Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ElectricianSemIICITSQB PDF
ElectricianSemIICITSQB PDF
Uploaded by
marvin2008Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ElectricianSemIICITSQB PDF
ElectricianSemIICITSQB PDF
Uploaded by
marvin2008Copyright:
Available Formats
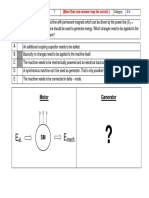
Electrician - Semester II - CITS -
Module 1: Three Phase and Single Phase Induction Motor
Questions: Level 1 4 What is the formula to calculate synchronous
speed of a A.C 3 phase induction motor?
1 What is the formula to calculate the slip 120F
A Synchronous speed =
speed (Nslip) of 3 phase squirrel cage P
induction motor? 120P
A Nslip = Ns - Nr B Synchronous speed =
F
B Nslip = Nr - Ns
120
N −N C Synchronous speed =
C Nslip = s r PF
Nr
PF
N −N D Synchronous speed =
D Nslip = s r 120
Ns 5 What is the fuse rate to run a 10 HP three
2 What is the type of control circuit? phase induction motor at full load?
A 10 A
B 15 A
C 25 A
D 30 A
6 What is the name of the contact marked ‘X’?
A Inching control
B ON remote control
C OFF remote control
X
D Forward & reverse control
3 What is the name of the A.C motor starter?
A Star contact
B Delta contact
C Auxiliary contact
D Over load relay contact
7 Which formula is used to calculate
percentage slip of an AC 3 phase induction
motor?
N − Nr
A %S= s x 100
Ns
Nr − Ns
B %S= x 100
Ns
Ns − Nr
C %S = x 100
A DOL starter Nr
B Auto transformer starter Nr − Ns
C Semi automatic star delta starter D %S = x 100
Nr
D Fully automatic star delta starter
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 10
8 Which operation the control circuit is used? 13 What is the working principle of single phase
induction motor?
A Lenz’s law
B Joule’s law
C Faraday’s laws of electrolysis
D Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction
14 What is the name of single phase motor?
A Remote control
B Jogging/Inching
C Sequential control
D Forward and reverse
9 What is the name of the part marked ‘X’?
A Permanent capacitor motor
B Induction start capacitor run motor
C Capacitor start capacitor run motor
D Capacitor start induction run motor
15 What is the name of single phase motor?
A Shaft
B Brushes
C Bearings
D Slip rings
10 Which speed is called as synchronous speed
in 3 phase induction motor?
A No load speed A Universal motor
B Full load speed B Permanent capacitor motor
C Rotating magnetic field speed C Capacitor start induction run motor
D Relative speed between stator and rotor D Capacitor start capacitor run motor
11 What is the name of the starter symbol? 16 Which is the application of universal motor?
A Jet pump
B Food mixer
C Teleprinter
D Compressor
17 Which single phase motor is fitted with
A D.O.L starter
wound rotor?
B Auto transformer starter
A Repulsion motors
C Automatic star/delta starter
B Shaded pole motors
D Semi automatic star/delta starter
C Permanent capacitor motors
12 What is the name of the starter symbol? D Capacitor start capacitor run motors
18 Which type of single phase induction motor
is used in food mixer?
A Universal motor
B Repulsion motor
C Shaded pole motor
A Star delta starter
D Permanent capacitor motor
B Rheostatic starter
C Direct on-line starter
D Autotransformer starter
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 10
19 Which motor is used in table fan?
A Universal motor
B Shaded pole motor
C Eddy current motor
D Permanent capacitor motor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 10
Questions: Level 2 8 Which motor is used to provide high starting
torque at variable speed?
1 What is the synchronous speed of a A.C 3 A Universal motor
phase induction motor having 6 poles at a B Permanent capacitor motor
frequency of 50 Hertz? C 3 Phase slip ring induction motor
A 800 rpm D 3 Phase single squirrel cage induction motor
B 1000 rpm 9 What is the relation between torque and slip
C 1200 rpm in an A.C induction motor?
D 1440 rpm A Slip increases torque decreases
2 Calculate the percentage slip in a 3 phase B Slip increases torque increases
induction motor having 6 poles with a C Slip decreases torque increases
frequency of 50 Hertz rotating with actual D Slip decreases torque decreases
speed of 960 rpm? 10 Why the rotor bars are mounted in a slightly
A 2% skewed position in 3 phase motor?
B 3%
C 4%
D 5%
3 What is the rotor frequency of a 3 phase
squirrel cage induction motor at the time of A Generate maximum flux
starting? B Reduce the stray losses
A Equal to supply frequency C Maintain the rotor speed constant
B 3 times less than supply frequency D Produce more uniform rotor field and torque
C 3 times more than supply frequency 11 Which loss is determined by no load test of 3
D times less than supply frequency phase induction motor?
4 How the voltage is received in the rotor of A Iron loss
induction motor? B Copper loss
A Direct connection from stator C Friction loss
B Due to back emf produced in stator D Windage loss
C Direct connection to rotor from supply
12 Which method of speed control two variable
D By the transformer action of stator and rotor
speeds only obtained in 3 phase motor?
5 Which method is applied to control the speed A By rotor rheostat control
of 3 phase squirrel cage induction motor B By changing applied frequency
from its rotor side? C By changing the applied voltage
A Cascade operation D By changing the number of stator poles
B Changing applied voltage
13 Why slip ring induction motor is fitted with
C Changing applied frequency
wound rotor?
D Changing the number of poles
A To reduce the slip
6 Which loss of 3 phase induction motor is B To control the speed
determined by blocked rotor test? C To reduce the losses
A Copper loss D To get high starting and running torque
B Friction loss 14 What is the function of timer in automatic star
C Hysteresis loss delta starter?
D Eddy current loss A Trip at over load
7 What is the purpose of using thermal cutout B Switch ON at pre set time
in addition to fuse in A.C motor circuit? C Change from star to delta
A Protect from heavy load D Switch OFF at pre set time
B Protect against high voltage
C Allow for continuous over loading
D Protect against dead short circuit
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 10
15 Which instrument is used to measure 22 Determine the torque in newton metres
insulation resistance of a 3 phase induction produced by a 7.5 HP squirrel cage motor
motor? rotating at 1440 rpm?
A Megger A 21.63 Nm
B Multimeter B 24.4 Nm
C Shunt type ohmmeter C 33.05 Nm
D Series type ohmmeter D 36.6 Nm
16 What is the starting current of an A.C 3 23 Which type of handle design of rotary switch
phase induction motor? is illustrated?
A 1 to 2 times of full load current
B 2 to 3 times of full load current
C 4 to 5 times of full load current
D 5 to 6 times of full load current
17 Which method is used to control the speed of
3 phase induction motor from stator side?
A By cascade operation
A Knob
B By rotor rheostat control
B Lever
C By injecting emf in rotor circuit
C Coin slot
D By changing the applied frequency
D Key operation
18 What is the speed control method of 3 phase
24 What is the purpose of using rotor resistance
induction motor?
starter to start 3 phase slip ring induction
motor?
A Reduce rotor voltage
B Reduce rotor current
C Increase the torque
D Reduce the power loss
25 Which method of speed control is only
A Cascade operation method applicable for 3 phase slipring induction
B Rotor rheostat control method motor?
C Changing applied voltage method A Cascade operation method
D Injecting emf in rotor circuit method B Rotor rheostat speed control
19 What are the two functional circuits C Changing the applied frequency method
incorporated with a three phase motor D Changing the number of stator poles method
starter? 26 Which type of A.C single phase motor is
A Open circuit and short circuit classified under commutator motor type?
B Closed circuit and open circuit A Stepper motor
C Short circuit and closed circuits B Repulsion motor
D Control circuit and power circuit C Shaded pole motor
20 Which type of starter is used to start and run D Permanent capacitor motor
the 3 phase slip ring induction motor? 27 Which method is adopted to start the single
A Direct on-line starter phase induction motor?
B Rotor rheostat starter A Split phase method
C Auto transformer starter B Varying supply voltage method
D Manual star-delta starter C Reversal of input supply terminals
21 Where the panel boards are used? D Reversal of running coil connection
A Industrial motor drives
B Single phase domestic wiring circuits
C 3 phase domestic wiring
D Load distribution for AC & DC supply
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 10
28 What is the type of A.C single phase motor? 33 What is the function of the part marked ‘x’ in
shaded pole motor?
A Permanent capacitor motor
B Capacitor start capacitor run motor A Increase the efficiency
C Induction start induction run motor B Maintain constant speed
D Capacitor start induction run motor C Initiate the rotor movement
29 What is the purpose of the capacitor (C) in D Strengthen the magnetic field
centrifugal switch speed control method of 34 How the direction of rotation of a capacitor
universal motor? start induction run motor is reversed?
A By changing the supply terminals
B By changing the capacitor connections
C By interchanging main winding terminals
D By interchanging both main and auxiliary
winding terminals
A Maintain constant speed 35 Which single phase motor tapped field speed
B Improve the power factor control method is employed?
C Protect from the over loading A Universal motor
D Reduce the sparks on the contacts B Shaded pole motor
30 Which type of AC single phase motor having C Capacitor start induction run motor
low starting torque? D Capacitor start capacitor run motor
A Induction start induction run motor 36 What is the angular displacement between
B Capacitor start induction run motor starting and running winding of a single
C Capacitor start capacitor run motor phase induction motor?
D Resistance start induction run motor A 45 electrical degree
31 What is the function of centrifugal switch in B 60 electrical degree
single phase motors? C 90 electrical degree
A Maintain constant speed D 120 electrical degree
B Break the starting winding 37 Why the hysteresis motor is suitable for
C Break the running winding sound recording instruments?
D Protect the motor from over loading A Small in size
32 What is the relation between running winding B High efficiency
and starting winding of a single phase C Noiseless operation
induction motor with respect to resistance? D Less error operation
A Both resistances will be equal 38 Which motor is preferred for domestic water
B Running winding is less, starting winding pumps?
more A Universal Motor
C Running winding is more, starting winding B Repulsion motor
less C Shaded pole motor
D Running winding is less, starting winding D Capacitor start motor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 10
39 How to produce starting torque in a shaded 46 What is the effect of A.C induction motor if
pole fan motor? rotor bar is open circuited?
A Using rings on poles A Vibration of shaft
B Using capacitor on winding circuits B Motor will not start
C Interchanging cage rotor windings by switch C Runs in slow speed
D Interchanging the field coil windings by D Over heating of motor
switch 47 Which type of AC induction motor is used in
40 What is the reason to use a permanent textile mills ?
capacitor in fan motor circuit? A Slip ring induction motor
A Speed regulation B Deepcut bar induction motor
B Lower power consumption C Single squirrel cage induction motor
C Splitting of phase for torque D Double squirrel cage induction motor
D Controlling electrical interference 48 Which type of motor takes higher starting
41 Why running winding is placed in the bottom current and works at low power factor?
of the core? A Repulsion motor
A To get low resistance B Permanent capacitor motor
B To get low inductance C Induction start, induction run motor
C To get high resistance D Capacitor start, capacitor run motor
D To get high inductance 49 Which type of motor is used for fax
42 What is the application of shaded pole machines?
motor? A Stepper motor
A Hair dryer B Universal motor
B Ceiling fan C Repulsion motor
C Wet grinder D Hysteresis motor
D Washing machine 50 Which single phase motor has higher power
43 Which type of single phase motor is used for factor?
hard disk drives? A Universal motor
A Stepper motor B Split phase motor
B Repulsion motor C Shaded pole motor
C Hysteresis motor D Capacitor start induction run motor
D Reluctance motor
44 What is the function of centrifugal switch
used in capacitor start, capacitor run
induction motor?
A Disconnect the running winding after
reached 75% to 80% speed
B Disconnect the starting winding after reached
75% to 80% speed
C Disconnect the starting capacitor after
reached 75% to 80% speed
D Disconnect the starting and running winding
after reached 75% to 80% speed
45 Which type of single phase motor is having
very high starting torque than any other type
of single phase motor?
A Universal motor
B Reluctance motor
C Repulsion start induction run motor
D Capacitor start induction run motor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 10
Questions: Level 3 8 What is the effect of open circuit in rotor of
an induction motor?
1 Why external resistance is included in the A Motor does not start
rotor circuit at starting through 3 phase B Over heating in motor
slipring induction motor starter? C Excess vibration of shaft
A To get high running torque D Motor runs with very low speed
B To get high starting torque 9 What is the reason for frequent blowing of
C To reduce the load current fuse after motor running some time?
D To get increased speed at starting A Improper earthing
2 What is the effect of motor, if the rotor B Over loading of motor
windings in slipring induction motor is open C Heavy voltage fluctuation
circuited at starting? D Poor insulation in winding
A Will not run 10 What happens to a 3 phase induction motor,
B Runs at slow speed if one phase fails during starting?
C Runs at very high speed A Motor runs and stop immediately
D Runs but not able to pull load B Motor runs in slow speed continuously
3 What is the effect on 3 phase induction C Motor runs and draws more current
motor if one phase is cut-off during running D Motor continues to run with irregular speed
with load? 11 Which is the cause for the 3 phase motor
A Motor stops at once starter with single phase preventer trips
B Motor will run normally frequently?
C Motor runs with humming noise with slow A Incorrect fuse ratings
speed B Unbalanced line voltages
D Motor will run slow speed but winding will be C Incorrect settings of OLR
burnt out shortly D Improper phase sequence
4 What is the defect if starter with single 12 Where the capacitor is connected in a single
phasing preventer does not switch ‘ON’? phase permanent capacitor motor?
A Improper phase sequence A In series with starting winding
B Fluctuations in line voltage B In series with running winding
C Loose contact in supply lines C In parallel with starting winding
D Wrong terminal connections at motor D In parallel with running winding
5 What is the defect in AC 3 phase induction 13 What is the effect in a repulsion motor, if the
motor runs at low speed if loaded? magnetic axis shifted to another side?
A Wrong motor connection
B Wrong starter connection
C Open circuit in rotor winding
D Partially shorted in stator winding
6 Which fault condition thermal overload relay
protects A.C induction motor?
A Short circuit
B Open circuit
C Over current
D Under voltage
7 What happens to the rotor of a 3 phase A Direction of rotation will change
induction motor if its speed attains to B Direction of rotation remains same
synchronous speed? C Motor speed increases from rated speed
A Rotor speed reduces D Motor speed will reduce from rated speed
B Rotor speed increases
C Rotor speed remains same
D Rotor bars get damaged
- NIMI Question Bank - Page8/ 10
14 What is the effect if the centrifugal switch is 19 What is the defect while a 3 phase motor
not disconnected after the motor starts? over heated if loaded?
A Motor will run normally A Loose rotor bars
B Motor will stop immediately B Defective bearing
C Starting winding will burn out C Short in stator winding
D Motor will run very slow speed D Wrong terminal connections
15 How the direction of rotation of repulsion 20 Why high contact resistance is provided at
motors is to be reversed? brushes in universal motor?
A By shifting the brush-axis A To increase the torque
B By interchanging the supply terminals B To increase the efficiency
C By changing the main winding terminals C To reduce sparking at brushes
D By changing the compensating winding D To reduce the armature current
terminals 21 Which is the cause for the universal motor
16 How the radio interference can be fails to start?
suppressed in centrifugal switch method of A Tight bearing
speed control of universal motor? B Insufficient current
A By connecting capacitor across centrifugal C Incorrect grading of brush
switch D Open circuited field or armature
B By connecting capacitor in series with 22 How the good working capacitor can be
centrifugal switch identified when it is tested by ohm meter?
C By adding compensating winding with A The needle deflects to centre position
armature B The needle will be in zero position but will
D By connecting an inductor in series with not go to infinity side
centrifugal switch C The needle will not go to zero position and
17 What is the reason if the handle of the remains in infinity side
Star/Delta starter shown in the figure does D The needle deflects towards zero and then
not hold at delta position? move towards infinity slowly
A hold on coil circuit is open at delta position
B hold on coil circuit will not get the potential
difference in delta
C motor terminal connection at delta position is
not correct
D connection is such that the hold on coil
circuit will function at star but not in delta.
18 Calculate the speed of a 4.4 KV 6 pole
alternator running at 1200 rpm supplies
energy to an induction motor which has 4
poles at 2 % slip?
A 1470 I/min (rpm)
B 1500 I/min (rpm)
C 1764 I/min (rpm)
D 1800 I/min (rpm)
- NIMI Question Bank - Page9/ 10
Module 1 : Three Phase and Single Phase Induction Motor
- Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 A 1 B 34 C 1 B
2 A 2 C 35 A 2 A
3 B 3 A 36 C 3 D
4 A 4 D 37 C 4 A
5 C 5 A 38 D 5 D
6 C 6 A 39 A 6 C
7 A 7 C 40 C 7 D
8 B 8 C 41 D 8 D
9 D 9 B 42 A 9 D
10 C 10 D 43 A 10 A
11 B 11 A 44 C 11 C
12 A 12 D 45 A 12 A
13 A 13 D 46 D 13 A
14 A 14 C 47 D 14 C
15 D 15 A 48 C 15 A
16 B 16 D 49 D 16 A
17 A 17 D 50 D 17 A
18 A 18 A 18 C
19 D 19 D 19 A
20 B 20 C
21 C 21 D
22 D 22 D
23 C
24 C
25 B
26 B
27 A
28 D
29 D
30 D
31 B
32 B
33 C
- NIMI Question Bank - Page10/ 10
Electrician - Semester II - CITS -
Module 2: Alternators and Synchronous Motor
Questions: Level 1 6 Which formula is used to calculate the
percentage voltage regulation (VR) in
1 Which formula is used to calculate alternator?
EMF/phase E in a ideal alternator? A % VR =
VFL − VNL
×100
A φFT VFL
E=
2.22 B VNL − VFL
% VR = ×100
φFT VFL
B E=
4.44 VNL − VFL
C % VR = ×100
VNL
C E = 2.22 ɸ FT
D E = 4.44 ɸ FT D VFL − VNL
% VR = ×100
VNL
2 Which rule is used to find the direction of
induced emf in an alternator? 7 What is the supply frequency of an
A Cork screw rule alternator having 6 poles runs at 1000 rpm?
