Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edamala - Biofest Poster PDF
Edamala - Biofest Poster PDF
Uploaded by
Amy Nottingham-MartinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Psychopathology of Schizophrenia (Theoretical)Document1 pagePsychopathology of Schizophrenia (Theoretical)Robert Joseph Sison100% (5)
- WHO Adherence 2003Document209 pagesWHO Adherence 2003jakob_ahlstedtNo ratings yet
- Feb 4 Pathophysiology Revised PTSDDocument4 pagesFeb 4 Pathophysiology Revised PTSDeri kimNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Presented By: Seng, Shena H. Siocon, Jewrich G. Ubag, Jazzyleene M. Vesagas, Christian Jay BDocument23 pagesSchizophrenia: Presented By: Seng, Shena H. Siocon, Jewrich G. Ubag, Jazzyleene M. Vesagas, Christian Jay BFatima Medriza DuranNo ratings yet
- Depression: Symptoms SerotoninDocument1 pageDepression: Symptoms SerotoninFatma ZorluNo ratings yet
- Neurotranssmitter Dan Efek Pada Organ ManusiaDocument3 pagesNeurotranssmitter Dan Efek Pada Organ ManusiaPANI78No ratings yet
- Psycho 1Document43 pagesPsycho 1Belia Bima NafisaNo ratings yet
- Paychiatric NursingDocument7 pagesPaychiatric NursingJe Carmel Marie ElentorioNo ratings yet
- Psycho Pa ThoDocument9 pagesPsycho Pa ThoJayrald RosalesNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Science Lecture 2Document34 pagesBehavioral Science Lecture 2Natia BadridzeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antidepressants: PHCL411Document76 pagesPharmacology of Antidepressants: PHCL411Mustapha ImadudeenNo ratings yet
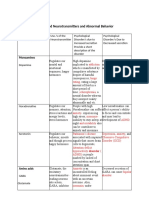
- Imbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorDocument3 pagesImbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorInah100% (1)
- Lecture 2 (Psychotropic Drugs)Document17 pagesLecture 2 (Psychotropic Drugs)ahmadslayman1No ratings yet
- The Affective DisordersDocument22 pagesThe Affective DisordersMUHD SUHAILNo ratings yet
- 7) 5th Semester - Depression & Affective DisordersDocument33 pages7) 5th Semester - Depression & Affective DisordersFizza ImamNo ratings yet
- Clinical ToxicologyDocument6 pagesClinical ToxicologyGrace MarinoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Klengel, T. - 2015Document15 pages2 - Klengel, T. - 2015João PedroNo ratings yet
- Mouse Party LabDocument4 pagesMouse Party LabEvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainDocument9 pagesChapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainciaraNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Bio Asmuni CutDocument40 pagesWeek 3 Bio Asmuni CutNavanisha SekarNo ratings yet
- Anti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCDocument17 pagesAnti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCÑiťhišh Śhankąŕ LóganáthánNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument171 pagesPsychopharmacologyVaib NigamNo ratings yet
- PSYCHDocument2 pagesPSYCHJacquelyn HasiandaNo ratings yet
- Psychoneuro-Endocrinology, Psychoneuro-Immunology, and ChronobiologyDocument2 pagesPsychoneuro-Endocrinology, Psychoneuro-Immunology, and ChronobiologyMark LopezNo ratings yet
- Sistema EndocrinoDocument18 pagesSistema Endocrinoanaelmoreira80No ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument12 pagesNeurotransmittersRahul DamorNo ratings yet
- Anti PsychoticDocument38 pagesAnti PsychoticAsep Cece IrhamNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters Cuadro PDFDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitters Cuadro PDFCarina Castillo ValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Ch2neurotrans PDFDocument2 pagesCh2neurotrans PDFKentNo ratings yet
- JOEY - S PHARM LECTURES - Neuro pg1-8Document9 pagesJOEY - S PHARM LECTURES - Neuro pg1-8shivani patelNo ratings yet
- Depressive-Disorders SheetDocument2 pagesDepressive-Disorders SheetCrystal MarloweNo ratings yet
- CNS Pathophysiology - Psychiatric DisorderDocument11 pagesCNS Pathophysiology - Psychiatric DisordersuereyaNo ratings yet
- Mood DisorderDocument22 pagesMood Disorderjosephvincent2001No ratings yet
- Presentation NeuronDocument7 pagesPresentation Neuronsuweino_harunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Brain and BehaviourDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Brain and Behaviour038 Suri HananNo ratings yet
