Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Class 11 Political Science Sample Paper 01 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 16
CBSE Class 11 Political Science Sample Paper 01 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 16
Uploaded by
NihalSoniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Class 11 Political Science Sample Paper 01 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 16
CBSE Class 11 Political Science Sample Paper 01 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 16
Uploaded by
NihalSoniCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE
Class 11 Political Science
Sample Paper 01 (2019-20)
Maximum Marks: 80
Time Allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
i. All questions are compulsory.
ii. Question nos. 1 to 20 carry 1 mark each. Answer should not exceed 20 words each.
iii. Question nos. 21 to 23 carry 2 marks each. Answer should not exceed 40 words each.
iv. Question nos. 24 to 27 carry 4 marks each. Answer should not exceed 100 words each.
v. Question nos. 28 to 30 carry 5 marks each. Two passage-based questions and one picture
based question. Answer should not exceed 150 words each.
vi. Question no 31 is a map-based question. Write its answers in your answer book.
vii. Question nos. 32 to 34 carry 6 marks each (each with an internal choice). Answer should
not exceed 150 words each.
Section A
1. Write any two features of Indian secular state.
OR
Why Fundamental Rights are important?
2. Mention the amendment made in constitution of India in 1989.
3. Correct the following statement and rewrite:
The legislature is the branch of government responsible for the implementation of
laws and policies adopted by the executive.
4. Mention two motions which the Parliament in India can adopt to control the
government.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 16
5. What are the different ways in which the independence of the Judiciary is ensured?
Choose the odd ones out.
a. Parliament has no say in the appointment of Judges.
b. Chief Justice of the Supreme Court is consulted in the appointment of other Judges
of the Supreme Court.
c. Judges are generally not removed before the age of retirement.
d. Judges of a High Court cannot be transferred to another High Court.
6. What is federalism?
7. Fill in the blanks:
________ allots election symbols to political parties and to the independent candidates.
8. Fill in the blanks:
________ is the pioneer of local government in India.
9. What is the origin of the word Politics?
10. Who acts as a link between Public and Government?
a. Parliament
b. Government officials
c. Judiciary
d. Religious leaders
11. Fill in the blanks:
According to ________ politics begins and ends with the state.
12. Fill in the blanks:
Education fills a person with ________ and gives him confidence.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 16
13. What do you mean by Apartheid?
14. Who is an Alien?
OR
What is under development?
15. Who said, 'A Nationality by acquiring unity and sovereign independence becomes a
Nation'?
a. Barber
b. Hayes
c. Gilehrist
d. Burgess
16. Which of these rejects religion completely and believe in the freedom of all religions.
a. Communalism
b. Spiritualism
c. Secularism
d. Capitalism
17. Correct the following statement and rewrite:
There are two sets of government created by the Indian Constitution: one for the
entire nation called the provincial government and one for each unit or state called
the Unit government.
18. What do you mean by international law?
19. Fill in the blanks:
State and ________ are the main subjects of political Theory.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 16
20. Correct the following statement and rewrite:
Morality is a powerful moral and political ideal that has inspired and guided human
society for many centuries.
Section B
21. What are political dimensions of justice?
22. What is implied by political development?
23. Mention the five principles of Panchsheel.
Section C
24. Write only two main points to express the need for a constitution.
25. Explain any two changing characteristics of the Indian Electorate.
26. Explain how Political Science begins and ends with the state.
27. What do you mean by states? Why is it necessary?
Section D
28. Look at the given cartoon. Read the following statement and question. Answer as per
requirement:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 16
1. Why does the cartoonist describe the new Iraqi Constitution as the castle of
cards? (2)
2. Would this description apply to the Indian Constitution? (3)
29. Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
The independence of India should mean the independence of the whole of India…
Independence must begin at the bottom. Thus every village will be a republic... It
follows therefore that every village has to be self-sustained and capable of managing
its affairs. In this structure composed of innumerable villages, there will be ever-
widening, ever-ascending circles. Life will be a pyramid with the apex sustained by
the bottom - Mahatma Gandhi
i. Which concept is Gandhiji explaining in the above passage?
ii. What are the Gandhiji's views regarding the decentralisation of powers?
iii. “Do you take decentralisation as a means to minimise the conflicts ?” Give your
viewpoint.
