Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW) PDF
NU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW) PDF
Uploaded by
Hernan Beñabon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views1 pageOriginal Title
NU_Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views1 pageNU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW) PDF
NU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW) PDF
Uploaded by
Hernan BeñabonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
HYDRAULICS
Lecture 6. Unsteady Flow
Learning Objectives. 2. For variable cross-sectional
After this lesson, students should be able to
1. Differentiate steady and unsteady fluid flow. area, As.
2. Derive the fomulas for unsteady flow of fluid out of an
orifice. Let: As = f(h)
3. Use the derived equations in solving different cases of
orifice-related problems on unsteady flow.
3. For constant As.
Required Knowledge in:
𝟐𝑨𝒔
1. Related Rates (Differential Calculus)
𝒕= [√𝒉𝟏 − √𝒉𝟐 ]
2. Continuity Equation
𝑪𝒅 𝑨𝒐 √𝟐𝒈
3. Geometry 4. For submerged orifice.
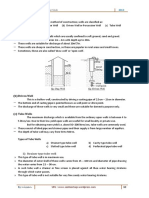
USTEADY FLOW – flow velocity and area of flow
varies with time. 𝟐𝑨𝑩
𝒕= [√∆𝒉𝟏 − √∆𝒉𝟐 ]
(𝑨 + 𝑩)𝑪𝒅 𝑨𝒐 √𝟐𝒈
Time to discharge liquid on a
vessel through an orifice. EXAMPLES.
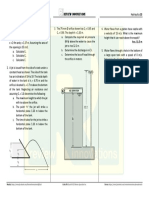
1. A circular tank of diameter 4 m contains water up to a
height of 5 m. The tank is provided with an orifice of
diameter 0.50 m at the bottom. Find the time taken by
water
a. To fall from 5 m to 2 m
b. For completely emptying the tank
Take Cd = 0.60
Ans. 39.58 sec , 107.7 sec
2. A circular tank of diameter 1.25 m contains water up to a
height of 5 m. An orifice of 50 mm diameter if provided at
Where: its bottom. If cd= 0.62, find the height of water above the
orifice after 1.5 minutes.
• As = cross sectional area of liquid Ans. 4.154 m
surface or vessel
3. A hemispherical tank of diameter 4 m contains water up to
• h1 = initial head producing the a height of 1.5 m. An orifice of diameter 50 mm is provided
at the bottom. Find the time required by water
flow
a. To fall from 1.5 m to 1.0 m
• h2 = final head producing the b. For completely emptying the tank.
Take Cd = 0.60
flow Ans. 921.40 sec , 2286.33 sec
• Ao = area of the orifice
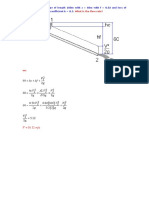
4. Two vertical cylindrical tanks, one 5 m in diameter and the
other 8 m have a common orifice having a cross sectional
1. General shaped vessel with an area of 0.004 m2 with Cd = 0.60 located at the bottom
portion. When the orifice is closed, the water surface in the
orifice at the bottom. smaller tank is 10 m higher than that in the bigger tank.
a. Determine the discharge in the tube immediately
after it is opened.
𝒉𝟐 b. Determine the time for the water surface in each tank
𝟏 to be at the same level.
𝒕=− ∫ 𝑨𝒔 (𝒉−𝟏/𝟐 ) 𝒅𝒉 c. Determine the time to discharge 30 m3 of water from
𝑪𝒅 𝑨𝒐 √𝟐𝒈 𝒉𝟏 the smaller tank to the bigger tank.
