Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8085 Micro Configuration
8085 Micro Configuration
Uploaded by
venuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8085 Micro Configuration
8085 Micro Configuration
Uploaded by
venuCopyright:
Available Formats
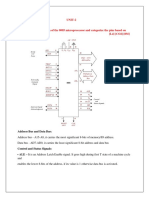
8085 Microprocessor Pin Configuration
The 40 pins of the microprocessor can be divided into six groups such as address bus, data bus, control &
status signals; power supply & frequency, externally started signals and serial input/output ports.
8085 Microprocessor pin Configuration
Address Bus (A8-A15)
The address bus pins are ranges from A8 to A15 and these are mainly applicable to the most considerable
memory address bit.
Address Bus (or) Data Bus (AD0-AD7)
The address bus pins or data bus pins are ranges from AD0 to AD7, and these pins are applicable for LSB
(least significant bits) of the address bus in the primary apparatus CLK cycle as well as employed as a data
bus for second clock cycle & third clock cycle.
A CLK cycle can be designed as, the time in use among two oscillator’s nearby pulses, or simply it can refer
to zero volts. Here the first clock is the primary transition of pulse ranges from 0V to 5V & then reaches
back to 0V.
Address Latch Enable (ALE)
Basically, ALE assists in de-multiplexing the data bus as well as low order address. This will go high
throughout the primary clock cycle as well as allows the address bits with low order. The address bus with
low order is added for memory otherwise any exterior latch.
Status Signal (IO/M)
The status signal IO/M resolves whether the address is intended for memory or input/output. When the
address is high then the address of the address bus is used for the devices of input/output devices. When
the address is low then the address of the address bus is used for the memory.
Status Signals (S0-S1)
The status signals S0, S1 gives different functions as well as status based on their status.
• When the S0, S1 are 01 then the operation will be HALT.
• the S0, S1 is 10 then the operation will be WRITE
• When the S0, S1 is 10 then the operation will be READ
• When the S0, S1 are 11 then the operation will be FETCH
Active Low Signal (RD)
The RD is an energetic low signal and an operation is executed whenever the indication goes small, and it
is used for controlling the microprocessor READ operation. When RD pin goes small then the 8085
microprocessor understands the information from I/O device or memory.
Active Low Signal (WR)
This is an energetic low signal, and it controls the microprocessor’s write operations. Whenever WR pin
goes small, then the information will be written to the I/O device or memory.
READY
The READY pin is employed with the 8085 microprocessor for ensuring whether a device is set for
accepting or transferring data. A device may be an A/D converter or LCD display, etc. These devices are
associated with the 8085 microprocessor with the READY-pin. When this pin is high, the device is prepared
for transferring the information, if it is not then the microprocessor stays until this pin goes high.
HOLD
The HOLD pin specifies when any device is demanding the employ of address as well as a data bus. The two
devices are LCD as well as A/D converter. Assume that if A/D converter is employing the address bus as
well as a data bus. When LCD desires the utilize of both the buses by providing HOLD signal, subsequently
the microprocessor transmits the control signal toward the LCD after that the existing cycle will be ended.
When the LCD procedure is over, then the control signal is transmitted reverse to A/D converter.
HLDA
This is the response signal of HOLD, and it specifies whether this signal is obtained or not obtained. After
the implementation of HOLD demand, this signal will go low.
INTR
This is an interrupt signal, and the priority of this among the interrupts is low. This signal can be allowed
or not allowed by the software. When INTR pin goes high then the 8085 microprocessor completes the
instruction of current which is being executed and then recognizes the INTR signal and progresses it.
INTA
When the 8085 microprocessor gets an interrupt signal, then it should be recognized. This will be done by
INTA. As a result, when the interrupt will be obtained then INTA will go high.
RST 5.5, RST 6.5, RST 7.5
These pins are the restart maskable interrupts or Vectored Interrupts, used to insert an inner restart
function repeatedly. All these interrupts are maskable, they can be allowed or not allowed by using
programs.
TRAP
Along with the 8085 microprocessor interrupts, TRAP is a non-maskable interrupt, and it doesn’t allow
or stopped by a program. TRAP has the maximum precedence between the interrupts. The priority order
from maximum to low includes TRAP, RST 5.5, RST 6.5, RST 7.5, and INTR.