30. Read the following passages and answer the questions that follow: (1x5=5)
Attainment of equality requires that all such restrictions or privileges should be
brought to an end. Since many of these systems have the sanction of law, equality
requires that the government and the law of the land should stop protecting these
systems of inequality. This is what our Constitution does. The Constitution prohibits
discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. Our
Constitution also abolishes the practice of untouchability. Most modern constitutions
and democratic governments have formally accepted the principle of equality and
incorporated it as an identical treatment by law to all citizens without any regard to
their caste, race, religion or gender.
i. How does our constitution stop protecting the system of inequality?
ii. Name (any two) types of inequalities, which still prevalent in our society.
iii. Is untouchability permitted in our society?
iv. Identify the values which violate the system of inequality.
v. Which article of Constitution abolishes untouchability?
31. In the given outline political map of India, five states have been marked as A, B, C, D
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 16
and E. These states have seats of Lok Sabha reserved for the SC. Identify these states
and write their correct names in your answer-book according to their seat number as
per the following format:-
Serial no. Alphabet used Name of the state
ii
iii
iv
The map of India.
Section E
32. Why have the Fundamental Duties been included in the Constitution?
OR
Describe the political philosophy of the Indian Constitution.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 6 / 16
33. How do political rights differ from economic rights? Explain with examples.
OR
Is Secularism suitable for India? Explain.
34. Mention the various stages through which the bill passes before becoming an Act.
OR
Indian democracy is now ready to shift from a rude First Past The Post System to a
system of Proportional Representation. Do you agree with this statement? Give your
reasons for or against this statement.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 7 / 16
CBSE Class 11 - Political Science
Sample Paper 01 (2019-20)
Solution
Section A
1. i. There is no state religion in India. No religion has been given special rights and no
religion has been given any special help by the state.
ii. The constitution grants religious freedom to all people. Every individual can have
faith in any religion.
OR
Fundamental Rights are important because:
i. These Rights ensure all those freedoms which make one's life worth living.
ii. It provide equality of status and opportunity as well as protect individuals from
any type of exploitation.
2. The amendment made in the constitution of India in 1989 lowered the voting age of
elections to the Lok Sabha and to the Legislative Assemblies of States from 21 years to
18 years.
3. The executive is the branch of government responsible for the implementation of
laws and policies adopted by the legislature.
4. Two motions which the Parliament in India can adopt to control the government is:
i. No-confidence motion.
ii. Adjournment motion.
5. (d) Judges of a High Court cannot be transferred to another High Court.
Explanation: Judges of a High Court cannot be transferred to another High Court.
6. Federalism is an institutional mechanism to accommodate two sets of politics one at
the national level and the other at the regional level.
7. Election Commission
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 8 / 16
8. Lord Ripon
9. The word ‘Politics’ is derived from the Greek word ‘Polis’ which means city-state. In
ancient Greek small cities were independent states and the subject concerned with
the struggle for power is a political activity.
10. (b) Government officials
Explanation: Government officials
11. Jems Wilford Garner
12. Knowledge
13. Apartheid is a policy of racial discrimination between the Blacks and the Whites,
which was largely practicised after Second World War.
14. Alien is a person who temporarily lives in a country other than his own and does not
enjoy all civil and political rights like the citizen of that country do.
OR
Underdevelopment refers to a low level of living, productivity, income related to
political, ecological and economic environment tends to result in a low level of life.
But it can be reversed by making changes in social, economic and political structures.
15. (b) Hayes
Explanation: Hayes
16. (c) Secularism
Explanation: Secularism
17. There are two sets of government created by the Indian Constitution: one for the
entire nation called the union government and one for each unit or state called the
State government.
18. International law regulates the mutual relations among different states. Lawrence
considers international law as “The rules which determine the conduct of the general
body of civilised states in their mutual dealing”.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 9 / 16
19. Government
20. Equality is a powerful moral and political ideal that has inspired and guided human
society for many centuries.
Section B
21. Political justice refers to the use of the judicial process for the purpose of gaining (or
upholding or enlarging) or limiting (or destroying) political power or influence.
