following rock forming minerals – Quartz family, felspar family, hornblende,
calcite, garnet - Properties, behaviour and engineering significance of clay minerals.
Unit II : Petrology and Structural Geology
Classification of rocks –Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks - Description,
Occurrence, Engineering properties and Distribution of following rocks - Igneous rocks –
granite, pegmatite and basalt - Sedimentary rocks – sandstone, limestone, shale and
conglomerate - Metamorphic rocks - quartzite, marble, slate, gneiss and schist - Attitude of beds
– outcrops – geological maps – study of structures – folds, faults and joints – their bearing on
Engineering investigations. – Geological conditions necessary for construction of dams and
tunnels.
Unit III: Stones, Bricks and Timber :
(i) Stones, Requirement of good building stone, characteristics of stones and their testing.
Common building stones. Preservation of stones.
(ii) Bricks : Manufacture of clay bricks, and their classification. Properties of clay bricks and
their testing. Problems of efflorescence & lime bursting in bricks & tiles.
iii) Timber : Classification and identification of timber, Fundamental Engineering properties.
Defects in timber, seasoning and preservation of timber.
Unit IV : Civil Engineering Materials
Cement and Concrete – raw material – manufacture – type and properties of cement – steel –
heat treatment process – alloy steels – plain and deformed bars – relative merits – strength
specifications - Desirable characteristics of reinforcing steel - Principles of cold working -
Detailed Discussion on reinforcing steel mechanical and physical properties chemical
composition - Uses of ceramics – refractories – terracotta and glazed products –Paints –
varnishes – distemper - Plastic emulsions - Rubber, Aluminium, Glass, Plastics.
Unit V: Gypsum, Lime and Puzzolona :
(i) Gypsum : Forms of gypsum and gypsum plaster, properties of gypsum plaster, building
products of gypsum and their uses.
(ii) Lime : Manufacture of lime, classifications of limes, properties of lime.
(iii) Puzzolona : Natural and Artificial fly ash, Surkhi (burnt clay puzzolona), rice husk and ash
puzzolona, properties and specifications for use in construction.
Text Books:
1. Parbin Singh, Engineering and general Geology, Katson publication House, 1987.
2. Krynine and Judd, Engineering Geology and Geotechniques, McGraw Hill Book
Company 1970.
3. Rangwala, S.C., " Engineering Materials ", Charotar Publishing House, Anand, 1997.
4. Surendra Singh, " Building Materials ", Vikas Publishing Company, New Delhi, 1996.
Reference Books:
1. Legget, R.F., and Hatheway, A.W., Geology and Engineering, McGraw Hill Book
Company. 1988.
2. Blyth, Geology for Engineers, BLBS, 1985.
You might also like
- Ii Year BDocument3 pagesIi Year Bvarun_srkitNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Objective Type Questions BookDocument764 pagesCivil Engineering Objective Type Questions Bookajaydevmalik100% (3)
- Gy 402 1Document54 pagesGy 402 1eliamosha36No ratings yet
- Engg - GeologyDocument49 pagesEngg - GeologyKyaw Zin HeinNo ratings yet
- Geology Course SyllabusDocument2 pagesGeology Course SyllabusanneNo ratings yet
- Presentation JanakDocument108 pagesPresentation JanakJanakNo ratings yet
- GeologyDocument1 pageGeologyArun SaiNo ratings yet
- Course Outline-Building Materials I & IIDocument5 pagesCourse Outline-Building Materials I & IIymukhtar897No ratings yet
- Building Construction and Materials Notes - Civilenggforall PDFDocument254 pagesBuilding Construction and Materials Notes - Civilenggforall PDFDebrahanath100% (2)
- Economic GeologyDocument84 pagesEconomic GeologyDeepakNo ratings yet
- polyNEXT Syllabus CEDocument33 pagespolyNEXT Syllabus CEpriyabrataguhaNo ratings yet
- CE 31-Engineering Geology SyllabusDocument2 pagesCE 31-Engineering Geology SyllabuspicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Building StonesDocument7 pagesBuilding StonesMich ArthurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1Document51 pagesChapter 1.1sifu asratNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Engineering GeologyDocument4 pagesCourse Title: Engineering GeologylostgirlNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument71 pagesRocksBikash ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Application of Engineering Geology Geological Study A. Naturally InteractionDocument49 pagesApplication of Engineering Geology Geological Study A. Naturally InteractionAbraham DerejeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - INTRODUCTION TO MATERIALS SCIENCEDocument56 pagesChapter 1 - INTRODUCTION TO MATERIALS SCIENCEMaximillian AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportChelvam sNo ratings yet
- BMC Full NotesDocument128 pagesBMC Full NotesarvindroychoudharyNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Presentationml Presentation&rendition 1Document12 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Presentationml Presentation&rendition 1jeffmugacha6No ratings yet