B Right hand palm rule A 25 Hz
C Fleming’s left hand rule B 40 Hz
D Fleming’s right hand rule C 50 Hz
3 What is the name of the part of alternator? D 60 Hz
8 What is the name of the converter?
A Stator
B Exciter
C Salient pole rotor A Metal rectifiers
D Smooth cylindrical rotor B Rotary convertor
4 What is the formula to calculate emf C Mercury arc rectifiers
equation of an alternator considering Kc and D Motor-Generator set
Kd? 9 Which 3 phase motor can be started only
A E = 4.44 Kd KcT φ with pony motor?
B E = 2.22 Kd Kc Fφ A Synchronous motor
C E = 4.44 Kd Kc FφmT B Squirrel cage induction motor
D E = 1.11 Kd Kc Fφ C Wound rotor motor
5 How alternators are rated? D Double cage motor.
A KVA
B KW
C MW
D KV
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 9
10 What is the working principle of an 16 What is the term used to state the order in
alternator? which the 3 phase voltage reach their
A Self induction maximum value?
B Mutual induction A Phase sequence
C Electro - magnetic induction B Wave form
D Electro - static C Phase displacement
11 How many slip rings are in the 3 phase star D Angular displacement
connected stationary armature type 17 Which part is used to collect the alternating
alternator? current from the armature of an alternator?
A 1 A Slip ring
B 2 B Commutator
C 3 C Stator terminals
D 4 D Armature terminals
12 What is the angle difference between any
two armature of 3 phase delta connected
alternator?
A 90°
B 120°
C 150°
D 180°
13 What is the wave form of output voltage of
an rotating field type alternator?
A Sine wave
B Square wave
C Triangular wave
D Saw - tooth wave
14 Which instrument used to find the instant of
closing the switch which connects the
alternators in parallel?
A Techo meter
B Phase sequence
C Telescope
D Sychroscope
15 What is the name if the part of an
alternator?
A Double cage rotor
B Projecting pole rotor
C Salient pole rotor
D Smooth cylindrical rotor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 9
Questions: Level 2 8 What condition the two lamps become bright
and one lamp dark during paralleling of two
1 Calculate the speed of an alternator having alternators?
2 poles at a frequency of 50 Hz? A Terminal voltages are equal
A 1500 rpm B Voltages and frequencies are equal
B 2500 rpm C Voltages and phase sequence are equal
C 3000 rpm D Both the alternators receive same frequency
D 6000 rpm 9 What causes the terminal voltage of an
2 What condition the lamps become dark in alternator reduces, if the load increases?
dark lamp method of parallel operation of A Field resistance
two alternators? B Armature reaction
A Terminal voltages are equal C Inductive reactance
B Voltage and frequency are equal D Armature resistance
C Voltage and power rating are equal 10 What is the type of alternator?
D Frequency are same in both alternator
3 What is the use of synchroscope?
A Adjust the output voltage
B Adjust the phase sequence
C Adjust the supply frequency
D Indicate the correct instant for paralleling
4 What is the name of the equipment that
provides D.C to the rotor of alternator?
A Brushless alternator
A Exciter
B Three phase alternator
B Inverter
C Single phase alternator
C Converter
D Salient pole type alternator
D Synchroniser
11 Calculate the speed in r.p.s of the 2 pole,
5 What is the purpose of damper winding in
50Hz alternator?
alternator?
A 50 rps
A Reduces the copper loss
B 100 rps
B Reduces windage losses
C 1500 rps
C Reduces the hunting effect
D 3000 rps
D Improves the voltage regulation
6 Which condition is to be satisfied before 12 What is the advantage of using rotating field
parallel operation of alternators? type alternator?
A Rating must be same A Easy to locate the faults in the field
B Phase sequence must be same B Easy to connect the load with alternator
C Rotor impedance must be same C Easy to dissipate the heat during running
D Stator impedance must be same D Two slip rings only required irrespective of
No. of phases
7 What is the speed of an alternator
connected with a supply frequency of 50 Hz 13 What is the effect in increasing the field
at rated voltage having 4 poles? excitation current in alternator?
A 1000 rpm A Prevents demagnetising
B 1500 rpm B Over voltage protection
C 3000 rpm C Dead short circuit protection
D 4500 rpm D Alternator will be over loaded
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 9
14 Why D.C supply is necessary for 20 Which characteristic is applicable to
synchronous motor operation? synchronous motors?
A Reduce the losses A Runs at variable speed at all loads
B Start the motor initially B Suitable to supply only electrical load
C Run the motor with over load C Can not be used for PF improvement
D Run the motor at synchronous speed D Not self starting
15 Which acts as both inverter and converter? 21 How the generated AC is connected to the
A Metal rectifier load in a stationary magnetic field type
B Mercury arc rectifier alternator?
C Semi conductor diode A Through split rings
D Synchronous converter B Directly through terminal connection
16 Why exciter is essential to run a C Through commutator
synchronous motor? D Through slip rings
A Carry more load in motor 22 Which method is easy to check the phase
B Improve the power factor relation of both alternators during parallel
C Reduce the losses in motor operation?
D Run the motor at synchronous speed A Using all dark lamp method
B Using a synchroscope
17 Which is the main application of
C Checking by a phase sequence indicator
synchronous motors?
D Checking by bright and dark lamp method
A Elevators
B Paper rolling mills 23 What factor the amount induced emf
C AC to DC converter depends upon?
D Power factor correction device A Number of poles of alternator
B Change of speed of alternator
18 What is the advantage of motor generator
C Rate of change of flux linkage
set?
D Direction of rotation of the alternator
A Noiseless
24 How the salient pole rotor could be
B High efficiency
identified?
C Low maintenance required
A By its larger diameter and longer axial
D DC output voltage can be easily controlled
length
19 What is the function of the part marked ‘X’ of
B By its larger diameter and shorter axial
the rotary converter?
length
C By its shorter diameter and larger axial
length
D By its shorter diameter and shorter axial
length
25 How the smooth cyclindrical type rotor could
be identified?
A By its larger diameter and longer axial
length
B By its larger diameter and shorter axial
A Converts AC to DC
length
B Reduces voltage drop
C By its shorter diameter and larger axial
C Helps to deliver without noise
length
D Collects the delivered direct current
D By its shorter diameter and shorter axial
length
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 9
26 Where the damper winding is palced in an 31 What is the disadvantage in salient pole
alternator? type rotor?
A In the pole shoe A Having move space for field
B In the armature B Having diffcult to obtain mechanical
C In the shaft balancing
D In the exciter C Having more space for heat dissipation
27 Which test of alternator is illustrated in this D Having projecting field poles
circuit? 32 What is the draw back of open type
armature slots?
A Difficult for placing form wound coils
B Not easy to remove and replace the coils
C Uneven distribution of the magnetic flux
D Uneven air gap between stator and rotor
33 Why alternator is rated in KVA?
A Output KW is proportional to power factor
A Continuity test between armature windings B It consumes apparent power
B Continuity test between field windings C Power consumed is in KVA
C Earth test between winding and body D To consider reactive power
D Insulation resistance test between armature
34 What is the purpose of earthing neutral
and field windings
conductor in alternators?
28 Which test of alternator is illustrated in this A To reduce the power losses
circuit? B To protect the operators from shock
C To maintain proper voltage in the system
D To bring down the leakage potential to zero
35 Which loss is eliminated by using laminated
steel cores in armature of an alternator?
A Copper loss
B Windage loss
C Hysteresis loss
A Continuity test field armature windings D Eddy current loss
B Insulation test between armature and body 36 What is the function of damper windings in
C Insulation test between armature and field synchronous motor?
D Insulation test between field and body A Maintain power factor
29 How many cycles will be completed, if a coil B Excite the field winding
of a 4 pole alternator under goes one C Maintain constant speed
revolution? D Start the synchronous motor
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
30 Which instrument used to check the phase
sequence of alternators?
A Synchroscope
B Phase sequence meter
C Techo meter
D Frequency meter
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 9
Questions: Level 3 7 How synchronous motor works as a power
factor corrector?
1 Calculate the pitch factor (KP) for a winding A Varying the line voltage
having 36 stator slots 4 pole with angle (α) B Varying the field excitation
is 30° in alternator? C Increasing the speed of motor
A 0.942 D Decreasing the speed of motor
B 0.965 8 Which is the cause for the lamps are dark at
C 0.978 different timings , during synchronising of
D 0.985 alternator?
2 What is the cause for hunting effect in A Frequency
alternators? B Speed
A Due to over load C Phase sequence
B Running without load D Voltage
C Running with fluctuation of speed 9 Calculate the distribution factor (Kd) of single
D Due to continuous fluctuation in load phase alternator has the winding housed in
3 How to compensate de-magnetizing effect 3 slots per pole and the slots in groups of
due to armature reaction in an alternator? three being 20° apart?
A By reducing the speed of alternator A 0.85
B By increasing the speed of alternator B 0.92
C By increasing the field excitation current C 0.94
D By decreasing the field excitation current D 0.96
4 Calculate the voltage regulation in 10 How the frequency of incoming alternator
percentage if the load is removed from an can be changed?
alternator, the voltage rises from 480V to A By changing the level of excitation
660V? B By changing the speed of prime mover
A 27.20% C By changing the direction of excitation
B 32.50% D By interchanging any two terminals of
C 37.50% alternator
D 38.50% 11 How the phase sequence of the incoming
5 Why the synchronous motor fails to run at alternator can be changed?
synchronous speed? A By adjusting the speed of alternator
A In sufficient excitation B By changing level of excitation
B Defective pony motor C By adjusting the fuel inlet level of prime
C Open in damper winding move
D Short in damper winding D By interchanging any two terminals of
6 How the synchronous motor is used as a alternator
synchronous condenser?
A Varying the motor load
B Varying the rotor excitation
C Varying stator voltage in motor
D Varying stator current in motor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 9
12 What is the defect, if the megger reads zero 16 Calculate pitch factor for a winding having
mega Ohm? 36 stator slots, 4 poles with coil span of 1 to
10?
A 0.94
B 1
C 0.87
D 98
17 What is the reason if the alternator is initally
loaded with resistive load , the voltage
A Short circuit between armature windings decreases but the voltage is increased after
B Short circuit between armature and field further loading?
winding A The winding heat increased
C Earth fault between armature winding and B Higher flux in armature
body C Due to automatic voltage regulator
D Earth fault between field winding and D Prime mover input reduced
13 What is the defect, if the megger reads zero 18 How the additional load can be added to the
mega Ohm? alternator?
A Increase excitation voltage
B Increse power input to prime mover
C Increase load power, factor
D Increase excitation current
19 When the minimum armature current is
drawn in synchronous motor?
A At normal excitation
B With over excitation
A Short circuit between the armature windings C With under excitation
B Short circuit between the armature and field D Above normal excitation
winding
20 What happens when synchronous motor is
C Earth fault between field winding and frame
loaded beyond pull out troque?
D Earth fault between armature winding and
A Motor will stop
frame
B Motor will run with less speed
14 Which load, the terminal voltage of an C Motor speed fluctuated
alternator will slightly fall? D Runs as generator
A Resistive
21 How much load current will be supplied by a
B Inductive
400V, 3 phase alternator to 1.73KW lamp
C Dielectric furnace
load?
D Induction furnace
A 4.32 A
15 What happens If phase sequence of two B 2.5 A
alternators are not same, while parallel C 2.3 A
operation? D 4.5 A
A Work, but with less power
B Short circuit
C Voltage fluctuates
D Incoming machine acts as motor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 9
22 Which is used to prevent the hunting effect
in alternator?
A Compensating winding
B Stator winding
C Damper winding
D Rotor winding
23 How to compensate de-magnetizing effect
due to armature reaction in an alternator?
A Reducing the speed of alternator
B Reducing field excitation current
C Increasing field excitation current
D Increasing the speed of alternator
- NIMI Question Bank - Page8/ 9
Module 2: Alternators and Synchronous Motor
- Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 D 1 C 1 B
2 D 2 B 2 D
3 C 3 D 3 C
4 D 4 A 4 C
5 A 5 C 5 A
6 B 6 B 6 B
7 C 7 B 7 B
8 B 8 B 8 C
9 A 9 D 9 D
10 C 10 A 10 B
11 B 11 A 11 D
12 B 12 D 12 B
13 A 13 A 13 C
14 D 14 D 14 A
15 D 15 D 15 B
16 A 16 D 16 A
17 A 17 D 17 C
18 D 18 B
19 D 19 A
20 D 20 A
21 D 21 B
22 C 22 C
23 C 23 C
24 B
25 C
26 A
27 D
28 D
29 B
30 B
31 B
32 C
33 A
34 C
35 D
36 D
- NIMI Question Bank - Page9/ 9
Electrician CITS - Semester- II
Module 3: Small Transformer and DC Machine Winding
Questions: Level 1 6 Identify the number of poles in the winding ?
1 Which instrument is used to measure
armature winding resistance?
A Megger
B Multimeter
C Series type Ohm meter
D Kelvin bridge
2 Which winding wire is used for DC field coil?
A Super enameled copper wire A 2
B Single silk covered copper wire B 4
C Double silk covered copper wire C 6
D PVC covered copper winding wire D 8
3 How many parallel paths in duplex lap 7 Which part of the core is to be referred to
winding in the armature of 4 pole D.C calculate cross section area ?
Motor?
A 2
B 4
C 6
D 8
4 What is the name of the equipment?
A Centre limb
B Yoke
C Any one of outer limb
D Window
8 Which term refers the winding ?
A Resistance
A Megger B Capacitance
B Earth resistance tester C Inductance
C Internal growler D Permeability
D External growler 9 What is the name of the winding . If the end
5 What is the name of winding, if coil pitch is is not overlaped each other?
less than pole pitch? A Flat loop winding
A Full pitch winding B Concentric winding
B Half pitch winding C Diamond coil winding
C Long chorded winding D Chain winding
D Short chorded winding
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 7
Questions: Level 2 6 What is the purpose of tapes in winding?
A Insulate slots
1 Which insulating material belongs to class B Bind the coils
‘B’ insulation? C Wrap the conductor
A Cotton D Insulate exposed conductors
B Bamboo 8 Which type of DC armature winding the front
C Fibre glass pitch (YF) is greater than back pitch (YB)?
D Leatheroid paper A Lap winding
2 What is the temperature value of class ‘F’ B Wave winding
insulation? C Progressive winding
A 90°C D Retrogressive winding
B 105°C 9 How to obtain opposite polarity in adjacent
C 120°C poles into a 4 pole DC motor?
D 155°C A Varying the number of turns in coil
3 Which is the most effective method of B Making series connection of coils
balancing armature? C Making parallel connection of coils
A Static balancing D Making current flow in different direction
B Dynamic balancing 10 What is the operation in the rewinding
C Attached with counter balancing process?
D Plugged with lead weight balancing
4 Which type of armature winding is
illustrated?
A Cleaning of slots
B Removing of winding
C Removing of wedges
D Cutting of winding wire
11 Which insulating material used in winding is
A Duplex lap winding a highly non -hygroscopic and possess good
B Triplex lap winding electrical strength?
C Simplex lap winding A Empire cloth
D Quadruplex lap winding B Triplex paper
5 Which growler test for armature is C Millinex paper
illustrated? D Leatheroid paper
A Open coil test
B Ground coil test
C Shorted coil test
D Shorted commutator tests
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 7
12 Which type of armature winding is 16 Which type of test for armature is
illustrated? illustrated?
A Triplex wave winding A Test for shorted commutator.
B Duplex wave winding B Test for grounded commutator.
C Progressive lap winding C Insulation resistance test between
D Retrogressive lap winding Commutator segments
13 Calculate the average pitch (YA) for D Growler test for grounded Commutator
retrogressive wave winding, if segments.
No. of armature conductor = 14 17 Why the enamel coating is to be applied in
No. of slots = 7 winding ?
No. of poles = 2 A It gives red colour appearance
A 4 B It gives nice fragrance
B 6 C It gives high insulation
C 8 D It acts as heating elements
D 14 18 What is the purpose of Bamboo in
14 Which type of test is illustrated for the rewindings ?
armature after rewound? A To keep extra coil
B Increase the size of the slot
C Prevents the coil from coming out during
operation
D Dummy slot making
19 Which insulating material is used for
rewinding ?
A Leatheroid paper
B Rubber
A Open coil test C P.V.C
B Shorted coil test D Bakelite
C Voltage drop test
20 Which refers Double layer winding?
D Grounded coil test
A Each slot contains 3 coils sides
15 Why the newly rewound armature must be B Each slot contains 4 coils sides
preheated before varnishing? C Each slot contains 2 coils sides
A Drive out the moisture from it D Each slot contains one coils side
B Help for quick drying of varnish
21 Where the damper windings are placed in
C Make easy to penetrate varnish inside
motor?