People enjoy the universal adult franchise. Government influences serve the interests
of all people. People enjoy the opportunities to put pressure on the government.
22. Political development closely refers to a process of organic change in the nature of a
political institution. Development in general means the process of cumulative change
and growth. So political development refers to this change and growth in the political
sphere.
23. The five principles of Panchsheel. are:
i. Mutual respect for each other's territorial integrity and sovereignty.
ii. Mutual non-aggression.
iii. Non-interference in each other's internal affairs.
iv. Equality and mutual benefits.
v. Peaceful co-existence.
Section C
24. Two main points to express the need for a constitution are:
i. The constitution is needed to provide a framework within which a government of
the concerned country has to work.
ii. The constitution is also required to check the misuse of power by the different
organs of the government as well as different authorities and to convey the
fundamental rights to the citizens of the country.
25. Important changes have taken place in the character of the Indian electorate. Two
important changes are as follows:
i. The Indian voter has become more politicized. Indian electorates are now taking
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 10 / 16
more interest in the political activities of the country and are now more conscious
politically.
ii. Indian electorates are more concerned with the contemporary events and
problems than with the past achievements or activities of the parties.
26. The state is the pivot around which Political Science revolves. The main object of
Political Science and the sphere of its activities in the State. Political Science deals
with the origin and end of the State. Political Science studies the present, the past and
the future of the State. Political Science attempts to explain the meaning and the
essential nature of the State and deals with the laws of its progress and development.
It throws a shade of light on its origin, form, structure and it is dealing with other
States and international organizations. Its scope is not restricted to the study of the
past and the present alone but it directs the future course of the development of the
State.
27. State is a community of persons who permanently occupy a definite portion of
organised government to which the great body of inhabitants renders habitual
obedience. A state is necessary because:
i. For the security of one's life and property.
ii. For the development of individuals.
iii. To remove hindrances in the life of citizens.
iv. To perform certain duties.
Section D
28. i. The cartoonist describes the new Iraqi Constitution as the castle of cards because it
is being prepared by pro-US. The people, as well as the Constituent Assembly of
Iraq is not representing all ethnic groups of the country. Hence, the Constitution is
imposed and will be scattered as a castle of cards.
ii. This description does not apply to Indian Constitution because:
a. Indian Constitution is not imposed on Indians, but it was framed from among
different shades of opinion after long discussions and debates.
b. It was adopted by people willfully.
c. It is a living document to be amended from time to time at par aspirations of
people.
29. i. Decentralisation of economic and political power.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 11 / 16
ii. He believed that strengthening village panchayats was a means of effective
decentralisation. All development initiatives must have local involvement in order
to be successful.
iii. When power is taken away from the Central and State governments, and given to
the Local governments, it is called decentralisation.
a. The basic idea behind decentralisation is that there are a large number of
problems and issues which are best settled at the local level. People have a
better knowledge of problems in their localities. They also have better ideas on
where to spend money, and how to manage things more efficiently.
b. At the local level, it is possible for the people to directly participate in decision
making. This helps to inculcate a habit of democratic participation. Basically
the local government is the best way to realise one important principle of
democracy, namely the Local Self-Government
30. i. Our constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or
place of birth to stop the system of protecting inequality.
ii. The two type of inequalities, which still prevalent in our society are:
a. Untouchability.
b. Caste system.
iii. No, our constitution abolishes the practice of untouchability.
iv. he values which violate the system of inequality are:
a. Social Equality
b. Caste Equality
v. Article 17 of the Constitution abolishes untouchability.
31.
Serial no. Alphabet used Name of the state
i D Uttar Pradesh
ii A Tamil Nadu
iii B Bihar
iv E Gujrat
v C Assam
Section E
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 12 / 16
32. The duty means the positive or negative work that a person has to do, he/she may be
willing for that or not. The Fundamental Duties are those duties that are essential for
every citizen for his own progress, for the progress of the society and for the well
being of the nation.
