Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COVID-19 MoHP Protocol May 2020
COVID-19 MoHP Protocol May 2020
Uploaded by
BARAKA ROKACopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nbme 27 With Answers and ExplanationsDocument15 pagesNbme 27 With Answers and ExplanationsZaid Marwan100% (2)
- BiPAP Full FlowchartDocument1 pageBiPAP Full FlowchartArjun KumarNo ratings yet
- MoHP Protocol For COVID19 November 2020Document28 pagesMoHP Protocol For COVID19 November 2020medya dostorNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 PathwayDocument17 pagesCovid 19 Pathwayferi adiantoNo ratings yet
- Aden Covid-19 Protocol 26-5-2020 (ASIA) 22-1Document14 pagesAden Covid-19 Protocol 26-5-2020 (ASIA) 22-1محمدرزازالتبعيNo ratings yet
- Advisory Antibody Testing 04042020 PDFDocument2 pagesAdvisory Antibody Testing 04042020 PDFSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Advisory To Start Rapid Antibody Based Blood Test For COVID-19 (4 April 2020)Document2 pagesAdvisory To Start Rapid Antibody Based Blood Test For COVID-19 (4 April 2020)narasimma8313No ratings yet
- Guide To COVID-19 in SKH ED: 30MAY22 Dennis CHIADocument35 pagesGuide To COVID-19 in SKH ED: 30MAY22 Dennis CHIAZainal Abidin Mohd Ruslan ShahNo ratings yet
- 3 Strengthening Referral System During COVID 19 PandemicDocument27 pages3 Strengthening Referral System During COVID 19 PandemicLapuyan Rural Health UnitNo ratings yet
- MoHP Protocol December 2021Document32 pagesMoHP Protocol December 2021Yoyo RashadNo ratings yet
- PHC ILI Guidlines COVID-19 FinalDocument4 pagesPHC ILI Guidlines COVID-19 Finalyalmas ugloNo ratings yet
- Sample Case Studies of COVID-19 in PregnancyDocument29 pagesSample Case Studies of COVID-19 in PregnancyAbdibaset Mohamed AdenNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus and PregnancyDocument17 pagesCorona Virus and PregnancyDESHVIKASH SWAINNo ratings yet
- Barnet Primary Care Pathway During Covid19 v1 PDFDocument1 pageBarnet Primary Care Pathway During Covid19 v1 PDFAndrew WilkinsonNo ratings yet
- FAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoDocument112 pagesFAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoAllene PaderangaNo ratings yet
- COVID Latest GuidelinesDocument48 pagesCOVID Latest Guidelinesarrestedinlove123No ratings yet
- SGD Fever and Chills Wrap UpDocument27 pagesSGD Fever and Chills Wrap UpNewbornMed FABELLANo ratings yet
- Coronavirus19 1Document60 pagesCoronavirus19 1bekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet
- PSMID Guidelines COVID 19 - EditedDocument8 pagesPSMID Guidelines COVID 19 - EditedIsrael H. ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Guía Rápida StanfordDocument6 pagesGuía Rápida StanfordDr. Victor Adolfo RochaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Protocol - MOHP 23march 2020Document4 pagesCOVID-19 Protocol - MOHP 23march 2020Sanaa SbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- Bu BudiDocument32 pagesBu Budinoi javuNo ratings yet
- Ruchi: InterpretationDocument2 pagesRuchi: InterpretationKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- MoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.1 PDFDocument6 pagesMoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.1 PDFHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- Covid Antiviral Medications How To Prescribe Mar 10 2022Document38 pagesCovid Antiviral Medications How To Prescribe Mar 10 2022ABDULLAH SDNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Protocol July 2022Document36 pagesCOVID-19 Protocol July 2022Mobile AsdNo ratings yet
- Tarun Kumar Report - 15012022 - 120821Document1 pageTarun Kumar Report - 15012022 - 120821navdeep madheshiyaNo ratings yet
- Bu Yovita Penanganan Medis Infeksi nCoV 05022020Document18 pagesBu Yovita Penanganan Medis Infeksi nCoV 05022020restulibrianiNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Nosocomial Covid 19 Another Challenge of The PandemicDocument2 pagesPrevention of Nosocomial Covid 19 Another Challenge of The PandemicZied FehriNo ratings yet
- Management Protocol Covid 19 V08 21-7-2020Document1 pageManagement Protocol Covid 19 V08 21-7-2020EdgarNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Initial Triaging & Case Management ProtocolDocument24 pagesCovid-19 Initial Triaging & Case Management ProtocolDeepak SugumarNo ratings yet
- COVID Latest Guidelines-1Document48 pagesCOVID Latest Guidelines-1Digvijay ChavanNo ratings yet
- CovidpcrtestingalgorithmDocument1 pageCovidpcrtestingalgorithmMWNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Kasus (13022020)Document31 pagesTatalaksana Kasus (13022020)junai arandetaNo ratings yet
- MoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.8-1 PDFDocument13 pagesMoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.8-1 PDFHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 in Patients With HIV: Clinical Case SeriesDocument3 pagesCOVID-19 in Patients With HIV: Clinical Case SeriesPutri MaheraNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020Document1 pageTreatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020meiraimNo ratings yet
- 5 Cases FungalDocument56 pages5 Cases Fungalkoteshwara raoNo ratings yet
- Covid Report PDFDocument2 pagesCovid Report PDFAthira NairNo ratings yet
- Tarun Kumar ReportDocument1 pageTarun Kumar Reportnavdeep madheshiyaNo ratings yet
- New May2020 PDFDocument7 pagesNew May2020 PDFDoctorMoodyNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Resource GuideDocument2 pagesCovid 19 Resource GuideSenthil VelliyangiriNo ratings yet
- Covid Basics Poster v2 20211230Document2 pagesCovid Basics Poster v2 20211230Swagat MohantyNo ratings yet
- Isolation Guide enDocument24 pagesIsolation Guide enbasil aliNo ratings yet
- 7 Cases FungalDocument56 pages7 Cases Fungalkoteshwara raoNo ratings yet
- Management Protocol For Covid-19: Department of Health and Family WelfareDocument34 pagesManagement Protocol For Covid-19: Department of Health and Family Welfarechandra sekharNo ratings yet
- PROTOCOL For Management of COVID-19 Cases WB 2nd Edition.Document49 pagesPROTOCOL For Management of COVID-19 Cases WB 2nd Edition.Shahin KhanNo ratings yet
- Management of Mild Cases of COVID-19 in Low-Resource CountriesDocument2 pagesManagement of Mild Cases of COVID-19 in Low-Resource CountriesAnthony HopkinsNo ratings yet
- Saudi Moh Protocol For Patients Suspected Of/Confirmed With Covid-19Document15 pagesSaudi Moh Protocol For Patients Suspected Of/Confirmed With Covid-19AldrinNo ratings yet
- Uganda - Advanced HIV Disease - Screening ToolDocument47 pagesUganda - Advanced HIV Disease - Screening Toolithran khoNo ratings yet
- Special Coding Advice During COVID-19 Public Health EmergencyDocument31 pagesSpecial Coding Advice During COVID-19 Public Health Emergencyplayjake18No ratings yet
- The Following Guidelines Must Be Implemented:: Omicron VariantDocument13 pagesThe Following Guidelines Must Be Implemented:: Omicron VariantLdrrmo RamonNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Inpatient Guide 092020.1Document1 pageCovid-19 Inpatient Guide 092020.1Anna JuniedNo ratings yet
- MoH Saudi Arabia COVID 19 ProtocolDocument13 pagesMoH Saudi Arabia COVID 19 Protocoladilah fazliNo ratings yet
- Covid For ClerksDocument60 pagesCovid For ClerksNehemiah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Irfan Shaikh 38Document2 pagesIrfan Shaikh 38Altamash AnsariNo ratings yet
- Status Klinis COVID-19 Kombinasi Dengan Penyakit KardiovaskularDocument21 pagesStatus Klinis COVID-19 Kombinasi Dengan Penyakit KardiovaskularMariaAmeliaGoldieNo ratings yet
- 5908 - Muh Firdaus Kasim-Covid 19 Public Health Perspective 28032020 PDFDocument20 pages5908 - Muh Firdaus Kasim-Covid 19 Public Health Perspective 28032020 PDFDave VentraNo ratings yet
- Unified Covid-19 Algorithms: Guidelines For Primary CareDocument9 pagesUnified Covid-19 Algorithms: Guidelines For Primary Careagnes bastonNo ratings yet
- 3B - COVID-19 Update - April 2020Document40 pages3B - COVID-19 Update - April 2020Tuệ HoàngNo ratings yet
- Decision Algorithms For The Telehome Care Management of Asymptomatic or Mildly Symptomatic COVID - 19 PatientsDocument12 pagesDecision Algorithms For The Telehome Care Management of Asymptomatic or Mildly Symptomatic COVID - 19 PatientsPatricia Franco-VillaNo ratings yet
- NICE Way to Cure COVID -19From EverandNICE Way to Cure COVID -19Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Oxygen ToxicityDocument4 pagesOxygen ToxicityRicard ClainkweeNo ratings yet
- Sleepandbreathing: Kelly Newton,, Vipin Malik,, Teofilo Lee-ChiongDocument6 pagesSleepandbreathing: Kelly Newton,, Vipin Malik,, Teofilo Lee-ChiongVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- The Evaluation, Diagnosis, and Treatment of The Adult Patient With Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure - UpToDateDocument37 pagesThe Evaluation, Diagnosis, and Treatment of The Adult Patient With Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure - UpToDateKiran AsrannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3rutba.ahmkhanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Delivery NHSDocument26 pagesOxygen Delivery NHSdr satnam kaurNo ratings yet