D Maintain uniform spreading of varnishing
A Bearing
B End closure
C Rotor
D Stator
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 7
22 Which type of transformer, sandwiched type 29 Which type of lap winding is illustrated ?
of winding is used?
A In current transformer
B In core type transformer
C In shell type transformer
D In potential transistor
23 Which winding wire is used for transformer
having more cross sectional area ?
A Copper winding A Progressive lap winding
B Steel winding B Duplex lap winding
C Aluminium winding C Retrogressive lap winding
D Iron winding D Triplex lap winding
24 Which winding has more number of turns? 29 Which type of lap winding is illustrated ?
A Low voltage winding
B High voltage winding
C Centre tap winding
D Secondary winding
25 Which part of transformer is mostly affected
from over heating?
A Iron core
B Copper winding A Progressive lap winding
C Winding insulation B Duplex lap winding
D Frame or Case C Retrogressive lap winding
D Triplex lap winding
26 What is the coil span for 4 pole, 12 slot
armature winding? 30 What is the property of insulating material ?
A 24 A Withstand vibrations
B 48 B Conduct heavily
C 8 C Have low melting point
D 3 D Have moistures
27 How many commutator segments are in a 2
pole DC machine with coil span equal to 6 ?
A 3
B 12
C 4
D 8
28 Which is used to test armature winding for
short and open circuit?
A Tong Tester
B Internal Growler
C External Growler
D Digital multimeter
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 7
Questions : Level 3 6 What is the reading of voltmeter if the
winding is short, during voltage drop test?
1 Which winding fault is determined by the A Zero reading
test? B Negative reading
C Low voltage reading
D High voltage reading
7 What is the type of DC armature winding, if
the coil sides are one pole pitch apart ?
A Multiplex
B Fractional pitch
C Full pitch
D Pole pitch
A Open coil fault
8 What is the spacing between the brushes for
B Short coil fault
a wave winding, if 6 pole armature with 16
C Grounded coil fault
slots having 2 coil sides per slot, 1 single
D Grounded core fault
turn coil?
2 What is the value if Y6 for simplex lap A 4 segments
winding with '4 Pole , 12 slot armature with B 8 segments
two coil side/ slot ? C 16 segments
A 3 D 12 segments
B 5
9 Calculate the current carried by a particular
C 7
brush in 2 pole machine when conductor
D 9
current is 4mA?
3 What is the value of YF for a lap winding with A 16 mA
a 4 pole, 12 slot armature with two coil side/ B 8 mA
slot - (Assume single tuens coil - C 2 mA
progressive winding)? D 10 mA
A 3
10 How many number of brushes required for
B 5
small and large machine respectively in
C 7
wave wound armature ?
D 9
A 2,2
4 How the unbalanced weight of wound B 4,2
armature side can be identified by static C 2,4
balancing method ? D 4,4
A It rolls without stopping on flat surface
11 How many number of slots, if Spacing
B It stops at particular position with sucessive
between the brushes for a 4 pole m/c in
rolling
term of commutator segments in equal to 6
C It stops initial position without rollin
?
D It stops at different position in each rolling
A 48
5 What is the value of YF for a lap winding with B 3
a 4 pole, 12 swt armature with two coil C 24
sides/ slot - (Assume single tuens coil - D 6
retrogressive winding)?
12 Which part, the temperature rise will occur
A 9
maximum if a transformer is continuously
B 3
operated ?
C 11
A Core
D 5
B Winding
C Tank
D Conversation
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 7
13 How many brushes are to be used in DC
machine if brushes are placed 4 commutator
segments apart for 16 commutator
segments?
A 8
B 12
C 2
D 4
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 7
Module 3: Small Transformer and DC Machine Winding- Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 D 1 C 1 A
2 A 2 D 2 C
3 A 3 B 3 B
4 D 4 A 4 B
5 D 5 A 5 A
6 B 6 C 6 A
7 A 7 D 7 C
8 C 8 D 8 B
9 A 9 C 9 B
10 C 10 C
11 C 11 C
12 B 12 B
13 B 13 D
14 A
15 B
16 C
17 C
18 A
19 C
20 C
21 C
22 A
23 B
24 C
25 D
26 B
27 C
28 C
29 A
30 A
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 7
Electrician - Semester II - CITS - Module 4: AC Machine winding
Questions: Level 1 6 Name the part marked ‘X’ of the winding
machine?
1 Which formula is used to calculate the total
electrical degree in stator of an A.C motor?
A Total electrical degree = 180° / No. of slots
B Total electrical degree = 180° x No. of slots
C Total electrical degree = 180° / No. of poles
D Total electrical degree = 180° x No. of poles
2 Which term represents the distance between
the two active sides of a coil?
A Coil pitch A Mandrel
B Coil group B Wire feed
C Pole pitch C Wire guides
D Pitch factor D Spool carrier
3 What is the phase displacement between 7 What is the electrical degree of 6 pole stator
windings in 3 phase motor? motor?
A 90° A 360°
B 120° B 720°
C 180° C 1080°
D 360° D 1440°
4 What is the name of AC winding? 8 Calculate the number of coils per phase per
pair of poles of 3 phase motor having 2 pole,
24 slots,12 coils?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
A Half coil winding 9 What is the formula to calculate pitch factor?
B Whole coil winding Pole pitch
A Pitch factor =
C Single layer winding Winding pitch
D Double layer winding Winding pitch
B Pitch factor =
5 What is the name of the coil winding? Pole pitch
Number of slots
C Pitch factor =
Number of poles
Number of poles
D Pitch factor =
Number of slots
10 How pole pitch is measured in terms of slots
in AC winding?
Total electrical degrees
A
A Concentric coil winding Number of slots
B Distributed coil winding Number of slots
C Mesh shaped coil winding B
Total electrical degrees
D Diamond mesh shaped coil winding
No of slots in the stator
C
No of poles
No of poles
D
No of slots in the stator
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 8
11 What is the formula to calculate the mean 17 What are the two methods by which polarity
circumference of the coil? of field (poles) of a winding can be checked ?
L −L A By Internal growler and External growler
A Lm = out in cm
2 B Magnetic compass and Search coil
L in − L out C Magnetic compass and Internal growler
B Lm = cm
2 D Search coil and External growler
2 18 Which winding is referred, if each slot
C Lm = cm
L out − L in contains two coil sides in a 3 phase stator
2 winding?
D Lm = cm
L in − L out A Balanced winding
B Single layer winding
12 Which winding wire is used for rewinding a
C Un balanced winding
submersible motor?
D Double layer winding
A Super-enamelled copper wire
B Single silk covered copper wire
C PVC covered copper winding wire
D Double cotton covered copper wire
13 Which is used winding wire is used for
rewinding the armature of a mixer/Liquidizer
motor ?
A Single silk-covered copper wire
B Super enamelled copper wire
C Single cotton covered copper wire
D Double silk covered winding wire
14 Which factor depends on total Electrical
degrees for a 3 phase winding?
A No. of slots
B No. of poles
C No. of coils
D No. of phases
15 What is the name of winding ?
A half coil winding
B full pitch winding
C whole coil winding
D series winding.
16 What is total electrical degrees of a 4 pole
AC machine ?
A 180°
B 360°
C 720°
D 1080°
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 8
Questions: Level 2 7 Which test of winding is illustrated?
1 Why pre heating is necessary for motors
before varnishing in rewinding process?
A To dry the varnish quickly in winding
B To easy flow of varnish in the winding
C To increase the insulation resistance value
D To drive out the moisture in between winding
layers A Polarity test
2 Which type of test is conducted using B Ground test
internal growler in AC motor winding? C Continuity test
A Ground test D Short circuit test
B Polarity test 8 Which is the main property of leatheroid
C Continuity test paper insulation?
D Short circuit test A Non moisturized material
3 Which device is used to test startor winding B Highly non-hygroscopic
short and open fault? C Very good for class F insulation
A Tong Tester D Better ageing and dielectric strength
B Internal Growler 9 Which type of insulating material is selected
C External Growler for binding the coils and over hangs?
D Digital multimeter A Cotton sleeves
4 Which type of wire is used for rewinding of B Empire sleeves
A.C 3 phase motors? C Terylene thread
A Super enamelled copper wire D Fibre glass tape
B PVC covered copper winding wire 10 Which insulation is used for cuffing in AC
C Single cotton covered copper wire winding?
D Double cotton covered copper wire A Fibre glass tape
5 Which material is used as wedges in B Leatheroid paper
winding process? C Empire fiber glass tape
A Empire D Fabric based adhesive tape
B Cotton 11 Which refers coil in AC winding?
C Bamboo A Number of turns connected in series
D Terylene B Number of turns connected in parallel
6 Which test in winding is essential before C Number of turns under two similar poles
giving supply? D Number of turns under two dissimilar poles
A Ground test 12 Which type of AC winding the number of
B Polarity test coil/pole/phase is more than one at different
C Open circuit test pitches?
D Short circuit test A Involute coil winding
B Diamond coil winding
C Flat loop over lapped winding
D Flat loop non-over lapped winding
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 8
13 Calculate the number of coils /phase/ pole 19 Where the space for cooling is provided for
for a 3 phase double layer distributed winding coils in motor?
winding for a motor having 36 slots, 36 coils A Between overhanging coils
and 4 poles? B Between overhanging coil and rotor
A 3 coils /phase/ pole C Between overhanging coils and yoke
B 6 coils / phase/pole D Between overhanging coil and wedge
C 9 coils / phase/pole 20 Which type of the winding is illustrated?
D 12 coils/ phase/ pole
14 What is the type of rewinding process?
A Skew winding
B Skein winding
A Hand winding C Involute coil winding
B Drilling machine winding D Diamond coil winding
C Former winding 21 What is the name of 3 phase motor winding,
D Machine winding if the coil pitch is less than pole pitch?
15 Which operation to be carried out after A Full pitch winding
baking of varnish? B Whole coil winding
A Varnish stripping C Long chorded winding
B Painting of stator body D Short chorded winding
C Cleaning of stator body 22 Which is the demerit of 3 phase concentric
D Assembling of stator and rotor winding?
16 What is the function of collar? A More space is required
B A stepped former is required
C More difficult to shape the coils uniformly
D It is not easy to make the end connection
23 Calculate the phase displacement in terms of
slots for a 3 phase, 36 slots, 12 coils, 4 pole
stator winding?
A 3 slots
A Provides insulation around field B 4 slots
B Provides insulation for coil tapping C 6 slots
C Helps tightening material for flange D 8 slots
D Provides insulation for heat transfer from coil 24 Which type of AC motor winding having the
17 What is the advantage of short pitch winding number of coil/pole/phase is more than one
of 3 phase induction motor? arranged in different slots?
A Easy for winding A Basket winding
B Running torque increases B Concentric winding
C Efficiency of machine is increased C Distributed winding
D Starting and running current reduces D Concentrated winding
18 What is the reason of long chord winding is
avoided in AC motors?
A Low efficiency
B Low starting torque
C More winding wire required
D Control the increased heat loss
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 8
25 Which type of testing of winding is 31 Which type of varnish is used for AC 3 phase
illustrated? squirrel cage induction motor after
rewinding?
A Baking varnishes
B Air-drying varnishes
C Solventless varnishes
D Thermo setting varnishes
A Polarity test 32 Which test in an AC 3 phase stator winding
B Resistance test is illustrated?
C Short circuit test
D Voltage drop test
26 Which is irrelevant feature of AC three phase
distributed winding?
A Number of coils / per pole must be equal
B Size of all the coils is same
C Pitch of all the coils is same
D It can be a single layer or double layer A Polarity test
27 How the auxiliary and main winding are B Insulation resistance test
placed in single phase motor winding? C Open circuit test by growler
A Auxiliary winding housed near the tip of slot D Short circuit test by internal growler
and main winding deep in the slot 33 What is the maximum temperature the
B Main winding housed near the tip of slot and winding is to be preheated before
auxiliary winding deep in the slot varnishing?
C No fixed rule for placement of windings is A 40°C
applicable B 60°C
D Both the windings are placed deep inside the C 90°C
slots to have proper phase displacement D 140°C
28 How to connect the capacitor in the circuit for 34 Calculate the slot distance in angle for a
testing and commissioning of table fan ? ceiling fan having 28 slots, 14 poles, 14 coils
A Series with auxiliary winding permanently in half coil connection?
B Series with main winding permanently A 90°
C Parallel to the supply mains B 120°
D Series with starting winding at the time of C 180°
starting D 240°
29 Which is a function of insulating varnish 35 Which motor is having half coil winding?
when applied on a newly wound motor? A Mixer
A Will not allow the ingress of moisture. B Grinder
B Bonds the conductors together C Ceiling fan
C Works against the action of oil, acids, D Washing machine
alcalies
D Cools the winding by admiting free flow of air
30 Which factor decides the permissible
temperature rise of electrical machine?
A Material used for winding wire
B Wedges used for winding
C Insulating varnish used
D Insulating materials used for winding
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 8
Questions: Level 3 5 What will happen if the overhang of the coil
is more in split phase motor winding?
1 What indication denotes the shorted coil A The insertion of the coils will be easy
defect in 3 phase motor stator winding while B The insertion of the coils will be difficult
testing with internal growler by keeping C The coils may not allow the end cover to be
hacksaw blade? fitted
A Hacksaw blade gets over heated D The coils may allow easily the end cover to
B Rapid vibration of hacksaw blade be fitted
C Hacksaw blade repels against the slots 6 How many coils are to be connected for both
D Attracted by the winding turns on the slot starting and running winding if concentric
2 How the corresponding labeled A1,B2,C1 winding for a capacitor motor having 24 slots
terminals ends are to be marked respectively 112 coils?
in other ends? A Starting 6, running 6 coils
B Starting 4, running 8 coils
C Starting 8, running 4 coils
D Starting 2, running 10 coils
7 Calculate degree/ slot of a single phase
capacitor type table fan having no of pole 4.
No of slots 8, and No of coils 8
A A2 B1C2
A 60°
B A2 C2 B1
B 75°
C B1 A2 C2
C 85°
D C2 B1 A2
D 90°
3 Which type of coils connection for the
developed winding diagram of a 28 slots 14 8 Calculate the slot displacement between
coils of a ceiling fan? main and starting winding for a single phase
capacitor type table fan having 4 poles and 4
coils.
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
A half coil connection for 28 poles
9 Calculate No of coil per pole for a single
B whole coil connection for 14 poles
phase capacitor type table fan 240v 50Hz
C whole coil connection for 28 poles
having 8 slots, 4 poles an No of coils 8.
D half coil connection for 14 poles
A 1
4 Which end connection is correct for a 32 B 2
slots, 16 coils, 16 poles ceiling fan motor C 3
winding in the figure?
D 4
10 Why removing of heated damaged coils are
avoided in stripping the winding from starter?
A Not able to measure the size of winding wire
B To avoid damage to the lamination
A 2-4, 3-5, 6-8, 7-9, 10-12, 11-13, 14-16, 15--- C Not able to measure the coil size
MW2 D To avoid damage in body
B 2-3, 4-5, 6-7, 8-9, 10-11, 12-13, 14-15, 16---
MW2
C 2-3, 4-8, 7-6, 5-9, 10-11, 12-16, 15-14, 13---
MW2
D 2-4, 3-6, 5-8, 7-10, 9-12, 11-14, 13-15, 16---
MW2
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 8
11 Calculate the number of coils for starting and 17 What is effect of low graded insulating
running winding for a ceiling fan number materials are used for re winding of motors?
slots - 28 no. of poles -14 if it is connected A Insulation resistance between conductor
for half coil connections? decrease
A 4 coils for starting 10 coils for running B Insulation resistance between body and
B 10 coils for starting 4 coils for running conductor decreases
C 8 coils for starting 6 coils for running C Short circuit fault occurs
D 7 coils for starting and 7 coils for running D Open circuit fault occurs
winding 18 What will happen, if the overhang of the coil
12 Calculate the pole pitch for a ceiling fan, if is less in size of a split phase motor winding
number of slots 28 number of poles 14 and A The insertion of the coils will be easy
number of coils 28? B The insertion of the coils will be difficult
A 2 C The coils allow easily the end cover to be
B 4 fitted
C 6 D The coils may not allow the end cover to be
D 8 fitted
13 Calculate the slot distance in terms of degree 19 What is the effect, if coil group connection is
for a ceiling fan having 28 slots, 14 poles, 14 wrongly connected in a single phase motor
coils half coil connection. rewinding?
A 90° A Motor runs slowly
B 120° B Motor will not run
C 180° C Motor runs in very high speed
D 240° D Motor runs and takes more current at no load
14 Why one slot gap is kept between starting &
running winding of a ceiling fan?
A To give shape to winding
B To get uniform magnetic field
C To give phase angle displacement
D To increase the torque
15 What is the effect if some slots in a split
phase motor left without winding after
completing concentric winding?
A Speed reduced
B Torque reduced
C Works normally
D Heat increase
16 What defect will occur if over hang of a
winding increase in split phase motor?