The causes for the inclusion of the list of Fundamental Duties in the Constitution:
i. Fundamental Duties are noncontroversial in nature: Politicians of different views
agree on the utility and importance of Fundamental Duties. They are in the best
interest of the country and awaken patriotism among the citizens.
ii. The Fundamental Duties are the ideals and the guidelines for the individual: These
are ideals in nature and lead the citizen in the right direction. The environment of
selfishness is rampant in the country. There is no balance between the interests of
society and the individual. This tendency is harmful to society. The Fundamental
Duties would serve as an ideal behaviour to all of them.
iii. The Fundamental Duties will create Consciousness among the people: The
fulfilment of the fundamental duties are voluntary and not compulsory. They will
slowly awake the consciousness of the people to do their duties. The late Prime
Minister Indira Gandhi said in the Parliament, “If people keep the Fundamental
Duties in their minds, we would soon witness a peaceful and friendly revolution”.
OR
Indian Constitution begins with a Preamble. The Preamble serves the purpose of a
window through which we peep into the intentions of the makers of the constitution.
In fact, the Preamble is a summary of the objectives and basic philosophy of the
constitution. The basic philosophy of the Indian Constitution is as follows:
i. People are the source of Authority: The Preamble expresses in a very clear
language that people are the ultimate source of all authority. It is the people who
have adopted and enacted the constitution. The constitution originates from the
people of India and is promulgated in the name of the people of India.
ii. Socialist State: By 42nd Amendment the word ‘Socialist’ is inserted in the Preamble
of the Constitution. The government is committed to socialism.
iii. Secularism: Indian Constitution is based on the philosophy of secularism. India is
a Secular State. All citizens enjoy the freedom of religion and there is no official
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 13 / 16
religion of the state.
iv. Democratic Principles: All democratic principles are adopted in the Indian
Constitution.
v. Justice: The basic philosophy of the Constitution is that all the citizens of India
should get justice in every sphere of life. In the preamble, the idea of achieving
social, economic and political justice for all citizens has been mentioned. To
achieve social, economic, and political justice provisions have been made in the
Constitution.
vi. Liberty: Indian Constitution is based on the philosophy of freedom. The citizens of
India have been guaranteed a number of freedoms by the Constitution. Some of
the very important freedoms such as freedom of thought, freedom of expression,
freedom of belief and worship, etc., are mentioned in the preamble.
33. Political Rights: The political rights are given to every citizen of the country when
he/she attains a certain age. The political right differs from country to country, it
depends upon the Constitution of a particular country. In India, anyone who attains
the age of 18 can vote to elect their representatives to the legislatures. Anyone
mentally sound attains the age of 25 can contest elections for the member of
Parliament. This right is given to only there citizens who are living in a particular
country only.
Economic Rights: Political rights are well defined in the Constitution at the same time
economic rights are not well defined. It is written in the Constitution the citizens of
India can own property in any part of India and take profession according to their
ability and qualification in any part of India. Political rights can be defended legally
but economic rights cannot be defended.
OR
Secularism is most suitable for India due to the following reasons:
i. Multi-Religious State: Secularism is most suitable for India because India is a
multi-religious state. In a multi-religious State, it is not desirable to accept one
single religion as the religion of the State.
ii. Karachi Session of the Congress: The Indian National Congress at its Karachi
Session in 1931 had declared, “The State shall observe neutrality in regard to all
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 14 / 16
religions”. All national leaders were in favour of secularism.
iii. India is a democratic State: The Indian polity is based on democratic principles
and democracy and theocracy are opposed to each other. Freedom of religion and
equality of all religions are the basic characteristics of democracy.
iv. Partition of the country: The division of the country, emphasized more than
ever, the importance of Secularism. It is because a large Muslim minority
constituting a tenth of the population continues to be the citizen of Independent
India. Besides Muslims, there are other minorities.
Mahatma Gandhi has said that even if India would have been a uni-religious State,
he would have gone for secularism.