- ARDS and Resp Failure by SardarDocument53 pagesARDS and Resp Failure by SardarQashqar & GB FolksNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Sinus ArrhythmiaDocument8 pagesRespiratory Sinus ArrhythmiaTatiana RecinosNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Common Errors in The Emergency Department-1002-1280Document280 pagesAvoiding Common Errors in The Emergency Department-1002-1280Hernando CastrillónNo ratings yet
- 2019 Article SismesxinationalcongressDocument117 pages2019 Article SismesxinationalcongresspantufoNo ratings yet
- Falla Respiratoria & Embarazo - Lapinsky 2015Document7 pagesFalla Respiratoria & Embarazo - Lapinsky 2015Fabiola Buelna GaxiolaNo ratings yet
- The Cave Divers Who Went Back For Their FriendsDocument5 pagesThe Cave Divers Who Went Back For Their FriendsRocio TobaresNo ratings yet
- Lo Tropmed 1Document49 pagesLo Tropmed 1belleNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument29 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurePurnima ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Modul: Intensive Care IDocument62 pagesModul: Intensive Care IHandayu GanitafuriNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Inergen® Fire Extinguishing AgentDocument7 pagesThe Physiology of Inergen® Fire Extinguishing AgentJEAN FELLIPE BARROSNo ratings yet
- 2003, Vol.36, Issues 3, Surgery For Sleep ApneaDocument151 pages2003, Vol.36, Issues 3, Surgery For Sleep Apneamed_amitNo ratings yet
- Course Material - Breathing Exercise - For Summer 2020Document4 pagesCourse Material - Breathing Exercise - For Summer 2020emruzzamanNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Handbook WordDocument55 pagesVentilation Handbook WordHndr100% (2)
- PIIS2058534920300202Document7 pagesPIIS2058534920300202Dwi WahyudiNo ratings yet
- COPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaDocument3 pagesCOPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Dr. Vernon Coleman - Masks and Mask Wearing - 100 Facts You Must Know - World Doctors AllianceDocument17 pagesDr. Vernon Coleman - Masks and Mask Wearing - 100 Facts You Must Know - World Doctors Alliancejamestahara95No ratings yet
- 281 FullDocument8 pages281 FullbcgvpilotNo ratings yet
- What Is Oxygen TheraphyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Oxygen TheraphyitsmekringNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepDocument8 pagesPhysiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepAchmad Hafidz BaraqbahNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument8 pagesAcute Respiratory FailureCayunk NorlianaNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Respiratory FunctionsDocument26 pagesAlterations in Respiratory FunctionsAjeeshNo ratings yet
- Noninvasive Ventilation in Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults - UpToDateDocument27 pagesNoninvasive Ventilation in Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults - UpToDatehugo roblesNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation: Gian Carlo T. Rabago RN MD Tondo Medical Center Department of SurgeryDocument16 pagesMechanical Ventilation: Gian Carlo T. Rabago RN MD Tondo Medical Center Department of SurgeryGian Carlo RabagoNo ratings yet
COVID-19 MoHP Protocol May 2020
COVID-19 MoHP Protocol May 2020
Uploaded by
BARAKA ROKAOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COVID-19 MoHP Protocol May 2020
COVID-19 MoHP Protocol May 2020
Uploaded by
BARAKA ROKACopyright:
Available Formats
Management Protocol for
CManagement
VID-19Protocol
Patients
in Hospitals
Ministry of Health and Population, Egypt
Management protocol for COVID-19
Patients
Version 1.4 / 30 th May 2020
th
Version 1.4 / 30 May 2020 1
2 Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020
Table of contents
Page
Item
Number
Management in Triage Hospitals
4
Management of Mild Cases 6
Management of Moderate Cases 7
Management of Severe and
Critically Ill Cases 8
Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020 3
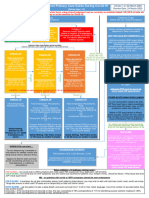
Management in Triage Hospitals
Patient enters Triage Hospital
(referred from another hospital, referred by 105, walkin)
Assess to identify suspected cases
A B C
OR OR
Any one of the epidemiological Asessing the presence of at Severe Acute Respiratory
history with any of the clinical least two of the following Infection
features. clinical features: (SARI) with no other
obvious cause.
epidemiological history: 1.Fever and/or respiratory
symptoms.