Ans. 0.0036 m3/s , 8400 sec, 946 sec
Hydraulics Leselle C. Quitaneg
You might also like
- Compilation Part 2 (11-19)Document100 pagesCompilation Part 2 (11-19)Joshua Zuniga50% (2)
- Constant Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportDocument12 pagesConstant Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportHaziq Zuhaimi100% (3)
- X Tan G : CE Review For Nov 2022 - Hydraulics 7Document1 pageX Tan G : CE Review For Nov 2022 - Hydraulics 7JuDeNo ratings yet
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Document3 pagesHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- Hyd 11Document1 pageHyd 11eufemiorodolfoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 01Document2 pagesTutorial 01Getahun TukaNo ratings yet
- CENG 197 Problem Set 2Document5 pagesCENG 197 Problem Set 2edmar limNo ratings yet
- NU - Lecture 5 ORIFICEDocument2 pagesNU - Lecture 5 ORIFICEMr. Mark B.No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (Continuity Equation)Document1 pageLecture 2 (Continuity Equation)Joshua TesoroNo ratings yet
- Hydau GeoDocument9 pagesHydau GeoAngelica TecsonNo ratings yet
- GW 7-Open WellsDocument17 pagesGW 7-Open Wellswajid malikNo ratings yet
- .LB - TankDocument11 pages.LB - TankjhntellerNo ratings yet
- Subject CodeDocument45 pagesSubject CodeHata MilišicNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 Fluid Dynamics Worksheet 1Document2 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 Fluid Dynamics Worksheet 1Khairunnisa FahrinaNo ratings yet
- 1.FLUIDS Relative EquilibriumDocument2 pages1.FLUIDS Relative Equilibriummark Gangsakit0% (3)
- Sheet 7Document1 pageSheet 7Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- Mega Review Assessment Exam (Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics)Document6 pagesMega Review Assessment Exam (Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics)maklincarl.diaz.dNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 9Document3 pagesExperiment No. 9Dindo YapyapanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics IOE Old Questions-1Document51 pagesFluid Mechanics IOE Old Questions-1Abishek Adhikari100% (1)
- ENE820 Possible SolutionDocument5 pagesENE820 Possible SolutionafafNo ratings yet
- Partha Q4Document1 pagePartha Q4ujjwal sahaNo ratings yet
- Review Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Mark Daren Patrona RamonNo ratings yet
- Civil 3 Sem Hydraulics c16 Nov 2019Document3 pagesCivil 3 Sem Hydraulics c16 Nov 2019Sundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- Determination of Coefficient of Permeability Using Constant-Head Test and Falling Head TestDocument7 pagesDetermination of Coefficient of Permeability Using Constant-Head Test and Falling Head TestVerra Myza AratNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water: Pine LeadDocument3 pagesFresh Water: Pine LeadRobby BajamondeNo ratings yet
- Wells PunmiaDocument10 pagesWells PunmiaBoddula SwathiNo ratings yet
- Time To Empty TanksDocument32 pagesTime To Empty Tankstimothyatambo383No ratings yet
- Hydraulics 3Document3 pagesHydraulics 3Marc Louiese LagataoNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Document1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Steady Flow in Open ChannelsDocument26 pagesLecture 11 - Steady Flow in Open ChannelsNawaz441No ratings yet
- ENGG2500 2022 Week2 Lecture4Document72 pagesENGG2500 2022 Week2 Lecture4max zebalaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1561345296282Document7 pagesOrca Share Media1561345296282Solomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- Visit: Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument9 pagesVisit: Civildatas - Blogspot.insankaran sNo ratings yet
- Rendon 4 - Refresher HYDDocument2 pagesRendon 4 - Refresher HYDMigaeaNo ratings yet
- AUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerFrancis HernandezNo ratings yet
- CE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Answer Key)Document4 pagesCE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Fluid ExamDocument1 pageFluid ExamSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics ProblemsDocument2 pagesHydraulics ProblemsDarlene Mae ZaraNo ratings yet
- F.M Qp.Document3 pagesF.M Qp.ankurthakurxNo ratings yet
- Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportDocument8 pagesFalling Head Permeability Test Lab Reportmr_sam91100% (1)
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument9 pagesFalling Head Permeability TestFaeez Zain83% (6)
- Adobe Scan Apr 03, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Apr 03, 2023JadeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Group 3 Ce32s1Document9 pagesExperiment No. 4 Group 3 Ce32s1Tyrone PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Topics Problem Set 6 - Hydraulics 3rd Term AY 2020-2021Document1 pageTopics Problem Set 6 - Hydraulics 3rd Term AY 2020-2021Mr. Mark B.No ratings yet
- HHM HandoutDocument16 pagesHHM HandoutArun ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulik RezensentDocument148 pagesHydraulik RezensentScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech Exercise 4 MotionDocument3 pagesFluid Mech Exercise 4 MotionyashNo ratings yet
- MCG3341 Midterm W2016 wSOLS PDFDocument12 pagesMCG3341 Midterm W2016 wSOLS PDFStefanGraczyk100% (1)
- Module 4.permeability and SeepageDocument34 pagesModule 4.permeability and Seepagejesica quijanoNo ratings yet