- Depressive DisordersDocument3 pagesDepressive Disordersnguyenlmchau169No ratings yet
- 2 Ligan First MassengerDocument32 pages2 Ligan First MassengerikhararaNo ratings yet
- Depression EBDocument2 pagesDepression EBalfonsougarteNo ratings yet
- ?antidepressantsDocument1 page?antidepressantsKarma iiiNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants DrugsDocument2 pagesAntidepressants DrugsSony Montaño CañeteNo ratings yet
- Stress Related To Nutritional ImbalancesDocument3 pagesStress Related To Nutritional ImbalancesSam PothNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Moa (Side Effects)Document1 pageAntidepressant Moa (Side Effects)graceNo ratings yet
- Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria PDFDocument5 pagesHunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria PDFSabri VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Substance Hallucinogens and Dissociatives - CompressedDocument39 pagesPsychotropic Substance Hallucinogens and Dissociatives - CompressedshuyuichewNo ratings yet
- Monoamine NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageMonoamine NeurotransmittersBharath CNo ratings yet
- Anti DepressentsDocument2 pagesAnti DepressentsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Depressive EpisodeDocument33 pagesDepressive EpisodeKp ANo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AntidepressantsDocument28 pagesPharmacology of Antidepressantsحيدر كريم سعيد حمزهNo ratings yet
- Dissanayake (2015) - The Physiology of Pain - An Update and Review of Clinical Relevance PDFDocument5 pagesDissanayake (2015) - The Physiology of Pain - An Update and Review of Clinical Relevance PDFnamirohsamiyahNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Antidepressents 2020Document21 pagesClass 1 Antidepressents 2020Arafat 039No ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs in Dermatology: FR-Utilización de Psicofármacos en DermatologíaDocument3 pagesPsychotropic Drugs in Dermatology: FR-Utilización de Psicofármacos en DermatologíaNilson Morales CordobaNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Document2 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Prince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- Changes of Immune System in DepressionDocument2 pagesChanges of Immune System in DepressionfarahNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of ParkinsonDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Parkinsoncuriosity_killsNo ratings yet
- Antipsycotic DrugDocument21 pagesAntipsycotic DrugShashank SatheNo ratings yet
- AMITRIPTYLINEDocument1 pageAMITRIPTYLINERicky Ramos Jr.No ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology in Psychopharmacology in Psychiatry PsychiatryDocument16 pagesPsychopharmacology in Psychopharmacology in Psychiatry PsychiatryHasnain HyderNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Powerpoint Group 1Document38 pagesPharmacology Powerpoint Group 1Daniel LaurenteNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument57 pagesCNS DrugsHussein Al-jmrawiNo ratings yet
- Current Concept For Management of Neuropathic PainDocument55 pagesCurrent Concept For Management of Neuropathic Painmpm8471No ratings yet
- 9 Reasons You Should Eat Dark Chocolate Every Single DayDocument2 pages9 Reasons You Should Eat Dark Chocolate Every Single DaySheilla GanironNo ratings yet
- (Tamtam) Hiperglikemia, Hipoglikemia, Hiperosmolar Asidosis Non KetotikDocument23 pages(Tamtam) Hiperglikemia, Hipoglikemia, Hiperosmolar Asidosis Non KetotikkynatroemanNo ratings yet
- 10-Nutritional Considerations in Joint HealthDocument18 pages10-Nutritional Considerations in Joint Healthapi-3851239No ratings yet
- NIMHANS ProformaDocument13 pagesNIMHANS ProformaMATHANKUMAR ENo ratings yet
- DS - Senna ConcentrateDocument7 pagesDS - Senna ConcentrateFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- Per System PreferablyDocument3 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument27 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Medical MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesWeek 15 Medical MicrobiologyRuth Ivo Maria TampuboLonNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)Document15 pagesMultiple Sclerosis (MS)Arianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Out of Step by Arnold LeeseDocument50 pagesOut of Step by Arnold Leesealfred rosenbergNo ratings yet