1. History of travel to or
residence in communities 2.Imaging characteristics.
where cases reported within CT scan is preferred, if not
the last 14 days. appicable do CXR
2. In contact with viral RNA 3.Differential CBC findings:
positive people white blood cells is normal
within the last 14 days. or decreased, with decreased
lymphocytic count.
3. In contact with a patient who
has fever or respiratory
symptoms or from a
community
with confirmed cases reported
within the last 14 days.
N.B.
- Asymptomatic contact to +ve case should undergo home isolation and should seek medical
advice whenever symptoms develop.
- Healthcare providers exposed to suspected or confirmed COVID-19 cases should follow the
algorithim shown in MoHP guide booklet.
4 Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020
Management in Triage Hospitals
Yes Suspected COVID-19 No
Non Covid-19 Cases
Assess patient
Is it an
emergency
case?
Yes No
Mild symptoms Impossible home isolation Refer to
Stabilize
(CT or CXR not or Stable general
patient
showing pneumonia) sever symptoms (dyspnea, hospital
tachypnea, tachycardia,
uncontrolled comorbidities, Unstable
Immunosuppressant, above
60 years) Admit to non
Stable
COVID area
Obtain PCR
sample Home Isolation if Obtain PCR sample
possible until
PCR result
- start managment:
* Rest If deteriorated to
* Infection control severe symptoms
(IPC measures)
* Antibiotic if needed
* Anti-pyretic Admitted to COVID-19 area
(Paracetamol) in triage hospital
Continue treatment and manage according
until the 7th day to protocol
-ve
PCR results
Symptoms
PCR result
resolved
-ve
Yes
Home isolation for No
14 days and close +ve Repeat PCR -ve
follow up after 48
-ve Repeat PCR
after 48 Transfer to Manage
Manage accordingly COVID-19 hospitals accordingly
Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020 5
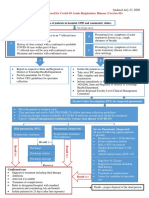
PCR Positive Cases
Mild Case
Symptomatic case
with lymphopenia or leucopenia
with no radiological signs for pneumonia
Check for
1. Age
2. Temperature > 38
3. SaO2 ≤ 92%
4. Heart Rate ≥ 110
5. Respiratory Rate ≥ 25 /min.
6. Neutrophil / lymphocyte ratio
All No on CBC ≥ 3.1 Any YES
7. Uncontrolled Comorbidities
8. Immunosuppressive Drug
AND 9. Pregnancy OR
10. Active Malignancy
11. On Chemotherapy
12. Obesity (BMI>40)
Age < 60 Age ≥ 60
• Strict Home Isolation (Symptomatic Isolation in
Treatment) a healthcare facility
• Follow and use personal protective guide
equipment
• If any deterioration occurs, back to
hospital
NB: Paracetamol is the preferred antipyretic
Treatment
- Hydroxychloroquine (400 mg twice in - Zinc 50mg daily
first day then 200 mg twice for 6 days) - Acelylcysteine 200 mg t.d.s.
- Vitamin C (1gm daily) - lactoferrin one sachet twice daily
6 Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020
PCR Positive Cases
Moderate Case
Patient has pneumonia manifestations on radiology associated with
symptoms &/Or leucopenia or lymphopenia
Hospitalization
• Lopinavir/Ritonavir (2 tab
200/50) every 12 hrs • Hydroxychloroquine (if NO
• Ribavirin 400 mg every 12 hrs contraindication) 400mg /12 hrs
for 14 days
(Not recommended if symptoms
started for more than 7 days)
OR for 1 day then 200 mg every 12
hours for 9 days
+
+ • Anticoagulation: prophylactic
• Anticoagulation: prophylactic or Therapeutic if D-dimer > 1000
or Therapeutic if D-dimer > 1000
Steroids if patients is dyspneic or CT SCAN showed significant deterioration
Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020 7
PCR Positive Cases
Severe and Critically Ill Case
If any of the following criteria is present
1. RR > 30
2. Sa02 < 92 at room air
3. PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300
4. Chest radiology showing
more than 50% lesion or
progressive lesion within 24 to 48 hrs
5. Critically ill if SaO2 <92, or RR>30,
or PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 200 despite Oxygen Therapy.