RESET IN
RESET IN pin is used to reset the program counter toward zero and rearranges interrupt enable as well as
HLDA flip-flops (FFs). The central processing unit is detained in RST condition till this pin is high. But the
registers as well as flags won’t get damaged apart from instruction register.
RST (RESET) OUT
RESET OUT pin specifies that the central processing unit has been rearranged with RST IN.
X1 X2
X1, X2 terminals that are associated with the exterior oscillator for generating the required as well as
appropriate operation of a clock.
CLK
Sometimes it is compulsory to generate CLK o/PS from 8085 microprocessors so they can be used in favor
of other peripherals or else other digital integrated circuits. This is offered with CLK pin. Its frequency is
continually similar because the frequency at which the microprocessor works.
SID
This is a serial i/p data, and the information on this pin is uploaded into the 7th-bit of the accumulator
while RIM (Read Interrupt Mask) instruction is performed. RIM verifies the interrupt whether it is covered
or not covered.
SOD
This is the serial o/p data, and the data on this pin sends its output toward the 7th-bit of the accumulator
whenever an instruction of SIM is performed.
VSS and VCC
VSS is a ground pin whereas Vcc is +5v pin.
You might also like
- Template NIST800-30 - Table I-5 Dan I-7 - Adversarial Dan Non-AdversarialDocument22 pagesTemplate NIST800-30 - Table I-5 Dan I-7 - Adversarial Dan Non-AdversarialNovra YunandaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank ItcDocument14 pagesQuestion Bank ItcVenu Madhav ChittaNo ratings yet
- Risabh Tyagi Rithik PrakashDocument16 pagesRisabh Tyagi Rithik PrakashSuryadev Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- 02 The 8085 MicroprocessorDocument27 pages02 The 8085 MicroprocessorSheena Ann StonehillNo ratings yet
- 8085 Pin Diagram and ArchitectureDocument8 pages8085 Pin Diagram and ArchitectureSneha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (1) Draw and Explain The Internal Architecture of 8085Document11 pagesUnit-1 (1) Draw and Explain The Internal Architecture of 8085Mann MehtaNo ratings yet
- Pin Diagram of MPU 8085Document4 pagesPin Diagram of MPU 8085Pankaj BelgaonkarNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument20 pages8085 Microprocessorrannvijay12345No ratings yet
- CS 208 2-2-8085 Microprocessor Signals and Their Functions by BaldevDocument12 pagesCS 208 2-2-8085 Microprocessor Signals and Their Functions by BaldevINFINITY GAmErNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document35 pagesChapter 3ajayroyNo ratings yet
- Pin Description and Signals of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument9 pagesPin Description and Signals of 8085 MicroprocessorKripanand JhaNo ratings yet
- MC8085Document7 pagesMC8085Bhavani BhavanNo ratings yet
- MIC 04 - Case Study One 8085 MPUDocument40 pagesMIC 04 - Case Study One 8085 MPUomar hanyNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 Architecture: AccumulatorDocument6 pagesIntel 8085 Architecture: AccumulatorDipesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 8086 System Bus Structures FullunitDocument36 pagesUnit 2 8086 System Bus Structures Fullunitlauro eugin brittoNo ratings yet
- Pin DaigramDocument3 pagesPin Daigramrathavachirag921No ratings yet
- Microprocess ArchitectureDocument24 pagesMicroprocess ArchitectureNew worldNo ratings yet
- Lecture1423722820 PDFDocument101 pagesLecture1423722820 PDFdavNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument29 pagesMicroprocessorArnab RayNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 1Document25 pagesNotes Unit 1Ashish YadavNo ratings yet
- 8085 Features, Signal DescriptionDocument13 pages8085 Features, Signal DescriptionRakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- EE6502 MPMC Two Marks With AnswerDocument10 pagesEE6502 MPMC Two Marks With Answervlsimani9110100% (1)