34. An ordinary bill has to pass through the following stages before it becomes an Act.
i. First Reading: An ordinary bill can be introduced in either House of the
Parliament. A minister or any private member introduce the bill in the House and
explains its objectives.
ii. Second Reading: At this stage a general discussion on the bill takes place and it is
put to vote.
iii. Committee Stage: Sometimes a bill is sent to a Select Committee. The Select
Committee discusses the bill in detail and debates the merits and demerits of the
bill.
iv. Report Stage: At the report stage, the bill is discussed clause by clause and item by
item.
v. Third Reading: This is the last stage in the passage of the bill and there is not
much discussion on the bill. The entire bill is put to vote at this stage and it is
either rejected or passed.
vi. Bill in the other House: The procedure followed in the first House is followed in
the other House.
vii. Assent of the President: After the Bill is passed by both the Houses, it is sent to
the President for his assent and becomes an Act after receiving his assent.
OR
In our opinion Indian democracy is not ready to adopt a system of
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 15 / 16
proportional representation due to the following reasons:
i. The system of proportional representation is very complex. An ordinary person
cannot understand this system very easily. It is difficult to determine quota, to
mark preference on the vote and to count the votes. Most of the Indian people are
illiterate.
ii. The system of proportional representation is harmful to national unity. It will
encourage small political parties because they are certain about getting
representation in the legislature.
iii. The system of proportional representation is not suitable for a big country like
India. In India, the number of voters is more than 71 crores. Hence, it is very
difficult to follow this system of election because it is almost impossible to transfer
crores of votes from one candidate to another candidate.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 16 / 16
You might also like
- Outline in Constitutional Law 1 (Cruz)Document8 pagesOutline in Constitutional Law 1 (Cruz)Arvin Antonio Ortiz93% (42)
- Foundations of Australian Law NotesDocument11 pagesFoundations of Australian Law NotesCarol TongNo ratings yet
- Statutory ConstructionDocument58 pagesStatutory ConstructionVenice Jamaila DagcutanNo ratings yet
- Uk Separation of PowerDocument10 pagesUk Separation of PowerJackson LoceryanNo ratings yet
- Ans Chapter 1 Constitution - Why and HowDocument16 pagesAns Chapter 1 Constitution - Why and HowAditi SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Correct AnswerDocument31 pagesCorrect AnswervijaykumarlambaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights and DutiesDocument22 pagesFundamental Rights and Dutiesnavdeepsahni100% (2)
- PoliticalScience SyllabusDocument57 pagesPoliticalScience SyllabusAayushi JhaNo ratings yet
- Class XI, General Worksheet Ch. 6 JudiciaryDocument1 pageClass XI, General Worksheet Ch. 6 JudiciaryHifza FatimaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Political Science - ExecutiveDocument20 pagesClass 11 Political Science - ExecutiveRamita Udayashankar80% (5)
- Class 11 Political Science - Election and RepresentationDocument16 pagesClass 11 Political Science - Election and RepresentationRamita Udayashankar67% (3)
- CBSE Class 9 Political Science (Civics) Chapter 4 Notes - Working of InstitutionsDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Political Science (Civics) Chapter 4 Notes - Working of InstitutionsDeepa MundadaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Political Science - LegislatureDocument18 pagesClass 11 Political Science - LegislatureRamita Udayashankar20% (5)
- Constitution of India, Law and EngineeringDocument74 pagesConstitution of India, Law and Engineeringmanish kumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Political Science Solved Sample Paper-02 (For 2011)Document16 pagesCBSE Class 12 Political Science Solved Sample Paper-02 (For 2011)cbsesamplepaperNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Political Science - Alternative Centre of Power PDFDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Political Science - Alternative Centre of Power PDFJaisikaNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian Political Thought - BidyutDocument474 pagesModern Indian Political Thought - BidyutDEEPIKA DASNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Political Science - EqualityDocument30 pagesClass 11 Political Science - EqualityRamita Udayashankar100% (2)