Admit to Intermediate Care Or Intensive care
Early Block
the storm Tocilizumab
if steroids 4-8mg/kg/dose
failed Max 2 doses
Antiviral Steroids Anti- Prone Avoid
Drugs As is In Methylpred- Coagulation Awake or Hypoxia
Severe case nisolone Enoxaparine ventilated O2/ NIV/
1-2 mg/kg/d 1 mg/kg BID HFNC/IMV
Don’t wait
Add 1 mg for non Consider Improves
too much for
Antibiotics ventilated D-dimer level V/Q matching
any type of
As per and 2 mg for as a guide and survival
support Keep
protocol ventilated
plateau<30
8 Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020
PCR Positive Cases
COVID 19 Critical Care Chain of Survival
Antiviral drugs
• Lopinavir/Ritonavir (2 tab
200/50) every 12 hrs. Hydroxychloroquine (if NO con-
+ Ribavirin 400 mg /12 hrs traindication) 400mg /12 hrs for 1
day then 200 mg every 12 hours
OR
+ Interferon beta 1b +
Azithromycin (500mg daily) or for 9 days +
doxycycline (200 mg first day • Lopinavir/Ritonavir (2tab
then 100mg daily OR 200/50) every 12 hrs.+
• Doxycycline 200 mg first day
NB: Remdesivir if available: 200 and 100 mg daily or Azithromy-
mg day 1 then 100 mg daily for 9 cin 500 mg
days
Non Invasive Ventilation or High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC):
• Conscious patients with minimal secretions.
• Hypoxia SpO2 < 90% on oxygen. Or PaCO2 >40 mmHg provided pH 7.3
and above.
• NIV trial shall be short with ABG 30 minutes apart.
• Any deterioration in blood gases from baseline or oxygen saturation or
consciousness level shift to IMV.
• CPAP gradually increased from 5-10 cmH2O.
• Pressure support from 10-15 cm H2O.
• HFNC can be alternative to NIV.
Invasive Mechanical Ventilation:
• Use PPE specially goggles during intubation and avoid bagging.
Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020 9
PCR Positive Cases
Indications:
• Failed NIV or not available or not practical.
• PaO2 < 60 mmhg despite oxygen supplementation.
• Progressive Hypercapnia.
• Respiratory acidosis (PH < 7.30).
• Progressive or refractory septic shock.
• Disturbed consciousness level (GCS ≤ 8) or deterioration in consciousness
level from baseline.
Step 1: Initiation of Invasive Mechanical Ventilation
VCV
TV 8 ml/kg
PEEP 5 cmH2O
Plateau
Pressure Inspiratory Pause for 1 second
Less than 30 Less than 30 More than 30
cmH2O Sat<93 ARDSnet
Sat >93 Increase PEEP protocol
Keep and Watch to 10
IF PLATEAU ABOVE 30 CMH2O
Step 2: Shift to ARDSNet protocol if needed
- ARDSNet protocol:
Plateau
P<30 cmH2O
LOW TV Incremental
6-4 ml/kg PEEP Driving
P<15 cmH2O
10 Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020
PCR Positive Cases
Start with tidal volume of 6 ml/Kg to keep plateau pressure on volume
controlled ventilation (VCV) below 30 cmH2O, decrease to 4 ml/kg if the
plateau remain higher than 30 allow permissive hypercapnia so long the
pH is above 7.3 compensate by increasing respiratory rate up to 30 breath/
minute. Consider heavy sedation and paralysis. If pressures are high or
any evidence of barotrauma shift to pressure controlled ventilation and be
cautious about low tidal volume alarms for fear of unnoticed endotracheal
tube obstruction. Consider ECMO early if eligible. Increase PEEP
gradually if the patient remains hypoxic according to FIO2 level to keep
driving pressure < 15cmH2O. NEVER FORGET PRONE POSITION.
Step 3: Assessment of respiratory support outcome
Assess
ABGs, Clinical
Radiological
Improved Stationary Deteriorating
Weaning of Continue Criteria for
respiratory respiratory ECMO*
support support as
needed
*Criteria for VV ECMO: Age below 55, mechanical ventilation duration
less than 7 days, no comorbidities, preserved conscious level, PaO2/FiO2
<100 despite prone RESPscore >0.
Expert opinion is needed and depends on availability.
Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020 11
Treatment Protocol
Revised By:
NAME AFFILIATION
Professor of Chest Diseases. Head of
Hossam Hosny Masoud Pulmonary Hypertension Unit, Faculty of
Medicine, Cairo University
Professor of Pulmonary Medicine
Gehan Elassal
Ain Shams University
Professor of Hepatogastroenterology and
Samy Zaky
Infectious Diseases, Al Azhar University
Consultant of Hepatoogy, Gastroenterology and
Infectious Diseases. National Hepatology and
Amin Abdel Baki
Tropical Medicine Research Institute
(NHTMRI),Cairo, Egypt
Consultant of infectious diseases and director
Hamdy Ibrahim of ICU, Imbaba Fever and infectious diseases
hospitals, MoHP
Wagdy Amin Director General for Chest Diseases, MoHP
Professor of critical care medicine, Cairo
Akram Abdelbary University Chairman elect of ELSO SWAAC
chapter
Lecturer of critical care medicine,
Ahmad Said Abdel Mohsen
Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University
Fellow of Infectious Diseases and
Endemic Hepatogastroentrology,
Mohamed Hassany
National Hepatology and
Tropical Medicine Research Institute
Alaa Eid Head of Preventive Medical Sector, MoHP
Minister’s Advisor for Research and
Health Development. Chairman of Research
Noha Asem Mohamed
Ethics Committee, MoHP. Lecturer of Public
Health, Cairo University
Researcher of Tropical Medicine.
Medical Division National Research
Ehab Kamal
Center. General Director of Directorate of Fever
Hospitals, MoHP
12 Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020
Ministry of Health and Population
Management protocol for COVID-19
Patients
Egypt / May 2020
Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020 13
Ministry of Health and Population
Egypt / May 2020
14 Version 1.4 / 30th May 2020
You might also like
- Nbme 27 With Answers and ExplanationsDocument15 pagesNbme 27 With Answers and ExplanationsZaid Marwan100% (2)
- BiPAP Full FlowchartDocument1 pageBiPAP Full FlowchartArjun KumarNo ratings yet
- MoHP Protocol For COVID19 November 2020Document28 pagesMoHP Protocol For COVID19 November 2020medya dostorNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 PathwayDocument17 pagesCovid 19 Pathwayferi adiantoNo ratings yet
- Aden Covid-19 Protocol 26-5-2020 (ASIA) 22-1Document14 pagesAden Covid-19 Protocol 26-5-2020 (ASIA) 22-1محمدرزازالتبعيNo ratings yet
- Advisory Antibody Testing 04042020 PDFDocument2 pagesAdvisory Antibody Testing 04042020 PDFSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Advisory To Start Rapid Antibody Based Blood Test For COVID-19 (4 April 2020)Document2 pagesAdvisory To Start Rapid Antibody Based Blood Test For COVID-19 (4 April 2020)narasimma8313No ratings yet
- Guide To COVID-19 in SKH ED: 30MAY22 Dennis CHIADocument35 pagesGuide To COVID-19 in SKH ED: 30MAY22 Dennis CHIAZainal Abidin Mohd Ruslan ShahNo ratings yet
- 3 Strengthening Referral System During COVID 19 PandemicDocument27 pages3 Strengthening Referral System During COVID 19 PandemicLapuyan Rural Health UnitNo ratings yet
- MoHP Protocol December 2021Document32 pagesMoHP Protocol December 2021Yoyo RashadNo ratings yet
- PHC ILI Guidlines COVID-19 FinalDocument4 pagesPHC ILI Guidlines COVID-19 Finalyalmas ugloNo ratings yet
- Sample Case Studies of COVID-19 in PregnancyDocument29 pagesSample Case Studies of COVID-19 in PregnancyAbdibaset Mohamed AdenNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus and PregnancyDocument17 pagesCorona Virus and PregnancyDESHVIKASH SWAINNo ratings yet
- Barnet Primary Care Pathway During Covid19 v1 PDFDocument1 pageBarnet Primary Care Pathway During Covid19 v1 PDFAndrew WilkinsonNo ratings yet
- FAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoDocument112 pagesFAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoAllene PaderangaNo ratings yet
- COVID Latest GuidelinesDocument48 pagesCOVID Latest Guidelinesarrestedinlove123No ratings yet
- SGD Fever and Chills Wrap UpDocument27 pagesSGD Fever and Chills Wrap UpNewbornMed FABELLANo ratings yet
- Coronavirus19 1Document60 pagesCoronavirus19 1bekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet
- PSMID Guidelines COVID 19 - EditedDocument8 pagesPSMID Guidelines COVID 19 - EditedIsrael H. ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Guía Rápida StanfordDocument6 pagesGuía Rápida StanfordDr. Victor Adolfo RochaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Protocol - MOHP 23march 2020Document4 pagesCOVID-19 Protocol - MOHP 23march 2020Sanaa SbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- Bu BudiDocument32 pagesBu Budinoi javuNo ratings yet
