Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diabetes Drugs
Diabetes Drugs
Uploaded by
med test0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
159 views1 pageThis document provides information on different types of diabetes medications, including their mechanisms of action, onset and duration times, side effects, and uses. It discusses rapid, short, intermediate and long-acting insulin medications for Type 1 diabetes. It also outlines various oral medications for Type 2 diabetes, such as sulfonylureas, biguanides, thiazolidinediones, meglitinides, as well as newer injectable therapies like GLP-1 analogs, amylin analogs, and DPP-4 inhibitors.
Original Description:
Diabetes Drugs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on different types of diabetes medications, including their mechanisms of action, onset and duration times, side effects, and uses. It discusses rapid, short, intermediate and long-acting insulin medications for Type 1 diabetes. It also outlines various oral medications for Type 2 diabetes, such as sulfonylureas, biguanides, thiazolidinediones, meglitinides, as well as newer injectable therapies like GLP-1 analogs, amylin analogs, and DPP-4 inhibitors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
159 views1 pageDiabetes Drugs
Diabetes Drugs
Uploaded by
med testThis document provides information on different types of diabetes medications, including their mechanisms of action, onset and duration times, side effects, and uses. It discusses rapid, short, intermediate and long-acting insulin medications for Type 1 diabetes. It also outlines various oral medications for Type 2 diabetes, such as sulfonylureas, biguanides, thiazolidinediones, meglitinides, as well as newer injectable therapies like GLP-1 analogs, amylin analogs, and DPP-4 inhibitors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
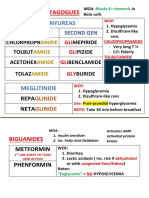
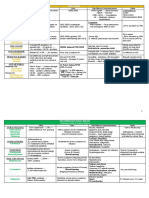
TYPE 1 DIABETES
Insulin Replacement Action Onset Peak Duration Uses
Lispro, Aspart, Glulisine Rapid -Acting ~20 min ~1 hr Up to 4 hrs Meals, acute hyperglycemia, acute diabetic ketoacidosis
Regular Short-Acting ~45 min ~ 2 hrs Up to 8 hrs Meals, acute hyperglycemia
NPH Intermediate ~2 hrs ~9 hrs Up to 24 hrs Basal insulin levels, overnight coverage
Glargine, Detemir Long-Acting ~2 hrs NONE Up to 24 hrs Basal insulin levels, overnight & 24 hr coverage
TYPE 2 DIABETES
MOA Side Effects Uses Other
α-glucosidase inhibitors →
NO hypoglycemia
Acarbose ↓cleavage of disaccharides in SI → MonoRx/ComboRx in Type 2 Additive effect in combo w/
GI side effects:
Miglitol ↓carbohydrate absorptions ↓Post-prandial hyperglycemia Sulfonylureas & Metformin
flatulent > diarrhea > nausea
SULFONYLUREAS Oral administration
st Hypoglycemia
1 Generation: Alcohol → ↑Effects
Chlorpropamide Drug interactions: Binds plasma
ND st
2 Generation: 1 gen = 24-48 hr half-life
proteins, P450 metabolism
Glyburide Less potent
ATP-dep. K+ channel blockers → Contraindications: pregnancy, nd
Glimepiride 2+ 2 gen = 3-5 hr half-life
cell depolarization → ↑Ca influx lactation, renal/hepatic MonoRx/ComboRx in Type 2
Glipizide More potent
→ ↑insulin release insufficiency
Diazoxide = opposite MOA,
Chlorpropamide - SIADH
Rx for hypoglycemia
MEGLINIDES
Less hypoglycemia Rapid absorption
Repaglinide
Caution: hepatic insuff. 1 hr half-life
Nateglinide
BIGUANIDES ↑AMP-dep. Kinase activation → NO hypoglycemia
Phenformin ↓Acetyl-CoA carboxylase → Metabolic (lactic) acidosis Overall Effects:
First line drug for Type 2
Metformin ↓lipogenesis → ↑fatty acid oxidation ↓Hepatic gluconeogenesis
Also ↓Triglyceride levels
↑GLUT4 & glycolytic enzymes Contraindications: ↑Muscle/Adipocyte glucose
↓Gluconeogenic enzymes Renal failure (Cr ≥1.5 / ≥1.4 ) uptake
Parenteral contrast media use
THIAZOLIDINEDIONES Activates PPAR- nuclear recept:
Pioglitazone Adipose: ↑fat synthesis, ↓lipolysis Heart failure Active metabolizes
MonoRx/ComboRx in Type 2
Adipose, muscle, liver: 99% Albumin bound
Also ↓HTN & atherosclerosis
↑GLUT4, ↑insulin sensitivity Weight gain GI excretion
AMYLIN ANALOG ↓Glucagon secretion BOTH Type 1 & Type 2
Amylin = co-secreted with
Pramlintide ↓Gastric emptying, Hypoglycemia ↓Post-prandial hyperglycemia
insulin by cells
↓Appetite Injected with major meals
GLP-1 ANALOGS ↑Insulin release
Injected: GLP-1 = incretin released
Exenatide ↓Glucagon secretion
Thyroid cancer Exenatide = 2x/day from gut, ↑glucose-induced
Bydureon ↓Gastric emptying
Pancreatitis Bydureon = 1x/week insulin secretion from
Liraglutide ↓Appetite
Liraglutide = 1x/day pancreas
↑β cell number
DDP-4 INHIBITORS
↓GLP-1 metabolism by DDP-4
Sitagliptin Contraindications: Renal failure MonoRx/ComboRx in Type 2 Oral administration
(same effects as GLP-1 analogs)
Linagliptin
You might also like
- Type Drug ChartDocument3 pagesType Drug ChartKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- Drug Cards CNSDocument23 pagesDrug Cards CNSChristine Schroeder100% (3)