- Garp-Nepal - Sa (Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership)Document90 pagesGarp-Nepal - Sa (Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership)Nivea VazNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase StudyArthur Brian100% (1)
- Psych Topiccompanion Schizophrenia SampleDocument4 pagesPsych Topiccompanion Schizophrenia SampleQueen Bee (Tt)100% (1)
- Fermented Foods and Food Safety: ArticleDocument9 pagesFermented Foods and Food Safety: ArticlesimurabiyeNo ratings yet
- Report Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesReport Tetralogy of FallotLieana AguilarNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Emotions: Redirecting Self-Therapy (RST) For Anxiety and DepressionDocument4 pagesThe Biology of Emotions: Redirecting Self-Therapy (RST) For Anxiety and DepressionoscarnineNo ratings yet
- Fire in The Blood Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesFire in The Blood Reflection PaperWIlfredo MirasolNo ratings yet
- EXAM Med Surg 1Document9 pagesEXAM Med Surg 1Gailstar GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Pathology For The Health Professions 4Th Edition Damjanov Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument20 pagesPathology For The Health Professions 4Th Edition Damjanov Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcrastzfeiej100% (12)
- Clinically Isolated Syndrome and Early Relapsing Multiple SclerosisDocument19 pagesClinically Isolated Syndrome and Early Relapsing Multiple Sclerosisnight.shadowNo ratings yet
- Consumer Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards The Use of Monosodium Glutamate and Food Grade Bullion Cubes As Dietary ConstituentsDocument5 pagesConsumer Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards The Use of Monosodium Glutamate and Food Grade Bullion Cubes As Dietary ConstituentsDeEpaa ManohanNo ratings yet
- Thesis 3Document41 pagesThesis 3Kundan dipNo ratings yet
- Allergy: Drug Reaction ClassificationDocument6 pagesAllergy: Drug Reaction ClassificationMatthieu FortinNo ratings yet
- NAMI YouAreNotAlone 2020Document1 pageNAMI YouAreNotAlone 2020inforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Myco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedDocument10 pagesMyco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- Aspectos Importantes de La Nutrición en Niños Con CáncerDocument11 pagesAspectos Importantes de La Nutrición en Niños Con CáncerNadia DonosoNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Submitted To: Application For The Registration of Subjects For Dissertation of TheDocument14 pagesSynopsis Submitted To: Application For The Registration of Subjects For Dissertation of TheAraafathNo ratings yet
- IMNCI - 6th SemDocument32 pagesIMNCI - 6th SemAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and ObesityDocument39 pagesAnesthesia and ObesityLucille IlaganNo ratings yet
Edamala - Biofest Poster PDF
Edamala - Biofest Poster PDF
Uploaded by
Amy Nottingham-MartinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edamala - Biofest Poster PDF
Edamala - Biofest Poster PDF
Uploaded by
Amy Nottingham-MartinCopyright:
Available Formats
Cytokines and Pathogenesis of Depressive Disorders During Chronic Illness
Sharon Edamala
What are Cytokines? Table 1. Psychological effects of cytokine immunotherapy. Behavioral side effects
Mechanisms Underlying Cytokine-Induced Depression associated with the administration of proinflammatory cytokines during the length
Inflammation is mediated by proteins called cytokines. of an illness are listed. Abbreviations: IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor
Serotonin hypothesis of depression suggests major depressive disorder (MDD) is characterized by
necrosis factor. Adapted from Schiepers et al. (2005).
• Synthesized by nucleated cells, secreted as a response to cell stress serotonin neurotransmission disorders which can be induced by chronic inflammation.