- Ruchi: InterpretationDocument2 pagesRuchi: InterpretationKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- MoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.1 PDFDocument6 pagesMoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.1 PDFHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- Covid Antiviral Medications How To Prescribe Mar 10 2022Document38 pagesCovid Antiviral Medications How To Prescribe Mar 10 2022ABDULLAH SDNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Protocol July 2022Document36 pagesCOVID-19 Protocol July 2022Mobile AsdNo ratings yet
- Tarun Kumar Report - 15012022 - 120821Document1 pageTarun Kumar Report - 15012022 - 120821navdeep madheshiyaNo ratings yet
- Bu Yovita Penanganan Medis Infeksi nCoV 05022020Document18 pagesBu Yovita Penanganan Medis Infeksi nCoV 05022020restulibrianiNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Nosocomial Covid 19 Another Challenge of The PandemicDocument2 pagesPrevention of Nosocomial Covid 19 Another Challenge of The PandemicZied FehriNo ratings yet
- Management Protocol Covid 19 V08 21-7-2020Document1 pageManagement Protocol Covid 19 V08 21-7-2020EdgarNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Initial Triaging & Case Management ProtocolDocument24 pagesCovid-19 Initial Triaging & Case Management ProtocolDeepak SugumarNo ratings yet
- COVID Latest Guidelines-1Document48 pagesCOVID Latest Guidelines-1Digvijay ChavanNo ratings yet
- CovidpcrtestingalgorithmDocument1 pageCovidpcrtestingalgorithmMWNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Kasus (13022020)Document31 pagesTatalaksana Kasus (13022020)junai arandetaNo ratings yet
- MoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.8-1 PDFDocument13 pagesMoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.8-1 PDFHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 in Patients With HIV: Clinical Case SeriesDocument3 pagesCOVID-19 in Patients With HIV: Clinical Case SeriesPutri MaheraNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020Document1 pageTreatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020meiraimNo ratings yet
- 5 Cases FungalDocument56 pages5 Cases Fungalkoteshwara raoNo ratings yet
- Covid Report PDFDocument2 pagesCovid Report PDFAthira NairNo ratings yet
- Tarun Kumar ReportDocument1 pageTarun Kumar Reportnavdeep madheshiyaNo ratings yet
- New May2020 PDFDocument7 pagesNew May2020 PDFDoctorMoodyNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Resource GuideDocument2 pagesCovid 19 Resource GuideSenthil VelliyangiriNo ratings yet
- Covid Basics Poster v2 20211230Document2 pagesCovid Basics Poster v2 20211230Swagat MohantyNo ratings yet
- Isolation Guide enDocument24 pagesIsolation Guide enbasil aliNo ratings yet
- 7 Cases FungalDocument56 pages7 Cases Fungalkoteshwara raoNo ratings yet
- Management Protocol For Covid-19: Department of Health and Family WelfareDocument34 pagesManagement Protocol For Covid-19: Department of Health and Family Welfarechandra sekharNo ratings yet
- PROTOCOL For Management of COVID-19 Cases WB 2nd Edition.Document49 pagesPROTOCOL For Management of COVID-19 Cases WB 2nd Edition.Shahin KhanNo ratings yet
- Management of Mild Cases of COVID-19 in Low-Resource CountriesDocument2 pagesManagement of Mild Cases of COVID-19 in Low-Resource CountriesAnthony HopkinsNo ratings yet
- Saudi Moh Protocol For Patients Suspected Of/Confirmed With Covid-19Document15 pagesSaudi Moh Protocol For Patients Suspected Of/Confirmed With Covid-19AldrinNo ratings yet
- Uganda - Advanced HIV Disease - Screening ToolDocument47 pagesUganda - Advanced HIV Disease - Screening Toolithran khoNo ratings yet
- Special Coding Advice During COVID-19 Public Health EmergencyDocument31 pagesSpecial Coding Advice During COVID-19 Public Health Emergencyplayjake18No ratings yet
- The Following Guidelines Must Be Implemented:: Omicron VariantDocument13 pagesThe Following Guidelines Must Be Implemented:: Omicron VariantLdrrmo RamonNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Inpatient Guide 092020.1Document1 pageCovid-19 Inpatient Guide 092020.1Anna JuniedNo ratings yet
- MoH Saudi Arabia COVID 19 ProtocolDocument13 pagesMoH Saudi Arabia COVID 19 Protocoladilah fazliNo ratings yet
- Covid For ClerksDocument60 pagesCovid For ClerksNehemiah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Irfan Shaikh 38Document2 pagesIrfan Shaikh 38Altamash AnsariNo ratings yet
- Status Klinis COVID-19 Kombinasi Dengan Penyakit KardiovaskularDocument21 pagesStatus Klinis COVID-19 Kombinasi Dengan Penyakit KardiovaskularMariaAmeliaGoldieNo ratings yet
- 5908 - Muh Firdaus Kasim-Covid 19 Public Health Perspective 28032020 PDFDocument20 pages5908 - Muh Firdaus Kasim-Covid 19 Public Health Perspective 28032020 PDFDave VentraNo ratings yet
