Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Database Technologies: RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 1
1.1 Database Technologies: RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 1
Uploaded by
Likith Chandan MOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1 Database Technologies: RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 1
1.1 Database Technologies: RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 1
Uploaded by
Likith Chandan MCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 DATABASE TECHNOLOGIES
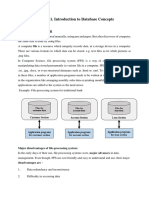
The essential feature of database technology is that it provides an internal representation
(model) of the external world of interest. Examples are the representation of a particular
date/time/flight/aircraft in airline reservation or of item code/item description/quantity on
hand/reorder level/reorder quantity in a stock control system. The technology involved is
concerned primarily with maintaining the internal representation consistent with external
reality; this involves the results of extensive R&D over the past 30 years in areas such as user
requirements analysis, data modelling, process modelling, data integrity, concurrency,
transactions, file organisation, indexing, rollback and recovery, persistent programming,
object-orientation, logic programming, deductive database systems, active database systems...
and in all these (and other) areas there remains much to be done.
The essential point is that database technology is a CORE TECHNOLOGY with links to:
• Information management / processing
• Data analysis / statistics
• Data visualization / presentation
• Multimedia and hypermedia
• Office and document systems
• Business processes, workflow, CSCW (computer-supported cooperative work)
Relational DBMS is the modern base technology for many business applications. It offers
flexibility and easy-to-use tools at the expense of ultimate performance. More recently
relational systems have started to extend their facilities in the directions of information
retrieval, object-orientation and deductive/active systems leading to the so-called 'Extended
Relational Systems'.
Information Retrieval Systems started with handling library catalogues and extended to full
free-text utilizing inverted index technology with a lexicon or thesaurus. Modern systems
utilize some KBS (knowledge-based systems) techniques to improve retrieval.
RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 1
Introduction
Object-Oriented DBMS started for engineering applications where objects are complex, have
versions and need to be treated as a complete entity. OODBMSs share many of the OOPL
features such as identity, inheritance, late binding, overloading and overriding. OODBMSs
have found favour in engineering and office systems but have not yet been successful in
traditional application areas.
Deductive / Active DBMS have emerged over the last 20 years and combine logic
programming technology with database technology. This allows the database itself to react to
external events an to maintain dynamically its integrity with respect to the real world.
1.2 CHARACTERISTICS OF DATABASE APPROACH
Traditionally, data was organized in file formats. DBMS was a new concept then, and all the
research was done to make it overcome the deficiencies in traditional style of data management.
A modern DBMS has the following characteristics
• Real-world entity − A modern DBMS is more realistic and uses real world entities to
design its architecture. It uses the behaviour and attributes too. For example, a school
database may use students as an entity and their age as an attribute.
• Relation-based tables − DBMS allows entities and relations among them to form
tables. A user can understand the architecture of a database just by looking at the table
names.
• Isolation of data and application − A database system is entirely different than its
data. A database is an active entity, whereas data is said to be passive, on which the
database works and organizes. DBMS also stores metadata, which is data about data,
to ease its own process.
• Less redundancy − DBMS follows the rules of normalization, which splits a relation
when any of its attributes is having redundancy in values. Normalization is a
mathematically rich and scientific process that reduces data redundancy.
• Consistency − Consistency is a state where every relation in a database remains
consistent. There exist methods and techniques, which can detect attempt of leaving
database in inconsistent state. A DBMS can provide greater consistency as compared
to earlier forms of data storing applications like file-processing systems.
• Query Language − DBMS is equipped with query language, which makes it more
efficient to retrieve and manipulate data. A user can apply as many and as different
RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 2
Introduction
filtering options as required to retrieve a set of data. Traditionally it was not possible
where file-processing system was used.
• ACID Properties − DBMS follows the concepts of Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation,
and Durability (normally shortened as ACID). These concepts are applied on
transactions, which manipulate data in a database. ACID properties help the database
stay healthy in multitransactional environments and in case of failure.
• Multiuser and Concurrent Access − DBMS supports multi-user environment and
allows them to access and manipulate data in parallel. Though there are restrictions on
transactions when users attempt to handle the same data item, but users are always
unaware of them. o Multiple views − DBMS offers multiple views for different users.