Immunotherapy Neuropsychiatric Effects Clinical Condition Treated
• Proinflammatory cytokines induce inflammation to activate an immune • Alters serotonin turnover in brain regions associated with MDD, lowers activity of presynaptic
response; anti-inflammatory cytokines reduce inflammation post-infection serotonergic neurons, and creates changes in serotonin reuptake from the synaptic cleft and to IFN- Fatigue Cancer
postsynaptic serotonin receptors Psychomotor slowing Multiple sclerosis
Tryptophan (TRP) is the precursor for serotonin synthesis. Depressed mood Chronic hepatitis C, other viral
infections
• High level of proinflammatory cytokines in the blood results in lower tryptophan levels and less
Anxiety
serotonin synthesized Social withdrawal
• Activation of Trp 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) results in tryptophan Irritability
Anorexia
degradation
Cognitive disturbances (mental
slowing, lack of concentration,
memory impairment)
IFN- Fatigue Multiple sclerosis
Figure 3. TRP can be Depressed mood
metabolized through the Cognitive impairment (Metastatic) cancer
serotonergic or kynurenic IL-1 Cognitive impairment (mental (Metastatic) cancer
Figure 1. A) Cytokines stimulate specific cells. Different cell types can secrete the pathway. When the immune slowing)
same cytokine, and one cytokine can act on multiple cells. B) Cytokines can be system is activated, IL-2 Fatigue
used to communicate over a variety of distances. Adapted from Creative tryptophan is pushed from Anhedonia
Diagnostics (n.d) the serotonergic pathway to Dysphoria
the kynurenic pathway, Cognitive impairment
resulting in quinolinic acid TNF- Fatigue Cancer
Proinflammatory cytokines also mediate sickness behavior. (which is neurotoxic) instead Anorexia
• Characteristics of sickness that accompany an infection: fever, decreased of serotonin. Adapted from
appetite, weight loss, lower levels of physical activity, loss of interest in social Anderson and Maes (2017).
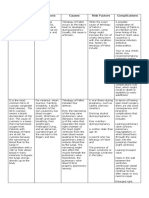
Conclusions and Future Directions
environments, etc.
• Helps sick individuals temporarily cope with the infection There are barriers to understanding depression through an immunological lens.
• Various types of depressive disorders influence the immune system differently
By activating the kynurenine pathway, proinflammatory cytokines cause the synthesis of quinolinic • Lack of generalizability of depression studies
The Problem acid (QUIN) and 3-hydroxykynurenine (3OH-KYN). • Role of genetics in increasing chances of developing depression during illness
Dysregulation of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels can • Linked to Parkinson’s disease, anxiety, and depression
cause endocrine and behavioral changes. • 3OH-KYN may lead to overproduction of reactive oxygen species and increased monoamine oxidase There is a large comorbidity of depression with the presence of proinflammatory
• Long-term exposure to a pathogen can lead to high sustained levels of activity, both associated with depressive disorders. cytokines.
proinflammatory cytokines resulting in chronic inflammation • MDD more prevalent in those with chronic inflammatory conditions e.g.,
• Psychological stressors contribute to a greater risk for infection, prolonged Depression is also associated with hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis hyperactivity caused rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes
length of infection, and slower wound healing by increased levels of cortisol in serum. • Major depressive disorder develops in 1/3 of patients that are treated with IL-2
• Proinflammatory cytokines activate HPA axis and induce corticosteroid receptor resistance in the • IFN- immunotherapies can increase mortality rates by 39%
hypothalamus and pituitary gland
• QUIN may cause hippocampal degeneration and loss of corticosteroid receptors Future research has potential to mitigate or stop development of depression
during chronic illness.
Figure 2. Interactions
between the central • Drugs that target the immune, endocrine, and neurotransmitter pathways
nervous system (top), Figure 4. The HPA axis is responsible for • Studies with consistent methods; cytokine levels can vary depending on the
endocrine system (right), the neuroendocrine response to stress kind of body fluid they were extracted from
immune system and is tightly regulated. With repeated • Investigate the relationship between poor behavioral coping strategies and the
(bottom), and autonomic exposure to a stressor, a person can body’s perception of stress, and how levels of proinflammatory cytokines may
nervous system (left). habituate to the stressor with continuous change as a result
Adapted from Schiepers, HPA activation.