- DatasheetDocument16 pagesDatasheetAmmu PuniNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor and Its SignalsDocument3 pages8085 Microprocessor and Its SignalsArchana TiwariNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor Architecture, Pin DiagramDocument10 pages8085 Microprocessor Architecture, Pin DiagramSachin Jaysenan0% (1)
- 8085 MaterialDocument12 pages8085 MaterialsameerNo ratings yet
- Intro To 8085Document43 pagesIntro To 8085Elisha NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Intro To 8085Document23 pagesIntro To 8085Vivek KumarNo ratings yet
- The 8085 Microprocessor Architecture: Dr. Kuda Nageswara RaoDocument32 pagesThe 8085 Microprocessor Architecture: Dr. Kuda Nageswara RaoKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- L4 - 8085 ArchitectureDocument24 pagesL4 - 8085 ArchitectureHabirah Mahmood MutanganaNo ratings yet
- Unit I PDFDocument25 pagesUnit I PDFSomnath2014No ratings yet
- C5 - Intro To 8085 - Hardware PDFDocument39 pagesC5 - Intro To 8085 - Hardware PDFsiti hajarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 FinalDocument31 pagesUnit 2 Finalswetha bagadi it's good but how it will workNo ratings yet
- MPDocument34 pagesMPAbhinandan JainNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Ramesh S GaonkarDocument25 pagesMicroprocessor Ramesh S GaonkarAbraiz Khan KhattakNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDocument5 pages8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDeep KambleNo ratings yet
- Pin Diagram of 8086 MicroprocessorDocument14 pagesPin Diagram of 8086 Microprocessorkranthi6190No ratings yet
- Syllabus: 8085 ArchitectureDocument25 pagesSyllabus: 8085 Architecturetamilvendhan87No ratings yet
- Hardware Architecture of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument16 pagesHardware Architecture of 8085 MicroprocessorCsNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication: INTEL 8085 MicroprocessorDocument20 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication: INTEL 8085 MicroprocessorVikrant DabralNo ratings yet
- 8085 Architecture & Pin DescriptionFileDocument19 pages8085 Architecture & Pin DescriptionFileKaseya TakahashiNo ratings yet
- 8085 Is Pronounced AsDocument9 pages8085 Is Pronounced AsArbaaz khan786No ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 Internal ArchitectureDocument25 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 Internal ArchitectureTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Overview or Features of 8086: It Is A 16-Bit MicroprocessorDocument33 pagesOverview or Features of 8086: It Is A 16-Bit MicroprocessorSamuel KuantumNo ratings yet
- 8085 Pin DiagramDocument4 pages8085 Pin Diagrammohan babuNo ratings yet
- 8085 1Document17 pages8085 1Amar GhogaleNo ratings yet
- MPMC Model Exam Answer KeyDocument21 pagesMPMC Model Exam Answer KeyVenkatesan SundaramNo ratings yet
- Mic Unit 1. SelfDocument21 pagesMic Unit 1. SelfPragati DagaleNo ratings yet
- Poriyaan 1cmfA62QmpEUSssZeK 4a3Lq-KUrzO1jADocument171 pagesPoriyaan 1cmfA62QmpEUSssZeK 4a3Lq-KUrzO1jAS. GobikaNo ratings yet
- Chap2!4!8085 Architecture and InstructionsDocument61 pagesChap2!4!8085 Architecture and Instructionsshyam bkNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Microprocessor Architecture Using 8085 As A Classic ProcessorDocument24 pagesAn Introduction To Microprocessor Architecture Using 8085 As A Classic ProcessorArnold JohnNo ratings yet
- PIN Diagram of Intel 8085 Microprocessor - Lecture 3Document14 pagesPIN Diagram of Intel 8085 Microprocessor - Lecture 3ojasbhosale07No ratings yet
- MP4 - Registers, Pin ConfigurationsDocument11 pagesMP4 - Registers, Pin ConfigurationsGAMING BUDDYNo ratings yet
- 8086 FullDocument72 pages8086 FullNandhini Nachiyar100% (4)