- B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations November/December 2016 Time: 3 HoursDocument2 pagesB.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations November/December 2016 Time: 3 HoursBrahmaiah Vendipalli 184No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversitydharmeshNo ratings yet
- Field and Lab Determination of KDocument2 pagesField and Lab Determination of KJed YasisNo ratings yet
- Problem Exercise No.5Document4 pagesProblem Exercise No.5Ey KaguriNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics ReviewerDocument146 pagesHydraulics ReviewerKarl Anne DomingoNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsFrom EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Configuration Requirements and Effect of Irregularity in StructureDocument14 pagesConfiguration Requirements and Effect of Irregularity in StructureHernan BeñabonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Reciprocal Leveling and Trigonometric Leveling: Fundamental of Surveying Engr. Richard VillamoraDocument18 pagesLesson 21 Reciprocal Leveling and Trigonometric Leveling: Fundamental of Surveying Engr. Richard VillamoraHernan BeñabonNo ratings yet
- Seismology Seismic Waves and Their PropagationDocument19 pagesSeismology Seismic Waves and Their PropagationHernan BeñabonNo ratings yet
- Compass Rule and Transit Rule Formula and ExampleDocument1 pageCompass Rule and Transit Rule Formula and ExampleHernan BeñabonNo ratings yet
- Bearing and AzimuthDocument13 pagesBearing and AzimuthSupot TuliNo ratings yet
- NU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW)Document1 pageNU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW)Hernan BeñabonNo ratings yet
- Sample Mass Weight Computation 1Document1 pageSample Mass Weight Computation 1Hernan BeñabonNo ratings yet
- Ticf KKDDV: Kerala GazetteDocument28 pagesTicf KKDDV: Kerala GazetteVivek KakkothNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Other Means of Generating Enolates: Osime Meli O Li + SimeDocument14 pages1.3. Other Means of Generating Enolates: Osime Meli O Li + SimeVirendra Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- 10 Traditional Chilean Desserts - Insanely Good PDFDocument1 page10 Traditional Chilean Desserts - Insanely Good PDFMarilynn SpringerNo ratings yet
- 9865 0040 01 Cop 1838+ He+ Mux+ Hux+ BrochureDocument4 pages9865 0040 01 Cop 1838+ He+ Mux+ Hux+ BrochuresofrankxNo ratings yet
- 26 MatricesDocument26 pages26 MatricesFazli KamawalNo ratings yet
- Soil Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control: January 2016Document15 pagesSoil Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control: January 2016Nagateja MondretiNo ratings yet
- Expo Class Methods DetailedDocument7 pagesExpo Class Methods DetailedAlison2360No ratings yet
- Information Systems For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument23 pagesInformation Systems For Sustainable DevelopmentnshekhaNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument129 pagesThesisOvaid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- pBrain-HexEngine Configuration Guide v1.2Document35 pagespBrain-HexEngine Configuration Guide v1.2lazer155No ratings yet
- Research Report - Aakanksha MistryDocument19 pagesResearch Report - Aakanksha MistryAakanksha MistryNo ratings yet
- Human Nutritional RequirementsDocument3 pagesHuman Nutritional RequirementsAgnesMagadiaNo ratings yet
- 6.MAY DIEN TIM 6-12 KENH - GreyDocument3 pages6.MAY DIEN TIM 6-12 KENH - GreyPhạm Thanh VyNo ratings yet
- Me 335 Exp 2Document8 pagesMe 335 Exp 2Brian AliasgharNo ratings yet
- LTE UE Initial AccessDocument7 pagesLTE UE Initial Accesss0pnadisht0No ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument57 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentKelvin kipkuruiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsJhanin BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- NCP HCVD (Final)Document8 pagesNCP HCVD (Final)khrizaleeh100% (1)
- Anode InfoDocument5 pagesAnode InfoEberg NlnoNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Document1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Ch PrasadNo ratings yet
- Islam Articles of FaithDocument1 pageIslam Articles of Faithapi-247725573No ratings yet
- Polyphenol Oxidase Activity and Browning of Three Avocado VarietiesDocument6 pagesPolyphenol Oxidase Activity and Browning of Three Avocado VarietiesMiguelArceMonroyNo ratings yet
- Side Effect of MilkDocument2 pagesSide Effect of Milkamalia setiawanNo ratings yet
- GroutDocument2 pagesGroutMarina Gomáriz ElgerNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Four PawsDocument7 pagesSynopsis Four PawsAnmol DubeyNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Rotary Piston Meter Asm LXH SA1508 15mm, 20mm & 25mmDocument19 pagesVolumetric Rotary Piston Meter Asm LXH SA1508 15mm, 20mm & 25mmGreen FarmersNo ratings yet
- A Review On Rasamanjari: It's Contribution in Pharmaceutical ScienceDocument3 pagesA Review On Rasamanjari: It's Contribution in Pharmaceutical ScienceEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Helicopter SafetyDocument11 pagesHelicopter SafetyWilliam Greco100% (2)
- CE 1102 Fundamentals of Civil Engineering: Your LecturerDocument36 pagesCE 1102 Fundamentals of Civil Engineering: Your Lecturersaumya irugalbandaraNo ratings yet
- Creator Excerpt PsycanicsDocument40 pagesCreator Excerpt Psycanicscheshirecatz348No ratings yet