A user who is in the Sales department will have a different view of database than a
person working in the Production department. This feature enables the users to have a
concentrate view of the database according to their requirements. o Security − Features
like multiple views offer security to some extent where users are unable to access data
of other users and departments.
DBMS offers methods to impose constraints while entering data into the database and
retrieving the same at a later stage. DBMS offers many different levels of security features,
which enables multiple users to have different views with different features. For example, a
user in the Sales department cannot see the data that belongs to the Purchase department.
Additionally, it can also be managed how much data of the Sales department should be
displayed to the user. Since a DBMS is not saved on the disk as traditional file systems, it is
very hard for miscreants to break the code.
1.3 APPLICATIONS OF DBMS
Applications where we use Database Management Systems are:
• Telecom: There is a database to keeps track of the information regarding calls made,
network usage, customer details etc. Without the database systems it is hard to
maintain that huge amount of data that keeps updating every millisecond.
• Industry: Where it is a manufacturing unit, warehouse or distribution centre, each one
needs a database to keep the records of ins and outs. For example distribution centre
should keep a track of the product units that supplied into the centre as well as the
RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 3
Introduction
products that got delivered out from the distribution centre on each day; this is where
DBMS comes into picture.
• Banking System: For storing customer info, tracking day to day credit and debit
transactions, generating bank statements etc. All this work has been done with the help
of Database management systems.
• Education sector: Database systems are frequently used in schools and colleges to
store and retrieve the data regarding student details, staff details, course details, exam
details, payroll data, attendance details, fees details etc. There is a hell lot amount of
inter-related data that needs to be stored and retrieved in an efficient manner.
• Online shopping: You must be aware of the online shopping websites such as
Amazon, Flip kart etc. These sites store the product information, your addresses and
preferences, credit details and provide you the relevant list of products based on your
query. All this involves a Database management system.
1.4 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION/STATEMENT
A manual management of data without help of a software in the field of RTO management an
lead to many mistakes some of which may have serious consequences. Therefore, there is a
need to implement an efficient software to do this work and prevent those mistakes.
In such cases this project provides a software to handle the work. The main aim of this project
is to create a database that can store and manage various RTO related information like Driver’s
License, Learner’s License, Vehicle Registrations etc.
RNSIT, Dept. of CSE 4
You might also like
- Etl Ab Initio PDFDocument2 pagesEtl Ab Initio PDFDustin0% (1)
- Ms Access TutorialDocument297 pagesMs Access Tutorialsameerroushan100% (2)
- UNIT 1 MaterialDocument22 pagesUNIT 1 Materialjai geraNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument58 pagesDBMSimran_nazir448687No ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument71 pagesDatabase Management SystemsinghanjansinghNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1Document31 pagesDBMS Unit-1Sai ShaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Notes - IntroductionDocument17 pagesChapter-1 Notes - IntroductionAdfar RashidNo ratings yet
- DBMS NotesDocument10 pagesDBMS NotesRagav RajNo ratings yet
- Use of Dbms in SportsorganizationDocument12 pagesUse of Dbms in SportsorganizationPrateek ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument40 pagesDBMS Lab ManualDalli Punith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Database Management System (DBMS)Document5 pagesDatabase Management System (DBMS)INSANE GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction To DatabaseDocument31 pagesUnit I - Introduction To DatabaseGaurav Patni100% (1)