A More copper required
B Length of slot liner to be minimum
C Not able to tighten the end covers
D Not able to install the rotor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 8
Module 4 : AC Machine winding - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 D 1 D 1 B
2 A 2 D 2 A
3 B 3 B 3 D
4 B 4 A 4 B
5 D 5 C 5 C
6 A 6 B 6 B
7 C 7 A 7 D
8 D 8 D 8 A
9 B 9 C 9 A
10 C 10 D 10 B
11 B 11 A 11 D
12 C 12 D 12 A
13 B 13 A 13 A
14 B 14 A 14 C
15 A 15 A 15 C
16 C 16 A 16 C
17 B 17 C 17 B
18 D 18 C 18 B
19 C 19 B
20 A
21 D
22 B
23 C
24 C
25 B
26 A
27 A
28 A
29 D
30 D
31 A
32 C
33 C
34 A
35 C
- NIMI Question Bank - Page8/ 8
Electrician - Semester II - CITS -
Module 5 : Rectifiers - Invertors AC/DC Drives
Questions: Level 1 6 What is the full form of B.O.P in D.C drive?
A Bridge Operation Panel
1 Which control system consumes very low B Basic Operational Panel
power for motion control in AC and DC C Basic Operation Programme
motors? D Bridge Operator Programme
A Field control 7 What is the minimum permissible single
B Drives control phase working voltage, if the declared
C Voltage control voltage is 240V as per ISI?
D Armature control A 233 V
2 Which drive is classified according to mode B 228 V
of operation? C 216 V
A Group drive D 211 V
B Manual drive 8 Which term refers that the mass of a
C Individual drive substance liberated from an electrolyte by
D Continuous duty drive one coloumb of electricity?
3 What is the name of the characteristic curve A Electrolysis
in D.C drive? B Electro plating
C Electro copying
D Electro chemical equivalent
9 What is the full form of abbreviation UPS?
A Uniform Power Supply
B Universal Power Supply
C Unregulated Power Supply
D Uninterrupted Power Supply
10 Which is frequency converter?
A Speed Vs torque characteristic
A Rectifiers
B Torque Vs field current characteristic
B D.C choppers
C Speed Vs armature current characteristic
C Cyclo converters
D Field current Vs armature
D D.C to A.C converters
4 What is the name of the component marked
11 What is the full from of PWM?
‘X’ in the block diagram of AC drive?
A Pulse Wide Modulation
B Pulse Width Modulation
C Phase Wide Modulation
D Phase Width Modulation
12 Which device in A.C drive controls the speed
A Rectifier of A.C motor?
B D.C bus A Field supply unit
C Inverter B COMMS technology bore
D A.C motor C Speed feedback technology bore
5 What is electric drive? D Micro processor controlled electronic device
A A device used as prime mover for generator
B A device converts A.C to D.C supply
C An electro mechanical device for controlling
motor
D A machine converts mechanical energy into
electrical
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 10
13 What is the relation between synchronous 19 Which is the AC input power receptacle in
speed (Ns) in RPM frequency (F) in hertz and UPS?
(P) of poles?
A 120 P
Ns =
F
B 120 F
Ns =
P
C N s = PF
120
D Ns = F
120 P
14 What are the two main components in A.C
drive? A 1
A Rectifier and inverter B 2
B Transformer and rectifier C 3
C Transformer and inverter D 4
D Transformer and control panel 20 Which is the correct equation, related to
15 What is the full form of VVVFD in A.C drive? phase voltage ‘V’ frequency ‘F’, No of turns
A Variable Voltage Variable Frequency Drives ‘N’ and magnetic flux ϕm of the DC motor?
B Voltage Variable Very high Frequency Drives A V = 4.444 f N ϕm
Variable Voltage Values and Frequency B 4.444Nf
C V=
Drives Nφ m
C 4.444Nf
D Variable Values of Voltage and Frequency V=
Drives φm
D V= 4 . 444 φm
16 What is the full form VFD in A.C drive?
Nf
A Volt Forward Drives
B Variable Force Drives 21 Which part is provided in UPS for source of
C Voltage Frequency Drives power, if supply fails?
D Variable Frequency Drives A Rectifier
B Inverter
17 What is the formula to calculate
C Battery
Volt/Frequency (V/F) ratio?
4.444φ M D Control relay
A
V /F =
N
B V/F = 4.444 NϕM
C V / F = 4.444N
φM
D V/F = 4.44/xϕM2
18 How the output capacity of UPS is
expressed?
A W
B VA
C AH
D KWH
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 10
Questions: Level 2 8 What is the purpose of LCD on basic
operator panel in D.C drive?
1 What is the function of power controller in A Indicate the fault
drive circuits? B Display the speed
A It sounds an alarm in no load conditions C Monitor the parameter
B It detects the overloading condition of motor D Display availability of supply
C It reduce motor current during transient 9 What is the reason of using shielded cable
operation for connecting low level signal circuits in DC
D It maintain the torque at low voltage drives?
conditions A Easy for connection
2 Why it is necessary to keep V/F ratio B Good appearance
constant in a drive? C Protects from mechanical injuries
A Keep the stator flux maximum D Eliminates the electrical interference
B Maintain the rotor current minimum 10 Which device controls the speed of A.C
C Maintain the speed of motor constant motor in A.C drive?
D Maintain the rated torque at all speeds A Field supply unit (FSU)
3 Which power modulator used in the electric B COMMS technology box
drive system? C Speed feedback technology box
A Cyclo converters D Microprocessor based electronic device
B Frequency multiplier 11 What is the main use of A.C drive?
C Phase sequence indicator A High starting torque
D Servo controlled voltage stabilizer B Group drive motors
4 Which type of sensing unit employed in drive C Control stepless speed in motors
system? D Interlocking system in industries
A Opto coupler 12 What is the function of IGBT in AC drive?
B Speed sensing A Smoothening incoming A.C supply
C Photo voltaic cell B Controls the power delivered to the motor
D Resistance temperature detector C Stabilize the output voltage from the rectifier
5 Which type of machine in industries is D Converts incoming A.C power into
provided with multi motor electric drive? D.C power output
A Rolling machine 13 Why the A.C drives are better suited for high
B As per supply voltage speed operation?
C As per no volt coil rating A High starting torque
D Heavy duty electric drilling machine B Robust in construction
6 Which control system is used for Eddy C Having lighter gauge winding
current drives? D No brushes and commutation
A Slip controller 14 What is the advantage of AC drive compared
B Rectifier controller to DC drive?
C AC voltage controller A Requires less space
D DC chopper controller B Installation and running cost is less
7 What is the purpose of JOG key in control C Fast response and wide speed range of
panel of D.C drive? control
A Stop the motor D Power circuit and control circuits are simple
B Restart the motor 15 Which is the application of single quadrant
C Inching operation loads operating in first quadrant in drives?
D Reverse the direction of motor A Hoists
B Elevators
C Conveyors
D Centrifugal pumps
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 10
16 What is the function of Field Supply Unit 22 What is IGBT in VF drive?
(FSU) in DC drive? A Inverter switching device
A Produces required firing current to the firing B D.C bus switching device
circuit C Rectifier switching device
B Provides variable voltage to the field winding D Field supply switching device
of motor 23 What is the function of VSI drives?
C Provides a constant voltage to the field A Converts A.C to D.C
winding of motor B Converts A.C to A.C
D Provides a constant voltage to the armature C Converts D.C to A.C
of the motor D Converts D.C to D.C
17 What is the disadvantage of DC drive? 24 Why the A.C drives are mostly used in
A Not suitable for high speed operation process plant?
B More complex with a single power A Easy to operate
conversion B Robust in construction
C More expensive than AC drive for high C Very high starting torque
capacity motor D Maintenance free long life
D Installation of DC drives is more complicated 25 What is the advantage of on-line UPS over
18 What is the purpose LCD in Basic Operator offline UPS
Panel (BOP) in AC drive? A Supplies constant power output
A Indicate the status of drive B It gives constant output frequency
B Monitor the parameter of AC drive C Works on single phase or three phase supply
C Indicate the display error in reading D Free from change over and transition
D Indicate the incorrect operation of BOP problems
19 Which is the correct sequence operation of 26 Which electronic circuit is used in a
key button in BOP of AC drive to change the automatic voltage stabilizer to produce
direction of rotation? constant output voltage?
A Press ON →REV → ON A Rectifier circuit
B Press OFF → REV → ON B Amplifier circuit
C Press ON → OFF → REV → ON C Oscillator circuit
D Press ON →REV → OFF → ON D Feedback circuit
20 What is the purpose of PROG / DATA button 27 Which feedback network is used for
in BOP of AC drive? automatic voltage stabilizers?
A To change the parameter setting A Current divider network
B To store the entered data and factory stored B Voltage divider network
data C Tapped transformer network
C To display the data direction of rotation D Resistance temperature detector network
forward / REV 28 Which electrical device is actuating the
D To display the data status of frequency and voltages in a stepped voltage stabilizer?
current A Autostat
21 Which is proportional to the torque in D.C B Output transformer
motor? C Over voltage relay
A Back E.M.F D Under voltage relay
B Field current 29 What is the effect in internal resistance of a
C Terminal voltage discharged cell?
D Armature current A Increase
B Decrease
C Becomes zero
D Remain same
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 10
30 Calculate the voltage and ampere/hour, if 37 What is the type of A.C voltage stabilizer?
four cells rated as1.5 v and 8 A.H are in
parallel?
A 6 v and 24 AH
B 3 v and 16 AH
C 4.5 v and 8 AH
D 1.5 v and 32 AH
31 Which is the application of automatic A Servo voltage stabilizer
stepped voltage stabilizer? B Automatic voltage stabilizer
A Geyser C Manual stepped voltage stabilizer
B Grinder D Constant voltage transformer stabilizer
C TV Receiver 38 Which instrument is used to check short
D Air conditioner circuit faults in electronic circuit in voltage
32 Which is the function of an inverter? stabilizer?
A Converts A.C voltage into D.C voltage A Ammeter
B Converts D.C voltage into A.C voltage B Voltmeter
C Converts D.C voltage into higher D.C voltage C Ohmmeter
D Converts A.C voltage into higher A.C voltage D Multimeter
33 What is the purpose of output transformer in 39 What are the important stages in a simple
inverters? inverter?
A Step up input AC A Oscillator and rectifier stages
B Step down input AC B Oscillator and amplifier stages
C Step up AC from amplifier C Amplifier and transformer output stages
D Step down AC from amplifier D Oscillator, amplifier and transformer output
34 Which type of output transformer is used in stages
automatic voltage stabilizer? 40 Where square wave inverters are used?
A Auto transformer A Computers
B Static transformer B TV receiver
C Ring core type transformer C DVD players
D Ferrite core type transformer D General lighting
35 Which principle the constant voltage 41 What is the function of inverter in A.C drive?
transformer works? A Converts A.C to D.C voltage
A Self induction principle B Stabilize the constant voltage
B Fall in potential principle C Varies the frequency to control the speed
C Ferro-resonant principle D Converts D.C voltage back to A.C voltage
D Mutual induction principle 42 Why as per the name plate detail, the
36 Which transformer is used in servo voltage voltage/frequency ratio of the motor must be
stabilizer? maintained in A.C drive?
A Step up transformer A To reduce the voltage drop
B Step down transformer B To obtain maximum efficiency
C Torodial autotransformer C To maintain constant frequency
D Constant voltage transformer D To maintain constant power factor
43 What is the main functions of A.C drive?
A Maintains constant frequency
B Changes the voltage as required
C Improves the power factor in industry
D Maintains constant speed
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 10
44 Which region A.C drive is operated above its 50 How supply is fed to the load by OFF-line
rated frequency? UPS, if power supply is available?
A Inverter directly supply power
A Constant time region
B Main supply directly supply power
B Constant volt/frequency region
C Main supply through filter & will supply power
C Constant horse power region
D Battery and inverter will supply power
D Constant voltage/current region
regulator
45 How the magnetic saturation can be avoided
51 How supply is fed to the load by ON-line
in AC drive?
UPS, when power supply is available?
A By reducing the magnetic force
B By keeping the flux density constant
C By keeping the magnetic flux constant
D By varying the number of turns of the coil
46 What is the disadvantage of A.C drive?
A Maintenance cost is very high
B It produces a simulated wave form
C Operation is complicated, not easier
A Inverter directly supply load
D Not suitable for high speed operation
B Main supply directly supply load
47 What is the use of D.C bus in A.C drive?
C Main supply through inverter to load
A It converts D.C into A.C
D Battery supply through inverter to load
B It delivers the power to the motor
52 Which are the important stages in a simple
C The power from rectifier is stored on it
inverter?
D It simulate the sine wave at particular
A Oscillator and rectifier stage
frequency
B Oscillator and amplifier stage
48 What is the use of P.W.M to the A.C motor in
C Amplifier and transformer output stage
A.C drive?
D Oscillator, amplifier and transformer output
A To convert A.C pulse into D.C
stage
B It deliveries the stored power to AC drive
53 Why the A.C drives are mostly used in
C It smoothness the incoming power supply
process plants?
D To simulate a current sine wave to the
A Easy to operate
desired frequency
B Robust in construction
49 Which precaution to be taken while
C Very high starting torque
connecting circuit breaker to main supply?
D Ruggedness and maintenance free long life
A Separate wiring from main wiring
54 What is the purpose of LED indicators in
B Share the full load of main wiring
BOP panel of DC drive?
C Can share 10% over load of KVA rating only
A To indicate the status of drive
D Can share 10% less load of KVA rating only
B To indicate system running
C To indicate fault occurred
D To indicate availability of power
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 10
55 Why the shielded cable is recommended for
the tachometer?
A To measure correct speed
B To avoid break of cable
C To eliminate electrical interference
D To reduce the device error
56 What does the green LED indicate in BOP of
DC drive?
A Warns before fault occur
B System running
C Status of drive
D Power supply is 'ON'
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 10
Questions: Level 3 8 Which is the cause for the fault if the output
voltage of UPS is higher than normal?
1 How the base speed of D.C shunt motor can A Battery get short circuited
be increased by using D.C drive? B Defective feedback circuit
A By reducing the field current C Input voltage is very high
B By increasing the field current D Relay points are joined together
C By increasing the supply voltage 9 What is the reason for tripping the UPS with
D By reducing the armature voltage full load?
2 How the constant torque can be obtained A Main supply failure
from armature and field controlled drives? B Incorrect overload settings
A By reducing the field current C Battery charger input fuse blown out
B By increasing the field current D Loose connection in battery terminal
C By reducing the armature current 10 How the A.C drives control the speed of A.C
D By controlling the armature voltage motor?
3 How the backup time of UPS can be A By providing double cage rotor
increased? B By changing the number of poles
A Increase the VA rating of UPS C By varying output voltage and frequency
B Increase the AH capacity of battery D By interchanging the connection terminals in
C Decrease the AH capacity of battery motor
D Maintain battery terminal voltage always 11 Which refers, if the A.C motor operates at
90% of rating less than rated V/Hz ratio and above rated
4 How the hard sulphation defect in name plate speed?
secondary cell can be prevented? A Field effect
A Provide trickle charging B Field operation
B Provide freshening charge C Field weakening
C Provide constant current charging D Field strengthening
D Provide constant potential method charging 12 How, the rated torque at all speeds can be
5 Which part in UPS supplies continuous maintained in A.C motor?
output voltage in case of input voltage A By keeping the voltage constant
failure? B By keeping the load constant
A Battery unit C By keeping the current-to-frequency ratio
B Inverter unit constant
C Rectifier unit D By keeping the voltage-to-frequency (V/F)
D Controller unit ratio constant
6 What is the effect during loading of the cell, 13 Why the A.C drives are better suited for high
the current strength falls and become zero? speed operation?
A Buckling A Not having brushes
B Polarization B Robust in construction
C Local action C High starting torque
D Polarity short D Having lighter gauge winding
7 What is the reason for having low back up 14 Why UPS works on 240v - AC mains only
time in UPS? and rotor on battery ?
A Fault in inverter circuit A Battery fuse is blown out
B Battery is short circuited B Inverter fuse is blown out
C Mains earthing is not proper C Input AC mains is very low
D Ampere hour (A.H) capacity of battery is not D Charger input fuse blown out
sufficient
- NIMI Question Bank - Page8/ 10
15 What is the reason, if the UPS is switched
ON without load but DC under voltage
indicator turns ON ?
A Short circuit
B Load too high
C Inverter fuse is blown
D Overload setting in wrong
16 Which is the reason that UPS does not
switch ON in battery mode?
A Check oscillator circuit
B Problem in inverter circuit
C Main filter capacitor problem
D Over control cord is not functioning properly
17 Which is the reason for the charger does not
turn ON when UPS in switched ON?
A Inverter fuse is blown out
B Mains input fuse blown out
C Mains earthing is not proper
D Main filter capacitor problem
18 What precautions to be observed while
removing components from PCB of voltage
stabilizer?
A Ascertain absence of D.C. voltage
B Ascertain the transistor are not shorted
C First ascertain from the possible test with in
the circuit
D Position of terminal connections and hook
up connection to be noted
19 What is the cause, if the relays in stabilizer
will show higher output voltage than input
voltage with boost indication?
A When both transists are short
B When both transistors are open
C Presence of D.C supply makes relays in
operative
D Presence of control voltage makes relays in
operative
20 When the relay will show lower output
voltage than input voltage buck indicator?