- Building Materials & Construction I (Hulumediaofficial)Document20 pagesBuilding Materials & Construction I (Hulumediaofficial)the hungrypanda101 pandaNo ratings yet
- Schedule Standard and Syllabus: Section A: Geomorphology and Remote SensingDocument6 pagesSchedule Standard and Syllabus: Section A: Geomorphology and Remote SensingPankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ce6301-Engineering Geology PDFDocument6 pagesCe6301-Engineering Geology PDFManikandan Selvam100% (1)
- CE 201 - Bricks@CE-21 - 2020Document54 pagesCE 201 - Bricks@CE-21 - 2020Nahid SultanNo ratings yet
- Lec-1 - CE 201 - Bricks@CE-22 - 2021Document33 pagesLec-1 - CE 201 - Bricks@CE-22 - 2021Rj 30No ratings yet
- Week 1Document17 pagesWeek 1Abdulwahab khanNo ratings yet
- Classification of MaterialsDocument113 pagesClassification of Materialsabhinavgiri17No ratings yet
- 1.6 Rock Design and SupportDocument54 pages1.6 Rock Design and Supportn0188741wNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Objective Type QuestionDocument764 pagesCivil Engineering Objective Type QuestionMuhammad Umar FarooqNo ratings yet
- GT 1Document19 pagesGT 1RRRNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering I CE 341Document32 pagesGeotechnical Engineering I CE 341Temesgen M. MandersoNo ratings yet
- Classification of MaterialsDocument113 pagesClassification of Materialsabhinavgiri17No ratings yet
- GT 2Document19 pagesGT 2RRRNo ratings yet
- 14phdme002 Advanced Materials and ProcessingDocument1 page14phdme002 Advanced Materials and ProcessingRing MasterNo ratings yet
- GT 3Document19 pagesGT 3RRRNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CeramicsDocument39 pagesIntroduction To CeramicsRasika MalodeNo ratings yet
- Metal CLGDocument18 pagesMetal CLGabhishekbanaraseNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology 2018Document89 pagesEngineering Geology 2018Aasif KaziNo ratings yet
- New Wordpad DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Wordpad DocumentAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- CE205 Engg GeologyDocument3 pagesCE205 Engg GeologyfromashokNo ratings yet
- AR620 Building Materials - Ii LTP/SC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAR620 Building Materials - Ii LTP/SC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivesSINDHU KUMARESANNo ratings yet
- Stem Dakahlia Geology Club: Skills: - Learning Outcome: 3Document19 pagesStem Dakahlia Geology Club: Skills: - Learning Outcome: 3romaehab201912No ratings yet
- BK 5Document21 pagesBK 5bambangNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Usability As Aggregate of DiffereDocument7 pagesInvestigation of Usability As Aggregate of DiffereEstefania Loyola FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Tech SyllabusDocument36 pagesCeramic Tech SyllabusvishwanathanskNo ratings yet
- Building Materials and Construction: Course Code: 15CE1103 L T P C 3 1 0 4Document3 pagesBuilding Materials and Construction: Course Code: 15CE1103 L T P C 3 1 0 4pawanNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechanics-I: Rock and Rock MassesDocument12 pagesRock Mechanics-I: Rock and Rock MassesLily Gurung cstNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Marble and Granite Slurry in Clay Bricks: Dr. Shailesh Chaudhary Mr. Om Prakash SinghDocument3 pagesUtilization of Marble and Granite Slurry in Clay Bricks: Dr. Shailesh Chaudhary Mr. Om Prakash SinghPrashant pandeNo ratings yet
- Building Materials: Building Material & Construction 15CV36Document32 pagesBuilding Materials: Building Material & Construction 15CV36Radhika K.NNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rock MechanicsDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Rock MechanicsPrabhat RanjanNo ratings yet
- 2162 Me 106 Ceramic MaterialsDocument1 page2162 Me 106 Ceramic MaterialsMu BaNo ratings yet
- SS 1 Agric Science 2ND Term E-NoteDocument58 pagesSS 1 Agric Science 2ND Term E-Notekanajoseph2009No ratings yet
- Ceramic-Raw-Materials-Lecture-2Document24 pagesCeramic-Raw-Materials-Lecture-2ephremNo ratings yet
- Building Materials & ConstructionDocument20 pagesBuilding Materials & Constructionharshalraut1215No ratings yet
- Iare BMCP Lecture Notes 0Document80 pagesIare BMCP Lecture Notes 0Marjon BazarNo ratings yet
- CE8392 - Engineering Geology - SyllabusDocument1 pageCE8392 - Engineering Geology - SyllabusJegatheeswaran BoompandiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Optical Mineralogy And Petrography - The Practical Methods Of Identifying Minerals In Thin Section With The Microscope And The Principles Involved In The Classification Of RocksFrom EverandIntroduction To Optical Mineralogy And Petrography - The Practical Methods Of Identifying Minerals In Thin Section With The Microscope And The Principles Involved In The Classification Of RocksRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