- Assignment Human Resources and Law & Social Justice Class 8Document2 pagesAssignment Human Resources and Law & Social Justice Class 8gurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- COI MODULE 3 PPT 2 KtuDocument9 pagesCOI MODULE 3 PPT 2 Kturain MCNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design - Padhle Class 9 Social Science PDFDocument20 pagesConstitutional Design - Padhle Class 9 Social Science PDFHUNTER X GAMING100% (1)
- Constituion PDFDocument248 pagesConstituion PDFlove yad100% (1)
- Class 11 Political Science - JudiciaryDocument14 pagesClass 11 Political Science - JudiciaryRamita Udayashankar40% (5)
- Class 11 Political Science - SecularismDocument23 pagesClass 11 Political Science - SecularismRamita Udayashankar100% (1)
- Class-8 Maths Case Study Worksheet (Annual Exam 2023-2024) 2Document2 pagesClass-8 Maths Case Study Worksheet (Annual Exam 2023-2024) 2arjan.singh.sawhneyNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Pol Chapter 1Document11 pagesClass 11 Pol Chapter 1Suhail AnsariNo ratings yet
- United Nations and Its Organisations Class 12 Q.ans. 2022-23Document18 pagesUnited Nations and Its Organisations Class 12 Q.ans. 2022-23druhi100% (1)
- Class 11 Political Science - RightsDocument25 pagesClass 11 Political Science - RightsRamita Udayashankar100% (1)
- Federalism WorksheetDocument5 pagesFederalism WorksheetAadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- Why Democracy What Democracy WorksheetDocument2 pagesWhy Democracy What Democracy Worksheetkarthikeyan vNo ratings yet
- XI-CHAPTER WISE Qs&As PDFDocument51 pagesXI-CHAPTER WISE Qs&As PDFNarayanan Mukkirikkad Sreedharan89% (9)
- Nationalism in India: The First World War, Khilafat and Non-Cooperation Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument29 pagesNationalism in India: The First World War, Khilafat and Non-Cooperation Multiple Choice Questionskavithanakkiran_3003No ratings yet
- Constitution As A Living DocumentDocument6 pagesConstitution As A Living Documentneeraj royalNo ratings yet
- 12 Political Science Challenges of Nation Building - Assignment PDFDocument3 pages12 Political Science Challenges of Nation Building - Assignment PDFHARMAN KAUR BABBARNo ratings yet
- Electoral Politics Worksheet-1 QN MA RKS 01 01Document4 pagesElectoral Politics Worksheet-1 QN MA RKS 01 01Anita PantNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Cbse History Sample Paper 2012-13Document24 pagesClass 12 Cbse History Sample Paper 2012-13Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper 2023-24Document17 pagesClass 10 Social Science Sample Paper 2023-24Yuvraj 9TH A100% (1)
- Podar International School (Cbse) Practice Sheet Grade: X Topic: CH 2. Federalism Subject: Social Science Maximum Marks: 25Document4 pagesPodar International School (Cbse) Practice Sheet Grade: X Topic: CH 2. Federalism Subject: Social Science Maximum Marks: 25SwapnilNo ratings yet
- Power Sharing Q Bank With AnswersDocument6 pagesPower Sharing Q Bank With AnswersRosylives79% (14)
- Programmes and Achievements of The Early NationalistsDocument4 pagesProgrammes and Achievements of The Early NationalistsAvi MathNo ratings yet
- Difference Between NITI Aayog and Planning CommissionDocument2 pagesDifference Between NITI Aayog and Planning CommissionSangram Asabe100% (1)
- Class9 Constitutional Design TermIDocument5 pagesClass9 Constitutional Design TermIvinod15770% (1)
- CHP 2 - B1 END OF BIPOLARITYDocument12 pagesCHP 2 - B1 END OF BIPOLARITYPrabhjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 10 Hindi Kshitij Chapter 11 Balgobin BhagatDocument9 pagesNCERT Class 10 Hindi Kshitij Chapter 11 Balgobin BhagatRamNo ratings yet
- HRC SolDocument119 pagesHRC SolfalguniNo ratings yet
- Chronicle Ias Academy PaperDocument2 pagesChronicle Ias Academy Paper78609No ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument14 pagesIndian ConstitutionS.K Singh Perfect Tech Engineers, Faridabad100% (1)
- Class 11 Political Science - Constitution - Why and How?Document7 pagesClass 11 Political Science - Constitution - Why and How?Ramita Udayashankar60% (5)