A When transistors are open
B When transistors are short
C Presence of D.C supply makes relays in
operative
D Presence of constant voltage makes relays
in operative
- NIMI Question Bank - Page9/ 10
Module - 5 : Rectifiers - Invertors AC/DC Drives - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 B 1 B 34 A 1 A
2 D 2 D 35 C 2 D
3 A 3 A 36 C 3 B
4 B 4 B 37 C 4 A
5 C 5 A 38 D 5 A
6 B 6 A 39 D 6 B
7 B 7 C 40 D 7 D
8 D 8 C 41 D 8 B
9 D 9 D 42 D 9 B
10 C 10 D 43 B 10 C
11 B 11 C 44 B 11 B
12 D 12 B 45 B 12 C
13 B 13 D 46 A 13 D
14 A 14 B 47 A 14 A
15 A 15 D 48 B 15 C
16 D 16 C 49 A 16 B
17 B 17 A 50 B 17 A
18 B 18 B 51 B 18 A
19 A 19 C 52 D 19 A
20 A 20 B 53 B 20 B
21 C 21 D 54 A
22 A 55 C
23 B 56 B
24 D
25 D
26 D
27 B
28 A
29 A
30 D
31 C
32 B
33 C
- NIMI Question Bank - Page10/ 10
Electrician - Semester II - CITS - Module 6: Industrial Wiring - Control Panel
Questions: Level 1 6 What is the name of the device marked ‘X’ in
the circuit?
1 Which supply indicates by the colour of
conductor exhibited on Red, Blue, Black?
A Supply DC 3 wire system
B Single phase AC system
C Supply AC system 3 phase
D Apparatus AC system 3 phase
2 Which cable ties are used to bunch the
wires? A Contactor
A Silk ties B No volt coil
B P.V.C ties C Stop button
C Nylon ties D Overload relay trip
D Cotton ties 7 What is the name of the accessory used in
3 Which device is avoided in the panel board control panel wiring?
assembly?
A Sensors
B Indicating lamp
C Isolating switch
D Push button switch
4 What is the name of the device marked ‘X’?
A Wire ferrules
B Wire sleeves
C Nylon cable ties
D Cable binding strap
8 What is the name of the accessory used in
control panel wiring?
A Stop button
B Start button
C Main contact
D Auxiliary contact
5 What is the name of the wiring accessory
used in control panel wiring?
A Lugs
B Thimble
C Crommet
D Terminal connector
A DIN rails
B G channel
C Grommets
D Race ways
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 7
9 What is the name of the contact marked as
‘X’?
A Star contact
B Delta contact
C Auxiliary contact
D Overload relay contact
10 What is the name of device, that operates
electrically controlled double break switch?
A Contactor
B Limit switch
C Isolating switch
D Relay
11 What is the name of the accessory that is
made by chromated metal?
A Race ways
B DIN Rail
C Lugs
D Contactors
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 7
Questions: Level 2 9 What is the criteria to select the contactor?
A Type of supply
1 What is the function of isolator switch? B Type of load connected
A Trips automatically at overload C Supply voltage and load
B Protect the circuit from short circuit D Place of use the contactor
C Operated by the motion of an object 10 Which accessory is used to mount MCB,OLR
D Manually operated switch to disconnect the in the panel board without using screws?
circuit A DIN Rail
2 Which trips the circuit, as it is over loaded? B G. channel
A MCB C Grommets
B ELCB D PVC channel
C Isolator 11 Which type of device protects motors from
D Contactors over heating and over loading in a panel
3 Which device protects from overload and board?
short circuit in a panel board? A Rectifier
A Isolating switch B Limit switch
B Time delay relay C Thermal relay
C Thermal overload relay D Electro mechanical relay
D Miniature circuit breaker 12 What is the use of ‘G’ channels in control
4 Which switch with an actuator is operated by panel?
the motion of a machine or part of an object? A For fixing relays
A Limit switch B For fixing contactors
B Toggle switch C For fixing instruments
C Isolating switch D For fixing terminal connectors
D Push button switch 13 Which is the standard duty cycle code of the
5 Which switch is operated at OFF load contactor for starting and stopping the AC
condition? resistive and inductive load?
A Limit switch A AC1
B Isolating switch B AC2
C Two way switch C AC3
D Push button switch D AC4
6 What is the reason for providing two 14 Which is the correct sequence operation of
separate Earthing in panel board? contactors for operating automatic star delta
A Panel board is made in metal box starter?
B Control the stray field in the panel A Main→Star→Delta →Timer
C Reduce the voltage drop in panel board B Star→ Main→Timer→Delta
D Ensure one earthing in case of other failure C Main→Timer→Delta→Star
7 Which circuit, the limit switches are used? D Star→Timer→ Main→Delta
A Lift circuits 15 Why control panels are provided with control
B Street lighting transformer?
C Motor control circuits A To maintain rated voltage to load
D Domestic power circuits B To operate the auxiliary circuits
8 How the control circuit voltage and power in C To maintain rated main supply voltage
a contactor are to be selected? D To supply reduced voltage to power circuit
A As per rated current
B As per supply voltage
C As per no volt coil rating
D As per the type of supply
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 7
16 What is the use of PVC channel in a control 23 Which type of contactors are used for
panel wiring? starting of shunt motors?
A Mounting MCB A DC1
B Mounting relays B DC2
C Path way for electrical wiring and protection C DC3
D Mounting double deck terminal contactor D DC4
17 What is the purpose of thermal over load 24 How many self holding normally open
relay in control panel? contacts are provided for two motor
A Switching ON/OFF the circuit sequential control?
B Protect the circuit from earth fault A 1
C Control the circuit based on time delay B 2
D Protect the motor from over heating C 3
and loading D 4
18 Why sequential control of motors is required 25 What is the use of nylon cable ties?
in an industrial application? A To connect the terminal
A To share more loads B To hold (or) bunch the cables
B To reduce power consumption C To identify the polarity of cables
C To minimise the operating cost D To increase mechanical strength
D To increase the accuracy of operation 26 Which standard AC duty cycle contactor is
19 Which material is used to make open frame used for heaters and furnaces?
bimetallic adjustable thermostat contacts? A AC1
A Silver B AC2
B Brass C AC3
C Copper D AC4
D Bronze
20 What is the purpose of DIN-rail used in
control panel wiring?
A It provides a path way for electrical wiring
B Install the high powered circuit accessories
C Mounting the double deck terminal
connectors
D Mounting the control accessories without
screws
21 Which device controls the operations in
sequential control systems?
A Timer
B Relays
C Contactor
D Control transformer
22 Which DC load is represented by the DC4
standard duty cycle of contactors?
A Resistive loads except motor loads
B Starting and stopping of shunt motor
C Starting and stopping of series motor
D Starting and stopping with in charge and
braking
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 7
Questions: Level 3 7 What happen, if time delay relay of a auto
star delta starter not open during starting?
1 How the contacts in a contactor can be A Does not start
engaged for working? B Runs normally
A By manual operation C Runs in star only
B By mechanical settings D Start and stops
C By operating electromagnet to change the 8 What is the effect of connecting cables in
position control panel without grommets?
D By using bimetallic strip to change the A Reduces voltage drop
position B Protect the cable from break
2 Which prevents flare out of stripped and C Increase the insulation resistance
stranded cables in the panel board? D Increase the current carrying capacity
A Sleeves 9 What is the reason, if DOL starter wired
B Wire ferrules motor stops immediately after switching ON?
C Lugs and thimbles A High speed
D Cable binding straps and button B Low overload current setting
3 How to protect the cable from insects and C Supply frequency incorrect
rats into the panel? D Over lubrication
A By using sleeve 10 What is the reason for the contactor coil is
B By using crommets failed with overheating?
C By using cable binding straps A Over load in motor
D By providing nylon cable ties B Over voltage
4 What essential feature to be considered C Open contactor coil
while designing a layout of control panel? D Higher voltage rate coil
A Proper type of protection and measuring 11 What will happen if 'ON " contact is damaged
system and permanent open?
B Inside area and number of indicating lights in
front panel
C Suitable method of labeling and cable
harnessing
D Outside dimensions and swing area of A Motor will not run
cabinet door B Over current in control circuit
5 Why power and control wirings run in C Remote control will not work
separate race ways? D Remote control only will work
A To reduce heat 12 What will happen if 'K1" contactor coil is used
B To reduce the radio interference on 500V instead of 240V?
C To increase the insulation resistance
D To increase the current carrying capacity
6 Why the motor is not changing the direction,
if reverse push button is pressed in forward
and reverse control star delta starter?
A No volt coil is not energized
B Fault in forward contactor A Work normally
C Due to interlock in reverse contactor B Circuit will damage
D No voltage exist in reverse contactor C Will not work
D will chatter the contacts
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 7
13 Why the forward reverse control circuit fails
to change direction of rotation. What is the
reason?
A Brake provided in one direction
B Phase sequence is same
C Phase sequence is not same
D Low voltage in one phase
14 What will happen if AC1 contractor is used for
jogging of crane motor?
A Works normally
B Contactor damages instantly
C Contactor coil heats up
D Contact faces damage
15 What happens, if time delay relay of a auto
star delta starter still in closed condition after
starting?
A Starts and stop
B Runs normally
C Runs in star only
D Runs in delta only
16 What happens in the control circuit of a 12V
DC contactor if a 12V AC contactor coil is
replaced ?
A The contactor does not function because of
less current through the coil
B The contactor will be damaged because of
excessive heating up of coil
C The contactor does function normally without
abnormal effects
D The contactor does function but will produce
more noise
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 7
Module 6 : Industrial Wiring - Control Panel - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 A 1 D 1 C
2 C 2 C 2 C
3 A 3 D 3 B
4 D 4 A 4 D
5 A 5 B 5 B
6 D 6 D 6 C
7 D 7 A 7 C
8 C 8 C 8 C
9 C 9 C 9 B
10 A 10 A 10 B
11 B 11 C 11 D
12 D 12 C
13 B 13 B
14 B 14 D
15 B 15 D
16 C 16 B
17 D
18 D
19 A
20 D
21 A
22 C
23 B
24 B
25 B
26 A
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 7
Electrician CITS - Semester- II Module 7: Domestic Appliances
Questions: Level 1 6 Which appliance-works by heating effect of
electric current ?
1 What is the name of the part of electric iron? A Food mixer
B Kettle
C Table fan
D Ceiling fan
7 Which part of the electric iron is pressed
over the clothes to be ironed?
A Sole plate
B Pressure plate
A Sole plate
C Heel plate
B Pressure plate
D Heating element
C Mica insulation
8 Which part is used to regulate the
D Asbestos sheet
temperature of automatic electric iron?
2 Which formula is used to calculate the heat
A Sole plate
generated as per Joules law?
B Pressure plate
A Heat generated = IRT / J cal
C Power cord
B Heat generated = I2RT / J cal
D Thermostat
C Heat generated = IR2T / J cal
9 Which part is used to connect the supply to
D Heat generated = (IR)2 T / J cal
the electric iron?
3 What is the magnetron tube filament voltage
A Handle
used in microwave oven?
B Sleeve
A 1.5 V A.C
C Power cord
B 2.0 V A.C
D Pressure plate
C 3.0 V A.C
10 Which part is marked as ‘X’ in the typical
D 3.2 V A.C
outline of a steam iron?
4 What is the name of the circuit?
A Sole plate
B Pressure plate
C Thermostat
A Electronic fan regulator
D Water tank
B Electronic voltage multiplier
C Electronic voltage stabilizer 11 Which electrical appliance is used to heat up
D Electronic triggering circuit of SCR the air space in a room?
A Kettle
5 What is the value of insulation resistance of
B Toaster
an electrical appliance?
C Room heater
A Should be less than one Ohm
D Hair drier
B Should be one Ohm
C Should not be less than one to 10 megohm
D Must be more than 10 megohm
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 9
12 How many types of room heaters are there 18 Which part is marked as ‘X’?
according to the method of air circulation?
A 2
B 4
C 5
D 6
13 What is the normal working temperature
range of heating element of a toaster?
A 285°C to 900°C
B 385°C to 900°C A Front cover
C 385°C to 800°C B Blade shank
D 285°C to 800°C C Speed regulator
D Oscillating knob
14 Which part is marked as ‘X’ in the schematic
diagram of a toaster? 19 What is the expansion of HDP?
A High Density Polythylene
B Hard Density Polythylene
C Heavy Density Polythylene
D High Density Polymer
20 Which electrical effect is used in electric
bell ?
A Heating effect
B Electromagnetic effect
A Thermostatic switch with timer C Lighting effect
B Centre heating element D Chemical effect
C Two side heating element 21 Which is an audio signalling device?
D Mechanical lever A Spring bell
15 Which is the rotating part of a ceiling fan? B Interupter bell
A Stator winding C Buzzer
B Suspension rod D Single stroke
C Canopy 22 What is the S.I unit of heat ?
D Rotor A Calorie
16 How is the capacity of a ceiling fan is B Joule
expressed? C Centigrade
A By this blade length D Fahrenheit
B By sweep and voltage
C By the voltage range
D By speed in r.p.m
17 What is the minimum clearance between
floor and blade of the ceiling fan?
A 2.4 meters
B 2.75 meters
C 3 meters
D 3.5 meters
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 9
Questions: Level 2 6 What is the purpose of protection grooves at
various places in a heater base plate?
1 Which material is used to make heating A Radiate the heat properly
element? B Retain the heating element firmly
A Silver C Place the vessels firmly on heater plate
B Copper D Protect the heating element from damage
C Nichrome 7 What is the purpose of sole plate in electric
D Aluminium kettle?
2 What is the function of stirrer motor in micro A Acts as a balancing weight
wave oven? B Acts as an insulator for element
A Draws cooling air inside C Protect the kettle base from damage
B Spreads the heat uniformly D Keep the element in close contact with
C Exhausts the hot air outside container
D Revolves and reflects the electromagnetic 8 What is the function of neutral path in AC
energy supply system for appliances?
3 What is the purpose of U bend marked as A Provides current return path
‘X’ in geyser? B Provides voltage level constant
C Reduces voltage drop in wiring
D Maintains load current constant
9 What is the function of magnetron tube in a
microwave oven?
A Amplifies the microwave signal
B Changes the polarity every half cycle
C Oscillate and produce cooking frequency
D Converts microwave energy to electrical
energy
A Prevents draining of water 10 Which type of motor is used in the wet
B Avoids the forming of scales grinder?
C Reduces the pressure of outlet pipe A Universal motor
D Restricts the air locking inside the tank B Repulsion motor
4 Which position of the heater range switch C Capacitor start induction run motor
will give maximum output? D Capacitor start capacitor run motor
11 How is the resistance of the heating element
is calculated?
A
A By using the formula R =
sI
sI
B By using the formula R =
A
A Position 1 W
B Position 2 C By using the formula R =
V2
C Position 3
D Position 4 V2
D By using the formula R =
5 Calculate the heat generated in a electric W
heater of 1000 watt, 240 volt, worked for 5 12 Which factor the heat produced in a heating
minutes? element depends upon?
A 70.5 Kilo calories A Position of the element
B 71.0 Kilo calories B Current flow and resistance
C 71.6 Kilo calories C Atmospheric condition
D 72.1 Kilo calories D Earthing system
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 9
13 What is the advantage of automatic electric 21 Which type of room heater has a provision
iron? to blow the air by electric fan through
A Cost is less electrically heated elements?
B Can regulate the temperature A Natural draft type room heater
C Can be used at any voltage B Forced draft type room heater
D Gives protection from over voltage C Bowl type room heater
14 What is the function of themostat? D Rod type room heater
A To control the voltage 22 How the capacitor is connected in a ceiling
B To adjust the resistance of heating element fan?
C To close or open a circuit predetermined A In series with the main winding
temperature B In series with the auxiliary winding
D To protect against earth leakage circuit C In parallel with main winding
15 Where is the heating element placed in D In parallel with auxiliary winding
electric irons? 23 How is the sweep of ceiling fan is
A On the sole plate determined?
B On the pressure plate A Diameter of the circle to be formed by one
C Over the heel plate rotation
D Over the top cover B Distance from the centre of the fan to tip of
16 What is the purpose of the part mechanical blade
timer in an automatic toaster? C Distance of the length of the blade
A To control the carriage handle D Distance of the width of the blade
B To adjust the toaster time 24 How the speed is varied in a ceiling fan?
C To adjust the current A By connecting a regulator in parallel
D To control supply voltage B By connecting a regulator in series
17 Which types of motors are used on smaller C By increasing the turns of windings
size of hair dryers? D By decreasing the turns of windings
A Reputation motor 25 Which type of capacitor is used in ceiling
B Permanent capacitor fan?
C Shaded pole motors A Air capacitor
D Capacitor start - induction run motor B Paper capacitor
18 Which type of motor is used on larger type C Ceramic capacitor
hair dryer? D Electrolytic non polarised type
A Reputation motor 26 What is the function of cotter pin at both
B Universal motor ends of down rod in a ceiling fan?
C Permanent capacitor motor A To prevent falling of this fan by slackening
D Reluctance motor of bolt nut
19 Which effect of electricity is used in electric B To support the top conopy fittings
toaster? C To avoid tight movement of this fan
A Heating effect D To avoid loose alignment of blade
B Chemical effect 27 What is the result of over loading a food
C Magnetic effect mixer?
D Lighting effect A Smoke coming from coupling
20 Which type of room heater is known as B Mixer runs a one speed only
radiant heaters? C Mixer runs but becomes hot
A Bowl type room heater D Mixer runs noisy
B Forced draft type room heater
C Oscillating type room heater
D Rod type room heater
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 9
28 Which type of food mixer is used with two 35 Which part is marked as ‘X’ in schematic
core with two pin type cord wire? diagram of table fan?