Wichers, and Maes
(2005). Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Dr. Nancy Wall and Dr. Judith Humphries for their advising and
support during this project.
Literature Cited
This project explores the relationship between elevated levels of
Anderson, G., & Maes, M. (2017). Interactions of tryptophan and its catabolites with melatonin and the alpha 7 nicotinic receptor in central nervous system and
proinflammatory cytokines and the development of depressive psychiatric disorders: Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and direct mitochondria regulation. International Journal of Tryptophan Research, 10,
117864691769173. doi: 10.1177/1178646917691738
symptoms or disorders in individuals with chronic illnesses from a Creative Diagnostics. (n.d.). Cytokines and cytokine receptors ELISA Kits. Retrieved from https://www.creative-diagnostics.com/cytokines-and-cytokine-receptors-
elisa-kits.htm
neuroimmunological perspective. Schiepers, O. J., Wichers, M. C., & Maes, M. (2005). Cytokines and major depression. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 29(2), 201–
217. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2004.11.003
You might also like
- Psychopathology of Schizophrenia (Theoretical)Document1 pagePsychopathology of Schizophrenia (Theoretical)Robert Joseph Sison100% (5)
- WHO Adherence 2003Document209 pagesWHO Adherence 2003jakob_ahlstedtNo ratings yet
- Feb 4 Pathophysiology Revised PTSDDocument4 pagesFeb 4 Pathophysiology Revised PTSDeri kimNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Presented By: Seng, Shena H. Siocon, Jewrich G. Ubag, Jazzyleene M. Vesagas, Christian Jay BDocument23 pagesSchizophrenia: Presented By: Seng, Shena H. Siocon, Jewrich G. Ubag, Jazzyleene M. Vesagas, Christian Jay BFatima Medriza DuranNo ratings yet
- Depression: Symptoms SerotoninDocument1 pageDepression: Symptoms SerotoninFatma ZorluNo ratings yet
- Neurotranssmitter Dan Efek Pada Organ ManusiaDocument3 pagesNeurotranssmitter Dan Efek Pada Organ ManusiaPANI78No ratings yet
- Psycho 1Document43 pagesPsycho 1Belia Bima NafisaNo ratings yet
- Paychiatric NursingDocument7 pagesPaychiatric NursingJe Carmel Marie ElentorioNo ratings yet
- Psycho Pa ThoDocument9 pagesPsycho Pa ThoJayrald RosalesNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Science Lecture 2Document34 pagesBehavioral Science Lecture 2Natia BadridzeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antidepressants: PHCL411Document76 pagesPharmacology of Antidepressants: PHCL411Mustapha ImadudeenNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorDocument3 pagesImbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorInah100% (1)
- Lecture 2 (Psychotropic Drugs)Document17 pagesLecture 2 (Psychotropic Drugs)ahmadslayman1No ratings yet
- The Affective DisordersDocument22 pagesThe Affective DisordersMUHD SUHAILNo ratings yet
- 7) 5th Semester - Depression & Affective DisordersDocument33 pages7) 5th Semester - Depression & Affective DisordersFizza ImamNo ratings yet
- Clinical ToxicologyDocument6 pagesClinical ToxicologyGrace MarinoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Klengel, T. - 2015Document15 pages2 - Klengel, T. - 2015João PedroNo ratings yet
- Mouse Party LabDocument4 pagesMouse Party LabEvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainDocument9 pagesChapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainciaraNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Bio Asmuni CutDocument40 pagesWeek 3 Bio Asmuni CutNavanisha SekarNo ratings yet
- Anti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCDocument17 pagesAnti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCÑiťhišh Śhankąŕ LóganáthánNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument171 pagesPsychopharmacologyVaib NigamNo ratings yet
- PSYCHDocument2 pagesPSYCHJacquelyn HasiandaNo ratings yet
- Psychoneuro-Endocrinology, Psychoneuro-Immunology, and ChronobiologyDocument2 pagesPsychoneuro-Endocrinology, Psychoneuro-Immunology, and ChronobiologyMark LopezNo ratings yet
- Sistema EndocrinoDocument18 pagesSistema Endocrinoanaelmoreira80No ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument12 pagesNeurotransmittersRahul DamorNo ratings yet