- Data Base Management SystemDocument30 pagesData Base Management SystemHrithick BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Likhith P Srms ReportDocument43 pagesLikhith P Srms ReportGirish B SNo ratings yet
- Information Technology: Chapter TwoDocument56 pagesInformation Technology: Chapter TwoĒrmias ÁlemayehuNo ratings yet
- DBMS (R20) Unit - 1Document14 pagesDBMS (R20) Unit - 1Kurumeti Naga Surya Lakshmana KumarNo ratings yet
- DBMS (R20) Unit - 1Document14 pagesDBMS (R20) Unit - 1MOHANKRISHNACHAITANYA KNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1Document58 pagesDBMS Unit 1MeeraNo ratings yet
- Database and Data ModelingDocument31 pagesDatabase and Data ModelingKudakwashe MotsiNo ratings yet
- Course: Object-Oriented Systems and Programming: 07B61CI241 (Theory) and 07B61CI801 (Lab)Document22 pagesCourse: Object-Oriented Systems and Programming: 07B61CI241 (Theory) and 07B61CI801 (Lab)Sanchit BatraNo ratings yet
- BSC CsIt Complete RDBMS NotesDocument86 pagesBSC CsIt Complete RDBMS NotesNilesh GoteNo ratings yet
- Mba DBMSDocument4 pagesMba DBMSRagav RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-IntroductionDocument38 pagesLecture 1-IntroductionMercy ChinyukuNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Unit-1-BsDocument30 pagesDBMS - Unit-1-BsKAVITHANo ratings yet
- DBMS - Unit-1Document12 pagesDBMS - Unit-1Dr. Nageswara Rao EluriNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Management Systems: UNIT-1Document120 pagesRelational Database Management Systems: UNIT-1Srinivas KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Management System : Co/Cm/If 3GDocument209 pagesRelational Database Management System : Co/Cm/If 3GHET JOSHINo ratings yet
- CSE - 311L, Lab - 01Document8 pagesCSE - 311L, Lab - 01RK RashikNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Management System NoDocument209 pagesRelational Database Management System NoHemant ThawaniNo ratings yet
- 2-Introduction To DBMS - Need - Characteristics - Advantages - Applications-28!04!2023Document19 pages2-Introduction To DBMS - Need - Characteristics - Advantages - Applications-28!04!2023konkimalla ganeshNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1,2 Notes - R21Document105 pagesDBMS Unit 1,2 Notes - R21eswar pNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: MR - Brwa M.Sc. Computer EngineerDocument24 pagesTutorial: MR - Brwa M.Sc. Computer Engineerzainab alhussainyNo ratings yet
- Complete Dbms NotesDocument138 pagesComplete Dbms NotesSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document28 pagesUnit 3Tisha JainNo ratings yet
- Database System: Some Application ProgramsDocument10 pagesDatabase System: Some Application Programsjitendra_k_jainNo ratings yet
- DBMS Complete NoteDocument89 pagesDBMS Complete NoteSan DipNo ratings yet
- 1 UnitDocument37 pages1 UnitK RANJITH REDDYNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument76 pagesDatabase Management Systemidisa005No ratings yet
- Information Technology (IT), As Defined by The Information Technology AssociationDocument3 pagesInformation Technology (IT), As Defined by The Information Technology Associationvinod418100% (1)
- DF Unit 3 NotesDocument46 pagesDF Unit 3 NoteschelamanenivishnuNo ratings yet
- 2017 Information Management Unit 3 DBMSDocument35 pages2017 Information Management Unit 3 DBMSkskumarrNo ratings yet
- 1 Dbms - Overview PDFDocument2 pages1 Dbms - Overview PDFপ্রমিত সরকারNo ratings yet
- History of DBMSDocument3 pagesHistory of DBMSLicht ZoraNo ratings yet
- DBMS Ctevt StudentsDocument230 pagesDBMS Ctevt StudentsDeepena PrykNo ratings yet
- Database NotesDocument23 pagesDatabase Notesmichellegichuhi94No ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument15 pagesDatabase Management SystemsDIWAKAR UNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document23 pagesModule 1SHABNAM SNo ratings yet
- 03.database Design ConceptsDocument45 pages03.database Design ConceptsJanaka SampathNo ratings yet
- Data Base Management SystemDocument29 pagesData Base Management SystemHarish DesalliNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam FDS PDFDocument35 pagesMidterm Exam FDS PDFAlthea ManlapazNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document17 pagesUnit 1prapadhya uppalapatiNo ratings yet
- ER and NormalizationDocument158 pagesER and NormalizationTulipNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Computing: Master of Computer Applications (MCA)Document10 pagesUniversity Institute of Computing: Master of Computer Applications (MCA)Rohit DahiyaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Notes - All UnitsDocument77 pagesDBMS Notes - All UnitsvibhavariNo ratings yet