A 3 speed mixer
B Single insulated mixer
C Double insulated mixer
D 2 speed mixer
29 Which schematic diagram is illustrated?
A Regulator
B Running winding
C Starting winding
D Connecting cord
36 Which type of resistors are used in auto fire
A Wet grinder circuit alarm circuit?
B Food mixer circuit A LDR
C Washing machine circuit B Varistors
D Hair drier circuit C Sensistors
D Thermistors
29 How the motor of a mixer is operated with
different speeds? 37 Which type of wiring is to be done in fire
A By tapping from different points of field coil alarm system?
windings A PVC conduit
B By connecting an additional variable B Metal conduit
resistance C PVC casing & capping
C By connecting the motor in series with load D CTS wiring (Repair wiring)
D By regulating the supply voltage 38 How the immersion heater tube ends are
30 How the speed is regulated in a table fan? sealed?
A By using a series resistor A By china clay
B By tapping the field winding B By insulating wax
C By using a capacitor C By pre adhesive
D By field divertor D By thermal and water proof compound
31 Where the stator windings are placed in a 39 Why water level indicator is provided in a
table fan? immersion heater?
A On crank disc shaft A To get appropriate heat
B In slots of the laminated iron core B To reduce the heat of the tube
C In the oscillating unit C To increase the heat efficiency
D In the vertical spindle D To protect water from entering terminal
32 What should be the minimum value of 40 How microwave converted as heat inside
insulation resistance of a table fan? microwave oven?
A Should be one Ohm A By high speed oscillation microwave
B Should not be less than one Ohm B By changing the polarity at low speed
C Should be three megohm C By low speed oscillation of microwave
D Should not be less than one megohm D By changing the frequency at high speed
34 Where is the blades are attached in a table 41 What is the frequency of microwave in
fan? microwave oven?
A To the front cover A 2000 MHz
B To the rotor shaft B 2250 MHz
C To the stator C 2350 MHz
D To cross gear D 2450 MHz
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 9
42 What is the value of output DC voltage that 49 Calculate the HP of the water pump motor,
converted by voltage doubler circuit in if has to deliver 1000 litre to a height of 30
microwave oven? metre within 15 minutes.
A 2800 v A 0.5 HP
B 3200 v B 0.44 HP
C 3800 v C 0.48 HP
D 3900 v D 0.39 HP
43 Which part of microwave oven helps uniform 50 Which pump is also called as piston pump?
heating of foods? A Jet pump
A Cook relay B Centrifugal pump
B Stirrer motor C Submersible pump
C Blower motor D Reciprocating pump
D Dual latch switch 51 Which type of A.C. single phase motor is
44 Which material is used as heat insulators in used for jet pumps?
geyser? A Universal motor
A PVC B Split phase motor
B Fiber C Permanent capacitor motor
C Asbestos D Capacitor start induction motor
D Glass wool 52 What is the purpose of heel plate in non -
45 Which type of AC single phase motor is automatic electric iron ?
used in washing machine? A To keep the heating element firmly
A Capacitor start induction run motor B To supply a resting point
B Repulsion motor C To transfer the heat from heating element
C Reluctance motor D To increase the weight of iron
D Shaded pole motor 53 Which type of motor is used in food mixer?
46 Which type of washing machine is fitted with A Shunt motor
concave shaped disc? B Compound motor
A Air wash C Universal motor
B Agitator wash D 3 phase motor
C Pulsator wash 54 Which type of motor is used in ceiling fan?
D Chaos punch wash A Repulsion motor
47 Which type of wash technique is used for B Reluctance motor
wash delicate fabrics? C Universal motor
A Agitator wash D Permanent capacitor motor
B Pulsator wash 55 What is the condition to change the brushes
C Air power wash of a food mixer?
D Chaos punch wash A If found short by 2/3rd of its original length
48 Which washing machine water is propelled B If found sparking on this brushes
up wards? C If the mixer is vibrating at low speed
A Agitator wash D If the speed of mixer is very high
B Pulsator wash 56 Which type of motor is used on table fan?
C Air power wash A Reputation motor
D Chaos punch wash B Universal motor
C Capacitor start- capacitor run motor
D Permanent capacitor motor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 9
Questions : Level 3 8 What is the reason for a food mixer runs at
one speed only?
1 What is the fault in a food mixer if it runs A Over loading of mixer
intermittently? B The field winding is partially burnt
A Worn out brushes C Worn out brushes
B Armature coil open D Improper coulping
C Defective commutator 9 What is the reason for running ceiling fan
D Field winding partially short hot?
2 What is the defect in a single phase pump A Misalignment of blades
motor if it runs with slow speed? B Slack capacitor housing
A Defective capacitor C Loose connection in terminals
B Open starting winding D Partial short circuit in the winding
C Short in starting winding 10 Which type of bearing is used in table fan
D Short in running winding motor?
3 What is the effect of the loose connection of A Ball bearing
pressure plate in an electric kettle? B Jewel bearing
A The heating element will be damaged C Fluid bearing
B Temperature will be more D Magnetic bearing
C Current will be increased 11 What is the reason for a table fan runs hot?
D Resistance will be increased A Blades are out of balance
4 Why the heating element of a kettle is B Due to shorted winding
placed and enclosed between two circular C Misalignment of blades
mica pieces? D Loose guards
A To distribute the heat uniformly 12 What is the reason of humming noise in a
B To avoid contact with any metallic part table fan?
C To reduce the resistance A Defect in control switch
D To reduce the voltage drop B Worn out bearing fit
5 What is the reason for not giving heat by C Shorted winding
hair dryer while the fan is working? D Blades are unbalanced
A Thermostat is closed 13 What will happen, if immersion heater is
B Short in power cord switched ON without water?
C Open in heater circuit A Fuse blown out
D Power is not available B Metal tube burst
6 What is the reason for the heater of hair C Heated up normally
dryer operateswhile the blower fan is not D Element will not heat
working? 14 What is the output of heat in a twin unit type
A The fan winding open circuited hot plate, if the heating elements are
B Improper mounting connected like this?
C Heater open circuited
D Loose parts of the blower
7 What is the reason for connecting a
capacitor in ceiling fan circuit?
A For good starting torque
B For controlling the speed
C For power factor improvement A OFF
D For increasing the sweep area B Low
C High
D Medium
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 9
15 What will happen, if blower motor failure in 19 What is the defect, if mixer makes more
microwave oven? noise?
A Over heat in power tranformer A Loose brushes
B Voltage doubler circuit damaged B Worn out carlom brushes
C No producting of electro magnetic waves C Uneven commutator surface
D Magnetron assembly damaged due to over D Partially burnt out field winding
heat 20 What is the defect, if a washing machine
16 What is the defect in microwave oven, if switch OFF frequency?
oven shuts down before end of cook cycle? A Low incoming supply
A Open cook switch B Incorrect setting of timer
B Open thermo cut out C Defective starting winding
C Open in power transformer D Defect in running winding of motor
D Open cook relay contacts 21 What is defect, if a washing machine gives
17 What is the defect, if microwave oven does shock?
not go into cook cycle when cook switch is A Weak capacitor
activated? B Incorrect centrifugal switch
A Defective magnetron tube C Low insulation resistance value of motor
B Defective front latch switch D High impedence value of starting winding
C Defective power transformer
D Defective voltage doubler circuit
18 What is defect, if a food mixer does not run?
A Worn out brushes
B Improper coupling
C Loose mounting screws
D Poor insulation resistance
- NIMI Question Bank - Page8/ 9
Module 7: Domestic Appliances - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 A 1 C 39 C 1 A
2 B 2 D 40 D 2 A
3 D 3 A 41 D 3 A
4 A 4 B 42 C 4 B
5 C 5 C 43 C 5 C
6 B 6 B 44 C 6 A
7 A 7 D 45 A 7 A
8 D 8 A 46 C 8 B
9 C 9 C 47 C 9 D
10 D 10 C 48 B 10 A
11 C 11 D 49 B 11 B
12 A 12 B 50 B 12 B
13 B 13 B 51 D 13 D
14 A 14 C 52 B 14 C
15 D 15 A 53 C 15 D
16 B 16 B 54 D 16 C
17 B 17 C 55 A 17 C
18 D 18 B 56 D 18 A
19 A 19 A 19 C
20 B 20 D 20 D
21 C 21 B 21 C
22 B 22 B
23 A
24 B
25 D
26 A
27 C
28 C
29 B
30 A
31 A
32 B
33 D
34 B
35 C
36 B
37 C
38 D
- NIMI Question Bank - Page9/ 9
Electrician - Semester II - CITS - Module - 8 : Estimation and Costing
Questions: Level 1 7 What is the formula to calculate the diversity
factor?
1 What is the reconmended height for Installation load
A Diversity factor =
swithches from the floor level as per Minimum actual load
NECode?
A 2.5m
Minimum actual load
B 2.25m B Diversity factor =
Installation load
C 2.0m
D 1.3m
2 Which is mainly required to determine the Maximum load
C Diversity factor =
dimension of building for preparing wiring Minimum load
estimation?
A Types of building
Minimum load
B Drawing layout D Diversity factor =
Maximum load
C Specification of materials
D Schedule of rate 8 What is the permissible load for the light and
3 What is the recommended size of conduit fan sub-circuits?
pipe used for 3 core copper cable? A 600 Watt
A 19mm heavy gauge conduit B 800 Watt
B 25mm heavy gauge conduit C 1000 Watt
C 10mm heavy gauge conduit D 1250 Watt
D 15mm heavy gauge conduit 9 What is the maximum number of point are
4 Which type of wiring is suitable for computer allowed in a light and fan sub-circuits?
room? A 8
A Battern wiring B 9
B P.V.C casing and capping C 10
D 12
C P.V.C conduit wiring
D Metal conduit Wiring 10 How many number of socket outlet points
5 What is the recommended height for the are to be provided in a light and fan sub
horizontal run of cables from floor level as circuit?
per NEC code? A 2
A 3.0m B 3
B 2.5m C 4
D 5
C 2.0m
11 What is the recommended rating of a ceiling fan
D 1.5m
for estimating the connected load?
6 Which place the rawl plug tool is used?
A 40 Watt
A Non-rigid walls
B 60 Watt
B Rigid walls
C 75 Watt
C Wooden board D 100 Watt
D Metal board
12 What is the recommended rating of a
incandescent lamp for estimating the
connected loads?
A 40 Watt
B 60 Watt
C 75 Watt
D 100 Watt
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
13 What is the recommended rating of a 6A 3
pin socket outlet for estimating connected
loads?
A 60 Watt
B 75 Watt
C 100 Watt
D 125 Watt
14 What is the recommended rating of a 16 A
power socket outlet for estimatiing
connected rods?
A 800 Watt
B 1000 Watt
C 2000 Watt
D 3000 Watt
15 What is the length of the conduits available
commercially?
A 3 meters
B 4 meters
C 5 meters
D 6 meters
16 What is the minimum size of non-metallic
conduit pipes used in wiring?
A 12 mm
B 16 mm
C 20 mm
D 24 mm
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
Questions: Level 2 7 What is the purpose of layout diagram in
estimation of conduit wiring?
1 What are the number of 16 A power socket A To calculate the length of conduit and wires
are recommended for the dwelling area of B To select number of Accessories
45m2? C To calculate the connected load
A 1 D To select the type of wire
B 2 8 What is the recommented cable size for 5
C 3 HP motor by considening full load current
D 4 and starting current?
2 What are the numbers of light and fan points are A 2.0 mm2 copper conductor
recommended for the divelling area of 55m2? B 4.00mm2 copper conductor
A 4 light and 2 fan points C 2.0mm2 aluminium conductor
B 3 light and 2 fan points D 1.0mm2 copper conductor
C 3 light and 3 fan points 9 When the work of concealed wiring
D 4 light and 3 fan points installation should begin in new building?
3 What is the full load current of 5 HP,400V 3 A Before finishing the plastering work
phase induction motor having the efficiency B After finishing the main structural civil work
80% and power factor of 0.85? C Before finishing the white wash and painting
A 5.2 Amps work
B 6.9 Amps D After completion of civil shuttering work
C 7.8 Amps 10 Which step to be considered first before
D 9.5 Amps preparing wiring estimation for house?
4 When the wiring diagram to be drawn while A Prepare the wiring layout
preparing wiring estimation? B Collect the data from consumer like light,
A Before taking measurement fan and power point required
B After finalising the layout C Collect the required wiring accessories and
C Before finalising the layout materials
D After selecting the size of wire D Collect the supply service from electricity
5 Which point is to be considered while board
planning for load in wiring installation? 11 What are the factors are to be considered
A Number of labour's required for estimating the cost of wiring?
B Provision for the anticipated increase in A Cost of hard ware and labour
loads B Cost of materials and hard ware
C Selections of brand of materials C Cost of materials and labours
D Type of dwelling area D Cost of materials, hardware and labour
6 Calculate the labour cost for the below 12 When laying of concealed conduits should
mentioned wiring work, if the labour cost per be started in a new building?
point is Rupees 100/- (i) Meter board - 2 A After completion of main structural civil work
points (ii) Distribution board - 2 points B Before finishing the plastering work
(iii) light and fan - 17 points (iv) power - 2 C Before finishing the white wash and painting
points? and centring
A Rs 2300 D After completion of civil centring work
B Rs 2500
C Rs 2700
D Rs 3000
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3 5 What is the minimum recommended size of
conduit required for connecting 1 HP motor
1 What is the total connected load of an office with its starter as per the given figure?
room having 2 numbers of 1200mm
fluoresent lamp, 1 fan and one 16 A socket?
A 260 Watts
B 280 Watts
C 1160 Watts
D 1180 Watts
2 What is the minimum recommended size copper
flexible cable required to connect a 3 HP 3 phase A 12.5 mm
motor? B 19 mm
A 1.5 Sq mm C 25.4 mm
B 2 Sq mm D 38 mm
C 2.5 Sq mm 6 What is the allowable current after
D 4 Sq mm considering the diversity factor in a 240V,
3 What is minimum recommended size 3000 Watts loads in hotel?
copper flexible cable required to connect on A 7.50 Amps
1 HP single phase motor? B 9.375 Amps
A 1.0 Sq mm C 11.25 Amps
B 1.5 Sq mm D 12.00 Amps
C 2 Sq mm 7 What is the allowable current after
D 2.5 Sq mm considering the diversity factor in a 240V,
4 What is the minimum recommended size of 2880 Watts lighting load in house as per
conduit required for connecting 5 HP motor with BIS?
its starter as per the given figure? A 7.20 Amps
B 7.92 Amps
C 9.60 Amps
D 12.00 Amps
8 What happens , if undersized cable is used for
connecting pump set motor?
A Over voltage and pump speed increases
B Under voltage and pump speed decreases
A 12.5 mm C Under loading of the cable and speed
B 19 mm decreases
C 25.4 mm D Overloading of the cable and speed
D 38 mm increases
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module - 8 : Estimation and Costing - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 D 1 B 1 C
2 B 2 D 2 B
3 A 3 C 3 A
4 B 4 B 4 C
5 B 5 B 5 B
6 B 6 A 6 B
7 B 7 A 7 B
8 B 8 A 8 A
9 C 9 A
10 A 10 B
11 B 11 D
12 B 12 D
13 C
14 B
15 A
16 B
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
Electrician - Semester II - CITS - Module 9 : Power Generation
Questions: Level 1 7 Name the constituent marked ‘X’ of the
schematic arrangement of hydro electric
1 Which fuel is available in plenty in India for plant.
power generation?
A Coal
B Diesel
C Gas oil
D Gasoline
2 Which is the conventional power generation?
A Penstock
A Wind power generation
B Surge tank
B Tidal power generation
C Valve house
C Solar power generation
D Power house
D Thermal power generation
8 Which is a non-conventional energy source?
3 Which material is used in solar cell?
A Lignite
A Silicon
B Sun rays
B Copper
C Stored water
C Antimony
D Pulverized coal
D Phosphorus
9 Which is the renewable energy source for
4 What is the name of the atomic material
producing electricity?
used for nuclear fission in nuclear power
A Fuel
station?
B Tidal
A Silicon
C Water
B Thorium
D Nuclear
C Antimony
10 Which energy is converted by the possessed
D Cadmium
water potential energy?
5 Which is the non conventional energy
A Heat energy
source?
B Kinetic energy
A Wind
C Electrical energy
B Water
D Mechanical energy
C Steam
11 Which is the main source of energy?
D Diesel
A Solar
6 Which is the natural source of energy?
B Wind
A Sun
C Water
B Heat
D Fuels
C Coal
12 Which prime mover cannot be used to
D Biogas
convert heat energy into mechanical energy?
A Steam engine
B Steam turbine
C Internal combustion engines
D Pressure combustion engines
13 Which energy source is most complex to
produce electricity?
A Fuel
B Wind
C Water
D Atomic material
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 9
14 Which power generating plant offers no
stand by losses?
A Wind
B Diesel
C Nuclear
D Hydro electric
15 Which electric generating plant offers only
low power generation?
A Wind
B Nuclear
C Diesel plant
D Hydro electric
16 Which is the example for a non convention
power generation?
A Tidel
B Hydel
C Nuclear
D Thermal /coal
17 Which equipment is excluded in main
constituent in a steam power station?
A Prime mover
B Condenser
C Circuit breaker
D Steam generating equipment
18 What is the washing fluid used in a gas
turbine of steam power plant?