- Anti PsychoticDocument38 pagesAnti PsychoticAsep Cece IrhamNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters Cuadro PDFDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitters Cuadro PDFCarina Castillo ValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Ch2neurotrans PDFDocument2 pagesCh2neurotrans PDFKentNo ratings yet
- JOEY - S PHARM LECTURES - Neuro pg1-8Document9 pagesJOEY - S PHARM LECTURES - Neuro pg1-8shivani patelNo ratings yet
- Depressive-Disorders SheetDocument2 pagesDepressive-Disorders SheetCrystal MarloweNo ratings yet
- CNS Pathophysiology - Psychiatric DisorderDocument11 pagesCNS Pathophysiology - Psychiatric DisordersuereyaNo ratings yet
- Mood DisorderDocument22 pagesMood Disorderjosephvincent2001No ratings yet
- Presentation NeuronDocument7 pagesPresentation Neuronsuweino_harunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Brain and BehaviourDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Brain and Behaviour038 Suri HananNo ratings yet
- Depressive DisordersDocument3 pagesDepressive Disordersnguyenlmchau169No ratings yet
- 2 Ligan First MassengerDocument32 pages2 Ligan First MassengerikhararaNo ratings yet
- Depression EBDocument2 pagesDepression EBalfonsougarteNo ratings yet
- ?antidepressantsDocument1 page?antidepressantsKarma iiiNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants DrugsDocument2 pagesAntidepressants DrugsSony Montaño CañeteNo ratings yet
- Stress Related To Nutritional ImbalancesDocument3 pagesStress Related To Nutritional ImbalancesSam PothNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Moa (Side Effects)Document1 pageAntidepressant Moa (Side Effects)graceNo ratings yet
- Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria PDFDocument5 pagesHunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria PDFSabri VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Substance Hallucinogens and Dissociatives - CompressedDocument39 pagesPsychotropic Substance Hallucinogens and Dissociatives - CompressedshuyuichewNo ratings yet
- Monoamine NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageMonoamine NeurotransmittersBharath CNo ratings yet
- Anti DepressentsDocument2 pagesAnti DepressentsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Depressive EpisodeDocument33 pagesDepressive EpisodeKp ANo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AntidepressantsDocument28 pagesPharmacology of Antidepressantsحيدر كريم سعيد حمزهNo ratings yet
- Dissanayake (2015) - The Physiology of Pain - An Update and Review of Clinical Relevance PDFDocument5 pagesDissanayake (2015) - The Physiology of Pain - An Update and Review of Clinical Relevance PDFnamirohsamiyahNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Antidepressents 2020Document21 pagesClass 1 Antidepressents 2020Arafat 039No ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs in Dermatology: FR-Utilización de Psicofármacos en DermatologíaDocument3 pagesPsychotropic Drugs in Dermatology: FR-Utilización de Psicofármacos en DermatologíaNilson Morales CordobaNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Document2 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Prince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- Changes of Immune System in DepressionDocument2 pagesChanges of Immune System in DepressionfarahNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of ParkinsonDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Parkinsoncuriosity_killsNo ratings yet
- Antipsycotic DrugDocument21 pagesAntipsycotic DrugShashank SatheNo ratings yet
- AMITRIPTYLINEDocument1 pageAMITRIPTYLINERicky Ramos Jr.No ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology in Psychopharmacology in Psychiatry PsychiatryDocument16 pagesPsychopharmacology in Psychopharmacology in Psychiatry PsychiatryHasnain HyderNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Powerpoint Group 1Document38 pagesPharmacology Powerpoint Group 1Daniel LaurenteNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument57 pagesCNS DrugsHussein Al-jmrawiNo ratings yet