- ECONOMICS Most Important Questions (Prashant Kirad)Document8 pagesECONOMICS Most Important Questions (Prashant Kirad)aladdinvszafar100% (3)
- Essay On Democracy in IndiaDocument3 pagesEssay On Democracy in IndiaRahul Gupta0% (1)
- Unit 1-3 PDFDocument41 pagesUnit 1-3 PDFAyush SarkarrNo ratings yet
- Electoral Politics NotesDocument4 pagesElectoral Politics NotesshambhaviNo ratings yet
- Coalition Politics and Its Emerging TrendsDocument5 pagesCoalition Politics and Its Emerging TrendsJasdeep KourNo ratings yet
- POLITICAL SCIENCE Most Important Questions (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesPOLITICAL SCIENCE Most Important Questions (Prashant Kirad)aladdinvszafar0% (1)
- Structure of Panchayat Raj System in U.P.Document19 pagesStructure of Panchayat Raj System in U.P.SAKSHI AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Map Work Questions Class 10Document2 pagesMap Work Questions Class 10ACENo ratings yet
- 845-Physical Activity TrainerDocument16 pages845-Physical Activity Traineramrishjai9125No ratings yet
- Democracy, Election and Governance Study Material and McqsDocument17 pagesDemocracy, Election and Governance Study Material and McqsSaklen SayyadNo ratings yet
- Project Work Sociology-12Document113 pagesProject Work Sociology-12Sahabdeep Singh100% (2)
- Indian Polity Chapter 11-Local Government MCQDocument12 pagesIndian Polity Chapter 11-Local Government MCQTAI LONGNo ratings yet
- Comparative Development Experience of India and Its Neighbours - Question BankDocument2 pagesComparative Development Experience of India and Its Neighbours - Question BankHari prakarsh NimiNo ratings yet
- UGC NET Political Science Books and ThinDocument11 pagesUGC NET Political Science Books and ThinAjayNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Political Science Sample Paper 02 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 16Document16 pagesCBSE Class 11 Political Science Sample Paper 02 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 16er.amitbajajNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument30 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSrinivas KamapantulaNo ratings yet
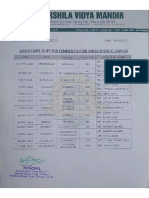
- Fro-Rat (Toto) 74Ht5/37 4Te4/Ifaat Frgfam/Fasr/2022-23: At5 FTT FahttDocument9 pagesFro-Rat (Toto) 74Ht5/37 4Te4/Ifaat Frgfam/Fasr/2022-23: At5 FTT FahttNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Class 11th - Business StudiesDocument4 pagesClass 11th - Business StudiesNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Social Science. Final Examination 2023Document4 pagesClass 9th Social Science. Final Examination 2023NihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Online Classes Time Table 2020-21 Class 9 & 10: Class Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument1 pageOnline Classes Time Table 2020-21 Class 9 & 10: Class Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Exam Slot Nursery GDocument2 pagesExam Slot Nursery GNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Document House CaptainDocument3 pagesDocument House CaptainNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- 10 - Term-II - Pre Board - II - 2021-22Document4 pages10 - Term-II - Pre Board - II - 2021-22NihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Accounts Pre Board IiDocument9 pagesAccounts Pre Board IiNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Document (TrueScanner) 2022-3-25 10.6.5Document1 pageDocument (TrueScanner) 2022-3-25 10.6.5NihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Home Assignment Class 11Document1 pageBusiness Studies Home Assignment Class 11NihalSoniNo ratings yet
- SDK LogDocument432 pagesSDK LogNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- ONLINE TIME - TABLE (CLASS 1st - 12th)Document6 pagesONLINE TIME - TABLE (CLASS 1st - 12th)NihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Online Classes Time Table 2020-21 Class 11 & 12: Clas S Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument1 pageOnline Classes Time Table 2020-21 Class 11 & 12: Clas S Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayNihalSoniNo ratings yet
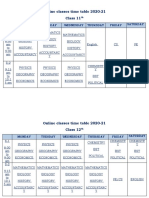