- Pharmacology Drug CardsDocument33 pagesPharmacology Drug CardssuedayrobinsonNo ratings yet
- Coagulation DrugsDocument1 pageCoagulation Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Drug Cards (PDF Library)Document5 pagesDrug Cards (PDF Library)Jim Stewart0% (2)
- Antiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Document2 pagesAntiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Linlin100% (1)
- Patho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept MapsDocument139 pagesPatho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept Mapslauramphs79100% (5)
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat SheetRachel Hensel93% (15)
- Antihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart PDFDocument9 pagesAntihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart PDFconcoz100% (1)
- Coagulation DrugsDocument1 pageCoagulation Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Garmin GWX 70 Radar Installation ManualDocument65 pagesGarmin GWX 70 Radar Installation ManualAlejandro Vique100% (2)
- Runner Design Guide Lines-Issue 5Document15 pagesRunner Design Guide Lines-Issue 5sivanandp100% (1)
- Middle East Chemical Market: Trends and Opportunities (2015-2019) - New Report by Daedal ResearchDocument16 pagesMiddle East Chemical Market: Trends and Opportunities (2015-2019) - New Report by Daedal ResearchDaedal ResearchNo ratings yet
- Summary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFDocument3 pagesSummary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFZinc YuloNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument2 pagesRespiratory Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Treatment: PancreatitisDocument2 pagesDiabetes Treatment: PancreatitisSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument6 pagesHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78No ratings yet
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Drug CardsDocument16 pagesDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Top-200-Drug ETSYDocument31 pagesTop-200-Drug ETSYBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument6 pagesEndocrine Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel BlockersDocument4 pagesLocal Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockersmed testNo ratings yet
- Top 200 Drug Study Reference RLPDocument31 pagesTop 200 Drug Study Reference RLPYathrika YathrikaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 pagesCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (3)
- Anemia ChartDocument1 pageAnemia ChartBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- SDL: Common Cardiac Drugs: Deala, Donna Marie Toledo Advanced Diploma in Medical Surgical-Group 1Document13 pagesSDL: Common Cardiac Drugs: Deala, Donna Marie Toledo Advanced Diploma in Medical Surgical-Group 1Donna Deala100% (2)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetSuha Abdullah100% (4)
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- ANS DrugsDocument2 pagesANS Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Common Psych DrugsDocument3 pagesCommon Psych Drugsrexinne noahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Exam Cram Cheet SheetDocument2 pagesExam Cram Cheet SheetSheila Stenson-Roberts100% (1)
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- Aluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & GerdDocument4 pagesAluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & Gerdmed testNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and Endocrine ChartsDocument3 pagesDiabetes and Endocrine ChartsAja Blue88% (8)
- Herbal Drug InteractionsDocument3 pagesHerbal Drug InteractionsFaradina Zulaili Ifa EvendyNo ratings yet
- Common MedicationsDocument4 pagesCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoNo ratings yet
- CVPR Prototype Drugs TableDocument27 pagesCVPR Prototype Drugs TablethommyvaNo ratings yet
- Med BundleDocument36 pagesMed Bundlejamie sealNo ratings yet
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDocument3 pagesLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- NCLEX REVIEW AntibioticsDocument7 pagesNCLEX REVIEW Antibioticsneonstar100% (1)
- Antibiotic TableDocument7 pagesAntibiotic TablenkuligowskiNo ratings yet
- FINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSDocument1 pageFINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSronique reidNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsMehdi SabeiNo ratings yet
- Basic Drug CardsDocument13 pagesBasic Drug Cardsnene lewis100% (2)
- Drug SuffixesDocument3 pagesDrug SuffixesjeromeasuncionNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAntibiotics Cheat SheetAlejandro Rodas Salinas100% (1)
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarfaizaNo ratings yet