- Dbms-3bcom-1-3 UnitsDocument160 pagesDbms-3bcom-1-3 UnitsPrameela KNo ratings yet
- Module - 1Document9 pagesModule - 1Yash Pathak YpNo ratings yet
- RDBMS Unit IDocument40 pagesRDBMS Unit IrogithaNo ratings yet
- EDIT 3101 - Database Management System - Lecture 1Document29 pagesEDIT 3101 - Database Management System - Lecture 1sichingadavies84No ratings yet
- UNIT 1 DBDocument26 pagesUNIT 1 DBMohd SalmanNo ratings yet
- Data Mesh: Building Scalable, Resilient, and Decentralized Data Infrastructure for the Enterprise. Part 2From EverandData Mesh: Building Scalable, Resilient, and Decentralized Data Infrastructure for the Enterprise. Part 2No ratings yet
- THE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)From EverandTHE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)No ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument24 pagesDatabase Management SystemDhivya A Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A XML Repository System Using Dbms and IrsDocument11 pagesDesign and Implementation of A XML Repository System Using Dbms and IrsmglhulinguestNo ratings yet
- Text Classification: Dr. Nguyen Van Vinh CS Department - UET, Hanoi VNUDocument50 pagesText Classification: Dr. Nguyen Van Vinh CS Department - UET, Hanoi VNUKỉ Nguyên Hủy DiệtNo ratings yet
- Section 9Document6 pagesSection 9Ancuta DanielaNo ratings yet
- How To Cli With NetappDocument2 pagesHow To Cli With NetappDennis DubeNo ratings yet
- AZ301 Exam PRPDocument13 pagesAZ301 Exam PRPranjeetsingh2908No ratings yet
- Online Platforms For ICT Content DevelopmentDocument24 pagesOnline Platforms For ICT Content DevelopmentBenedicta UncianoNo ratings yet
- PGDDB - Assignment 5 - Your Data StrategyDocument2 pagesPGDDB - Assignment 5 - Your Data StrategyShafana OsmanNo ratings yet
- Apa Reference Format GeneratorDocument7 pagesApa Reference Format Generatorzug0badej0n2100% (1)
- Food Establishment Inspections ReportDocument14 pagesFood Establishment Inspections ReportWienna RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Management System For The Office of The Senior Citizen Affairs (Osca) With Sms NotificationDocument8 pagesManagement System For The Office of The Senior Citizen Affairs (Osca) With Sms NotificationMorsid MangindraNo ratings yet
- SLIMS User Manual - Developers v1Document28 pagesSLIMS User Manual - Developers v1PETERNAC26No ratings yet
- Unit: Database Design and Development: Assignment Title: Harvey Car Hire Summer 2019Document33 pagesUnit: Database Design and Development: Assignment Title: Harvey Car Hire Summer 2019siam rezaNo ratings yet
- TOGAF 9 Template - Architecture RepositoryDocument8 pagesTOGAF 9 Template - Architecture RepositoryGala AlmoutiriNo ratings yet
- How Do NIKE Use Demand Forecasting in Their Process DesignDocument2 pagesHow Do NIKE Use Demand Forecasting in Their Process Designshiraj nilamNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Desain WebsiteDocument14 pagesEvaluasi Desain WebsiteAgung NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- BioinformaticsDocument18 pagesBioinformaticskendalsjordanNo ratings yet
- What Is Data ScienceDocument13 pagesWhat Is Data ScienceRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- AudcisDocument2 pagesAudcisLaiza LuzanoNo ratings yet
- Monitor and Administer Module AADocument28 pagesMonitor and Administer Module AADo DothingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 AIS Reviewer/summaryDocument2 pagesChapter 10 AIS Reviewer/summaryRose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- Mendeley Workshop PresentationDocument43 pagesMendeley Workshop PresentationSalma PatelNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Web Sites & Electronic Communication (Lecture)Document10 pagesWeek 5 - Web Sites & Electronic Communication (Lecture)arturogallardoedNo ratings yet
- SQL Learning Plan To Become Data Analytics ProDocument10 pagesSQL Learning Plan To Become Data Analytics Prochetan topreNo ratings yet
- PDF Oracle Academy Section 4 Quiz Answer - CompressDocument4 pagesPDF Oracle Academy Section 4 Quiz Answer - Compressksvlog167No ratings yet
- Data WarehouseDocument2 pagesData WarehouseLovely NavarroNo ratings yet
- NLP Unit 6Document16 pagesNLP Unit 6Tejaswini PotabattiNo ratings yet
- 005 Business ContinuityDocument29 pages005 Business Continuitysakthimurugan_sezhiyanNo ratings yet