- Unified Covid-19 Algorithms: Guidelines For Primary CareDocument9 pagesUnified Covid-19 Algorithms: Guidelines For Primary Careagnes bastonNo ratings yet
- 3B - COVID-19 Update - April 2020Document40 pages3B - COVID-19 Update - April 2020Tuệ HoàngNo ratings yet
- Decision Algorithms For The Telehome Care Management of Asymptomatic or Mildly Symptomatic COVID - 19 PatientsDocument12 pagesDecision Algorithms For The Telehome Care Management of Asymptomatic or Mildly Symptomatic COVID - 19 PatientsPatricia Franco-VillaNo ratings yet
- NICE Way to Cure COVID -19From EverandNICE Way to Cure COVID -19Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Oxygen ToxicityDocument4 pagesOxygen ToxicityRicard ClainkweeNo ratings yet
- Sleepandbreathing: Kelly Newton,, Vipin Malik,, Teofilo Lee-ChiongDocument6 pagesSleepandbreathing: Kelly Newton,, Vipin Malik,, Teofilo Lee-ChiongVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- The Evaluation, Diagnosis, and Treatment of The Adult Patient With Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure - UpToDateDocument37 pagesThe Evaluation, Diagnosis, and Treatment of The Adult Patient With Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure - UpToDateKiran AsrannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3rutba.ahmkhanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Delivery NHSDocument26 pagesOxygen Delivery NHSdr satnam kaurNo ratings yet
- ARDS and Resp Failure by SardarDocument53 pagesARDS and Resp Failure by SardarQashqar & GB FolksNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Sinus ArrhythmiaDocument8 pagesRespiratory Sinus ArrhythmiaTatiana RecinosNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Common Errors in The Emergency Department-1002-1280Document280 pagesAvoiding Common Errors in The Emergency Department-1002-1280Hernando CastrillónNo ratings yet
- 2019 Article SismesxinationalcongressDocument117 pages2019 Article SismesxinationalcongresspantufoNo ratings yet
- Falla Respiratoria & Embarazo - Lapinsky 2015Document7 pagesFalla Respiratoria & Embarazo - Lapinsky 2015Fabiola Buelna GaxiolaNo ratings yet
- The Cave Divers Who Went Back For Their FriendsDocument5 pagesThe Cave Divers Who Went Back For Their FriendsRocio TobaresNo ratings yet
- Lo Tropmed 1Document49 pagesLo Tropmed 1belleNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument29 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurePurnima ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Modul: Intensive Care IDocument62 pagesModul: Intensive Care IHandayu GanitafuriNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Inergen® Fire Extinguishing AgentDocument7 pagesThe Physiology of Inergen® Fire Extinguishing AgentJEAN FELLIPE BARROSNo ratings yet
- 2003, Vol.36, Issues 3, Surgery For Sleep ApneaDocument151 pages2003, Vol.36, Issues 3, Surgery For Sleep Apneamed_amitNo ratings yet
- Course Material - Breathing Exercise - For Summer 2020Document4 pagesCourse Material - Breathing Exercise - For Summer 2020emruzzamanNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Handbook WordDocument55 pagesVentilation Handbook WordHndr100% (2)
- PIIS2058534920300202Document7 pagesPIIS2058534920300202Dwi WahyudiNo ratings yet
- COPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaDocument3 pagesCOPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Dr. Vernon Coleman - Masks and Mask Wearing - 100 Facts You Must Know - World Doctors AllianceDocument17 pagesDr. Vernon Coleman - Masks and Mask Wearing - 100 Facts You Must Know - World Doctors Alliancejamestahara95No ratings yet
- 281 FullDocument8 pages281 FullbcgvpilotNo ratings yet
- What Is Oxygen TheraphyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Oxygen TheraphyitsmekringNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepDocument8 pagesPhysiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepAchmad Hafidz BaraqbahNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument8 pagesAcute Respiratory FailureCayunk NorlianaNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Respiratory FunctionsDocument26 pagesAlterations in Respiratory FunctionsAjeeshNo ratings yet
- Noninvasive Ventilation in Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults - UpToDateDocument27 pagesNoninvasive Ventilation in Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults - UpToDatehugo roblesNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation: Gian Carlo T. Rabago RN MD Tondo Medical Center Department of SurgeryDocument16 pagesMechanical Ventilation: Gian Carlo T. Rabago RN MD Tondo Medical Center Department of SurgeryGian Carlo RabagoNo ratings yet