- Questionnaire MICROPROCESSOR PART 1 UNIT 1 and 2Document20 pagesQuestionnaire MICROPROCESSOR PART 1 UNIT 1 and 2aditya2021cs081No ratings yet
- System BusDocument20 pagesSystem BusshyamNo ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument2 pagesObjectiveram lakhanNo ratings yet
- Cs2 Practical PDFDocument62 pagesCs2 Practical PDFMaitri ShahNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Artigo Seminario Internacional UNISC 2011 PDFDocument281 pagesArtigo Seminario Internacional UNISC 2011 PDFMarcio FloresNo ratings yet
- 1Document9 pages1Kavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- HPE Ipsec TroubleshootingDocument23 pagesHPE Ipsec TroubleshootingchellahariharanNo ratings yet
- Events and Entertainment IndustryDocument6 pagesEvents and Entertainment IndustryShreyansh KhichaNo ratings yet
- MP1700 Install Manual enDocument49 pagesMP1700 Install Manual enYadi RudiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lan TechnologyDocument11 pagesVirtual Lan TechnologyrishabhNo ratings yet
- LTE Advanced Relaying Standard: A Survey: Wireless Personal Communications October 2013Document16 pagesLTE Advanced Relaying Standard: A Survey: Wireless Personal Communications October 2013bassam el alyNo ratings yet
- Ytmp3 Digital, Safe Fast YouTube mp3 Converter (Ytmp3Document2 pagesYtmp3 Digital, Safe Fast YouTube mp3 Converter (Ytmp3Neon. CatNo ratings yet
- TL WR940N (EU) 6.0 Datasheet PDFDocument5 pagesTL WR940N (EU) 6.0 Datasheet PDFYusuf J. KuproyNo ratings yet
- Basic LED TV TH 24F305GDocument3 pagesBasic LED TV TH 24F305GAndika TriandaNo ratings yet
- User Manual Tronsmart t6 Pro Bluetooth SpeakerDocument16 pagesUser Manual Tronsmart t6 Pro Bluetooth Speakersamir yayaNo ratings yet
- PS 3200Document2 pagesPS 3200Alfian KamilNo ratings yet
- Slides.01 Distributed SystemDocument87 pagesSlides.01 Distributed SystemSusu MelodyNo ratings yet
- 200-PABX Alphatron AlphaConnect 48-128-Classic TechSpec Manual FIO4 1-1-2016Document5 pages200-PABX Alphatron AlphaConnect 48-128-Classic TechSpec Manual FIO4 1-1-2016quan vuNo ratings yet
- Size Type Brand Series Model Products Supported: ST1000VX005Document5 pagesSize Type Brand Series Model Products Supported: ST1000VX005Carlos HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Defense Information Systems Agency P. O. Box 549 Fort Meade, Maryland Joint Interoperability Test Command (Jte) 31 May 12Document46 pagesDefense Information Systems Agency P. O. Box 549 Fort Meade, Maryland Joint Interoperability Test Command (Jte) 31 May 12Eder Ollora ZaballaNo ratings yet
- SHS 1 Lesson 2 - Information Processing CycleDocument25 pagesSHS 1 Lesson 2 - Information Processing CycleMartinson AppiahNo ratings yet
- IT 601: Mobile Computing: Session 1Document15 pagesIT 601: Mobile Computing: Session 1SteffyRobertNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Router MemoryDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Router Memorydash huntersNo ratings yet
- Compact, High-Performance 1U GPON OLTDocument4 pagesCompact, High-Performance 1U GPON OLTrazvanbarbulescuNo ratings yet
- Multicast Impelementations Case Study PDFDocument5 pagesMulticast Impelementations Case Study PDFOmer GNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 A - Mobile ComputingDocument64 pagesChapter - 1 A - Mobile ComputingOz GNo ratings yet
- HkixDocument28 pagesHkixMrbuy SellNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Source Coding Made EasyDocument155 pagesRadio Frequency Source Coding Made EasyChristopher AiyapiNo ratings yet
- A Survey On FEC Codes For 100G and BeyonDocument15 pagesA Survey On FEC Codes For 100G and BeyonnghtlghtNo ratings yet
- 01 Data Communication Network BasisDocument35 pages01 Data Communication Network BasisQuality ScholarNo ratings yet
- PTT Mpls PSTN Vsat DSLDocument5 pagesPTT Mpls PSTN Vsat DSLAndy TenorioNo ratings yet
- 21 SFX 10 FDocument91 pages21 SFX 10 FWasantha MunasingheNo ratings yet