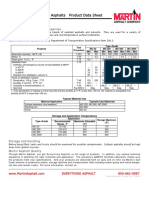
- Medium Curing Cutback Asphalts Product Data Sheet: Description and Physical PropertiesDocument1 pageMedium Curing Cutback Asphalts Product Data Sheet: Description and Physical PropertiesEsrom AbebeNo ratings yet
- Unit Costs of Infrastructure Projects in Sub-Saharan AfricaDocument10 pagesUnit Costs of Infrastructure Projects in Sub-Saharan AfricaEsrom AbebeNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.4 Quiz and Discussion: The Ifrs For SmesDocument18 pagesTopic 1.4 Quiz and Discussion: The Ifrs For SmesEsrom AbebeNo ratings yet
- 1ppt ScoolDocument66 pages1ppt ScoolEsrom AbebeNo ratings yet
- Development and Behavior, Vol. 51 PDFDocument287 pagesDevelopment and Behavior, Vol. 51 PDFEsrom AbebeNo ratings yet
- English For Ethiopia: Grade 6Document3 pagesEnglish For Ethiopia: Grade 6Esrom Abebe100% (2)
- Concrete Sweating - Phenomenon, Causes and PreventionDocument8 pagesConcrete Sweating - Phenomenon, Causes and Preventionvenkateswara rao pothinaNo ratings yet
- Dipshikha Meti SchoolDocument13 pagesDipshikha Meti SchoolNasrinNaharTuliNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HssliveDocument16 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HsslivemartyNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Treatment and Periodical Test of The Cooling WaterDocument4 pagesCooling Water Treatment and Periodical Test of The Cooling WaterGaurav MaithilNo ratings yet
- SizingDocument54 pagesSizingRafiqul Alam100% (1)
- BS 493 1995Document13 pagesBS 493 1995EdmundNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company Identificationmohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Making Hot and Cold Packs 2Document5 pagesMaking Hot and Cold Packs 2anilkumarmuntha868_5No ratings yet
- High-Temperature Oxidation of Fe Si Alloys in The Temperature Range 900-1250°CDocument7 pagesHigh-Temperature Oxidation of Fe Si Alloys in The Temperature Range 900-1250°CandyNo ratings yet
- Airbus A380: A Double Deck, Wide-Body, Four-Engine Airliner Manufactured by The European Corporation AirbusDocument19 pagesAirbus A380: A Double Deck, Wide-Body, Four-Engine Airliner Manufactured by The European Corporation Airbuspseudonomous actualityNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education 6: Industrial ArtsDocument13 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education 6: Industrial ArtsCorazon Diong Sugabo-TaculodNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Polyethylene Terephthalate PETand Polystyrene PS Dynamic PyrolysisDocument9 pagesKinetics of Polyethylene Terephthalate PETand Polystyrene PS Dynamic PyrolysisBobby AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- Airseal Installation Instruction - enDocument4 pagesAirseal Installation Instruction - enkamendrix kamendrixNo ratings yet
- Swagelok Vacuum FittingsDocument4 pagesSwagelok Vacuum FittingstotcsabNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument38 pagesMattergabbie dumpNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Technology of Epoxy Resins - B. Ellis (1993) PDFDocument342 pagesChemistry and Technology of Epoxy Resins - B. Ellis (1993) PDFIsadora HenriquesNo ratings yet
- Drawing (p15 Ace 857)Document14 pagesDrawing (p15 Ace 857)ritoh8657No ratings yet
- Ruby Charcoal - Company ProfileDocument3 pagesRuby Charcoal - Company ProfileNurhasanahNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Terms Used in The Hides, Skins, and Leather TradeDocument69 pagesDictionary of Terms Used in The Hides, Skins, and Leather TradePablo DíazNo ratings yet
- NACE SP 0294 2006 (Parte 3)Document12 pagesNACE SP 0294 2006 (Parte 3)Carlos Lluen AquinoNo ratings yet
- BS 729Document12 pagesBS 729Arun NagrathNo ratings yet
- Kerala BOQDocument47 pagesKerala BOQSmith SivaNo ratings yet
- Sprue System DesignDocument24 pagesSprue System DesignErnesto RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Stitchless and SeamlessDocument18 pagesStitchless and Seamlessrangtulai456No ratings yet
- Brooklin: Construction Specifications Precast Concrete Utility ManholeDocument1 pageBrooklin: Construction Specifications Precast Concrete Utility ManholesnobumNo ratings yet
- BPG RangeDocument40 pagesBPG RangeHossam AbdelmoneimNo ratings yet
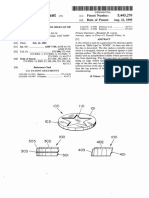
- United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,443,270Document5 pagesUnited States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,443,270Tyler Jordan DavisonNo ratings yet
- A351A351M 2003 Specification For Castings, Austenitic, Austenitic-Ferritic (Duplex), For Presure-Containing PartsDocument5 pagesA351A351M 2003 Specification For Castings, Austenitic, Austenitic-Ferritic (Duplex), For Presure-Containing PartsPhong ThanhNo ratings yet
- Back UP Data R1Document57 pagesBack UP Data R1ilhamNo ratings yet
- Steam Coal Specification: Parameter Basis GuaranteedDocument1 pageSteam Coal Specification: Parameter Basis GuaranteedanggiefebriyantoNo ratings yet