- Online Classes Time Table 2020-21 Class 11: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument2 pagesOnline Classes Time Table 2020-21 Class 11: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- SSTDocument4 pagesSSTNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Class 10th EconomicsDocument4 pagesClass 10th EconomicsNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- BST HW Class 12thDocument1 pageBST HW Class 12thNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- PooyaTafsir Quran Surah41 45 PDFDocument58 pagesPooyaTafsir Quran Surah41 45 PDFNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment ReportDocument7 pagesSelf Assessment ReportNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Building Competence For School Inspection (Teachers Discussion)Document4 pagesBuilding Competence For School Inspection (Teachers Discussion)NihalSoni100% (1)
- PDF PDFDocument13 pagesPDF PDFNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment ReportDocument10 pagesSelf Assessment ReportNihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Document4 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 4NihalSoniNo ratings yet
- Article VI - Legislative DepartmentDocument16 pagesArticle VI - Legislative DepartmentCarlo GulapaNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Case Digest - Police PowerDocument7 pagesConsolidated Case Digest - Police PowerAronJamesNo ratings yet
- Macalintal Vs Comelec DigestDocument2 pagesMacalintal Vs Comelec DigestArecarA.ReforsadoNo ratings yet
- Political Law Review (Pre-Midterm) 1 of 2Document68 pagesPolitical Law Review (Pre-Midterm) 1 of 2Juril PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Model Exit Exam UP (0) EcsuDocument2 pagesModel Exit Exam UP (0) EcsuEliphaz KalaweNo ratings yet
- Rationalization Constitution Soc. Sci.Document3 pagesRationalization Constitution Soc. Sci.RODILLO TAJALENo ratings yet
- Definition of Administrative LawDocument11 pagesDefinition of Administrative LawSherminasNo ratings yet
- The Province of North Cotabato Case DigestDocument3 pagesThe Province of North Cotabato Case Digestrachel cayangao100% (2)
- GS 2 Polity and Economy For NewspaperDocument20 pagesGS 2 Polity and Economy For NewspaperjourneybpscNo ratings yet
- FINAL JURNAL DEMOKRASIhhhbhvjguhnDocument12 pagesFINAL JURNAL DEMOKRASIhhhbhvjguhnDian marsyahNo ratings yet
- 43rd AmendmentDocument14 pages43rd AmendmentSharad VermaNo ratings yet
- Vivekananda Institute of Professional Studies School of Law and Legal StudiesDocument13 pagesVivekananda Institute of Professional Studies School of Law and Legal StudiesMayankNo ratings yet
- NAPAS CONSTITUTION-WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesNAPAS CONSTITUTION-WPS Officesaidsulaiman2095No ratings yet
- Cases-Public CorporationDocument223 pagesCases-Public CorporationAr LineNo ratings yet
- The Province of North Cotabato v. The Gov. of The Republic of The Phils. Peace PanelDocument4 pagesThe Province of North Cotabato v. The Gov. of The Republic of The Phils. Peace PanelNoreenesse SantosNo ratings yet
- Municipal of Jimenez DigestDocument3 pagesMunicipal of Jimenez DigestkarlonovNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of Myanmar A Contextual AnalysisDocument4 pagesThe Constitution of Myanmar A Contextual AnalysisNay AungNo ratings yet
- All India Bar Examination Book 2Document173 pagesAll India Bar Examination Book 2Vaishnav KumarNo ratings yet
- CSC v. SalasDocument4 pagesCSC v. SalasRoyen Lacson De MesaNo ratings yet
- Module 10 To 12 With Pre-Final ExamDocument8 pagesModule 10 To 12 With Pre-Final ExamBryan Lester M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 11 Legal SA1Document2 pages11 Legal SA1lavarocks23No ratings yet
- Sci HubDocument5 pagesSci HubThị Hương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Dumlao Vs ComelecDocument1 pageDumlao Vs ComelecNanz JermaeNo ratings yet
- Le Jugement de La Cour Dans Le Cas de Pravind JugnauthDocument5 pagesLe Jugement de La Cour Dans Le Cas de Pravind JugnauthL'express MauriceNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court Bill ReconsiderationDocument3 pagesSupreme Court Bill ReconsiderationArif Alvi100% (1)
- Responsive Document - CREW: Department of The Treasury: Regarding Presidential Authority To Raise The Debt CeilingDocument433 pagesResponsive Document - CREW: Department of The Treasury: Regarding Presidential Authority To Raise The Debt CeilingCREWNo ratings yet