A Air
B LPG
C Diesel
D Methene gas
19 Which material is used to make solar cell?
A Silicon
B Antimony
C Tantalium
D Germanium
20 What is the name of material used for
nuclear fission process in nuclear power
plant?
A Uranium
B Cadmium
C Silicon
D Germanium
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 9
Questions: Level 2 9 Which is the non conventional power
generation?
1 What is the main disadvantage of non- A Diesel power generation
conventional power generation? B Nuclear power generation
A Poor efficiency C Wind mill power generation
B No constant generation D Hydro-electric power generation
C Can use only light loads 10 Which is the residue of bio-mass?
D Heavy load cannot be operated A Slurry
2 Which power generation requires heavy B Bio fuel
water treatment plant? C Manure
A Hydel power generation D Bio gas
B Diesel power generation 11 Which is the main constituent of biogas?
C Thermal power generation A Oxygen
D Nuclear power generation B Methane
3 Which device senses the wind speed in a C Hydrogen
wind power generation? D Carbon dioxide
A Exciter unit 12 How electricity produced in solar panel?
B Turbine controller A While sunlight strikes glass
C Chopper controller B While sunlight strikes nickel plate
D Line controller unit C While sunlight strikes manganese
4 Which turbine is used for high heads in hydro D While sunlight strikes on photovoltaic cell
electric power plant? 13 What is the function of air pre heater in a
A Kaplan turbine steam power station?
B Impulse turbine A Heats feed water
C Francis turbine B Supplies hot air to economiser
D Reaction turbine C Supplies hot air to super heater
5 What is the function of penstocks in hydro D Extracts heat from flue gases and heats
power stations? input air
A Carries water to dam 14 What is the main disadvantage of nuclear
B Carries water to turbines plant?
C Carries water away from power house A Disposal of waste
D Discharges surplus water from reservoir B Running cost is more
6 Which is the purpose of boiler in a steam C Plant requires large space
power station? D Installed away from load centre
A Super heats the steam 15 What is the function of economiser in steam
B Heats feed water and air power plant?
C Converts water in to steam A Converts water into steam
D Liberates the heat from burnt fuel B Heats the air by the flue gases
7 Which type of power plant is more efficient? C Heats the feed water by the flue gases
A Diesel plant D Purifies the feed water by chemical treatment
B Steam power 16 What is the disadvantage of diesel power
C Hydro electric plant?
D Nuclear power A Makes more noise
8 Which material is used as control rod in a B More space is required
nuclear reactor? C Cannot be started quickly
A Thorium D Efficiency is lower than other plants
B Graphite
C Cadmium
D Tungsten
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 9
17 What is the advantage of non conventional 24 Which is the disadvantage of non
power generation? conventional power generation over
A More reliable conventional power generation?
B More efficient A Increase pollution
C Low initial cost B Security risk is more
D Reduce pollution C Requires more maintenance
18 What is the function of charge controller in D Cannot be used for base load demand
battery based micro hydel power generation? 25 What is the major disadvantage of wind
A Controls the over voltage power generation?
B Disconnects turbine from the battery A Pollution effect is more
C Prevents the over charging of battery B Requires high technology
D Controls the over speed of the turbine C Plant installation more complicated
19 What is the purpose of barrage in tidal power D Wind power is not constant and steady
station? 26 What is the function of turbine used in tidal
A Controls the tidal waves power generation?
B Releases water towards the sea A Prevents water flow to other parts of dam
C Tap the water at the entrance of gulf B Converts potential energy into kinetic energy
D Converts potential energy into kinetic energy C Keeps the water flow from low to higher level
20 Which component in a steam power plant is D Converts kinetic energy into potential energy
used to heat the feed water from the flue 27 What is the advantage of non-conventional
gas? energy source?
A Boiler A More reliable
B Economizer B Low initial cost
C Super heater C Efficiency is high
D Air pre heater D Green house effect is avoided
21 What is the function of governing system in 28 What is the main draw back of wind mill
diesel power plant? energy production?
A Start the engine from cold by supplying the A Wind mill installs in hills
compressed air B Uncertainty of wind available
B Maintain the speed of the engine constant C Wind mill has too heavy structure
C Control the heat from the engine cylinder to D It requires large area to install
keep safe temperature 29 What is the example of a conventional power
D Reduce the friction of moving parts in engine generation?
22 What is the advantage of pressurized water A Sun
reactor (PWR)? B Tidel
A No heat loss C Wind
B High thermal efficiency D Nuclear
C High power density 30 Which item is unavailable in the steam
D Metal surface temperature is lower generating equipment?
23 Which power generation plant is having more A Boiler
reliability in operation? B Super heater
A Hydro power plant C Air preheats
B Diesel power plant D Boiler furnace
C Nuclear power plant 31 What is the function of a boiler in the steam
D Thermal power plant power plant?
A Water is converted into steam
B Feeds input to economise
C Used only for preheating of air
D Used for making hot water in the plant
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 9
32 What is the function of a surface heater in a 39 Which device is unavailable part of
steam power station? lubrication system in the diesel power plant?
A Air pre heating A Filters
B Supply flue gases to boiler B Air tank
C Raises the temperature of steam C Oil tank
D Decrease the temperature of steam D Oil pump
33 What is the function of economiser in the 40 What is the main draw back of gas turbine in
steam power station? steam power plant
A Heats air for boiler A Smaller in size
B Heats the feed water B No stand by losses
C Supply flue gases to boiler C No condenser in used
D Opens the valve of turbine D Efficiency and output are low
34 What is the function of air pre heaters in a 41 What is the necessity of a combustion
steam power station? chamber in a gas turbine power plant?
A Heats feed water A Heating of air
B Supply hot air to economiser B Filtering of air
C Supply hot air to super heater C Compressing of air
D Extract heat from flue gases and heat input D Atomization of oil
air 42 Which energy is utilized to hydro electric
35 Which device converts steam energy into power generation using waters?
mechanical energy in a steam power A Heat energy
stations? B Kinetic energy
A Turbine C Potential energy
B Alternator D Magnetic energy
C Condenser 43 Which statement is unrelated to the hydro
D Prime mover electric power stations?
36 What is the function of super charger in the A Penstock
diesel power plant? B Surge tank
A Reduce the air pressure C Reservoir
B Increase the air pressure D Small running charge
C Increase the engine efficiency 44 Which is unrelated for selection of site for
D Regulate the diesel consumption hydro electric power stations?
37 Which part of a fuel system is unavailable in A Transportation
a diesel power plant? B Storage of water
A Silencer C Low capital cost
B Strainer D Availability of water
C Storage tank 45 What is the purpose of surge tank in a hydro
D Fuel transfer pump electric power plant?
38 What is the purpose of cooling system in a A To regulate water flow
diesel power plant? B To maintain the water level
A Control the oil temperature C To reduce the pressure in condenser
B Control the strainer temperature D To control the water flow in spill ways
C Control the silencer temperature 46 What is the purpose of using penstocks in
D Control the cylinder temperature hydro electric power plant?
A To control water flow
B To maintain water level
C Supply water to turbines
D To regulate water pressure
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 9
47 What factor is irrelevant for selecting steam 55 What effect is called heat generating
power stations? electricity using solar energy on materials?
A Supply of fuel A Photovoltaic
B Availability of water B Electrostatic
C Availability of exports C Electromotive
D Transportation facilities D Magnetomotive
48 Which apparatus used for nuclear fission in a 56 What is the main constituent of biogas?
nuclear plant? A Hydrogen
A Exciter B Nytrogen
B Reactor C Methene
C Condenser D Carbon dioxide
D Heat exchanger 57 Which mixture of gases is forming from
49 Which is the disadvantage of nuclear plant? animal excrete, vegetable waste and under
A Disposal of waste go decomposition?
B Low running charges A LPG
C Plant require by space B Biogas
D Installed near to load entre C Nitrogen gas
50 Which material enclose the fuel rods in the D Hydrogen gas
reactor? 58 What is the converting bio mass into liquid
A Antimay fuels for transportation?
B Graphite A Bio fuels
C Manganise B Bio gases
D Phospherium C Bio power
51 Which reactor used fuel enriched uranium? D Bio products
A BWR 59 Which energy of the fuel is converted into
B PWR mechanical energy into solarcell?
C Berryllium A Heat
D Graphite reactors B Light
52 Which is the disadvantage of heat exchanger C Kinetic
in a pressurized water reactor? D Potential
A Heat loss 60 What is the name called for the steam
B Heat regaining passed into turbine in a steam/thermal power
C Heat uncontrollable station?
D Heat pressure increases A Combusted steam
53 What is used to access the peoples per B Pre heated steam
capita consumption of energy? C Pressurized steam
A Education level D Super heated steam
B Health standard 61 Which is the disadvantage of steam power
C Standard of living plant?
D Per capita income A High lubrication cost
54 Which chemical gas is produced while B High maintenance cost
forming silicon from silica? C No continuous over loading
A Ammonia D long manufacturing periods
B Nitrogen 62 Which is the disadvantage of diesel plant
C Chlorine over steam plant?
D Carbon dioxide A No ash handling
B Unit cost in more
C No stand by losses
D Installing near to load centre
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 9
63 Which material used as control rod in a
reactor?
A Mercury
B Thorium
C Tungsten
D Cadmium
64 What is the function of regenerator in a gas
turbine power plant?
A Supply air
B Heating of air
C Compressing of air
D Cooling of chamber
65 Which turbine in used for high heads in a
hydro electric power plant?
A Francis turbines
B Impulse turbines
C Kaplam turbines
D Reaction turbines
66 What is the function of water turbine?
A Drains alternator
B It controls water flow
C Regulate turbine speed
D Decides the potential energy
67 What is the efficiency of a diesel power plant
over steam power plants?
A Very low
B Very High
C Very poor
D Medium
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 9
Questions: Level 3 8 How the disposal of waste in a nuclear
power plant is disposed?
1 How the heat is produced for making steam A It burnt out
in a nuclear power station? B Send for recycling
A By fission method C Dump in open yard
B By doping method D Buried in deep trenches
C Burning the material 9 What is the name called for the process of
D By applying pressure breaking nucleus of a heavy atom?
2 How the potential energy from water flowing A Fusion
is converted as kinetic energy to generate B Fission
power? C Chain fission
A By storing water in high quantity D Bombardement
B By using surge tanks at the water canal 10 What is the name called, number of fission
C By using water turbine to drive alternator taking place at each successive stage goes
D By creating high head through penstocks on increasing?
3 What is the effect of radio active rays A Chain reaction
produced during nuclear fission? B Successive reaction
A Damages the reactors C Progressive reaction
B Creates health hazards D Continuous reaction
C Reduces fission process 11 Which material is the cause for emitting
D Enormous heat is produced poisonous radioactive rays during solar cell
4 What happens to solar cell, if the intensity of fabrications?
light is low? A Lead
A Output increases B Antimony
B Output decreases C Solarium
C Output remain same D Cadmium
D No output in the cell 12 How the power is governed in the diesel
5 What is the output voltage of a solar cell, if power plants?
light intensity is high? A Vaying the fuel
A No output in the cell B Vaying the voltage
B Output voltage is increased C Controlling the load
C No effect and remain same D Adding capacitor bank
D Output voltage is decreased 13 How the power is produced by wind mills?
6 What is the main reason to keep steam A Wind mill radiates power
power station far away from populated B Wind mill drawn generator
areas? C Wind mill converts electrical energy
A Any time plant will burst D Wind mill blade cuts the wind and produce
B To avoid people’s interference power
C Because of environmental reasons
D To keep the secrecy of plant operations
7 How to maintain longer life and better
efficiency of boilers in a steam power plant?
A Use soft water
B Unless quality coal
C Remove ash timely
D Reduce size of boiler
- NIMI Question Bank - Page8/ 9
Module 9 : Power Generation - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 A 1 A 38 A 1 C
2 D 2 D 39 D 2 D
3 A 3 B 40 D 3 B
4 B 4 B 41 A 4 B
5 A 5 B 42 B 5 B
6 A 6 C 43 D 6 B
7 B 7 C 44 A 7 D
8 B 8 C 45 A 8 C
9 C 9 C 46 C 9 C
10 B 10 A 47 C 10 A
11 D 11 B 48 B 11 D
12 D 12 D 49 D 12 A
13 A 13 D 50 B 13 A
14 B 14 A 51 B
15 A 15 C 52 B
16 C 16 A 53 B
17 C 17 D 54 D
18 D 18 C 55 A
19 A 19 C 56 D
20 A 20 B 57 B
21 B 58 B
22 C 59 B
23 C 60 A
24 D 61 D
25 D 62 C
26 B 63 A
27 D 64 C
28 C 65 B
29 D 66 D
30 C 67 B
31 A
32 B
33 A
34 C
35 D
36 A
37 B
- NIMI Question Bank - Page9/ 9
Electrician - Semester II - CITS - Module - 10 :
Transmission of Electric Power, U.G Cable & Distribution of Power
Questions: Level 1 6 What is the name of line insulator?
1 Which electric lines connect the substation
to distributors in distribution system?
A Feeders
B Distributors
C Service lines
D Service mains
2 What is the insulation resistance between any
two conductors in a medium voltage domestic A Pin type insulator
installation as per IE rules? B Disc type insulator
A Infinity C Shackle type insulator
B More than one Mega ohm D Suspension type insulator
C Below than one Mega ohm 7 Which is the permissble load for power
D More than 100 Mega ohms circuit in domestic wiring as per IE rules?
3 What is diversity factor (D.F)? A 800 W
A DF = minimum actual load B 1200 W
Installed load C 2400 W
Installed load
B DF = D 3000 W
minimum actual load
8 What is the name of the insulator?
minimum installed load
C DF =
actual load
actual load
D DF =
minimum installed load
4 What is the voltage ratio in A.C distribution
line adopted for domestic consumers?
A 415 V/240 V
A Stay insulator
B 240 V/110 V
B Shackle insulator
C 415 V/110 V
C Suspension insulator
D 11 KV/415 V
D Single shed pin insulator
5 What is the name of the insulator used in
9 Which voltage rate is coming under primary
O.H lines?
transmission?
A 11 KV
B 33 KV
C 66 KV
D 220 KV.
10 Which voltage rate is coming under
secondary transmission?
A 66 KV
B 110 KV
C 220 KV
A Pin insulator
B Post insulator D 500 KV
C Strain insulator
D Shackle insulator
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 8
11 Which material is used to make the insulators?
A Mica
B Ceramic
C Asbestos
D Parelin clay
12 What is the normal working voltage rate
uses in suspension type insulators?
A Beyond 11 KV
B Beyond 33 KV
C Less than 33 KV
D Less than 11 KV
13 What is the maximum span of wooden pole
can be used for distribution?
A Upto 25 meters
B Upto 50 meters
C Upto 75 meters
D Upto 100 meters
14 What is the phenomenon known of violet
glow, during noise and producting ozone
gas in a OH transmission line?
A Flash
B Surge
C Corona
D Ferranty
15 What is the maximum percentage of
tolerance is allowed in variation of decleared
voltage in lines medium voltage makes rule
54?
A 5%
B 10%
C 2.5%
D 7.5%
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 8
Questions: Level 2 7 What is the reason of keeping binding wire
gap too close and very tight in pin insulator?
1 What is the reason for the conductor cross- A Avoid sparking
sectional area can fully utilised on B Avoid corrosion
transmission of DC as compared to AC? C Avoid oxide formation
A No heat loss D Avoid atmospheric pressure
B No skin effect 8 What is the name of conductor used on
C No power loss overhead lines??
D No corona loss A ACSR
2 Why the disc pin insulators outer surface is made B Aluminium
by glazing and bent the sides inward? C Galvanised iron
A To withstand high voltage D Hard drawn copper
B Not to attract birds to sit on it 9 What is the main purpose of cross arm used in
C To offer high mechanical strength electric poles?
D Disables continuous water flow in rainy A Supporting the line conductors
season B Holding the insulators on overhead line
3 What is the type of over head line joint? C Avoids short circuit between conductors
D Reduces conductor sag between supports
10 Which type of line insulator is used at the dead
ends of the H.T overhead lines?
A Pin insulator
B Disc insulator
A Twisted joint C Stay insulator
B Straight sleeve joint D Post insulator
C Compression joint for ACSR 11 What is the advantage of AC power
D Straight joint through connectors transmission?
4 Why steel is reinforced in ACSR conductors A Corona loss negligible
used for over head lines? B Stress on transmission lines is minimum
A To minimize the line sag C Low voltage drop in transmission lines
B To reduce the line voltage drop D Voltages can be stepped up and stepped down
easily
C To increase the tensile strength
D To increase the current carrying capacity 12 What is ACSR stands for?
5 Which type of A.C transmission is A All Conductors Steel Reinforced
universallly adopted? B Aluminium Core Steel Reinforced
A Two phase four wire C Aluminium Covered Steel Reinforced
B Two phase three wire D Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced
C Single phase two wire 13 What is the purpose of cross-arm in O.H
D Three phase three wire lines?
6 Which type of line insulator is used for A Provide more support to the O.H pole
terminating on corner post? B Protect from short between conductors
A Pin insulator C Reduce the sag of the lines between poles
B Strain insulator D Holding the insulators were the conductors are
fastened
C Shackle insulator
D Suspension insulator
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 8
14 What is the advantage of over head lines 20 What is the advantage of UG cable
compared to underground cable? compared to OH line transmission?
