Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical Properties
Uploaded by
nicz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views46 pagesA piece of copper originally 305 mm long is subjected to a tensile stress of 276 MPa. The document asks to calculate the elongation if the deformation is entirely elastic. It also provides instructions on determining mechanical properties like modulus of elasticity, yield strength and change in length from a stress-strain plot of a brass specimen subjected to tensile stresses. Finally, it states that hardness tests are the most commonly performed mechanical test because they are simple, inexpensive, nondestructive and can estimate other mechanical properties.
Original Description:
Original Title
mechanical properties
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA piece of copper originally 305 mm long is subjected to a tensile stress of 276 MPa. The document asks to calculate the elongation if the deformation is entirely elastic. It also provides instructions on determining mechanical properties like modulus of elasticity, yield strength and change in length from a stress-strain plot of a brass specimen subjected to tensile stresses. Finally, it states that hardness tests are the most commonly performed mechanical test because they are simple, inexpensive, nondestructive and can estimate other mechanical properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views46 pagesMechanical Properties
Mechanical Properties
Uploaded by
niczA piece of copper originally 305 mm long is subjected to a tensile stress of 276 MPa. The document asks to calculate the elongation if the deformation is entirely elastic. It also provides instructions on determining mechanical properties like modulus of elasticity, yield strength and change in length from a stress-strain plot of a brass specimen subjected to tensile stresses. Finally, it states that hardness tests are the most commonly performed mechanical test because they are simple, inexpensive, nondestructive and can estimate other mechanical properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 46
Elongation
(Elastic) Computation
A piece of copper originally 305 mm (12 in.)
long is pulled in tension with a stress of 276
MPa (40,000 psi). If the deformation is entirely
elastic, what will be the resultant elongation?
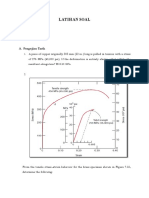
Mechanical Property Determinations from Stress–Strain Plot
From the tensile stress–strain behavior for the brass specimen
shown in Figure 6.12, determine the following:
(a) The modulus of elasticity
(b) The yield strength at a strain offset of 0.002
(c) The maximum load that can be sustained by a cylindrical
specimen hav- ing an original diameter of 12.8 mm (0.505 in.)
(d) The change in length of a specimen originally 250 mm (10
in.) long that is subjected to a tensile stress of 345 MPa (50,000
psi)
Hardness tests are performed more frequently than any
other mechanical test for several reasons:
1. They are simple and inexpensive—ordinarily no special
specimen need be prepared, and the testing apparatus is
relatively inexpensive.
2. The test is nondestructive—the specimen is neither
fractured nor excessively deformed; a small indentation is
the only deformation.
3. Other mechanical properties often may be estimated
from hardness data, such as tensile strength
You might also like
- Chapt 05Document25 pagesChapt 05Jesse McClure100% (9)
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Raiham EffendyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material: Assignment # 01Document3 pagesEngineering Material: Assignment # 01Hussain AliNo ratings yet
- Material Yr1 - Tutorial 6Document16 pagesMaterial Yr1 - Tutorial 6Ahmed TahaNo ratings yet
- Taller 3 - Propiedades MecánicasDocument2 pagesTaller 3 - Propiedades MecánicasJuan Pablo Rinc�n Ru�zNo ratings yet
- CH6 AssignmetDocument11 pagesCH6 AssignmetHasan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Aula 4 - ExercíciosDocument16 pagesAula 4 - ExercíciosGustavo ChavesNo ratings yet
- Assessment 15Document3 pagesAssessment 15ccharp123No ratings yet
- EMAT04C01/EAX - S - 210 2015-2016 S2: Q (1) (15 Marks, Divided Equally)Document4 pagesEMAT04C01/EAX - S - 210 2015-2016 S2: Q (1) (15 Marks, Divided Equally)sherif115040 BueNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 (Solution)Document1 pageTutorial 3 (Solution)dudescapeNo ratings yet
- HW Ch7 1Document12 pagesHW Ch7 1Chenhg ChengNo ratings yet
- ME 352 - All Problem Class - 14-18 BatchDocument125 pagesME 352 - All Problem Class - 14-18 BatchEntertainment GamingNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Simple StressesDocument39 pagesAnalysis of Simple StressesEduCartNo ratings yet
- Latihan SoalDocument3 pagesLatihan SoalDaus100% (1)