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 pagesDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- Pharm - Endocrine - Anti-DiabeticsDocument1 pagePharm - Endocrine - Anti-DiabeticsAbhineeth BhatNo ratings yet
- Topiramate: May Decrease Glyburide Levels Colesevelam:decreases The Absorption of SulfonylureasDocument3 pagesTopiramate: May Decrease Glyburide Levels Colesevelam:decreases The Absorption of SulfonylureaserinNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics Diabetes DrugchartDocument4 pagesTherapeutics Diabetes DrugchartSharan SahotaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitusmaham jahangirNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- DM TTTDocument2 pagesDM TTTBell GatesNo ratings yet
- Table 173-3 - Agents Used For Treatment of Type 1 or Type 2 DiDocument2 pagesTable 173-3 - Agents Used For Treatment of Type 1 or Type 2 DiKiran ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes PDFDocument4 pagesDrugs For Diabetes PDFDylan RastoNo ratings yet
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocument2 pagesNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testNo ratings yet
- Aluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & GerdDocument4 pagesAluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & Gerdmed testNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument6 pagesEndocrine Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel BlockersDocument4 pagesLocal Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockersmed testNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument2 pagesRespiratory Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- ANS DrugsDocument2 pagesANS Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Foxboro Evo™ Process Automation System: Product SpecificationsDocument12 pagesFoxboro Evo™ Process Automation System: Product SpecificationsSukdeb MaityNo ratings yet
- Food Control: Natalia Arroyo-Manzanares, Jos e F. Huertas-Perez, Ana M. García-Campa Na, Laura G Amiz-GraciaDocument5 pagesFood Control: Natalia Arroyo-Manzanares, Jos e F. Huertas-Perez, Ana M. García-Campa Na, Laura G Amiz-GraciaXuân PhúcNo ratings yet
- UOP Amine Guard Technology For Acid Gas Removal Tech Presentation PDFDocument40 pagesUOP Amine Guard Technology For Acid Gas Removal Tech Presentation PDFzaini_irawantoNo ratings yet
- SAG Cookery NC IIDocument4 pagesSAG Cookery NC IIMac Dareel UrianoNo ratings yet
- AR12BVFAAWK2AZDocument4 pagesAR12BVFAAWK2AZFilipe Dias0% (1)
- Mpman High-Tech Mini Electric Scooter User Manual Model: TR800Document18 pagesMpman High-Tech Mini Electric Scooter User Manual Model: TR800ChrisNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks ExamDocument3 pagesNeural Networks Examfruit1991No ratings yet
- PSYCHOSOCIAL Care in elderly-MODULE 5Document8 pagesPSYCHOSOCIAL Care in elderly-MODULE 5camile buhangin100% (1)
- Codigos Falla Linde h40Document18 pagesCodigos Falla Linde h40adrián castilloNo ratings yet
- Utility Request Form (SAP BRP) Revision2Document2 pagesUtility Request Form (SAP BRP) Revision2junaidi100% (1)
- ZF 9 S 1310 Transmission Spare Parts CatalogDocument6 pagesZF 9 S 1310 Transmission Spare Parts CatalogxewidyvyNo ratings yet
- IUPAC & Nomenclature PDFDocument6 pagesIUPAC & Nomenclature PDFjaspreet singh100% (1)
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Export RoHS 20190806 09291129 PDFDocument2 pagesExport RoHS 20190806 09291129 PDFИльнур ТагировNo ratings yet
- Water ConingDocument96 pagesWater ConingMubin Ashraf Sheikh100% (1)
- Global Problem AMR-NAP - EATDocument32 pagesGlobal Problem AMR-NAP - EATWolfy D Harold100% (1)
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument18 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpurk krishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Barudan-Bens PDFDocument103 pagesBarudan-Bens PDFJoseph KimNo ratings yet
- Benito Canfield - Rule of Perfection PDFDocument81 pagesBenito Canfield - Rule of Perfection PDFcalenduloNo ratings yet
- Geosphere ReportDocument3 pagesGeosphere ReportKenneth Navia GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting The Stencil Printing Process: Chrys Shea, Shea Engineering ServicesDocument44 pagesTroubleshooting The Stencil Printing Process: Chrys Shea, Shea Engineering ServicesXuan HoangNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Merkle TreeDocument4 pagesBlockchain Merkle TreeResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- HarvestlandDocument687 pagesHarvestlandJanetNo ratings yet
- ASMi 54CDocument8 pagesASMi 54Cs_meherNo ratings yet
- Turboexpander: o o o o oDocument7 pagesTurboexpander: o o o o oYoesuf DecipherNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying Notes Measurements-1Document32 pagesQuantity Surveying Notes Measurements-1matunduraNo ratings yet
- Vessel Summary: MT-VESS Rev.4.5.0Document18 pagesVessel Summary: MT-VESS Rev.4.5.0Ale NotNo ratings yet