- Current Concept For Management of Neuropathic PainDocument55 pagesCurrent Concept For Management of Neuropathic Painmpm8471No ratings yet
- 9 Reasons You Should Eat Dark Chocolate Every Single DayDocument2 pages9 Reasons You Should Eat Dark Chocolate Every Single DaySheilla GanironNo ratings yet
- (Tamtam) Hiperglikemia, Hipoglikemia, Hiperosmolar Asidosis Non KetotikDocument23 pages(Tamtam) Hiperglikemia, Hipoglikemia, Hiperosmolar Asidosis Non KetotikkynatroemanNo ratings yet
- 10-Nutritional Considerations in Joint HealthDocument18 pages10-Nutritional Considerations in Joint Healthapi-3851239No ratings yet
- NIMHANS ProformaDocument13 pagesNIMHANS ProformaMATHANKUMAR ENo ratings yet
- DS - Senna ConcentrateDocument7 pagesDS - Senna ConcentrateFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- Per System PreferablyDocument3 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument27 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Medical MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesWeek 15 Medical MicrobiologyRuth Ivo Maria TampuboLonNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)Document15 pagesMultiple Sclerosis (MS)Arianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Out of Step by Arnold LeeseDocument50 pagesOut of Step by Arnold Leesealfred rosenbergNo ratings yet
- Garp-Nepal - Sa (Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership)Document90 pagesGarp-Nepal - Sa (Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership)Nivea VazNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase StudyArthur Brian100% (1)
- Psych Topiccompanion Schizophrenia SampleDocument4 pagesPsych Topiccompanion Schizophrenia SampleQueen Bee (Tt)100% (1)
- Fermented Foods and Food Safety: ArticleDocument9 pagesFermented Foods and Food Safety: ArticlesimurabiyeNo ratings yet
- Report Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesReport Tetralogy of FallotLieana AguilarNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Emotions: Redirecting Self-Therapy (RST) For Anxiety and DepressionDocument4 pagesThe Biology of Emotions: Redirecting Self-Therapy (RST) For Anxiety and DepressionoscarnineNo ratings yet
- Fire in The Blood Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesFire in The Blood Reflection PaperWIlfredo MirasolNo ratings yet
- EXAM Med Surg 1Document9 pagesEXAM Med Surg 1Gailstar GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Pathology For The Health Professions 4Th Edition Damjanov Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument20 pagesPathology For The Health Professions 4Th Edition Damjanov Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcrastzfeiej100% (12)
- Clinically Isolated Syndrome and Early Relapsing Multiple SclerosisDocument19 pagesClinically Isolated Syndrome and Early Relapsing Multiple Sclerosisnight.shadowNo ratings yet
- Consumer Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards The Use of Monosodium Glutamate and Food Grade Bullion Cubes As Dietary ConstituentsDocument5 pagesConsumer Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards The Use of Monosodium Glutamate and Food Grade Bullion Cubes As Dietary ConstituentsDeEpaa ManohanNo ratings yet
- Thesis 3Document41 pagesThesis 3Kundan dipNo ratings yet
- Allergy: Drug Reaction ClassificationDocument6 pagesAllergy: Drug Reaction ClassificationMatthieu FortinNo ratings yet
- NAMI YouAreNotAlone 2020Document1 pageNAMI YouAreNotAlone 2020inforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Myco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedDocument10 pagesMyco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- Aspectos Importantes de La Nutrición en Niños Con CáncerDocument11 pagesAspectos Importantes de La Nutrición en Niños Con CáncerNadia DonosoNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Submitted To: Application For The Registration of Subjects For Dissertation of TheDocument14 pagesSynopsis Submitted To: Application For The Registration of Subjects For Dissertation of TheAraafathNo ratings yet
- IMNCI - 6th SemDocument32 pagesIMNCI - 6th SemAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and ObesityDocument39 pagesAnesthesia and ObesityLucille IlaganNo ratings yet