- Load (N) Length (MM) : SolutionDocument8 pagesLoad (N) Length (MM) : Solutionاحمد الشوافيNo ratings yet
- 6 PDFDocument8 pages6 PDFmegaNo ratings yet
- Tensile Testing Mild Steel As Received Sample: Experiment 1 Group1Document9 pagesTensile Testing Mild Steel As Received Sample: Experiment 1 Group1Adarsh BujadeNo ratings yet
- FRP Tensile Strength PPT-3Document15 pagesFRP Tensile Strength PPT-3laurenjiaNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document12 pagesCH 07Madeline NgoNo ratings yet
- SheetDocument15 pagesSheetHossam Sallam100% (1)
- Homework#6 F14 - M E 311Document1 pageHomework#6 F14 - M E 311Jeremy PriestNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - DevdevDocument19 pagesExperiment 1 - DevdevVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Question No 21:: D=15Mm L=150Mm Σ=50MpaDocument10 pagesQuestion No 21:: D=15Mm L=150Mm Σ=50MpaEngr. Syed FarazNo ratings yet
- ME 303 Study Set PDFDocument44 pagesME 303 Study Set PDFFajar RumantoNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Bentuk Takikan (Notched) Pada Poros Baja Karbon St. 60 Akibat Beban TarikDocument5 pagesPengaruh Bentuk Takikan (Notched) Pada Poros Baja Karbon St. 60 Akibat Beban TarikDelioPradanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Mech 321 Properties and Failure of Materials Jan 2009Document2 pagesAssignment 1 Mech 321 Properties and Failure of Materials Jan 2009DSGNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Abhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Strength of Materials Tutorial - IDocument1 pageDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Strength of Materials Tutorial - IrameshtrkNo ratings yet
- DME Question BankDocument4 pagesDME Question BankILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Hasan AliNo ratings yet
- TUGAS Sifat MEKANISDocument10 pagesTUGAS Sifat MEKANISHelmi FuadiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Polymer Engineering and ScienceDocument1 pagePrinciples of Polymer Engineering and SciencebishoyNo ratings yet
- MBM Lab ReportDocument11 pagesMBM Lab ReportPavan Kalyan PNo ratings yet
- Matthew Sinclairs Assessment 2 Labotatory ReportDocument8 pagesMatthew Sinclairs Assessment 2 Labotatory Reportapi-319042534No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 (Question)Document1 pageTutorial 3 (Question)dudescapeNo ratings yet
- QB Unit-1,2Document5 pagesQB Unit-1,2Agranshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Monolithic Insulated Joint BrochureDocument8 pagesMonolithic Insulated Joint Brochuremarita_msNo ratings yet
- Hapter: MetalsDocument55 pagesHapter: Metalsbedo39No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-29 at 3.16.52 PMDocument22 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-29 at 3.16.52 PMabdoshetayaNo ratings yet
- Machine Design VthSem MEDocument10 pagesMachine Design VthSem MEsureshm_raj5434No ratings yet
- MCEN30017 Tutorial 3Document2 pagesMCEN30017 Tutorial 3vsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Sheet#8Document7 pagesSheet#8oreaby05No ratings yet
- Gtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankDocument5 pagesGtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankJaideep ZalaNo ratings yet
- HW8 ch07Document7 pagesHW8 ch07Jeremy HernandezNo ratings yet
- 3M 300 Kcmil, Type 16 ACCR Conductor Stress Strain and Tensile TestsDocument13 pages3M 300 Kcmil, Type 16 ACCR Conductor Stress Strain and Tensile TestsadrijamatNo ratings yet
- Set12 Metallurgy 2,3,4,5,6Document19 pagesSet12 Metallurgy 2,3,4,5,6Pritamjit RoutNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 07Document4 pagesAssignment - 07KKNo ratings yet
- R7310305 Design of Machine Members - IDocument1 pageR7310305 Design of Machine Members - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Mechanical PropertiesDocument1 pagePractice Questions - Mechanical Propertiesalexchitongwe48No ratings yet
- EXODocument1 pageEXOmoriantsegangNo ratings yet
- Sample 2Document14 pagesSample 2Wesam MalehNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Supratim Bhattacharjee100% (1)
- ME2303Document5 pagesME2303balameckNo ratings yet
- Dme Question BankDocument4 pagesDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- TE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFDocument4 pagesTE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFonkar nikamNo ratings yet
- Chapt 05 PDFDocument25 pagesChapt 05 PDFdoraNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsFrom EverandCyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave Dispersion: Instrumentation and Experiment InterpretationFrom EverandMechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave Dispersion: Instrumentation and Experiment InterpretationYvon ChevalierNo ratings yet