A Public safety is more A No lightening hazards
B Faults can be located easily B Faults can be detected easily
C No interference with the communication C Easy to extend the lines
lines D Less material cost
D Not liable to the hazards from lightning 21 What is the electrical switch gear?
discharges A Load control switch
15 Which type of lightning arrester? B Switching device
C Distribution analyser
D AC production control
22 How to make contact pressure in pantograph
isolator?
A Automatic lever control
B By using counter weight
C Motorised contact setting
D Disc springs arrangement
23 What is the current and voltage in a short
A Rod gap arrester circuited condition?
B Horn gap arrester A Both current and voltage is zero
C Multi gap arrester B Both current and voltage is same
D Expulsion type arrester C Current is zero and voltage is maximum
16 Which type of lightning arrester is used for D Voltage is zero and current is maximum
only for backup protection? 24 What is the function of Lightening arrestor?
A Rod gap arrester A Protection against surges
B Horn gap arrester B Controls high current in line
C Multi gap arrester C Protection of line from earthing
D Valve type arrester D Providing voltage regulation in line
17 Which substation the transmission line 25 What is the name called the cable
voltage is stepped down to consumer supply connected between distributors and
voltage? consumer load terminal?
A Mobile substation A Load line
B Mining substation B Power line
C Secondary substation C Supply line
D Distribution substation D Service line
18 Which insulation material is limited use to 26 Which is disadvantage of DC over AC
provide insulation to UG cables? transmission?
A Impregnated paper A More corona loss
B Varnished cambric B Cannot generate high voltage
C Rubber mineral compound C Requires more space
D Plastic coated PVC sheets D More line losses
19 What is the purpose of providing metallic 27 Which is considered as a advantage of DC
sheets in UG cables? over AC for transmission?
A Protection from heat A No skin effect
B Protection from ageing B High DC voltage can be generated
C Protection from moisture C Frequency related circuits can be used
D Protection from mechanical damages D Step-up or step down using transformer is
possible
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 8
28 Which is an advantage of AC over DC for 35 What is the advantage of ring main
transmission? distribution system?
A Less corona loss A Less voltage fluctuation
B Less voltage drop B direct access of distribution
C Can be step-up and step down easely C Increases efficiency of the system
D Less line loss D Increase service reliability
29 Which device converts high power high 36 Where the earth switch is connected in a
voltage AC to DC conventional for substation?
transmission? A Between isolator switch and earth
A Zener diodes B Between earth and uncharged conductor
B PN junction diodes C Between power transmission terminal and
C High power inverter earth
D Mercurry arc rectifies D Between uncharged conductor and
30 What is the effect of corona in the line? lightening arrestor
A No voltage regulation 37 Which cooling method used to a 11KV /
B Line frequency will reduce 440V distribution transmission?
C Transmission efficiency reduces A Natural air cooling
D Lightening charges are increased B Air blast oil cooling
31 What is the effect on conductor. If the C Oil natural air natural
ozone produced by corona? D Water cooling method
A Reduce resistance 38 Which electric lines connect generating
B Increase resistance station to distributors?
C Reduce tensile strength A Feeders
D Corrossion due to chemical action B Power lines
32 What is the name called the difference in C Service lines
level between points of supports and the D Distribution lines
lower point of the conductor? 39 What is the advantage of high voltage AC
A Sag of the conductor line transmission?
B Distance of the conductor A Reduce power
C Tensile strength of conductor B Reduce current
D Clearance of the conductor line C Reduce resistance
33 What is the term called the difference in D Increase power factor
voltage at receiving end and sending end
expressed in percentage in a transmission
line?
A Line constant
B Line regulation
C Voltage regulation
D Transmission regulation
34 What is the function of relay in a switchgear
protection circuit?
A Control the circuit current
B Regulate the voltage
C To detect the fault in circuit
D Protect the circuit
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 8
Questions: Level 3 7 What is the cause for the defect if phase to
ground fault on the transmission line?
1 What happens to the string arrangement of A Components failure
disc insulators, if one of the disc insulator B Insulation failure
gets damaged? C Skin effect
A Whole string become useless D Fuse failure
B No effect operates normally 8 What is the process of mixing pure rubber with
C Only the damaged disc will not function mineral mattes and sulphur?
D Damaged insulator and the adjacent insulator will A Annealing
not function B Compounding
2 How the sparking on the aluminium cored C Impregnating
conductors binding joints can be prevented? D Vulcanizing
A Keeping binding turns very close 9 Why the VIR insulation is generally used
B Making binding turns very tight tinned copper conductor?
C Providing guard wires below the conductors A To prevent electrical fire
D Providing more than one binding B To avoid chemical reaction
3 What happens to the skin effect on the O.H C To reduce electrical losses
conductors, if the conductor diameter is D To maintain maximum insulation
small (<1cm)? 10 Why the belt is provided in the belted cables?
A Becomes negligible A Protection of leakage current
B Increases to maximum B Preventing conductor temperature
C No effect, remain same C Housing the core material in tight condition
D Decreases half of the value D Providing insulation and protection from
4 What is the effect, if the test button marked as ‘X’ moisture
is closed permanently in ELCB? 11 What will happen, if the tangertial stresses
set up in paper insulation beyond 22 KV in a
belted cable?
A Causes leakage current
B Causes insulation failure
C Breaks the cable immediately
D Causes short circuits instantaneously
‘X’
12 Why isolator always to be operated after
A Circuit trips intermittently circuit breaker is opened?
B Circuit functions normally A To share the load current
C Circuit switch off completely B To reduce the breaking line
D Circuit will not trip on leakage C To avoid huge area quenching
5 What is the defect in an air circuit breaker, if D To avoid contact damage
trips intermittenly on loading? 13 What is the intention of glazing the line
A Incorrect setting of relay insulators in OH lines?
B Excessive heat A To provide good loading
C Insufficient air pressure B Avoid birds to set on them
D Line voltage is too high C Avoid absorption of moisture
6 What is the defect in oil circuit breaker, if the oil D To increase mechanical strength
heats up excessively? 14 Which is unrelated to the property of pin
A Line voltage is too high insulator in H.V.T transmission lines?
B Excessive load A High ratio of puncture
C Poor dielectric strength B High dielectric strength
D Defective tripping mechanism C High mechanical strength
D High brittle resist capacity
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 8
15 What will happen, if the pin insulator is
porous, lot of impurition and cracks?
A Lowers the permitivity
B Lower the dielectric strength
C Lowers the electrical resistance
D Reduce the ratio of puncture strength
16 Why the steel tower footings are usually
grounded by driving rods?
A Prevents surges
B Carry high voltage
C Minimize lightening troubles
D Maintain constant voltage in line
17 What situation OH lines are surrounded by a
faint violet glow formed?
A Too much of voltage surges
B Size of conductor very small
C Not used stranded conductors
D Voltage exceeds critical disruptive level
18 Which is to be considered to reduce corona
effect?
A Regulate power utilisation
B Maintain line voltage constant
C Reduce the electro static stresses
D Increase the electro static stresses
19 Which fault in power system is no longer
present if, power is disconnected for a short
time?
A Transient line fault
B Persistant line fault
C Symmetric line fault
D Asymmetric fault
- NIMI Question Bank - Page7/ 8
Module - 10 :Transmission of Electric Power, U.G Cable &
Distribution of Power - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 A 1 B 37 B 1 C
2 B 2 D 38 A 2 B
3 A 3 C 39 B 3 A
4 A 4 C 4 C
5 D 5 D 5 A
6 D 6 C 6 C
7 D 7 A 7 B
8 D 8 A 8 D
9 D 9 B 9 B
10 A 10 B 10 D
11 B 11 D 11 A
12 B 12 D 12 C
13 B 13 D 13 C
14 A 14 B 14 D
15 B 15 A 15 D
16 A 16 C
17 D 17 A
18 C 18 C
19 B 19 A
20 A
21 B
22 D
23 A
24 A
25 D
26 B
27 A
28 C
29 C
30 C
31 D
32 A
33 C
34 C
35 A
36 A
- NIMI Question Bank - Page8/ 8
You might also like
- PDI ChecklistDocument2 pagesPDI ChecklistAmmar Baig67% (6)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Manual Operasi Dan Maintenance ARU PDFDocument105 pagesManual Operasi Dan Maintenance ARU PDFDwi Cahya SeptiawanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - ENEL 280Document6 pagesLab 4 - ENEL 280Felipe CamargoNo ratings yet
- Epira Primer From Doe WebsiteDocument4 pagesEpira Primer From Doe WebsiteMartin Benjamin Tomelden LagmayNo ratings yet
- Report 6 (EEE111)Document3 pagesReport 6 (EEE111)Kamal Ahmad75% (8)
- ElectricianATSBlockDocument42 pagesElectricianATSBlockgilbertshadeyaNo ratings yet
- Electrician 3 Semester - Module 1: DC Generator: Questions: Level 1 1 5Document40 pagesElectrician 3 Semester - Module 1: DC Generator: Questions: Level 1 1 5sreeNo ratings yet
- Electrician 3 Rds em Ns QFDocument40 pagesElectrician 3 Rds em Ns QFAbdul SubanNo ratings yet
- Questions On Efficiency and RegulationDocument29 pagesQuestions On Efficiency and Regulationkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Weeks 5-6 DeliveryDocument73 pagesWeeks 5-6 DeliverymichaelprriorNo ratings yet
- DCM Lab Manual - 0 PDFDocument45 pagesDCM Lab Manual - 0 PDFVenkata HemanthNo ratings yet
- Electrical100 Important Expected MCQ PDF With SolutionDocument24 pagesElectrical100 Important Expected MCQ PDF With SolutionNandakumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- EDA (MCT) Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEDA (MCT) Lab ManualThanigaigriezmann GkNo ratings yet
- MT8311 - Electrical Machines ManualDocument20 pagesMT8311 - Electrical Machines ManualArivanandanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFDocument52 pagesElectrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFSantosh VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Exercise:: Power Electronics - Section 1: Answer: ExplanationDocument1 pageExercise:: Power Electronics - Section 1: Answer: ExplanationMa. Corazon DumalaogNo ratings yet
- VL TLX - Service - ManualDocument56 pagesVL TLX - Service - ManualanupthattaNo ratings yet
- Analysed Electrical QueriesDocument33 pagesAnalysed Electrical QueriesmadhivananspNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering QuestionsDocument1,174 pagesElectrical Engineering Questionskartavyajain50% (4)
- Brake Test DC Shunt MotorDocument3 pagesBrake Test DC Shunt MotorVARAPRASADNo ratings yet
- C. 500w C. One Amp - OhmDocument4 pagesC. 500w C. One Amp - Ohmfiraol100% (2)
- Objective Type Questions: The Motor WillDocument12 pagesObjective Type Questions: The Motor WillMohamad SannanNo ratings yet
- Relay Identification: Example CDG31FF002SACHDocument5 pagesRelay Identification: Example CDG31FF002SACHRohit RanaNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0009 MCQ EE Board Problem 2011 10Document1 pageIMG - 0009 MCQ EE Board Problem 2011 10Master JaguarNo ratings yet
- ELEC Power Electronics IndiabixDocument80 pagesELEC Power Electronics IndiabixRomz Ayuman100% (1)
- Electronic Circuits: A - B - C - DDocument7 pagesElectronic Circuits: A - B - C - DaravindhNo ratings yet
- Brake Test DC Series MotorDocument3 pagesBrake Test DC Series MotorVARAPRASADNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Ecp 483L1 2015Document4 pagesFinal Exam Ecp 483L1 2015Ronn Albert GabucayNo ratings yet
- Parte A Ins EleDocument37 pagesParte A Ins EleDiego Alberto Arellano ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Rural ElectrificationDocument7 pagesRural ElectrificationAlfredo CondeNo ratings yet
- D. Maintain A Constant Voltage Under Varying LoadsDocument4 pagesD. Maintain A Constant Voltage Under Varying LoadsRonn Albert GabucayNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Course 4 Compilation - SolutionsDocument12 pagesLevel 2 Course 4 Compilation - SolutionsTatianna linsleyNo ratings yet
- PSD 2 MarksDocument4 pagesPSD 2 Marksnarendra kumarNo ratings yet
- IMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Document223 pagesIMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Rishi Kant Sharma100% (1)
- AE10 SolDocument223 pagesAE10 SolDrGopikrishna PasamNo ratings yet
- 0 Conventional Relay Nomenclature-1Document3 pages0 Conventional Relay Nomenclature-1Archer 19No ratings yet
- ELectrician 4 Thsem NSQFDocument38 pagesELectrician 4 Thsem NSQFAbhimanyu Kilania100% (3)
- FDC Lab ManualDocument25 pagesFDC Lab ManualtovilasNo ratings yet
- CE ElexDocument4 pagesCE Elexjj012586No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Abb Megamax F2Document62 pagesAbb Megamax F2marvin2008No ratings yet
- If101 Iom Ds Turbine Pumps OBSOLETEDocument48 pagesIf101 Iom Ds Turbine Pumps OBSOLETEmarvin2008No ratings yet
- Catalago de Breakers Fuji ElectricDocument98 pagesCatalago de Breakers Fuji Electricmarvin2008No ratings yet
- Corken Pump TroubleshootingDocument21 pagesCorken Pump Troubleshootingmarvin2008No ratings yet
- Corken C10 C12 C13 Electric Motor Change and New Wiring DiagramDocument2 pagesCorken C10 C12 C13 Electric Motor Change and New Wiring Diagrammarvin2008No ratings yet
- Inteligen: General Purpose High-End Gen-Set ControllerDocument4 pagesInteligen: General Purpose High-End Gen-Set Controllermarvin2008No ratings yet
- Infineon Motorcontrol - Handbook AdditionalTechnicalInformation v01 - 00 EN PDFDocument110 pagesInfineon Motorcontrol - Handbook AdditionalTechnicalInformation v01 - 00 EN PDFmarvin2008No ratings yet
- Service Manual: Mini Component Sound SystemDocument35 pagesService Manual: Mini Component Sound SystemRandy LeonNo ratings yet
- ELECTRODYNAMOMETERDocument14 pagesELECTRODYNAMOMETERaisyahNo ratings yet
- State Electricity CommissionDocument4 pagesState Electricity CommissionShubh PathroliaNo ratings yet
- Charging System Troubleshooting (1406) : Instrucción EspecialDocument16 pagesCharging System Troubleshooting (1406) : Instrucción EspecialMiguel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: RCD From 30 Ma To 500 MaDocument3 pagesTechnical Data: RCD From 30 Ma To 500 Makhairalla mohamedNo ratings yet
- 18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Document57 pages18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Mohammed JavidhNo ratings yet
- Operation of MicrogridDocument52 pagesOperation of Microgridketan bhere100% (1)
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument26 pagesIlovepdf MergedOP PRINCE100% (1)
- Whelen Ups 64cDocument5 pagesWhelen Ups 64c140853No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Electric Vehicle Component Performance Over Eco-Driving CyclesDocument17 pagesEvaluation of Electric Vehicle Component Performance Over Eco-Driving CyclesPawan DhakalNo ratings yet
- Flyer Referenzen 2019Document2 pagesFlyer Referenzen 2019Elias RizkNo ratings yet
- ZX32 VF JYMC Variable Speed DC Motor ControlsDocument3 pagesZX32 VF JYMC Variable Speed DC Motor ControlsriegerautoNo ratings yet
- HTC Korea TAEJIN Tech LM1117GS 5 0 - C465002Document12 pagesHTC Korea TAEJIN Tech LM1117GS 5 0 - C465002allradNo ratings yet
- Vse Company Profile MalaysiaDocument21 pagesVse Company Profile MalaysiaYan AungNo ratings yet
- The X-R Static UNIVET 37-400 Is A Cost-Effective Versatile High-Frequency X-Ray System That Delivers High-Quality RadiographsDocument3 pagesThe X-R Static UNIVET 37-400 Is A Cost-Effective Versatile High-Frequency X-Ray System That Delivers High-Quality RadiographsAlexutza StanNo ratings yet
- CVT in Electrical Capacitive Voltage TransformerDocument5 pagesCVT in Electrical Capacitive Voltage TransformersrifaceNo ratings yet
- ABB Shore-To-Ship Power - Brochure - 11.2010 - LR PDFDocument8 pagesABB Shore-To-Ship Power - Brochure - 11.2010 - LR PDFRahul SinganiaNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits: Electronics IDocument25 pagesDiode Circuits: Electronics I呼除預No ratings yet
- Dse5510 Installation InstDocument2 pagesDse5510 Installation Instricardo_dionisi2700No ratings yet
- Integrated Multi-Channel DC-DC Converters For TFT LCD PanelsDocument11 pagesIntegrated Multi-Channel DC-DC Converters For TFT LCD PanelsYuksel NuhogluNo ratings yet
- Contactor Abb-Af116-Af146Document8 pagesContactor Abb-Af116-Af146Ivan HerreaNo ratings yet
- EE6411 Electrical Machines - 1 Lab ManualDocument173 pagesEE6411 Electrical Machines - 1 Lab ManualSubramaniam Gnanasekaran0% (1)
- TG-4033 Dubai Metro - ViaDuct - Cables 7250LMEDocument48 pagesTG-4033 Dubai Metro - ViaDuct - Cables 7250LMEJason SecretNo ratings yet
- Cynthia MachucaDocument3 pagesCynthia MachucaCynthia MachucaNo ratings yet
- MR OltcDocument264 pagesMR Oltcas0922476351No ratings yet